Professional Documents
Culture Documents
(a) (i) Estimation method 1: (Area) Area of circular pavement = (300 π - 100 π) cm = 800π cm Area of a tile = 25 cm x 10 cm = 250 cm
(a) (i) Estimation method 1: (Area) Area of circular pavement = (300 π - 100 π) cm = 800π cm Area of a tile = 25 cm x 10 cm = 250 cm
Uploaded by
Villcent AyxOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
(a) (i) Estimation method 1: (Area) Area of circular pavement = (300 π - 100 π) cm = 800π cm Area of a tile = 25 cm x 10 cm = 250 cm
(a) (i) Estimation method 1: (Area) Area of circular pavement = (300 π - 100 π) cm = 800π cm Area of a tile = 25 cm x 10 cm = 250 cm
Uploaded by
Villcent AyxCopyright:
Available Formats
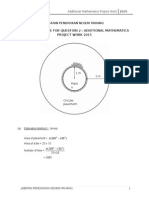
Question 2
(a) (i) Estimation method 1 : (Area)
Area of circular pavement = (300
2
- 100
2
) cm
2
= 800 cm
2
Area of a tile = 25 cm x 10 cm
= 250 cm
2
Number of tiles =
= 1005
2 m
1 m
Circular pavement
Plants
Estimation method 2 : (Concept of arithmetic progression)
Starting from the interior,
The number of tiles for the first layer =
)
The number of tiles for the second layer =
)
The number of tiles for the third layer =
)
This is an arithmetic progression with
)
+
)
+
)
+ ... +
)
Number of tiles =
+
25
) 290 ( 2
25
) 100 ( 2 t t
= 980
(ii) Method 2 is more accurate as compared with method 1. This is because method
2 takes into consideration the spaces between tiles whereas method 1 does not.
Method 1 is quick and simple and therefore easy to understand.
(iii) Method 1 is being used by most experienced mason with some medication as
this method is quick and simple and easy to understand. Due to their
experience, they deduct a certain number of tiles from the total number
required by the area calculation to compensate for the spaces between tiles, and
they are quite accurate.
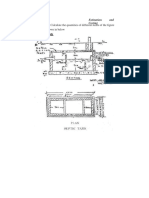
(b) Octagonal pavement
(i) Method 1 : (Area)
Area of octagonal pavement = 8[
(300)(300) -
(100)(100) ]
= 8 x
(80000)
= 320000
Number of tiles =
= 905
Method 2 : (Concept of arithmetic progression)
Referring to the diagram on the right,
This is an arithmetic progression with ,
Number of layers =
= 18.4776 18
=
=
| | + 5 . 22 tan 20 ) 1 18 ( ) 5 . 22 sin 200 ( 2
Number of tiles =
= 105.81 106
Total number of tiles for octagonal pavement = 8 x 106
= 848
There is quite a difference between method 1 and method 2. This is probably due
to the number of layers of tiles. Method 2 only considers 18 complete tiles which
does not cover the whole area of octagonal pavement whereas method 1
considers the whole area.
(ii) Comparing the circular design and the octagonal design, the octagonal design
will be easier to construct because of its straight line layers and management of
the few empty spaces between the tiles. To lay the tiles in circles will be quite a
task and there empty spaces to fill between every tile.
FURTHER EXPLORATION
(a) Two circular plots pavement
Refer to diagram beside.
Method 1 :
Z
Area of segment KLMN =
(300
2
)(1.171-)
= 11238.60 cm
2
Number of tiles required =
= 44.95
Number of tiles required for the pavement
= 2(1005-45)
= 1920
Method 2 :
To calculate the number of tiles required for the arcs passing through points K
1
, K
2
,
K
3
and K
4
.
(i) Arc passing through point K
1
Arc length = 290(
x 2
)
= 308.25 cm
Number of tiles required = 12.33
(ii) Arc passing through point K
2
Arc length = 280(
x 2
)
= 261.60 cm
Number of tiles required = 10.46
(iii) Arc passing through point K
3
Arc length = 270(
x 2
)
= 209.15 cm
Number of tiles required = 8.366
(iv) Arc passing through point K
4
Arc length = 260(
x 2
)
= 144.69 cm
Number of tiles required = 5.788
(v) Total number of tiles required for the pavement
= 2S
20
2(12.33+10.46+8.366+5.788)
= 2 x
+
25
) 290 ( 2
25
) 100 ( 2 t t
- 73.89
= 1886
(b) Refer to diagram beside.
