Professional Documents
Culture Documents
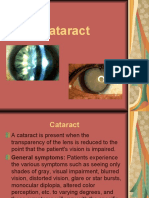
Types of Cataracts
Types of Cataracts
Uploaded by
Mj Baltazar ArtamiaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Types of Cataracts
Types of Cataracts
Uploaded by
Mj Baltazar ArtamiaCopyright:
Available Formats
Types of Cataracts by Location Cataracts are classified by doctors according to the location of the opacity, or clouding, of the lens.
Nuclear Sclerotic Cataract: A nuclear sclerotic cataract is the most common type of age-related cataract. This type of cataract causes a gradual yellow cloudiness and hardening of the central part of the lens called the nucleus. Changes in vision are usually gradual. In some cases, patients may see an actual improvement in near vision before their vision deteriorates to a significant degree. Referred as "second sight," this stage is usually only temporary.
Cortical Cataract: A cortical cataract generally appears as a cloudy opacity in the part of the lens called the cortex. The cortex consists of the peripheral, or outer part, of the lens. These cataracts often resemble wheel spokes that point inward toward the center of the lens. Light tends to scatter when it hits the spoke-like opacities.
Posterior Subcapsular Cataract: Often referred to as a PSC, a posterior subcapsular cataract is an opacity that develops on the back surface of the lens, directly underneath the lens caspsular bag that houses the lens. This type of cataract causes light sensitivity, blurred near vision, and glare and halos around lights. They are more common in diabetic patients and patients who have taken steriods for extended periods of time.
Types of Cataracts by Origin Eye doctors also classify cataracts according to their origin. Age-related Cataract: Most cataracts develop as we age. Although signs can be seen as early as your 40s to 50s, cataracts usually do not become significant until the late 60s or 70s.
Secondary Cataracts: Cataracts can sometimes develop after undergoing eye surgery, such as surgery for glaucoma or retinal surgery. Patients with diabetes sometimes develop cataracts earlier than normal. Also, patients who are taking steroids for an extended period of time may develop cataracts.
Traumatic Cataract: Cataracts sometimes result from direct injury or trauma to the eye. Cataracts may develop immediately or years after an event that damages the eye. Traumatic cataracts often occur after blunt trauma to the eye or from exposure to certain chemicals.
Congenital Cataract: Some children are born with cataracts. In some cases, the inherited cataract is not significant enough to affect vision. If significant, however, the cataract should be removed in order to avoid vision problems, such as strabismus or amblyopia.
Radiation Cataract: Although rare, cataracts sometimes form after exposure to certain types of radiation. This type of cataract may be caused from exposure to ultraviolet lightfrom the sun and other forms of radiation.
You might also like
- Cecilia Laurente Theory of Nursing Practice and CareerDocument2 pagesCecilia Laurente Theory of Nursing Practice and CareerAsh Lee100% (11)
- Perioperative Nursing 50 QuestionsDocument14 pagesPerioperative Nursing 50 QuestionsPaul Anthony Lorica100% (3)
- Womens Health - Post Clinical ReflectionDocument5 pagesWomens Health - Post Clinical Reflectionapi-494643478100% (1)
- Intern Note 終極版Document168 pagesIntern Note 終極版楊芷No ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Nov 2022 B213298B OPTC202Document5 pagesAssignment 1 Nov 2022 B213298B OPTC202Kudzai RusereNo ratings yet
- Biology - The Eye (Cateracts)Document5 pagesBiology - The Eye (Cateracts)Shannen NaraceNo ratings yet
- Cataract-Case Study - ADOMPINGDocument8 pagesCataract-Case Study - ADOMPINGboogeyman6dimakutaNo ratings yet
- CataractDocument17 pagesCataractrhopmaeNo ratings yet
- Biology Invesigatory Project: Group MembersDocument13 pagesBiology Invesigatory Project: Group MembersNavaneeth KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Symptoms and Detection: Crystalline Lens Eye Opacity MyopiaDocument5 pagesSymptoms and Detection: Crystalline Lens Eye Opacity MyopiaNica Joy CandelarioNo ratings yet
