Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ri - SMS3023
Ri - SMS3023
Uploaded by
Putera Gunong LepakCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- BBFA2203Document13 pagesBBFA2203Haryanie JNo ratings yet
- SMS1034 (GROUP C) The Perception of The Factors That Contribute To Baby Dumping ProblemDocument7 pagesSMS1034 (GROUP C) The Perception of The Factors That Contribute To Baby Dumping ProblemArvind RaveeNo ratings yet
- Strategies and Methods For Teaching The Talented and Gifted ChildrenDocument17 pagesStrategies and Methods For Teaching The Talented and Gifted ChildrenfadzerniNo ratings yet
- Group Project MTS3013 A181Document3 pagesGroup Project MTS3013 A181Zaro IqmaNo ratings yet
- Stress Guru Pendidikan KhasDocument11 pagesStress Guru Pendidikan KhasAdam Ziyyad100% (1)
- Lesson 2 Refleksi Video DR.TDocument2 pagesLesson 2 Refleksi Video DR.Tamirah shariffudin0% (1)
- 6 Motivasi Intrinsik Dan EkstrinsikDocument56 pages6 Motivasi Intrinsik Dan EkstrinsikNajib FeshalNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis TestingDocument210 pagesHypothesis TestingShreya50% (2)
- Soalan HMEF5083 Instructional TechnologyDocument8 pagesSoalan HMEF5083 Instructional TechnologyCikgu Azry Azeem PetronessaNo ratings yet
- 2SGRM3113-DIFFUSION OF INNOVATION-1iiiDocument11 pages2SGRM3113-DIFFUSION OF INNOVATION-1iiiCameron RiceNo ratings yet
- Jsu Form 4Document6 pagesJsu Form 4Haslinda Sheikh0% (1)
- Instrumen Komitmen Organisasi 3 ConstructDocument2 pagesInstrumen Komitmen Organisasi 3 ConstructSuhaila SallehNo ratings yet
- 44 Integration2010 ProceedingsDocument8 pages44 Integration2010 ProceedingsKhirulnizam Abd RahmanNo ratings yet
- Cel 2103 - THT Week 1Document1 pageCel 2103 - THT Week 1Amirah Ramli0% (1)
- Teaching and Learning Supervision Teachers AttituDocument15 pagesTeaching and Learning Supervision Teachers AttituRevathi KanasanNo ratings yet
- Analysing and Implications of Teacher Development StagesDocument17 pagesAnalysing and Implications of Teacher Development StagesNadwa Nasir100% (1)
- Pembinaan Item Bahasa Inggeris Tahun 3 (Plan)Document3 pagesPembinaan Item Bahasa Inggeris Tahun 3 (Plan)Anwar RadhiNo ratings yet
- Analisis Dan Sintesis PDFDocument21 pagesAnalisis Dan Sintesis PDFSamsul BahtiarNo ratings yet
- Official Lab 01 SBF3033Document14 pagesOfficial Lab 01 SBF3033Foster Van VossenNo ratings yet
- Kuliah InteraktifDocument50 pagesKuliah InteraktifAmirul SyaqirNo ratings yet
- Pembangunan Modul Kemahiran Berfikir Aras Tinggi DDocument8 pagesPembangunan Modul Kemahiran Berfikir Aras Tinggi DNur Ezzati SulaimanNo ratings yet
- RI BIU2042 English Proficiency 4Document13 pagesRI BIU2042 English Proficiency 4Syafiqah PikaNo ratings yet
- Ri Gru60104 10 Sept m171 EngDocument11 pagesRi Gru60104 10 Sept m171 EngAnonymous rlZ9gm8HnNo ratings yet
- Kemahiran Berfikir Kritis Dalam Buku Teks Bahasa MelayuDocument12 pagesKemahiran Berfikir Kritis Dalam Buku Teks Bahasa MelayuRahmiaty Fauziyah100% (1)
- Stand and DeliverDocument3 pagesStand and DelivermopaekNo ratings yet
- Persoalan N HipotesisDocument10 pagesPersoalan N HipotesisSchahyda ArleyNo ratings yet
- Edutainment TheoriesDocument3 pagesEdutainment TheoriesJosh Simmons100% (1)
- Kurikulum Unit Kompetensi C01Document8 pagesKurikulum Unit Kompetensi C01Mohamad Afiq Akmal Bin Mohd NizamNo ratings yet
- T TestDocument17 pagesT TestCherylLingNo ratings yet
