Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Intel 8085 Microprocessor Architecture
Intel 8085 Microprocessor Architecture
Uploaded by
Faheem Ahmed ShaikhOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Intel 8085 Microprocessor Architecture
Intel 8085 Microprocessor Architecture
Uploaded by
Faheem Ahmed ShaikhCopyright:
Available Formats
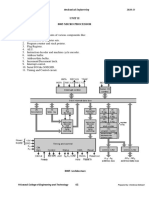
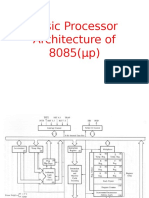
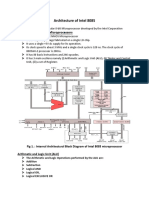
Intel 8085 microprocessor architecture
Memory
Program, data and stack memories occupy the same memory space. The total addressable memory size is 64 KB. Program memory - program can be located anywhere in memory. Jump, branch and call instructions use 16-bit addresses, i.e. they can be used to jump/branch anywhere within 64 KB. All jump/branch instructions use absolute addressing. Data memory - the data can be placed anywhere as the 8085 processor always uses 16-bit addresses. Stack memory is limited only by the size of memory. Stack grows downward. First 64 bytes in a zero memory page should be reserved for vectors used by RST instructions.
Interrupts
The 8085 microprocessor has 5 interrupts. They are presented below in the order of their priority (from lowest to highest): INTR is maskable 8080A compatible interrupt. When the interrupt occurs the processor fetches from the bus one instruction, usually one of these instructions:
One of the 8 RST instructions (RST0 - RST7). The processor saves current program counter into stack and branches to memory location N * 8 (where N is a 3-bit number from 0 to 7 supplied with the RST instruction). CALL instruction (3 byte instruction). The processor calls the subroutine, address of which is specified in the second and third bytes of the instruction.
RST5.5 is a maskable interrupt. When this interrupt is received the processor saves the contents of the PC register into stack and branches to 2Ch (hexadecimal) address. RST6.5 is a maskable interrupt. When this interrupt is received the processor saves the contents of the PC register into stack and branches to 34h (hexadecimal) address. RST7.5 is a maskable interrupt. When this interrupt is received the processor saves the contents of the PC register into stack and branches to 3Ch (hexadecimal) address. Trap is a non-maskable interrupt. When this interrupt is received the processor saves the contents of the PC register into stack and branches to 24h (hexadecimal) address.
All maskable interrupts can be enabled or disabled using EI and DI instructions. RST 5.5, RST6.5 and RST7.5 interrupts can be enabled or disabled individually using SIM instruction.
I/O ports
256 Input ports 256 Output ports
Registers
Accumulator or A register is an 8-bit register used for arithmetic, logic, I/O and load/store operations. Flag is an 8-bit register containing 5 1-bit flags:
Sign - set if the most significant bit of the result is set. Zero - set if the result is zero. Auxiliary carry - set if there was a carry out from bit 3 to bit 4 of the result. Parity - set if the parity (the number of set bits in the result) is even. Carry - set if there was a carry during addition, or borrow during subtraction/comparison.
General registers:
8-bit B and 8-bit C registers can be used as one 16-bit BC register pair. When used as a pair the C register contains low-order byte. Some instructions may use BC register as a data pointer. 8-bit D and 8-bit E registers can be used as one 16-bit DE register pair. When used as a pair the E register contains low-order byte. Some instructions may use DE register as a data pointer. 8-bit H and 8-bit L registers can be used as one 16-bit HL register pair. When used as a pair the L register contains low-order byte. HL register usually contains a data pointer used to reference memory addresses.
Stack pointer is a 16 bit register. This register is always incremented/decremented by 2. Program counter is a 16-bit register.
Instruction Set
Instruction set of Intel 8085 microprocessor consists of the following instructions:
Data moving instructions. Arithmetic - add, subtract, increment and decrement. Logic - AND, OR, XOR and rotate.
