Professional Documents
Culture Documents
To Analyze The Ohm
To Analyze The Ohm
Uploaded by
Hana VvnaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
To Analyze The Ohm
To Analyze The Ohm
Uploaded by
Hana VvnaCopyright:
Available Formats
To Analyze the Ohms Law Through Virtual Experiment
Abstract- This experiment was conducted to analyze the Ohms Law.
III.
EXPERIMENT AND RESULT
Table 1
I. INTRODUCTION When a free electrons are continuously move in a conductive path it will formed an electric circuit. As for the continuous movement of free electrons which is often referred to in a terms of "flow", through the conductors of a circuit is called current. While for the voltage, it is a specific measure of potential energy distance between two points. Voltage is the force that motivating electrons to flow in a circuit, we are referring to the measurement of how much potential energy exists to move electrons from one particular point in that circuit to another particular point. If there is no reference to two particular points, the term voltage has no meaning. Whereas, resistance is the opposition to motion of electrons with some degree of friction that move through conductors. These three elements are correlated to a law, called Ohms law. The law stating that the direct current flowing in a conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference between its ends. It is usually formulated as V = IR, where V is the potential difference, or voltage, I is the current, and R is the resistance of the conductor.
V/V 2
I/mA
12
16
R = 500 .
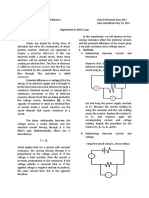
II. PROCEDURE 1. 2. ohms-law_en.jar was opened. The resistance, R was set to 500 . The value of current, I, recorded in Table 1 by the value of voltage changed. The graph of voltage versus current was plotted. The conductance represents by the slope. The value of G was found. The reciprocal of the conductance is the resistance. R was found. The voltage, V was set to 3V. The value of current, I was recorded in Table 2 by the value of resistance changed. The graph of resistance versus current was plotted.
3. 4. 5. 6.
The value of G and R, G = Y2 - Y1 X2 X1 = (12-8) (6-4) =2 G R = 1/G = =0.5
Assuming that resistance is constant, describe what happen to current when voltage is increased and decreased. When the resistance is constant, the voltage is proportional to the
Table 2
7.
directly current
R/
R=V/I
200 400 600 800
I/mA
15
7.5
3.8
V = 3V
Graph of resistance versus current current (mA)
20 10 0 0 500 1000 What is the curve for 3V source? Exponential growth graph Resistance
()
Assuming that voltage is constant, describe what happen to current when resistance is increased and decreased. When the resistance increase the current decrease and vice versa Based on the experiment above, what is the relationship between; a) Voltage and current Voltage is directly proportional to current and vice versa b) Current and resistance Current is inversely proportional to resistance and vice versa
IV. CONCLUSION
From this experiment, actually we were approved the ohms law is available. V V I R =IR : Voltage with unit volt,V : Current with unit ampere,A : Resistance with unit ohm,
Ohm's law states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the potential difference across the two points. Introducing the constant of proportionality, the resistance, one arrives at the usual mathematical equation that describes this relationship. I=V/R This is also equivalent to: V=IxR And
You might also like
- Igcse - Chemistry - Worksheet States of MatterDocument4 pagesIgcse - Chemistry - Worksheet States of MatterMarin Pesic100% (5)
- Experiment 5: Electrical Resistance and Ohm's LawDocument10 pagesExperiment 5: Electrical Resistance and Ohm's LawsyafNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Law ReportDocument8 pagesOhm's Law ReportFelicia Paya FrancisNo ratings yet
- Electricity-As Level Physics NotesDocument10 pagesElectricity-As Level Physics Noteschar100% (1)
- Ohm S Law TutorialDocument17 pagesOhm S Law Tutorialchristopher pazmiño panchanaNo ratings yet
- General Tutorial PHY 122Document3 pagesGeneral Tutorial PHY 122Mirabel SikaNo ratings yet
- Scalar Physics - Alternative Energy - Free EnergyDocument95 pagesScalar Physics - Alternative Energy - Free Energymarc_vg100% (5)
