Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Table of English Tenses
Table of English Tenses
Uploaded by
Kashif WakeelOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Table of English Tenses
Table of English Tenses
Uploaded by
Kashif WakeelCopyright:
Available Formats
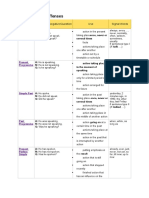
Table of English Tenses tense Simple Present Affirmative/Negative/Question Use A: He speaks. N: He does not speak. Q: Does he speak?
Signal Words action in the present taking place once, never or several times facts actions taking place one after another action set by a timetable or schedule action taking place in the moment of speaking action taking place only for a limited period of time action arranged for the future action in the past taking placeonce, never or several times actions taking place one after another action taking place in the middle of another action action going on at a certain time in the past actions taking place at the same time action in the past that is interrupted by another action putting emphasis on the result already, ever, just, never, not when, while, as long as yesterday, 2 minutes ago, in 1990, the other day, last Friday if sentence type II (If I talked, ) at the moment, just, just now, Listen!, Look!, now, right now always, every , never, normally, often, seldom, sometimes, usually if sentences type I (If Italk, )
Present A: He is speaking. Progressive N: He is not speaking. Q: Is he speaking?
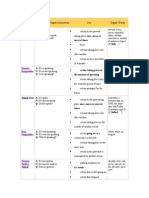
Simple Past
A: He spoke. N: He did not speak. Q: Did he speak?
Past A: He was speaking. Progressive N: He was not speaking. Q: Was he speaking?
Present Perfect
A: He has spoken. N: He has not spoken.
Simple
Q: Has he spoken?
action that is still going on action that stopped recently finished action that has an influence on the present action that has taken place once, never or several times before the moment of speaking putting emphasis on the course or duration (not the result)
yet, so far, till now, up to now
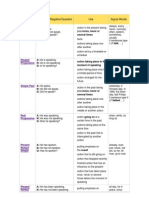
Present A: He has been speaking. Perfect N: He has not been speaking. Progressive Q: Has he been speaking?
all day, for 4 years, since 1993, how long?, the action that recently stopped or whole week is still going on finished action that influenced the present action taking place before a certain time in the past sometimes interchangeable with past perfect progressive putting emphasis only on thefact (not the duration) action taking place before a certain time in the past sometimes interchangeable with past perfect simple putting emphasis on theduration or course of an action action in the future that cannot be influenced in a year, next , tomorrow already, just, never, not yet, once, until that day if sentence type III (If Ihad talked, ) for, since, the whole day, all day
Past Perfect Simple
A: He had spoken. N: He had not spoken. Q: Had he spoken?
Past A: He had been speaking. Perfect N: He had not been speaking. Progressive Q: Had he been speaking?
Future I Simple
A: He will speak. N: He will not speak. Q: Will he speak?
spontaneous decision assumption with regard to the future
If-Satz Typ I (If you ask her, she will helpyou.) assumption: I think, probably, perhaps in one year, next week, tomorrow
Future I Simple (going to)
A: He is going to speak. N: He is not going to speak. Q: Is he going to speak?
decision made for the future conclusion with regard to the future action that is going on at a certain time in the future action that is sure to happen in the near future
Future I A: He will be speaking. Progressive N: He will not be speaking. Q: Will he be speaking?
in one year, next week, tomorrow
Future II Simple
A: He will have spoken. N: He will not have spoken. Q: Will he have spoken?
action that will be finished at a by Monday, in a certain time in the future week
Future II A: He will have been speaking. Progressive N: He will not have been speaking. Q: Will he have been speaking?
action taking place before a certain time in the future putting emphasis on the courseof an action action that might take place
for , the last couple of hours, all day long
Conditional A: He would speak. N: He would not speak. I Simple Q: Would he speak?
if sentences type II (If I were you, I would go home.)
Conditional A: He would be speaking. I N: He would not be speaking. Progressive Q: Would he be speaking?
action that might take place putting emphasis on the course/ duration of the action action that might have taken if sentences type III
Conditional A: He would have spoken. N: He would not have spoken.
II Simple
Q: Would he have spoken?
place in the past
(If I had seen that, Iwould have helped.)