- Gggb6012 Penulisan Akademik 1 SET 1 2020/2021: KursusDocument3 pagesGggb6012 Penulisan Akademik 1 SET 1 2020/2021: KursusCaryn Yeap100% (4)
- Pelan Perancangan PengajianDocument4 pagesPelan Perancangan Pengajiansarutobi2077No ratings yet
- Assignment QuestionDocument13 pagesAssignment QuestionMunsang NyumbuohNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 6 - Literature ReviewDocument47 pagesKuliah 6 - Literature ReviewSyaz WazierahNo ratings yet
- Group Vs Individual AssignmentDocument12 pagesGroup Vs Individual AssignmentYvonne TiongNo ratings yet
- Lemlech, J. K. (1988) - Classroom Management. Longman Inc. Second Ed. New YorkDocument1 pageLemlech, J. K. (1988) - Classroom Management. Longman Inc. Second Ed. New YorkFareez Al-IdrusNo ratings yet
- LSP 300 Course Ip Sem II 20142015Document4 pagesLSP 300 Course Ip Sem II 20142015Afifáh Spèncèr EpaálockáNo ratings yet
- Assignment HPGD 2203 Educational Management September 2021 SemesterDocument7 pagesAssignment HPGD 2203 Educational Management September 2021 SemesterHaiqal FirdausNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Qualitative StudyDocument26 pagesIntroduction To Qualitative StudyDr. Muhammad Sofwan MahmudNo ratings yet
- Hubungan Kepimpinan Guru Dengan Pencapaian Akademik Pelajar Di Sibu, SarawakDocument11 pagesHubungan Kepimpinan Guru Dengan Pencapaian Akademik Pelajar Di Sibu, SarawakAngsNo ratings yet
- KOMPETENSIDocument13 pagesKOMPETENSIShakir AizatNo ratings yet
- MTES3013 Numbers and Number StructureDocument9 pagesMTES3013 Numbers and Number Structurehyy100% (1)
- Pemimpin Dan Komuniti Pembelajaran ProfesionalDocument22 pagesPemimpin Dan Komuniti Pembelajaran ProfesionalpaspologenNo ratings yet
- Tugasan 1 - KPD3016Document17 pagesTugasan 1 - KPD3016Awan PutihNo ratings yet
- L4 Kerangka Konseptual (Conceptual Framework)Document18 pagesL4 Kerangka Konseptual (Conceptual Framework)Muhamad Fizri Bin JamalNo ratings yet
- A Question of DowryDocument2 pagesA Question of DowryNatalie Payne0% (1)
- Book Review:: Fundamentals of Curriculum: Passion and Professionalism (2nd Edition) by Decker WalkerDocument4 pagesBook Review:: Fundamentals of Curriculum: Passion and Professionalism (2nd Edition) by Decker WalkerGenesis MallariNo ratings yet
- The Mathematics Assessment in Finland, Vietnam and MalaysiaDocument15 pagesThe Mathematics Assessment in Finland, Vietnam and MalaysiaNurFarra AizaNo ratings yet
- GROUP ASSIGNMENT (2) Arunah N Saranya NewDocument62 pagesGROUP ASSIGNMENT (2) Arunah N Saranya NewSaranya KaliappanNo ratings yet
- Tugasan 2 - Submit Week3Document10 pagesTugasan 2 - Submit Week3Fatin Zulina100% (1)
- Full TextDocument34 pagesFull TextAina Nadhirah100% (2)
- Analisis Keperluan Terhadap Pengguna Sasaran Modul Pendekatan Berasaskan Bermain Bagi Pengajaran Dan Pembelajaran Kemahiran Bahasa Kanak-Kanak PrasekolahDocument9 pagesAnalisis Keperluan Terhadap Pengguna Sasaran Modul Pendekatan Berasaskan Bermain Bagi Pengajaran Dan Pembelajaran Kemahiran Bahasa Kanak-Kanak Prasekolahhanie93No ratings yet
- Cel 2106 Portfolio 1 Task 2 - 192396Document3 pagesCel 2106 Portfolio 1 Task 2 - 192396Luqman HakimNo ratings yet
- Assignment ANOVADocument21 pagesAssignment ANOVAsuhaimi sobrieNo ratings yet
- Item Specifications For English Language UPSRDocument2 pagesItem Specifications For English Language UPSRwahidah78No ratings yet