Control transfer - conditional, unconditional, call subroutine, return from subroutine and restarts. Input/Output instructions. Other - setting/clearing flag bits, enabling/disabling interrupts, stack operations, etc.
Addressing modes
Register - references the data in a register or in a register pair. Register indirect - instruction specifies register pair containing address, where the data is located. Direct. Immediate - 8 or 16-bit data. Comments: 8 4 comments were recently rejected. Please see a reason here.
8085 microprocessor architecture
2011-10-18 05:47:49 Posted by: Amit Tyagi
functioning of ALU in 8085
2012-01-02 11:48:00 Posted by: p.sri pallavi the arithmetic and logical unit will be performing *8 bit addition with /with out carry *8bit substraction with /with out borrow *2 bit BCD(Binary coded decimal) addition *16 bit binary addition*16 bit logical operations-OR,AND,EX-OR,COMPLEMENT and BIT SHIFT OPERATIONS
address/data buffer
2012-01-06 08:10:13 Posted by: punna sri pallavi
the address bus will be having 16 address lines[A15-A0] .In which A7-A0 are called as lower addressing lines and these are multiplexed with data lines[D7-D0] to form multiplexed address /data buffer .The address/data buffer is the bidirectional bus.
address buffer
2012-01-06 08:14:29 Posted by: punna sri pallavi the remaining higher order address lines form the address buffer ranging from[A15-18].This is having the unidirectional buffer
Instruction register
2012-01-06 08:19:21 Posted by: punna sri pallavi there are 74 instructions in 8085 .these instructions are classified in to 5 addressing modes they are 1)immediate addressing mode 2)register addressing mode 3)direct addressing mode 4)indirect addressing mode 5)implied addressing mode
serial i/o control
2012-01-06 08:24:19 Posted by: punna sri pallavi these are control signals used for controlling 8085 these are subdivided into 2 types 1)SID(serial input data):this is used for transferring of data into the memory serially 2)SOD(serial output data):this is used for transferring of data from memory to external devices
Intel 8085 microprocessor
2012-01-13 10:58:13 Posted by: Shuvendu sekhar sahu PSW-Five bits are indicate the set of flag and three bits are indicate undefined.The combination of 8bit is programble status word.
Instruction resister or Decoder:-Once the instruction is fetch from thememory,it is reloaded in the instruction resistor for some time, after the decoder decode the instruction performing some event or task.
Resistor Array:-It consists of several types of resistor such as general purpose resistor, stack
pointer,& program counfer (PC).There are 6,8 bit general purpose resistor those are B,C, D, E, H, L, all the resistor are called program
components of 8085
2012-04-24 16:33:05 Posted by: ASHISH TIWARY..gla university. the architecture of 8085 consist various components like. 1:Register. 2:ALU. 3:Instruction decoder and machin cycle encoder. 4:Address buffer. 5:Address/data buffer. 6:Inc/Dec latch. 7:Interrupt controll. 8:Serial i/o like SOD,SID. 9:Timing and Controll circuit.