- SCI409L - Expt-9 - Ohm's LawDocument8 pagesSCI409L - Expt-9 - Ohm's LawluisabellemcsNo ratings yet
- E306 Report - Parallel and Series CircuitsDocument5 pagesE306 Report - Parallel and Series CircuitsAbdul Rahman Mariscal100% (1)
- Advance Physics For Grade 10 STE StudentsDocument5 pagesAdvance Physics For Grade 10 STE StudentsJoshua AsuncionNo ratings yet
- UG DocumentDocument6 pagesUG DocumentSliman 1No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 15 - Electric CircuitsDocument6 pagesCHAPTER 15 - Electric CircuitsGerry Lou QuilesNo ratings yet
- Resistance Was Discovered by Georg Simon Ohm. The Relationship and The Unit of ElectricalDocument4 pagesResistance Was Discovered by Georg Simon Ohm. The Relationship and The Unit of ElectricalAliNo ratings yet
- Circuits LoveDocument10 pagesCircuits LoveMabethNo ratings yet
- Bab 2 ElectricityDocument65 pagesBab 2 ElectricityAnonymous oW9OeJvEvNo ratings yet
- Physics Lab ReportDocument3 pagesPhysics Lab ReportRey Malvin SG PallominaNo ratings yet
- Phy12l E306 ISI-PaperDocument8 pagesPhy12l E306 ISI-PaperGrace ReyesNo ratings yet
- Assessment Rubric Lab2Document8 pagesAssessment Rubric Lab2Felix Erwin RajakNo ratings yet
- OhmslawDocument17 pagesOhmslawBright OvieNo ratings yet
- Learning Objectives:: V I R Voltage Current ResistanceDocument7 pagesLearning Objectives:: V I R Voltage Current ResistanceEfrainNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Mst557Document13 pagesLab Report Mst557hyebibie0% (1)
- Module1 1Document46 pagesModule1 1Disha GoyalNo ratings yet
- Ohm - S LawDocument23 pagesOhm - S LawEngr Abdul Samad MalikNo ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument32 pagesOhm's LawDezz Balleta-BonaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 Ohms LawDocument5 pagesExperiment 2 Ohms LawnatlasNo ratings yet
- مختبر ابلايد2Document6 pagesمختبر ابلايد2عبد الرحمن أبوخاطر, أبو رزقNo ratings yet
- University of BotswanaDocument7 pagesUniversity of BotswanaLast BofeloNo ratings yet
- Widya F. Rompas 19101105017Document14 pagesWidya F. Rompas 19101105017Widya RompasNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical MeasurementDocument10 pagesBasic Electrical MeasurementselniNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic EngineeringDocument8 pagesElectrical and Electronic Engineeringخہٰہٰالہٰد ۦ' ۦ'No ratings yet
- تجربة 4Document10 pagesتجربة 4alamryzhra62No ratings yet
- Hysics Ohms Law Summative 2022 Grad E10Document15 pagesHysics Ohms Law Summative 2022 Grad E10raosamhith1No ratings yet
- PHYS 41 - University Physics III: Laboratory Activity No. 5Document3 pagesPHYS 41 - University Physics III: Laboratory Activity No. 5Carlos Antonio OchavilloNo ratings yet
- D.C. CircuitDocument64 pagesD.C. CircuitKim MNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledJanet ChenNo ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument9 pagesOhm's Lawkare-kare CJNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document7 pagesUnit 5NurFajrina MuthmainnahNo ratings yet
- Ohm S Law TutorialDocument17 pagesOhm S Law Tutorialchristopher pazmiño panchanaNo ratings yet
- RamedialDocument5 pagesRamedialTE21 FERDIAN YOGA PERDANANo ratings yet
- Ohms LawDocument5 pagesOhms LawRaj Kumar PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Year 9 Science CAT Lab ReportDocument5 pagesYear 9 Science CAT Lab ReportKaitlyn CarrNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of DC CircuitsDocument8 pagesFundamentals of DC CircuitstettehsackeyNo ratings yet
- Ohms LawDocument4 pagesOhms LawAshley O'Neal100% (7)
- M 424Document28 pagesM 424Epic WinNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Law ExperimentDocument11 pagesOhm's Law ExperimentScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 2Document20 pagesUnit-1 2Akhilesh Kumar MishraNo ratings yet
- Ohms and ElectricityDocument15 pagesOhms and ElectricityJaybisdon DonNo ratings yet
- Circuit's LabDocument11 pagesCircuit's LabJane HangerNo ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument4 pagesCurrent ElectricityPeter KachouhNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument14 pagesElectricityTECH RISERNo ratings yet