Area of triangle EFG = 2 x
x HF x EH
= 50 x 50
Total area of pavement
= 2 x 8 x
(80000) - 2 x 2500
= 440477.27 cm
2
Number of tiles required = 1761.91
(c) I will choose the overlapping double octagonal design as shown in Diagram 3. The
alternative design that I will suggest is an overlapping double rhombus design.
This is because the number of tiles used is lesser and it makes a better landscape.
(d) It is not practical to use aluminium tins and sand to lay the pavement. Brick is very
heavy as compared to aluminium but it costs cheaper than other materials and
gives good cold and heat insulation. It is also waterproof and fireproof. However,
aluminium is not suitable to be used in pavement because there is a sharp edge on
the aluminium tin which can even cause injuries to the people who step on it.
You might also like
- ATI TEAS Calculation Workbook: 300 Questions to Prepare for the TEAS (2023 Edition)From EverandATI TEAS Calculation Workbook: 300 Questions to Prepare for the TEAS (2023 Edition)No ratings yet
- BAYLOR 7040 166-54238 Rev FDocument68 pagesBAYLOR 7040 166-54238 Rev FPablo Galvez Rodriguez100% (4)
- Exercise 1 (Permeability And Seepage) : i= h S hcosα SDocument11 pagesExercise 1 (Permeability And Seepage) : i= h S hcosα SMuhammad Abi Rafdi100% (1)
- Toward A Theory of DeceptionDocument37 pagesToward A Theory of DeceptionThe Angry ManNo ratings yet
- Transportation and LogisticsDocument2 pagesTransportation and LogisticsBorwinVistin59% (22)
- 8.solution - Project 2-Circular MeasureDocument10 pages8.solution - Project 2-Circular MeasurekedaitakafulbsnNo ratings yet
- Additional Mathematics - Circular Measure (SPM Project Work)Document15 pagesAdditional Mathematics - Circular Measure (SPM Project Work)Mukhriz ZubaidiNo ratings yet
- Surface Area of Solids AnsDocument4 pagesSurface Area of Solids Ansmoggadavid480No ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Mar 06, 2024Document7 pagesAdobe Scan Mar 06, 2024Simbai MuganoNo ratings yet
- BEM 6th Ed Sol To Exerc Chap 25 2013Document13 pagesBEM 6th Ed Sol To Exerc Chap 25 2013Josh AmuraoNo ratings yet
- UEM Sol To Exerc Chap 027Document13 pagesUEM Sol To Exerc Chap 027Joshua Phil100% (1)
- UEM Sol To Exerc Chap 027Document13 pagesUEM Sol To Exerc Chap 027TriciaNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 13 Surface Areas and VolumesDocument37 pagesNCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 13 Surface Areas and VolumesAnshu ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Module 10Document6 pagesModule 10Be LoveNo ratings yet
- Surveying Area and VolumeDocument15 pagesSurveying Area and VolumeSyahir HamidonNo ratings yet
- Regular Evaluation Test IV Maths VIII ADocument4 pagesRegular Evaluation Test IV Maths VIII AB.L. Indo Anglian Public School, Aurngabad, BiharNo ratings yet
- Class Vii Ae 2023-24 Revision WorksheetDocument4 pagesClass Vii Ae 2023-24 Revision Worksheetruchikhatri085No ratings yet
- Area and Volume - Additional NotesDocument32 pagesArea and Volume - Additional Notesdkariuki383No ratings yet
- Applcations of CalculusDocument9 pagesApplcations of CalculusJayanth VenkateshNo ratings yet
- EfafrDocument50 pagesEfafrRonel ViolantaNo ratings yet
- Selangor 2011 P2Document4 pagesSelangor 2011 P2Sim Kwang YawNo ratings yet
- Sheet ch.2 - FinsDocument15 pagesSheet ch.2 - Finshoran8750No ratings yet
- Assignment 3 Solutions PDFDocument11 pagesAssignment 3 Solutions PDFrockbottom 123No ratings yet
- Survey II NotesDocument95 pagesSurvey II NotesJoshua KiptooNo ratings yet