You might also like
- Training BrochureTRICONEXDocument16 pagesTraining BrochureTRICONEXNissi JimmyNo ratings yet
- AZ-900 Exam - Free Actual Q&as, Page 1 - ExamTopicsDocument562 pagesAZ-900 Exam - Free Actual Q&as, Page 1 - ExamTopicsJoão Victor0% (1)
- Intel 8085 Microprocessor ArchitectureDocument3 pagesIntel 8085 Microprocessor ArchitectureNisha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Intel 8085 Microprocessor ArchitectureDocument2 pagesIntel 8085 Microprocessor ArchitectureipoonamNo ratings yet
- 8085 Is Pronounced AsDocument9 pages8085 Is Pronounced AsArbaaz khan786No ratings yet
- MCT Unit 2Document26 pagesMCT Unit 2Aravind RajNo ratings yet
- Unit Ii 8085 Micro Processor 8085 Architecture:: ME 6702 Mechatronics Mechanical Engineering 2019-20Document26 pagesUnit Ii 8085 Micro Processor 8085 Architecture:: ME 6702 Mechatronics Mechanical Engineering 2019-20GopinathNo ratings yet
- Micro Processor DineshDocument9 pagesMicro Processor DineshsandyNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor 8085 ArchitectureDocument19 pagesMicroprocessor 8085 ArchitectureSindhujaSindhuNo ratings yet
- 8085 MicroprocessorDocument13 pages8085 MicroprocessorSajid Akram100% (1)
- Experiment 1 4 SemesterDocument6 pagesExperiment 1 4 Semesteraman YadavNo ratings yet
- MTE-605 Assingment2 ProcessorDocument6 pagesMTE-605 Assingment2 ProcessorAeronautical EngineerNo ratings yet
- Microsad Q2Document66 pagesMicrosad Q2John Railey P. PamintuanNo ratings yet
- EE6502MPMC1Document31 pagesEE6502MPMC1nirmal_inboxNo ratings yet
- Syllabus: 8085 ArchitectureDocument25 pagesSyllabus: 8085 Architecturetamilvendhan87No ratings yet
- Organization of Intel 8085Document6 pagesOrganization of Intel 8085Athiesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire MICROPROCESSOR PART 1 UNIT 1 and 2Document20 pagesQuestionnaire MICROPROCESSOR PART 1 UNIT 1 and 2aditya2021cs081No ratings yet
- Micro-Processors 8085: D.Arun KumarDocument52 pagesMicro-Processors 8085: D.Arun Kumarsrihari yandrapragadaNo ratings yet
- 8085 Microprocessor ArchitectureDocument3 pages8085 Microprocessor Architecturetguna21No ratings yet
- Architechture of 8085: Q. Explane Micro Processor 8085 With Its Block Diagram?Document13 pagesArchitechture of 8085: Q. Explane Micro Processor 8085 With Its Block Diagram?Shubham SahuNo ratings yet
- 8085 MicroprocessorDocument25 pages8085 Microprocessorprofessor2062No ratings yet
- Z80 CPU ArchitectureDocument7 pagesZ80 CPU ArchitecturelyfsaverNo ratings yet
- Unit I PDFDocument25 pagesUnit I PDFSomnath2014No ratings yet
- MICROPORCESSOR 8085 Lab ManualDocument53 pagesMICROPORCESSOR 8085 Lab ManualAjay PatilNo ratings yet
- 8085 Intel MicroprocessorDocument16 pages8085 Intel MicroprocessorMartino Ojwok AjangnayNo ratings yet
- Archi 8086Document3 pagesArchi 8086Shashin KaswateNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Lab Viva Questions & AnswersDocument11 pagesMicroprocessor Lab Viva Questions & AnswersOishika C.100% (1)
- 8085 Microprocessor - Functional Units: AccumulatorDocument20 pages8085 Microprocessor - Functional Units: AccumulatorCarlnagum 123456789No ratings yet
- MPC 2Document29 pagesMPC 2rohit sharmaNo ratings yet
- Micrprocessor Notes 2023Document18 pagesMicrprocessor Notes 2023GautamNo ratings yet
- Viva Questions and Answers in MP Lab - 1Document6 pagesViva Questions and Answers in MP Lab - 1Sai KrishnaNo ratings yet