- DC CircuitsDocument26 pagesDC CircuitsMary Jean ParagsaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 DC Circuit TheoryDocument37 pagesChapter 2 DC Circuit TheoryTynoh MusukuNo ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument12 pagesOhm's LawJerome BricenioNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Law AnimationDocument3 pagesOhm's Law Animationholisticwarehou94No ratings yet
- Module 2Document4 pagesModule 2surajNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 Charges and Ohm LawDocument12 pagesExperiment 2 Charges and Ohm Lawعلي محمودNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Lab - Basic MeasurementsDocument2 pagesWeek 6 Lab - Basic MeasurementsRowen PratherNo ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument10 pagesOhm's LawMohamed KamilNo ratings yet
- Current and Resistance Current and Current DensityDocument20 pagesCurrent and Resistance Current and Current Densityminhajul.cse.diuNo ratings yet
- Practical EDDocument23 pagesPractical EDSuvigayaNo ratings yet
- UNIT I NotesDocument34 pagesUNIT I NotesKarthikeyan VNo ratings yet
- Complete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsFrom EverandComplete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- MacCormack MethodDocument1 pageMacCormack MethodAbhishek AjansondkarNo ratings yet
- Matriculation Chemistry (Thermochemistry)Document54 pagesMatriculation Chemistry (Thermochemistry)ridwan100% (2)
- 4 MotionOneDimensionFull PDFDocument38 pages4 MotionOneDimensionFull PDFmagiclcjNo ratings yet
- The Relationship Between Voltage and DC Motor Output SpeedDocument3 pagesThe Relationship Between Voltage and DC Motor Output SpeedVijayanandh RNo ratings yet
- 75 04 01 012Document33 pages75 04 01 012EmreNo ratings yet
- Ntroduction: Dr. Hammad Iqbal SheraziDocument14 pagesNtroduction: Dr. Hammad Iqbal SherazisamoleNo ratings yet
- MTL 200 OutlineDocument3 pagesMTL 200 OutlineputhiawanNo ratings yet
- Valderrama Cubic Eos PDFDocument16 pagesValderrama Cubic Eos PDFJorge SotoNo ratings yet
- System Ekoplastik: Pressure Loss TablesDocument18 pagesSystem Ekoplastik: Pressure Loss TablesAndresNo ratings yet
- Exam Assessment Level Full Marks Program BCT A Pass Marks Year/Part I/II TimeDocument4 pagesExam Assessment Level Full Marks Program BCT A Pass Marks Year/Part I/II Timeविशाल पुडासैनीNo ratings yet
- Personal History Chien-Hao, LiuDocument2 pagesPersonal History Chien-Hao, LiujenhouNo ratings yet
- 10 Meter Walk Test InstructionsDocument3 pages10 Meter Walk Test InstructionsDavid SugiartoNo ratings yet
- MCQ On Quantum ChemistryDocument10 pagesMCQ On Quantum ChemistryRahul kumarNo ratings yet
- MFEMD Ch09Document10 pagesMFEMD Ch09Abdel DaaNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronics Engineering Materials - J. B. GuptaDocument70 pagesElectrical and Electronics Engineering Materials - J. B. GuptakundanabcNo ratings yet
- Timber Engineering Assignment 2 (Group Lydia)Document12 pagesTimber Engineering Assignment 2 (Group Lydia)dominicNo ratings yet
- MOCKDocument6 pagesMOCKchristian mooreNo ratings yet
- ERROR: Shigley's Mechanical Engineering Design 10th EdDocument1 pageERROR: Shigley's Mechanical Engineering Design 10th EdTimNo ratings yet
- CH 4 Isotope LabDocument4 pagesCH 4 Isotope LabHarvinderNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Sensor Simulator SchematicDocument4 pagesOxygen Sensor Simulator SchematicДејан Петровић0% (1)
- Lockheed EMMLDocument4 pagesLockheed EMMLbring it onNo ratings yet
- Biophysics of Lasers - PartIDocument9 pagesBiophysics of Lasers - PartINina RadicNo ratings yet
- PHD Thesis (Final Ver.2)Document254 pagesPHD Thesis (Final Ver.2)Carlos DuqueNo ratings yet
- TNPSC Group 1 Preparation Strategy Prelims Syllabus Analysis WWW - TNPSC .AcademyDocument7 pagesTNPSC Group 1 Preparation Strategy Prelims Syllabus Analysis WWW - TNPSC .Academysheeja kannanNo ratings yet
- Hookes Law ExpeirmentDocument8 pagesHookes Law ExpeirmentTanieka PowellNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry, Chapter 20, ElectrochemistryDocument7 pagesAP Chemistry, Chapter 20, ElectrochemistrysethisoddNo ratings yet
- Tzempelikos D. Et Al - Airflow Patterns in A Laboratory Batch-Type, Tray Air Dryer - Ic-Scce2012 - ProceedingsDocument10 pagesTzempelikos D. Et Al - Airflow Patterns in A Laboratory Batch-Type, Tray Air Dryer - Ic-Scce2012 - ProceedingsAndronikos FiliosNo ratings yet