- Scheme of Work Chemistry Form 5Document31 pagesScheme of Work Chemistry Form 5Dilla IderesNo ratings yet
- Teacher Education in MalaysiaDocument13 pagesTeacher Education in MalaysiaSaufi bin Abdullah100% (3)
- Comparative AssigDocument7 pagesComparative AssigBhannu RamananNo ratings yet
- Cel2106 SCL Worksheet 8Document4 pagesCel2106 SCL Worksheet 8YAN WENHUI / UPMNo ratings yet
- Stat 205Document4 pagesStat 205Nasir AliNo ratings yet
- Sms2309 Intro To Statistics OutlineDocument6 pagesSms2309 Intro To Statistics OutlineSiti SyurieyatiNo ratings yet
- Course Plan - 2023 - LMSDocument5 pagesCourse Plan - 2023 - LMSharshitbudhraja0No ratings yet
- Wooldridge 6e AppB IMDocument3 pagesWooldridge 6e AppB IMHan ChenNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Document - MN B2026 (16082023)Document97 pagesCurriculum Document - MN B2026 (16082023)Sarah SaskiaNo ratings yet
- Time Series Solution ManualDocument147 pagesTime Series Solution ManualA.s. CharanNo ratings yet
- Expectations - NotesDocument3 pagesExpectations - NotesPranav SuryaNo ratings yet
- Terrence Tao - Free ProbabilityDocument32 pagesTerrence Tao - Free ProbabilitycaprioloNo ratings yet
- Decision TheoryDocument5 pagesDecision TheoryhiteshvavaiyaNo ratings yet
- MA516-816 Contingencies I Section 10 Assurances and Annuities Involving Two Lives Complete NotesDocument9 pagesMA516-816 Contingencies I Section 10 Assurances and Annuities Involving Two Lives Complete NotesYomi BrainNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document4 pagesAssignment 4NeutronNo ratings yet
- STAT201 Probability Theory and Applications (1410) - Kwong Koon ShingDocument2 pagesSTAT201 Probability Theory and Applications (1410) - Kwong Koon ShinghappystoneNo ratings yet
- (Bloomsbury Study Skills) Jessica Bownes - The Science Student's Guide To Dissertations and Research Projects-Bloomsbury Academic (2023)Document177 pages(Bloomsbury Study Skills) Jessica Bownes - The Science Student's Guide To Dissertations and Research Projects-Bloomsbury Academic (2023)aaron.stefano.romero.velazcoNo ratings yet
- WQU - MScFE - Discrete-Time Stochastic Processes - M2 PDFDocument35 pagesWQU - MScFE - Discrete-Time Stochastic Processes - M2 PDFmuwada huzairu100% (1)
- New CMA Part 1 Section ADocument114 pagesNew CMA Part 1 Section AMichael SumpayNo ratings yet
- 2: Life TablesDocument28 pages2: Life TablesKen NuguidNo ratings yet
- BSC-301 - Probability - Distribution 4Document11 pagesBSC-301 - Probability - Distribution 4Precisive OneNo ratings yet
- MauboussinDocument37 pagesMauboussinwmthomson100% (1)
- Supplements Available On The Text Website: Conf Irming PagesDocument4 pagesSupplements Available On The Text Website: Conf Irming PagesAngelo SilvaNo ratings yet
- Proposed Solution/ Algorithm For Problem 1: Determining The Minimum Number of Bank TellersDocument1 pageProposed Solution/ Algorithm For Problem 1: Determining The Minimum Number of Bank TellersGwen Bess N. CacanindinNo ratings yet
- Syllabus 1T2020 PDFDocument2 pagesSyllabus 1T2020 PDFBenNo ratings yet
- CH06 Mean, Variance, and Transform PDFDocument67 pagesCH06 Mean, Variance, and Transform PDFMahedi HassanNo ratings yet
- Statistics For Business and Economics: Bab 5Document28 pagesStatistics For Business and Economics: Bab 5baloNo ratings yet
