Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pathophysiology of Gastroenteritis, Dehydration, and Necatoriasis
Pathophysiology of Gastroenteritis, Dehydration, and Necatoriasis
Uploaded by
Ralph Delos SantosOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pathophysiology of Gastroenteritis, Dehydration, and Necatoriasis
Pathophysiology of Gastroenteritis, Dehydration, and Necatoriasis
Uploaded by
Ralph Delos SantosCopyright:
Available Formats
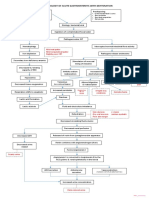
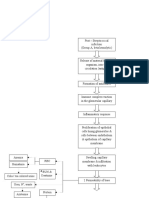
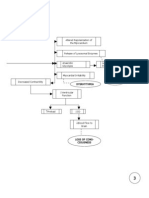
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF ACUTE GASTROENTERITIS WITH NECATORIASIS
MODIFIABLE FACTORS: infectious agent ( Acylostoma duodenale, Necator americanus); Hygiene; Food preparation; Safety Gears Oral (A. Duodenale) Entry into the small intestine Hematophagy Iron depletion Secondary irondeficiency anemia O2 binding capacity of RBC Hypoxemia tissue oxygenation Respiration shifts to anaerobic Lactic acid formation Entry of filariform into the body Dec. Absorption of proteins
NON-MODIFIABLE FACTORS: - Inherent susceptibility; Weak immunity; Endemicity of infectious agent Percutaneous (N.Americanus) Maculopapular rashes Pruritus Dew itch Papulovesicular eruption Post- eruption skin lesions Bleeding Hemoptysis Bronchitis Infiltration of parenchyma Pneumonitis CO2 Eosinophils / leukophils infiltration Respi. acidosis oxygenation Airway obstruction Ascending URT Larva enters the bloodstream Accumulation in the lungs Infiltration of parenchyma
Hypoalbuminemia Abdominal pain Villi damage Bleeding Melena Entry of intestinal bacteria Establishment of infection Bacteremia
Luminal trauma
Dec. osmotic pressure Steatorrhea
Edema
Exposure to other intestinal microorganisms
Inflammation of lumen
Development of hemorrhage
mucus production HCO3- wasting Metabolic acidosis Septic shock Compensatory fluid shift intraluminally
Lung consolidation
Lactic acidosis Expulsion of ova Cerebral hypoxia Hypoxic encephalopathy Depression of vasomotor and respiratory center Respiratory arrest Death Aldosterone release Na reabsorption Fluid retention LOC cerebral perfusion
Diarrhea Fluid and electrolyte imbalance
GI motility
Compression Lung compliance DOB
Compensatory hyperventilation RR
(+) ova in stool Dry mouth
Dehydration
Sunken eyeballs
Poor skin turgor
circulating volume C.O. Hypotension Accumulation of metabolic products Tachycardia
Hypovolemia Adrenal perfusion Cortical activation
renal perfusion Release of rennin from juxtaglomerular apparatus Renin combines with angiotensin Angiotensin I Combination with ACE
GFR urine output
catecholamines , agonist BP PR
azotemia Urine concentration Uremia
edema
Angiotensin II Vasoconstriction and Na retention BP Inhibitory feedback to BP
Prepared by: Ralph R. delos Santos BSN III-2 Pamantasan ng Lungsod ng Maynila College of Nursing Case Study on Acute Gastroenteritis with Moderate Dehydration and Intestinal Parasitism
You might also like
- Fluids Concept MappingDocument1 pageFluids Concept Mappingmariagarcia415100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Risk For Disuse SyndromeDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Risk For Disuse SyndromeRozsy FakhrurNo ratings yet
- St. Anthony College of Roxas City, Inc.: Case Study For Pediatric Nursing Clinical RotationDocument15 pagesSt. Anthony College of Roxas City, Inc.: Case Study For Pediatric Nursing Clinical RotationJudy Mae ObamosNo ratings yet
- Pathophy (Age)Document1 pagePathophy (Age)Michelle Ann CasamayorNo ratings yet
- PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesPathophysiologyKita kita100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Acute GastroenteritisDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Acute GastroenteritisAiza Yee Bacani83% (6)
- Pa Tho Physiology of PyelonephritisDocument2 pagesPa Tho Physiology of PyelonephritisYuan Li100% (1)
- Acute Gastroenteristis Case Study GRP 3Document22 pagesAcute Gastroenteristis Case Study GRP 3juel_navarro88% (8)
- Weaknes S/ Fatigue Polyphag IaDocument5 pagesWeaknes S/ Fatigue Polyphag IaEwert Hesketh Nillama PaquinganNo ratings yet
- Leonardo Drug Study On SangobionDocument6 pagesLeonardo Drug Study On SangobionMonique LeonardoNo ratings yet
- PLM Nursing CurriculumDocument3 pagesPLM Nursing CurriculumRalph Delos Santos67% (3)
- Pathophsyiology of AGEDocument1 pagePathophsyiology of AGEmariaNo ratings yet
- AGE PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesAGE Pathophysiologyjosephcanlas67% (3)
- Pathophysiology of Acute GastroenteritisDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Acute GastroenteritisAlliah Grejie AnneNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of AGE With DHNDocument1 pagePathophysiology of AGE With DHNFarr Krizha Tangkusan50% (2)
- Pathophysiology of AGEDocument1 pagePathophysiology of AGEtinatin9890% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Acute GastroenteritisDocument5 pagesPathophysiology of Acute Gastroenteritisheron_bayanin_15No ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of Acute GastroenteritisDocument2 pagesPa Tho Physiology of Acute Gastroenteritisromeo rivera100% (16)
- Pathophysiology of Acute Gastroenteritis: Perforati-NgDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Acute Gastroenteritis: Perforati-NgBryan Voltaire Santos LannuNo ratings yet
- Age With Moderate Dehydration New 1Document74 pagesAge With Moderate Dehydration New 1Jhade Relleta100% (1)
- AGE With Pa Tho PhysiologyDocument3 pagesAGE With Pa Tho PhysiologyChichi Licuben OresacamNo ratings yet
- Marjorie A. Carganilla BSN 3-2 Pathophysiology of Urinaryy Tract Infection Precipitating FactorsDocument8 pagesMarjorie A. Carganilla BSN 3-2 Pathophysiology of Urinaryy Tract Infection Precipitating FactorsMarjorie CarganillaNo ratings yet
- Case (Acute Gastroenteritis) Group 4Document36 pagesCase (Acute Gastroenteritis) Group 4EljhayrosNo ratings yet
- Ix. Pathophysiology of Acute Gastroenteritis: Etiological Factor: Predisposing FactorDocument1 pageIx. Pathophysiology of Acute Gastroenteritis: Etiological Factor: Predisposing FactorJon Corpuz AggasidNo ratings yet
- Predisposing Factors Age Diet Dehydration Precipitating Factors Family or Personal History Digestive Diseases and SurgeryDocument2 pagesPredisposing Factors Age Diet Dehydration Precipitating Factors Family or Personal History Digestive Diseases and SurgeryChloé Jane HilarioNo ratings yet
- Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDocument3 pagesRheumatic Heart DiseaseDee SarajanNo ratings yet
- Case Study AGE With DehydrationDocument12 pagesCase Study AGE With Dehydrationmwdlc_22100% (2)
- NafarinDocument2 pagesNafarinianecunar100% (2)
- Schistosomiasis (From Anatomy To Pathophysiology)Document10 pagesSchistosomiasis (From Anatomy To Pathophysiology)Tiger Knee100% (1)
- NCPsDocument13 pagesNCPsRocel DevillesNo ratings yet
- NCP 4Document1 pageNCP 4marohunkNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea Care PlanDocument2 pagesDiarrhea Care Planzepoli_zepoly6232100% (1)
- Measles PathophysiologyDocument1 pageMeasles PathophysiologyAl TheóNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Hypercalcemia Prepared By: Carbonilla, Leda GraceDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Hypercalcemia Prepared By: Carbonilla, Leda Graceshielamaygo05100% (1)