- Lens Iris Pupil Retina: Cataract OverviewDocument5 pagesLens Iris Pupil Retina: Cataract Overviewrizky_kurniawan_14No ratings yet
- Causes of Blurred VisionDocument3 pagesCauses of Blurred Visionsintia mariaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Introduction To The Lens and CataractDocument6 pagesChapter 10 Introduction To The Lens and CataractFarah FarahNo ratings yet
- Lens CataractDocument16 pagesLens CataractSari RakhmawatiNo ratings yet
- CataractDocument19 pagesCataractShan YahyaNo ratings yet
- Cataracts The Mayo ClinicDocument6 pagesCataracts The Mayo ClinicJandz MNNo ratings yet
- CataractDocument6 pagesCataractKarel LuNo ratings yet
- CataractDocument5 pagesCataractTriXie SorrillaNo ratings yet
- CataractDocument19 pagesCataractBryan DorosanNo ratings yet
- CataractDocument5 pagesCataractAbhinandan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Cataract: Mohd Roslee Bin Abd GhaniDocument46 pagesCataract: Mohd Roslee Bin Abd GhaniSaha DirllahNo ratings yet
- Retinal DetachmentDocument6 pagesRetinal DetachmentNader Smadi100% (3)
- Terminology: Nuclear Sclerotic CataractsDocument4 pagesTerminology: Nuclear Sclerotic CataractsBenjamin NgNo ratings yet
- Cataract SurgeryDocument9 pagesCataract SurgerygandikotavtpsNo ratings yet
- Retinal DetachmentDocument8 pagesRetinal DetachmentMaisarah BakariNo ratings yet
- UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES"REZONANCA"-Halil Ajvazi/Ophthalmology/Prishtina/Republic of KosovaDocument98 pagesUNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES"REZONANCA"-Halil Ajvazi/Ophthalmology/Prishtina/Republic of KosovaHALIL Z.AJVAZI100% (1)
- PSSS-Mata Tenang Visus Turun PerlahanDocument48 pagesPSSS-Mata Tenang Visus Turun PerlahanYesi 'faiqa Putir100% (1)
- CataractDocument2 pagesCataractatilano_patrickNo ratings yet
- Retinal DetachmentDocument19 pagesRetinal DetachmentJohn Hans CaturasNo ratings yet
- Eye Disorders: Presented by Carmelita Ramos, RNDocument65 pagesEye Disorders: Presented by Carmelita Ramos, RNJayme_Galang_7078100% (1)
- TimRoot - Chapter 10 - Introduction To The Lens and Cataract SurgeryDocument1 pageTimRoot - Chapter 10 - Introduction To The Lens and Cataract SurgeryBaeyerNo ratings yet
- Retinal DetachmentDocument2 pagesRetinal Detachmentwieka mawieNo ratings yet
- A Cataract Is A Clouding of The EyeDocument5 pagesA Cataract Is A Clouding of The EyeHikari 光 ShidouNo ratings yet
- Activity3 (Refraction-Errors)Document8 pagesActivity3 (Refraction-Errors)Gabbii CincoNo ratings yet
- Cataract: Antony Halim I4061162030Document50 pagesCataract: Antony Halim I4061162030Gilang PramanayudhaNo ratings yet
- Cataract CasestudyDocument3 pagesCataract CasestudyJamal AgontongNo ratings yet
- Retinal DetachmentDocument16 pagesRetinal DetachmentCandice Lim Swee LingNo ratings yet
- Cataracts Teaching PlanDocument4 pagesCataracts Teaching PlanShaina Diya100% (2)
- CataractsDocument7 pagesCataractsOktovia KakaNo ratings yet
- Cataracts: What Are They?Document3 pagesCataracts: What Are They?RSarkawyNo ratings yet
- CATARACTDocument1 pageCATARACTYan SolivenNo ratings yet
- Rhegmatogenous (reg-ma-TODGE-uh-nus) - These Types of Retinal DetachmentsDocument2 pagesRhegmatogenous (reg-ma-TODGE-uh-nus) - These Types of Retinal Detachmentsmedhat444444No ratings yet
- Retinal DetachmentDocument7 pagesRetinal Detachmentjay dewanagnNo ratings yet
- CataractsDocument72 pagesCataractsKusum RoyNo ratings yet
- Lens DiseaseDocument80 pagesLens Disease39 Akshit SetiaNo ratings yet
- Vitreous Gel Eye Retinal Detachment OphthalmologistDocument12 pagesVitreous Gel Eye Retinal Detachment OphthalmologistLesTrechSaNo ratings yet
- Cataract Surgery - : After The ProcedureDocument16 pagesCataract Surgery - : After The ProcedureAmandeep Singh GandhiNo ratings yet
- Adult Cataract: Cortical or Soft CataractDocument6 pagesAdult Cataract: Cortical or Soft CataractJohn Christopher LucesNo ratings yet
- Learn About CataractsDocument41 pagesLearn About CataractsRizkyAgustriaNo ratings yet
- LASIK (Laser Assisted in Situ Keratomileusis) :: MyopiaDocument18 pagesLASIK (Laser Assisted in Situ Keratomileusis) :: MyopiaFawaz Bin AbdullahNo ratings yet
- CataractDocument63 pagesCataractMutti KakarNo ratings yet
- Extracapsular Cataract Extraction (OR)Document4 pagesExtracapsular Cataract Extraction (OR)Jet-Jet GuillerganNo ratings yet