- Binder 1Document55 pagesBinder 1dkariuki383No ratings yet
- Surface Areas and Volumes: Points To RememberDocument28 pagesSurface Areas and Volumes: Points To RememberSipra PaulNo ratings yet
- 2015 James Ruse Agricultural HS Ext 2Document26 pages2015 James Ruse Agricultural HS Ext 2omhreemaimhreemNo ratings yet
- Sample 2 MsDocument5 pagesSample 2 MsjobyvallikunnelNo ratings yet
- 1 FT 12 63 LB: Weight of Ice 25 X X FT x93Document4 pages1 FT 12 63 LB: Weight of Ice 25 X X FT x93Ron PascualNo ratings yet
- Generator RoomDocument9 pagesGenerator Roomankit suriNo ratings yet
- Sec 1 Paradigm Math Basic GeometryDocument5 pagesSec 1 Paradigm Math Basic GeometryIzabelleNo ratings yet
- 2012 MJC MBT QN Paper For JC2 MBT RevisionDocument3 pages2012 MJC MBT QN Paper For JC2 MBT RevisionAng Wei NengNo ratings yet
- Maths Class VI Practice Test 07 Mensuration AnswersDocument6 pagesMaths Class VI Practice Test 07 Mensuration AnswersSHWETA SOODNo ratings yet
- Mhuka Form 1 p1 MathsDocument5 pagesMhuka Form 1 p1 MathsHillary DzudaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-4 Review RevisedDocument4 pagesChapter 3-4 Review RevisedMUHAMMAD ARSALAN ASIF (ARSAL)No ratings yet
- Mathematics CXC 2011Document12 pagesMathematics CXC 2011dggoode100% (1)
- Concrete Quantity For Basement Floor Roof SlabDocument5 pagesConcrete Quantity For Basement Floor Roof SlabRamilArtatesNo ratings yet
- Om Chuajedton - BDocument4 pagesOm Chuajedton - Bapi-480822405No ratings yet
- Mathematics (Ii)Document2 pagesMathematics (Ii)Dante MutzNo ratings yet
- BEX1033 Supplementary ExamDocument11 pagesBEX1033 Supplementary ExamIbrahim MusaNo ratings yet
- Path To Boards 18 (Maxima and Minima)Document7 pagesPath To Boards 18 (Maxima and Minima)KokilaNo ratings yet
- Class 8 - Maths - MensurationDocument26 pagesClass 8 - Maths - Mensurationrathore400No ratings yet
- Mock MidtermDocument2 pagesMock MidtermElton LuNo ratings yet
- MAT183Document4 pagesMAT183hydraknightkraken78No ratings yet
- Estimation and Costing Lecture 3Document13 pagesEstimation and Costing Lecture 3Chopra ShubhamNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics TestDocument4 pagesEngineering Mathematics TestWilliam PeterNo ratings yet
- Mathematics F2 Exam Term 1 Qs Teacher - Co .KeDocument14 pagesMathematics F2 Exam Term 1 Qs Teacher - Co .KehillarynyabaroNo ratings yet
- Obyju'S: 12x1.5x0.65+2x1.25x0.65+1.5x1.25) MDocument6 pagesObyju'S: 12x1.5x0.65+2x1.25x0.65+1.5x1.25) MAm ActivitiesNo ratings yet
- Test Calculus AIDocument19 pagesTest Calculus AIyts36902No ratings yet
- T.E (2019 Pattern)Document794 pagesT.E (2019 Pattern)Vishal KambleNo ratings yet
- Part A (Answer All Questions) Question 1 (20 Marks) : Material To Remove 30.0 70.0 40.0Document19 pagesPart A (Answer All Questions) Question 1 (20 Marks) : Material To Remove 30.0 70.0 40.0Shah MalikNo ratings yet
- TNPSC Aptitude Solved Sums Part 1Document13 pagesTNPSC Aptitude Solved Sums Part 1VickyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 MeasurementDocument19 pagesChapter 3 MeasurementMustafa Nabeel Zaman100% (1)
- Septic Tank, Soak PitDocument9 pagesSeptic Tank, Soak PitManish ShashikantNo ratings yet
- Samples VJC Mathcompetition QuestionsDocument4 pagesSamples VJC Mathcompetition QuestionsSovan NugrohoNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Mathematics Model Paper - 2Document9 pagesIGCSE Mathematics Model Paper - 2Kothakonda Praveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Analytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportFrom EverandAnalytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportNo ratings yet