- AMA Final Summer2022Document201 pagesAMA Final Summer2022sidra khalidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Decision Making With Risk and UncertaintyDocument10 pagesChapter 7 - Decision Making With Risk and UncertaintyJeremiah NcubeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document6 pagesChapter 4Rocel Marie LopezNo ratings yet
- Twenty Problems in ProbabilityDocument13 pagesTwenty Problems in ProbabilityGopi KrishnaNo ratings yet
- MIT18 05S14 Prac Exa1 Long-1Document14 pagesMIT18 05S14 Prac Exa1 Long-1Ryan SooknarineNo ratings yet
- Essential Statistics 2E: William Navidi and Barry MonkDocument30 pagesEssential Statistics 2E: William Navidi and Barry Monkkaled1971No ratings yet
- 4 Learning CurvesDocument8 pages4 Learning Curvessabinaeghan1No ratings yet
- The Geometric Distribution AssignmentDocument2 pagesThe Geometric Distribution Assignmentshaw taonamesoNo ratings yet
- Principles of Actuarial Science Games of Chance (1) : Week 1Document23 pagesPrinciples of Actuarial Science Games of Chance (1) : Week 1jlosamNo ratings yet
Ri - SMS3023
Ri - SMS3023
Uploaded by
Putera Gunong LepakOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ri - SMS3023
Ri - SMS3023
Uploaded by
Putera Gunong LepakCopyright:
Available Formats
Head of Departments verification:
Date:
UNIVERSITI PENDIDIKAN SULTAN IDRIS
COURSE CURICULUM DESIGN AND INSTRUCTIONAL PLAN
Faculty Department Semester Session Course Code Credit Hour Prerequisite : FACULTY OF SCIENCE AND MATHEMATICS : MATHEMATICS :1 : 2011/2012 : THEORY OF STATISTICS & PROBABILITY : SMS3023 :3 : INTRODUCTORY STATISTICS (SMS 3013)
LECTURERS INFORMATION : Name E-mail Phone No. Office Consultation Hour : : : : : DR. NOR AFZALINA BINTI AZMEE afzalina@fsmt.upsi.edu.my 05-4506420 BC2-29 WED: 2-4 pm, THUR: 2-4 pm, FRI: 2-4 pm Others by appointment.
COURSE SYNOPSIS: This course discusses and enhances the understanding of probability concepts, axioms of probability, mutually exclusive event, independent events, conditional probability and Bayes theorem; random variables; density functions and probability density functions; discrete probability distributions; expectation and moment, probability generating function, moment generating function, continuous probability distributions, uniform distribution, normal distribution, normal approximation to the binomial and Poisson, t-distribution, chi-squared distribution, and F-distribution.
LEARNING OUTCOMES: At the end of this course, students should be able to: i. Explain the development of the field of statistics and probability. ii. Analyze the difference between the discrete and continuous probability distributions and their types/families. iii. Explain the concept of random variables. iv. Analyze the concept in mathematical expectation. v. Describe several types of distribution by applying to the concept of sampling distributions. vi. Work in teams, communicate effectively and manage information to improve the quality of learning.
MAIN REFERENCE:
Lindgren, B.W. (1993) Statistical theory (4th edition). Florida: Chapman & Hall.
ADDITIONAL REFERENCES: Casella, G. (2002) Statistical inference. Boston, MA: Duxbury Press.
Freund, J.E. (2004) Mathematical statistics (7th ed.). New York, NY: Prentice Hall. Stuart, A., Ord, K. & Arnold, S. (1999) Advanced theory of statistics (Volume 2A). New York: Oxford University Press. Stuart, A. & Ord, K. (1994) Advanced theory of statistics (Volume 1). New York: Oxford University Press.
METHODS OF TEACHING Lecture, group discussion and group presentation.