- Astigmatism 1Document14 pagesAstigmatism 1Adewumi AdinoyNo ratings yet
- Ochiul Si Bolile SaleDocument7 pagesOchiul Si Bolile SaleRares PopeiaNo ratings yet
- Impaired VisionDocument3 pagesImpaired VisionJannelle Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Traumatic Cataracts Occur Secondary To Blunt or Penetrating Ocular TraumaDocument3 pagesTraumatic Cataracts Occur Secondary To Blunt or Penetrating Ocular TraumaGrandy TalanilaNo ratings yet
- Сataract 09Document32 pagesСataract 09somebody_maNo ratings yet
- Cataracts: When To See A DoctorDocument4 pagesCataracts: When To See A DoctorMohammed Shamiul ShahidNo ratings yet
- Mata Tenang Visus Turun MendadakDocument74 pagesMata Tenang Visus Turun MendadakYeni AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- Cataract LectureDocument22 pagesCataract Lecturenashadmohammed99No ratings yet
- Low Vision: Assessment and Educational Needs: A Guide to Teachers and ParentsFrom EverandLow Vision: Assessment and Educational Needs: A Guide to Teachers and ParentsNo ratings yet
- Spirit Attachment and Human HealthDocument7 pagesSpirit Attachment and Human HealthShiva Shankar100% (4)
- National Medication Safety Guidelines Manual: June 2013Document29 pagesNational Medication Safety Guidelines Manual: June 2013enik praNo ratings yet
- Signs in MedicineDocument25 pagesSigns in MedicinepavanNo ratings yet
- Lyme DiseaseDocument133 pagesLyme Diseaseernestval100% (3)
- CinacalcetDocument4 pagesCinacalcetSorina HermanNo ratings yet
- Special Considerations in IV TherapyDocument19 pagesSpecial Considerations in IV TherapyThad AlstrupNo ratings yet
- Motor neurone disease د.رشاد عبدالغنيDocument18 pagesMotor neurone disease د.رشاد عبدالغنيMohammad BelbahaithNo ratings yet
- PharmacokineticsDocument32 pagesPharmacokineticsmursidstone.mursid50% (2)
- The Quarantine War: The Burning of The New York Marine Hospital in 1858Document14 pagesThe Quarantine War: The Burning of The New York Marine Hospital in 1858Patricia DillonNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation Station 3B Drug Study ClinidineDocument6 pagesCase Presentation Station 3B Drug Study ClinidinehahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Prof DR Mark Fitzgerald What Is A Trauma System and Trauma System ComponentsDocument36 pagesProf DR Mark Fitzgerald What Is A Trauma System and Trauma System ComponentsBrunoNo ratings yet
- Chapter Seven: Making and Maintaining BedDocument79 pagesChapter Seven: Making and Maintaining Bedesubalew diress100% (1)
- Ailyn - Perez - ResumeDocument6 pagesAilyn - Perez - ResumeJhullian Frederick Val VergaraNo ratings yet
- Ob 1Document13 pagesOb 1iandame100% (1)
- Star Health InsuranceDocument21 pagesStar Health InsuranceShubham Chaudhari100% (1)
- Forensic Files: Setting Up A Death Row Psychiatry ProgramDocument4 pagesForensic Files: Setting Up A Death Row Psychiatry Programxiejie22590No ratings yet
- Quality Assurance For Intensive Care UnitsDocument3 pagesQuality Assurance For Intensive Care UnitsCHANDAK HOSPITALNo ratings yet
- Inneffective Health Maintenence Care PlanDocument3 pagesInneffective Health Maintenence Care PlanTammy Litzenberger-HarrisNo ratings yet
- The Single-Tooth Dental Implant: Practical Guidelines For Hard Tissue AugmentationDocument16 pagesThe Single-Tooth Dental Implant: Practical Guidelines For Hard Tissue Augmentation歐亦焜100% (1)
- Radiotherapy and Oncology: Brachytherapy of Cervical CancerDocument8 pagesRadiotherapy and Oncology: Brachytherapy of Cervical CancerodivarNo ratings yet
- Meckel's DiverticulumDocument8 pagesMeckel's DiverticulumNurul An NisaNo ratings yet
- Dr. Akhil Agrawal, DR Dipankar Deb, DR Bijush Difoesa, DR Arup Sarma Dept of Medicine, Silchar Medical Colege & HospitalDocument1 pageDr. Akhil Agrawal, DR Dipankar Deb, DR Bijush Difoesa, DR Arup Sarma Dept of Medicine, Silchar Medical Colege & HospitalNATHANAEL SUNGTENo ratings yet
- QATAR Western Asia. InformaticsDocument2 pagesQATAR Western Asia. Informaticsanne marieNo ratings yet
- Class 1 Type 5Document61 pagesClass 1 Type 5Buchangot Dollentas60% (5)
- Tooth ExtractionDocument14 pagesTooth ExtractionGarry B Gunawan100% (2)
- Contoh Original ArticleDocument4 pagesContoh Original ArticlecaesaredoNo ratings yet