- Aplastic Anemia Pa Tho PhysiologyDocument3 pagesAplastic Anemia Pa Tho Physiologyneil052275% (4)
- AGE PathophysiologyDocument1 pageAGE PathophysiologyZhenmeiNo ratings yet
- HepatitisDocument3 pagesHepatitisRosendo Dacuyan50% (2)
- Non-Modifiable Factor Modifiable Factor: South-East Asia, Eastern, Mediterranean, Western Pacific, and The AmericasDocument2 pagesNon-Modifiable Factor Modifiable Factor: South-East Asia, Eastern, Mediterranean, Western Pacific, and The Americaschristian quiaoitNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho PhysiologyDocument1 pagePa Tho PhysiologyEiztirfNo ratings yet
- Concept Map Tetralogy of FallotDocument2 pagesConcept Map Tetralogy of FallotKarl KiwisNo ratings yet
- Acute PyelonephritisDocument105 pagesAcute Pyelonephritisyasira50% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Hypersensitivity Type IIDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Hypersensitivity Type IItwin_smartyNo ratings yet
- Pathophysio Chronic GlomerulonephritisDocument1 pagePathophysio Chronic GlomerulonephritisRan Ma100% (1)
- Concept Map AsthmaDocument4 pagesConcept Map AsthmaAstrid Moreno De LeonNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramDocument1 pageAppendicitis Pathophysiology - Schematic Diagrambayu jaya adigunaNo ratings yet
- Individual Case Study Acute GlomerulonephritisDocument26 pagesIndividual Case Study Acute GlomerulonephritisBatrisyia HalimsNo ratings yet
- Hydronephrosis Fred LuceDocument69 pagesHydronephrosis Fred LuceKMNo ratings yet
- Tranexamic AcidDocument2 pagesTranexamic AcidIrish Ivy VibethNo ratings yet
- PathophyDocument2 pagesPathophymharz_astilloNo ratings yet
- Ov Ov OvDocument15 pagesOv Ov OvHayyana Mae Taguba LadiaNo ratings yet
- Case Study OpdDocument35 pagesCase Study OpdMicah MagallanoNo ratings yet
- JRMMC - Patho of Ruptured AppendicitisDocument3 pagesJRMMC - Patho of Ruptured Appendicitis9632141475963No ratings yet
- The Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeFrom EverandThe Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- End-Stage Renal DiseaseDocument3 pagesEnd-Stage Renal DiseaseAkira Pongchad B100% (1)
- Tau Chempath - Acid Base Imbalance & Pahology of Resp FailureDocument31 pagesTau Chempath - Acid Base Imbalance & Pahology of Resp FailureChipego ChiyaamaNo ratings yet
- Myocardial Infarction Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramDocument3 pagesMyocardial Infarction Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramAbi Habiling100% (3)
- Pathway: Aterosklerosis, Suplai Darah GinjalDocument3 pagesPathway: Aterosklerosis, Suplai Darah GinjalFitriah Sa'diahNo ratings yet
- Module 3 A PresentationDocument79 pagesModule 3 A PresentationJesus William Arizapana MamaniNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument123 pagesFluid and Electrolyte ImbalanceBrealaiNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Hemorrhagic StrokeDocument1 pagePathophysiology Hemorrhagic StrokeJeffrey Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Copd Cad Pathophysiology (Revised)Document3 pagesCopd Cad Pathophysiology (Revised)Israel Soria EsperoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Erythroblastosis Fetalis - RH IsoimmunizationDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Erythroblastosis Fetalis - RH IsoimmunizationRalph Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Erythroblastosis Fetalis - RH IsoimmunizationDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Erythroblastosis Fetalis - RH IsoimmunizationRalph Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Cerebrospinal Fluid CirculationDocument1 pageCerebrospinal Fluid CirculationRalph Delos SantosNo ratings yet