METHODS OF SOFT SKILLS EMBEDDED
Activity Communication Skill (KOM) Thinki ng and Problem Solving Skill (KBP M) Life Long Learning and Information Management Skill (PBPM) Tea m Wo rk Skil l (PS K) Leadership Skill (PIM) Professional Ethic (ETIK) Entrepreneurship Skill (KU)
Assignment
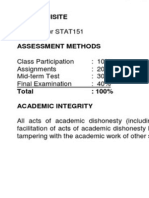
STUDENT EVALUATION Your grade will be based on quizzes, a test and assignments. The distribution is as follows: Quizzes Tests Assignments 20% 40% 40%
Students are expected to attend every class meeting and attendance will be taken regularly. Please obtain the lecture notes from your classmates, should you fail to attend the class on that day. Please notify the instructor at least one week prior to the exam, should you know that you will be missing an exam/test/quiz. A score of 0 will be given to those who miss the exam/test/quiz without an advanced notice. ACADEMIC GRADING SCALE Grade A AB+ B BC+ C CD+ D F Marks 80-100 75-79 70-74 65-69 60-64 55-59 50-54 45-49 40-44 35-39 0-34 GPA/CGPA 4.0 3.7 3.4 3.0 2.7 2.4 2.0 1.7 1.4 1.0 0 Level Excellent Excellent Credit Credit Credit Pass Pass Weak Pass Weak Pass Weak Pass Fail
SOFT SKILLS GRADING SCALE Scale 5 4 3 2 1 Criteria Has attained the elements of soft skills at the level of excellence Has attained the elements of soft skills at a good level Has attained the elements of soft skills at a satisfactory level Has attained the elements of respected soft skills at a minimum level Poor and need to improve
14 WEEKS TEACHING SCHEDULE:
Week Chapter/Topic CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION TO PROBABILITY & STATISTICS Introduction to course curriculum design and instructional plan. 1-2 Sample space, sample points, events, probability model, counting principle, experiment with symmetries, law of large numbers, subjective probability, probability axioms, conditional probability, Bayes theorem. CHAPTER 2: RANDOM VARIABLES 3-4 Discrete and continuous random variables, distribution functions, functions of random variables, conditional distributions, independence. Learning Outcomes T&L Activities Soft Skills Reference
1. To explain the basic elements of
probability and statistics. 2. To understand the development of the field of statistics and probability.
Lecture, class discussion Quiz 1
Main reference
1. To explain the concept of random
variables. 2. To analyze the difference between discrete and continuous random variables.
Lecture, class discussion Assignment 1
KOM, KBPM, PBPM, PSK
Main reference
CHAPTER 3: EXPECTATIONS 5-6 Expected value of the following cases; discrete, continuous and functions of random variables. Moments, variance, Chebyshevs inequality, covariance, correlation.
1. To analyze the concept of mathematical expectation. 2. To explain the terms variance, covariance and correlation. .
Lecture, class discussion Test 1
Main reference
CHAPTER 4: SOME PARAMETRIC FAMILIES 7-8 Bernoulli, binomial, hypergeometric, negative binomial, Poisson process, exponential, gamma, beta, normal, chisquare, multinomial. CHAPTER 5: SAMPLING AND REDUCTION OF DATA 9-10 Random sampling, sampling distributions of sample moments and normal populations, likelihood, sufficiency, information in a sample. CHAPTER 6: ESTIMATION 11-12 Estimator, mean squared error, efficiency, consistency, maximum likelihood estimators, interval estimates.
1. To describe some widely
used/known distributions. 2. To study characteristics of some widely used/common distributions.
Lecture, class discussion, presentation Assignment 2
KOM, KBPM, PBPM, PSK
Main reference
1. To apply the concept of sampling
distributions. 2. To explain the concept of reduction of data.
Lecture, class discussion
Main reference
1. To explain the concept estimator.
2. To obtain an estimator using the maximum likelihood estimators. 3. To obtain the interval estimates.
Lecture, class discussion Test 2
Main reference
CHAPTER 7: TESTING HYPOTHESIS Likelihood ratio statistics, assessing evidence, decision rules, test the mean and variance (normal population), simple null hypothesis versus simple alternative hypothesis, power function.
1. To explain the idea of hypothesis
testing.