- 8085Document2 pages8085$vidyaNo ratings yet
- MPMC Eee Unit - I 8085 ProcessorDocument35 pagesMPMC Eee Unit - I 8085 ProcessorAnonymous zaMNkL100% (1)
- C5 - Intro To 8085 - Hardware PDFDocument39 pagesC5 - Intro To 8085 - Hardware PDFsiti hajarNo ratings yet
- Notes Unit 1Document25 pagesNotes Unit 1Ashish YadavNo ratings yet
- FMM Unit-1Document28 pagesFMM Unit-1CS ENo ratings yet
- Microprocessor 8085 & 8086 BASICSDocument11 pagesMicroprocessor 8085 & 8086 BASICSbhavyaNo ratings yet
- BABARAN - ASSIGNMENT (Motorola 6800 Microprocessor)Document5 pagesBABARAN - ASSIGNMENT (Motorola 6800 Microprocessor)Maybelyn BorresNo ratings yet
- MPDocument34 pagesMPAbhinandan JainNo ratings yet
- Intel 8086 Microprocessor ArchitectureDocument16 pagesIntel 8086 Microprocessor Architecturelu4rohitNo ratings yet
- MPMC - Unit 1 - 8085 ArchitectureDocument17 pagesMPMC - Unit 1 - 8085 ArchitectureWickNo ratings yet
- 8085 Architecture & Pin DescriptionFileDocument19 pages8085 Architecture & Pin DescriptionFileKaseya TakahashiNo ratings yet
- MIC 04 - Case Study One 8085 MPUDocument40 pagesMIC 04 - Case Study One 8085 MPUomar hanyNo ratings yet
- 8085 Microprocessor - Functional Units: AccumulatorDocument3 pages8085 Microprocessor - Functional Units: AccumulatorANKIT SHARMANo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Ree602Document235 pagesUnit 3 Ree602Praveen YadavNo ratings yet
- 8086 Architecture:: 8. Single Bit Serial I/O PortsDocument67 pages8086 Architecture:: 8. Single Bit Serial I/O PortsSri ShandilyaNo ratings yet
- 8085 ArchitectureDocument13 pages8085 ArchitectureShubham BokoliaNo ratings yet
- Microprocessors and Microcontrollers Answer KeyDocument14 pagesMicroprocessors and Microcontrollers Answer KeyselvaNo ratings yet
- Architecture of 8085 MicroprocessorDocument69 pagesArchitecture of 8085 Microprocessornamrata puranikNo ratings yet
- EE6502 MPMC Two Marks With AnswerDocument10 pagesEE6502 MPMC Two Marks With Answervlsimani9110100% (1)
- Microprocessors and Microcontrollers NotesDocument293 pagesMicroprocessors and Microcontrollers NotesKumar ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Intel 8085 ArchitectureDocument8 pagesIntel 8085 ArchitectureAravind VJNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor NotesDocument21 pagesMicroprocessor NotesAdhithyaNo ratings yet
- Part 2 Chapter 1Document26 pagesPart 2 Chapter 1zor123oooNo ratings yet
- Intel 8086 Microprocessor ArchitectureDocument15 pagesIntel 8086 Microprocessor ArchitectureShashank SoodNo ratings yet
- MPMC Eee Unit - III 8051 MicrocontrollerDocument35 pagesMPMC Eee Unit - III 8051 MicrocontrollerAnonymous 4u5XkWGONo ratings yet
- 8085 Features, Signal DescriptionDocument13 pages8085 Features, Signal DescriptionRakesh Kumar DNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Lab Viva Questions With AnswersDocument11 pagesMicroprocessor Lab Viva Questions With AnswersReddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet
- MPMC Model Exam Answer KeyDocument21 pagesMPMC Model Exam Answer KeyVenkatesan SundaramNo ratings yet
- 8051 TutorialDocument8 pages8051 TutorialVivek GuptaNo ratings yet
- Memory: Motorola 6800 Microprocessor ArchitectureDocument2 pagesMemory: Motorola 6800 Microprocessor ArchitectureShavel KumarNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Specifications: Programmed Data Processor Model Three (PDP-3) October, 1960From EverandPreliminary Specifications: Programmed Data Processor Model Three (PDP-3) October, 1960No ratings yet