Conditional A: He would have been II speaking. Progressive N: He would not have been speaking. Q: Would he have been speaking?
action that might have taken place in the past puts emphasis on the course /duration of the action
You might also like
- ESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideFrom EverandESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- English TensesDocument4 pagesEnglish TensesAgung ArdyantoNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument3 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsAbdulaziz2012No ratings yet
- Table of English TensesDocument2 pagesTable of English TensesMariana Crăciun100% (1)
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument4 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDenis SăndicăNo ratings yet
- TenseDocument3 pagesTenseKiki MulqiahNo ratings yet
- Table TensesDocument4 pagesTable TensesmariminniNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentSorin Mihai VassNo ratings yet
- Simple Present: I Talk, )Document3 pagesSimple Present: I Talk, )Krupesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: PresentRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Table of English TensesDocument3 pagesTable of English TensesCristina-Raluca RuşeţNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument3 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsAndrea Paredes GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument4 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentXorianopoulou SofiaNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument3 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsTaris TallasaNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentVeronica BurdujaNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentLyana LorenzaNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentJavier J SalazarNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentHazel-mae LabradaNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentAdaNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Questi On Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Questi On Use Signal Words: Simple PresentRuxanda RusuNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Questio N Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument5 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Questio N Use Signal Words: Simple PresentFitrie RnaNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentPavlina HaralampievaNo ratings yet
- Table of English TensesDocument3 pagesTable of English TensesGonzalo AstorgaNo ratings yet
- TenseDocument3 pagesTenseMădălina RădulescuNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Questi On Use Signal Words: Present SimpleDocument4 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Questi On Use Signal Words: Present SimpleRobertaNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Presentdddiana21No ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Use Signal WordsDocument4 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Use Signal WordsAdriana MuresanNo ratings yet
- Table of English TensesDocument4 pagesTable of English Tensesdieba105No ratings yet
- Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument3 pagesTenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Wordsyingying1102No ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentMariana PasatNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument4 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Wordsanon1000No ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Wordshpeter195798No ratings yet
- Verb Tense Overview With ExamplesDocument5 pagesVerb Tense Overview With ExamplesSaulo ZunigaNo ratings yet
- English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument3 pagesEnglish Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsAndreaNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument4 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsthirtysecondsmarsNo ratings yet
- Summary Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument1 pageSummary Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsCTMundialNo ratings yet
- English TensesDocument2 pagesEnglish TensesGustavo SteffenNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument5 pagesTensesGanesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument6 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsRatmi 'Bundanya Rena'No ratings yet
- Simple Present: TalkedDocument4 pagesSimple Present: TalkedDangVanTamNo ratings yet
- Tense Positive/negative/question Usage Signal WordsDocument4 pagesTense Positive/negative/question Usage Signal WordsMyriam GGoNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument4 pagesTensesZandaNo ratings yet
- Table of English TensesDocument5 pagesTable of English TensesMaria CristianNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Questi On Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument6 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Questi On Use Signal Words: Simple PresentTigercubx9No ratings yet