- Materials Science and Technology of Optical FabricationFrom EverandMaterials Science and Technology of Optical FabricationNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 1 - Module 9Document25 pagesScience: Quarter 1 - Module 9Randy Edrada0% (1)
- The Elusive Chemical Potential PDFDocument12 pagesThe Elusive Chemical Potential PDFbonesisaliveNo ratings yet
- Turbojet Engine With T-S DiagramDocument10 pagesTurbojet Engine With T-S Diagramprakash tyagiNo ratings yet
- ESADE MSC Brochure 2015Document8 pagesESADE MSC Brochure 2015Daniel SifuentesNo ratings yet
- 3-MIDA Investment Opportunities in GT IndustryDocument40 pages3-MIDA Investment Opportunities in GT IndustryWong Yong Sheng WongNo ratings yet
- Role of Design Department in Printing TextileDocument14 pagesRole of Design Department in Printing TextileAbdul RaphayNo ratings yet
- 2022in-02241 - Csuv Eng - Apac-May-Delphi-Testboard-Usd-V01Document15 pages2022in-02241 - Csuv Eng - Apac-May-Delphi-Testboard-Usd-V01Ihsan PermadiNo ratings yet
- PDF PDFDocument162 pagesPDF PDFJoe NjoreNo ratings yet
- EBS Full ReportDocument74 pagesEBS Full ReportEd SalangaNo ratings yet
- Filtration Solution To Problems - Pdf-Midterm-Exam-AnswerDocument7 pagesFiltration Solution To Problems - Pdf-Midterm-Exam-AnswerDubu Kim100% (1)
- The Pure Land On Earth The Chronicles of PDFDocument9 pagesThe Pure Land On Earth The Chronicles of PDFBhikshu GovindaNo ratings yet
- A289A289M-97 (2013) Standard Specification For Alloy Steel Forgings For Nonmagnetic Retaining Rings For GeneratorsDocument3 pagesA289A289M-97 (2013) Standard Specification For Alloy Steel Forgings For Nonmagnetic Retaining Rings For GeneratorsShico1983No ratings yet
- 1430-Article Text-4196-2-10-20220929Document21 pages1430-Article Text-4196-2-10-20220929Annisa SophiaNo ratings yet
- Example #14 Tunnel With Concrete Lining: Civilfem Manual of Advanced Examples - Ingeciber, S.A.Document14 pagesExample #14 Tunnel With Concrete Lining: Civilfem Manual of Advanced Examples - Ingeciber, S.A.Andre OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Cida Bulletin of Construction Statistics January 2021Document29 pagesCida Bulletin of Construction Statistics January 2021Niruban ThaventhiranNo ratings yet
- Class - 12th Annual ReportDocument4 pagesClass - 12th Annual ReportPreksha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Breaking Christian Curses - Dennis CramerDocument233 pagesBreaking Christian Curses - Dennis CramerLe Po50% (4)
- Republic Act No 7920Document3 pagesRepublic Act No 7920Ako Si Goldie100% (1)
- HR Assistant - Job DescriptionDocument2 pagesHR Assistant - Job DescriptionArchana GiriNo ratings yet
- Abortion - A Philosophical Perspective: OpsommingDocument7 pagesAbortion - A Philosophical Perspective: OpsommingGeorge RaresNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of A HackDocument43 pagesAnatomy of A Hackczar777No ratings yet
- Rt7010 Lighting of Railway Premises PDFDocument17 pagesRt7010 Lighting of Railway Premises PDFCezary P.No ratings yet
- 1 Concept Paper On The 6-Year CurriculumDocument9 pages1 Concept Paper On The 6-Year CurriculumJoseph Tabadero Jr.100% (3)
- Mod 6 Soft Tissue InjuriesDocument5 pagesMod 6 Soft Tissue Injuriesrez1987100% (1)
- IC Style Guide 2020Document20 pagesIC Style Guide 2020John Kihungi100% (1)
- Module 2: Single-Area Ospfv2 Configuration: Instructor MaterialsDocument76 pagesModule 2: Single-Area Ospfv2 Configuration: Instructor MaterialsHồngPhúc100% (1)