- Tu-Bf Mapping Ehp 2-7 F Erp 6 v1Document47 pagesTu-Bf Mapping Ehp 2-7 F Erp 6 v1Faheem Ahmed ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Dbacockpit ErrorDocument1 pageDbacockpit ErrorFaheem Ahmed ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Gate Questions Microprocessor and MicrocontrollerDocument32 pagesGate Questions Microprocessor and Microcontrollersjo05No ratings yet
- JunaidDocument2 pagesJunaidFaheem Ahmed ShaikhNo ratings yet
- AutoDesk UniversityDocument16 pagesAutoDesk UniversitytakudomeNo ratings yet
- Solaris 10 Boot Process SparcDocument3 pagesSolaris 10 Boot Process SparcMohaideen100% (1)
- White Paper Has Oop FailedDocument13 pagesWhite Paper Has Oop FailedBayram İnançNo ratings yet
- LogcatDocument8,075 pagesLogcatBrenda HernandezNo ratings yet
- Computer Science: Topic 2.4 Boolean LogicDocument5 pagesComputer Science: Topic 2.4 Boolean Logicnouse glNo ratings yet
- Bell Product List 2019Document20 pagesBell Product List 2019m.p.enterprisesNo ratings yet
- AS72xx - AN000488 - 3-00 How To Program AS72xx Firmware With FlashCatUSB 1V24Document10 pagesAS72xx - AN000488 - 3-00 How To Program AS72xx Firmware With FlashCatUSB 1V24Victor Calinao Jr.No ratings yet
- DB 2 TopDocument4 pagesDB 2 TopImran ShaikhNo ratings yet
- PC PackageDocument104 pagesPC Packageanmol sainiNo ratings yet
- Macintosh II - IixDocument87 pagesMacintosh II - IixApolloOneNo ratings yet
- What Is Arduino?Document4 pagesWhat Is Arduino?Zakaria MourtadiNo ratings yet
- Module 3 ACA NotesDocument50 pagesModule 3 ACA NotesShylajaNo ratings yet
- R5905948 - 05 - UserGuide - EM Copy HighlightsDocument538 pagesR5905948 - 05 - UserGuide - EM Copy HighlightsEric DezNo ratings yet
- Oracle® Enterprise Manager: Management Agent Release Notes For Solaris x86 and x86-64 10g Release 2 (10.2.0.2)Document18 pagesOracle® Enterprise Manager: Management Agent Release Notes For Solaris x86 and x86-64 10g Release 2 (10.2.0.2)sathish4sree581No ratings yet
- C++ Chapter 7 Solution of Data Handling by Sumita AroaDocument12 pagesC++ Chapter 7 Solution of Data Handling by Sumita AroaKamal Joshi43% (7)
- Oracle Session TracingDocument19 pagesOracle Session TracingSHAHID FAROOQNo ratings yet
- Vifm HelpDocument5 pagesVifm Helpmytemporaryusername100% (1)
- Asus N53JQDocument2 pagesAsus N53JQFathima FarhanNo ratings yet
- Eclipse PDFDocument18 pagesEclipse PDFanjaniNo ratings yet
- MCA Part-I - Part-II - Part-IIIDocument23 pagesMCA Part-I - Part-II - Part-IIIAvinash SinghNo ratings yet
- Intel Desktop Board D525MW Technical Product SpecificationDocument88 pagesIntel Desktop Board D525MW Technical Product SpecificationArcangelo Di BattistaNo ratings yet
- Readme 30Document6 pagesReadme 30oquiwebNo ratings yet
- Ict Performance Task 2 Quarter 2Document48 pagesIct Performance Task 2 Quarter 2caguioarhiannechloe91No ratings yet
- Unit 4Document62 pagesUnit 4dawnglianiNo ratings yet
- Python Telegram Bot Readthedocs Io en StableDocument282 pagesPython Telegram Bot Readthedocs Io en StablePOTS BDJNo ratings yet
- Juniper Sky Enterprise: Product OverviewDocument6 pagesJuniper Sky Enterprise: Product OverviewKevin SNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Java Programming With LinuxDocument77 pagesUnit 4 Java Programming With Linuxmelbin mathewNo ratings yet
- Estudio 385SDocument2 pagesEstudio 385SSamo AbdalaNo ratings yet