- Timpuri LeDocument3 pagesTimpuri LemadybyaNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument2 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDebyPuspitaNo ratings yet
- Chart of English TensesDocument2 pagesChart of English TensesNorafiqah Rifhan RamlanNo ratings yet
- Simple Present: I Talk, )Document2 pagesSimple Present: I Talk, )romina5_13No ratings yet
- Table of English TensesDocument3 pagesTable of English TensesShoba DevarajanNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument1 pageTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentVlasta LoncaricNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument18 pagesTensesNora Mestiri100% (1)
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/ Use Signal Words: Ifi TalkDocument4 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/ Use Signal Words: Ifi Talkshel087No ratings yet
- Table of English TensesDocument5 pagesTable of English TenseskaterynavelNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentLecherooMendozaNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple Presentgulzar72No ratings yet
- English Tenses SummaryDocument2 pagesEnglish Tenses SummaryRedi BylekNo ratings yet
- Simple TenseDocument13 pagesSimple TenseChad HayesNo ratings yet
- 8 Parts of Speech TableDocument6 pages8 Parts of Speech TableAnonymous UadvwxNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument2 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentMario SalinasNo ratings yet
- A Global LanguageDocument5 pagesA Global LanguagefthtlNo ratings yet
- Planif IV SC 21 FairylandDocument9 pagesPlanif IV SC 21 FairylandYou YouNo ratings yet
- First Year Hindi Course-Part 2Document376 pagesFirst Year Hindi Course-Part 2Sanjay KumaranNo ratings yet
- Articles, Verbs, NounsDocument5 pagesArticles, Verbs, Nounsكريم نبيل عبدالرحيم محمد محمدNo ratings yet
- Collective NounDocument3 pagesCollective NounHamimah Nasution IsmailNo ratings yet
- Course of Slovenian LanguageDocument3 pagesCourse of Slovenian LanguageRafael Rodrigues100% (1)
- Grammar Rules - List of Attached PhrasesDocument3 pagesGrammar Rules - List of Attached PhrasesMarlon KhanNo ratings yet
- Talkers Magazine New York Times Reader's Digest Washington Post Saturday ReviewDocument2 pagesTalkers Magazine New York Times Reader's Digest Washington Post Saturday ReviewSharad GaushalNo ratings yet
- SPEAK OUT - TB - UINGLB - Unit3Document12 pagesSPEAK OUT - TB - UINGLB - Unit3Daniela AndradeNo ratings yet
- Ahmad Saifur RizalDocument11 pagesAhmad Saifur RizalDony Ilham SyahNo ratings yet
- Tagalog QuizDocument11 pagesTagalog QuizJohn ZerrudoNo ratings yet
- Narrative Text: An Ugly ChickDocument4 pagesNarrative Text: An Ugly ChickTeguh AnwarNo ratings yet
- 1A Present Simple and Continuous (Solo Texto)Document3 pages1A Present Simple and Continuous (Solo Texto)Jean Vinilo100% (1)
- Beginner Unit 3aDocument2 pagesBeginner Unit 3agallipateroNo ratings yet
- Deletion D TDocument4 pagesDeletion D TJORGE ATRIANONo ratings yet
- Grammar Review - 2 Alim '12 - MixDocument5 pagesGrammar Review - 2 Alim '12 - MixkewayzeyNo ratings yet
- Fisa 3Document1 pageFisa 3Toader DianaNo ratings yet
- Pera Pera Penguin 63Document1 pagePera Pera Penguin 63brentk112100% (1)
- A) - Escríbe Las Frases Completas Usando La Forma CorrectaDocument8 pagesA) - Escríbe Las Frases Completas Usando La Forma CorrectasenatinosNo ratings yet
- W / 5 Ÿ NX GDocument71 pagesW / 5 Ÿ NX GIslamic Reserch Center (IRC)No ratings yet
- Adjectives &the Correlative Comparative 2Document4 pagesAdjectives &the Correlative Comparative 2redahakim713No ratings yet
- Grade 5 English Listening Changing The Meaning of Words Caused by Shift in StressDocument4 pagesGrade 5 English Listening Changing The Meaning of Words Caused by Shift in StressSsbf Budong Mordeno JapsonNo ratings yet
- Beginner SyllabusDocument3 pagesBeginner SyllabusDaniel tesfayNo ratings yet
- Past Time ClauseDocument9 pagesPast Time Clausemutii1189No ratings yet
- Guidelines For Transcription of English Consonants and VowelsDocument6 pagesGuidelines For Transcription of English Consonants and VowelsFrancisco MachadoNo ratings yet
- Expressing PossessionDocument5 pagesExpressing PossessionvaniaNo ratings yet
- Phrasal Verbs On CooperateDocument4 pagesPhrasal Verbs On Cooperatekeexalinee muniandyNo ratings yet
- Consonants of Pakistani English: A Study Of: Syeda Iqra Shabbir, Abdur Rehman Tariq, Hafiz Ahmad Bilal, Huma NazarDocument9 pagesConsonants of Pakistani English: A Study Of: Syeda Iqra Shabbir, Abdur Rehman Tariq, Hafiz Ahmad Bilal, Huma NazaradnanNo ratings yet
- A Checklist of Linguistic and Stylistic CategoriesDocument4 pagesA Checklist of Linguistic and Stylistic CategoriesVioleta Nacheva100% (2)
- Spelling Words: How Can Experiencing Nature Change The Way You Think About It? Genre: Narrative NonfictionDocument1 pageSpelling Words: How Can Experiencing Nature Change The Way You Think About It? Genre: Narrative Nonfictionapi-295839823No ratings yet