Lecture, class discussion Quiz 2
Main reference
13-14
2. To assess the evidence of the test.
3. To explain the decision rules. 4. To explain the concept of power function.
You might also like
- BBFA2203Document13 pagesBBFA2203Haryanie JNo ratings yet
- SMS1034 (GROUP C) The Perception of The Factors That Contribute To Baby Dumping ProblemDocument7 pagesSMS1034 (GROUP C) The Perception of The Factors That Contribute To Baby Dumping ProblemArvind RaveeNo ratings yet
- Strategies and Methods For Teaching The Talented and Gifted ChildrenDocument17 pagesStrategies and Methods For Teaching The Talented and Gifted ChildrenfadzerniNo ratings yet
- Group Project MTS3013 A181Document3 pagesGroup Project MTS3013 A181Zaro IqmaNo ratings yet
- Stress Guru Pendidikan KhasDocument11 pagesStress Guru Pendidikan KhasAdam Ziyyad100% (1)
- Lesson 2 Refleksi Video DR.TDocument2 pagesLesson 2 Refleksi Video DR.Tamirah shariffudin0% (1)
- 6 Motivasi Intrinsik Dan EkstrinsikDocument56 pages6 Motivasi Intrinsik Dan EkstrinsikNajib FeshalNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis TestingDocument210 pagesHypothesis TestingShreya50% (2)
- Soalan HMEF5083 Instructional TechnologyDocument8 pagesSoalan HMEF5083 Instructional TechnologyCikgu Azry Azeem PetronessaNo ratings yet
- 2SGRM3113-DIFFUSION OF INNOVATION-1iiiDocument11 pages2SGRM3113-DIFFUSION OF INNOVATION-1iiiCameron RiceNo ratings yet
- Jsu Form 4Document6 pagesJsu Form 4Haslinda Sheikh0% (1)
- Instrumen Komitmen Organisasi 3 ConstructDocument2 pagesInstrumen Komitmen Organisasi 3 ConstructSuhaila SallehNo ratings yet
- 44 Integration2010 ProceedingsDocument8 pages44 Integration2010 ProceedingsKhirulnizam Abd RahmanNo ratings yet
- Cel 2103 - THT Week 1Document1 pageCel 2103 - THT Week 1Amirah Ramli0% (1)
- Teaching and Learning Supervision Teachers AttituDocument15 pagesTeaching and Learning Supervision Teachers AttituRevathi KanasanNo ratings yet
- Analysing and Implications of Teacher Development StagesDocument17 pagesAnalysing and Implications of Teacher Development StagesNadwa Nasir100% (1)
- Pembinaan Item Bahasa Inggeris Tahun 3 (Plan)Document3 pagesPembinaan Item Bahasa Inggeris Tahun 3 (Plan)Anwar RadhiNo ratings yet
- Analisis Dan Sintesis PDFDocument21 pagesAnalisis Dan Sintesis PDFSamsul BahtiarNo ratings yet
- Official Lab 01 SBF3033Document14 pagesOfficial Lab 01 SBF3033Foster Van VossenNo ratings yet
- Kuliah InteraktifDocument50 pagesKuliah InteraktifAmirul SyaqirNo ratings yet
- Pembangunan Modul Kemahiran Berfikir Aras Tinggi DDocument8 pagesPembangunan Modul Kemahiran Berfikir Aras Tinggi DNur Ezzati SulaimanNo ratings yet
- RI BIU2042 English Proficiency 4Document13 pagesRI BIU2042 English Proficiency 4Syafiqah PikaNo ratings yet
- Ri Gru60104 10 Sept m171 EngDocument11 pagesRi Gru60104 10 Sept m171 EngAnonymous rlZ9gm8HnNo ratings yet
- Kemahiran Berfikir Kritis Dalam Buku Teks Bahasa MelayuDocument12 pagesKemahiran Berfikir Kritis Dalam Buku Teks Bahasa MelayuRahmiaty Fauziyah100% (1)
- Stand and DeliverDocument3 pagesStand and DelivermopaekNo ratings yet
- Persoalan N HipotesisDocument10 pagesPersoalan N HipotesisSchahyda ArleyNo ratings yet
- Edutainment TheoriesDocument3 pagesEdutainment TheoriesJosh Simmons100% (1)
- Kurikulum Unit Kompetensi C01Document8 pagesKurikulum Unit Kompetensi C01Mohamad Afiq Akmal Bin Mohd NizamNo ratings yet
- T TestDocument17 pagesT TestCherylLingNo ratings yet
- Gggb6012 Penulisan Akademik 1 SET 1 2020/2021: KursusDocument3 pagesGggb6012 Penulisan Akademik 1 SET 1 2020/2021: KursusCaryn Yeap100% (4)
- Pelan Perancangan PengajianDocument4 pagesPelan Perancangan Pengajiansarutobi2077No ratings yet
- Assignment QuestionDocument13 pagesAssignment QuestionMunsang NyumbuohNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 6 - Literature ReviewDocument47 pagesKuliah 6 - Literature ReviewSyaz WazierahNo ratings yet
- Group Vs Individual AssignmentDocument12 pagesGroup Vs Individual AssignmentYvonne TiongNo ratings yet
- Lemlech, J. K. (1988) - Classroom Management. Longman Inc. Second Ed. New YorkDocument1 pageLemlech, J. K. (1988) - Classroom Management. Longman Inc. Second Ed. New YorkFareez Al-IdrusNo ratings yet
- LSP 300 Course Ip Sem II 20142015Document4 pagesLSP 300 Course Ip Sem II 20142015Afifáh Spèncèr EpaálockáNo ratings yet
- Assignment HPGD 2203 Educational Management September 2021 SemesterDocument7 pagesAssignment HPGD 2203 Educational Management September 2021 SemesterHaiqal FirdausNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Qualitative StudyDocument26 pagesIntroduction To Qualitative StudyDr. Muhammad Sofwan MahmudNo ratings yet
- Hubungan Kepimpinan Guru Dengan Pencapaian Akademik Pelajar Di Sibu, SarawakDocument11 pagesHubungan Kepimpinan Guru Dengan Pencapaian Akademik Pelajar Di Sibu, SarawakAngsNo ratings yet
- KOMPETENSIDocument13 pagesKOMPETENSIShakir AizatNo ratings yet
- MTES3013 Numbers and Number StructureDocument9 pagesMTES3013 Numbers and Number Structurehyy100% (1)
- Pemimpin Dan Komuniti Pembelajaran ProfesionalDocument22 pagesPemimpin Dan Komuniti Pembelajaran ProfesionalpaspologenNo ratings yet
- Tugasan 1 - KPD3016Document17 pagesTugasan 1 - KPD3016Awan PutihNo ratings yet
- L4 Kerangka Konseptual (Conceptual Framework)Document18 pagesL4 Kerangka Konseptual (Conceptual Framework)Muhamad Fizri Bin JamalNo ratings yet
- A Question of DowryDocument2 pagesA Question of DowryNatalie Payne0% (1)
- Book Review:: Fundamentals of Curriculum: Passion and Professionalism (2nd Edition) by Decker WalkerDocument4 pagesBook Review:: Fundamentals of Curriculum: Passion and Professionalism (2nd Edition) by Decker WalkerGenesis MallariNo ratings yet
- The Mathematics Assessment in Finland, Vietnam and MalaysiaDocument15 pagesThe Mathematics Assessment in Finland, Vietnam and MalaysiaNurFarra AizaNo ratings yet
- GROUP ASSIGNMENT (2) Arunah N Saranya NewDocument62 pagesGROUP ASSIGNMENT (2) Arunah N Saranya NewSaranya KaliappanNo ratings yet
- Tugasan 2 - Submit Week3Document10 pagesTugasan 2 - Submit Week3Fatin Zulina100% (1)
- Full TextDocument34 pagesFull TextAina Nadhirah100% (2)
- Analisis Keperluan Terhadap Pengguna Sasaran Modul Pendekatan Berasaskan Bermain Bagi Pengajaran Dan Pembelajaran Kemahiran Bahasa Kanak-Kanak PrasekolahDocument9 pagesAnalisis Keperluan Terhadap Pengguna Sasaran Modul Pendekatan Berasaskan Bermain Bagi Pengajaran Dan Pembelajaran Kemahiran Bahasa Kanak-Kanak Prasekolahhanie93No ratings yet
- Cel 2106 Portfolio 1 Task 2 - 192396Document3 pagesCel 2106 Portfolio 1 Task 2 - 192396Luqman HakimNo ratings yet
- Assignment ANOVADocument21 pagesAssignment ANOVAsuhaimi sobrieNo ratings yet
- Item Specifications For English Language UPSRDocument2 pagesItem Specifications For English Language UPSRwahidah78No ratings yet
- Scheme of Work Chemistry Form 5Document31 pagesScheme of Work Chemistry Form 5Dilla IderesNo ratings yet
- Teacher Education in MalaysiaDocument13 pagesTeacher Education in MalaysiaSaufi bin Abdullah100% (3)
- Comparative AssigDocument7 pagesComparative AssigBhannu RamananNo ratings yet
- Cel2106 SCL Worksheet 8Document4 pagesCel2106 SCL Worksheet 8YAN WENHUI / UPMNo ratings yet
- Stat 205Document4 pagesStat 205Nasir AliNo ratings yet
- Sms2309 Intro To Statistics OutlineDocument6 pagesSms2309 Intro To Statistics OutlineSiti SyurieyatiNo ratings yet
- Course Plan - 2023 - LMSDocument5 pagesCourse Plan - 2023 - LMSharshitbudhraja0No ratings yet
- Wooldridge 6e AppB IMDocument3 pagesWooldridge 6e AppB IMHan ChenNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Document - MN B2026 (16082023)Document97 pagesCurriculum Document - MN B2026 (16082023)Sarah SaskiaNo ratings yet
- Time Series Solution ManualDocument147 pagesTime Series Solution ManualA.s. CharanNo ratings yet
- Expectations - NotesDocument3 pagesExpectations - NotesPranav SuryaNo ratings yet
- Terrence Tao - Free ProbabilityDocument32 pagesTerrence Tao - Free ProbabilitycaprioloNo ratings yet
- Decision TheoryDocument5 pagesDecision TheoryhiteshvavaiyaNo ratings yet
- MA516-816 Contingencies I Section 10 Assurances and Annuities Involving Two Lives Complete NotesDocument9 pagesMA516-816 Contingencies I Section 10 Assurances and Annuities Involving Two Lives Complete NotesYomi BrainNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document4 pagesAssignment 4NeutronNo ratings yet
- STAT201 Probability Theory and Applications (1410) - Kwong Koon ShingDocument2 pagesSTAT201 Probability Theory and Applications (1410) - Kwong Koon ShinghappystoneNo ratings yet
- (Bloomsbury Study Skills) Jessica Bownes - The Science Student's Guide To Dissertations and Research Projects-Bloomsbury Academic (2023)Document177 pages(Bloomsbury Study Skills) Jessica Bownes - The Science Student's Guide To Dissertations and Research Projects-Bloomsbury Academic (2023)aaron.stefano.romero.velazcoNo ratings yet
- WQU - MScFE - Discrete-Time Stochastic Processes - M2 PDFDocument35 pagesWQU - MScFE - Discrete-Time Stochastic Processes - M2 PDFmuwada huzairu100% (1)
- New CMA Part 1 Section ADocument114 pagesNew CMA Part 1 Section AMichael SumpayNo ratings yet
- 2: Life TablesDocument28 pages2: Life TablesKen NuguidNo ratings yet
- BSC-301 - Probability - Distribution 4Document11 pagesBSC-301 - Probability - Distribution 4Precisive OneNo ratings yet
- MauboussinDocument37 pagesMauboussinwmthomson100% (1)
- Supplements Available On The Text Website: Conf Irming PagesDocument4 pagesSupplements Available On The Text Website: Conf Irming PagesAngelo SilvaNo ratings yet
- Proposed Solution/ Algorithm For Problem 1: Determining The Minimum Number of Bank TellersDocument1 pageProposed Solution/ Algorithm For Problem 1: Determining The Minimum Number of Bank TellersGwen Bess N. CacanindinNo ratings yet
- Syllabus 1T2020 PDFDocument2 pagesSyllabus 1T2020 PDFBenNo ratings yet
- CH06 Mean, Variance, and Transform PDFDocument67 pagesCH06 Mean, Variance, and Transform PDFMahedi HassanNo ratings yet
- Statistics For Business and Economics: Bab 5Document28 pagesStatistics For Business and Economics: Bab 5baloNo ratings yet
- AMA Final Summer2022Document201 pagesAMA Final Summer2022sidra khalidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Decision Making With Risk and UncertaintyDocument10 pagesChapter 7 - Decision Making With Risk and UncertaintyJeremiah NcubeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document6 pagesChapter 4Rocel Marie LopezNo ratings yet
- Twenty Problems in ProbabilityDocument13 pagesTwenty Problems in ProbabilityGopi KrishnaNo ratings yet
- MIT18 05S14 Prac Exa1 Long-1Document14 pagesMIT18 05S14 Prac Exa1 Long-1Ryan SooknarineNo ratings yet
- Essential Statistics 2E: William Navidi and Barry MonkDocument30 pagesEssential Statistics 2E: William Navidi and Barry Monkkaled1971No ratings yet
- 4 Learning CurvesDocument8 pages4 Learning Curvessabinaeghan1No ratings yet
- The Geometric Distribution AssignmentDocument2 pagesThe Geometric Distribution Assignmentshaw taonamesoNo ratings yet
- Principles of Actuarial Science Games of Chance (1) : Week 1Document23 pagesPrinciples of Actuarial Science Games of Chance (1) : Week 1jlosamNo ratings yet