Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hartly
Hartly
Uploaded by
Srivatsava SriluOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hartly
Hartly
Uploaded by
Srivatsava SriluCopyright:
Available Formats
17.
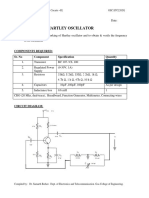
HARTLEY OSCILLATOR
AIM: To study and calculate frequency of oscillations of Hartley oscillator. Compare the frequency of oscillations, theoretically and practically. APPARATUS: Transistor BC 107 Capacitors 0.1F, 10 F Resistors 6.8Kohm, 1Kohm and 100Kohm Decade inductance box (DIB) Decade resistance box (DRB) Cathode ray oscilloscope Bread board Regulated power supply (0-30V) Connecting wires CIRCUIT DIAGRAM:
THEORY: Hartley oscillator is very popular and is commonly used as a local oscillator in radio receivers. It has two main advantages viz... Adaptability to wide range of frequencies and easy to tune. The tank circuit is made up of L1, L2, and C1. The coil L1 is inductively coupled to coil L2, the combination functions as auto transformer. The resistances R2 and R3 provide the necessary biasing. The capacitance C2 blocks the d.c component. The frequency of oscillations is determined by the values of L1, L2 and C1 and is given by, F=1/(2(C1(L1+L2))) The energy supplied to the tank circuit is of correct phase. The auto transformer provides 180 out of phase. Also another 180 is produced By the transistor. In this way, energy feedback to the tank circuit is in phase with the generated oscillations. PROCEDURE: 1. Connections are made as per the circuit diagram. 2. Connect CRO at output terminals and observe wave form. 3. Calculate practically the frequency of oscillations by using the Expression. F=1/T, Where T= Time period of the waveform 4. Repeat the above steps 2, 3 for different values of L1 and note Down practical values of oscillations of colpitts oscillator. 5. Compare the values of frequency of oscillations both theoretically And Practically.
OBSERVATIONS: CAPACITANCE(F) Theoritical frequency (KHZ) Practical frequency (KHZ)
MODEL GRAPH:
PRECAUTIONS: 1. All the connections should be correct. 2. Transistor terminals must be identified properly. 3. Reading should be taken without any parallax error. RESULT: Frequency of oscillations is calculated and compared with theoretical values.
VIVA QUESTIONS: 1. What are the applications of LC oscillations? 2. What type of feedback is used in oscillators? 3. What the expression for frequency of oscillations? 4. Whether an oscillator is dc to ac converter? 5. What is the loop gain of an oscillator? 6. What is the difference between amplifier and oscillator? 7. What is the condition for oscillations? 8. How many inductors and capacitors are used in Hartley Oscillator? 9. How the oscillations are produced in Hartley oscillator? 10. What is the difference between damped oscillations undamped oscillations?
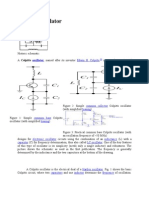
18. COLPITTS OSCILLATOR
AIM: To study and calculate frequency of oscillations of colpitts oscillator. APPARATUS: Transistor BC 107 Capacitors 0.1F 10F 47F Resistors - 2Nos - 2Nos - 1No (DIB) (DRB)
6.8k, 1k,100k
Decade Inductance Box Decade Resistance Box
Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (CRO) Regulated Power Supply (0-30V) Connecting Wires CIRCUITDIAGRAM:
THEORY: The tank circuit is made up of L1,C4 and C5 .The resistance R2 and R3 provides the necessary biasing. The capacitance C2 blocks the D.C component. The frequency of oscillations is determined by the values of L1,C4 and C5, and is given by f = 1 / (2 (CTL1)1/2) Where CT = C1C2 / ( C1 + C2) The energy supplied to the tank circuit is of correct phase. The tank circuit provides 1800 out of phase. Also the transistor provides another 1800 . In this way, energy feedback to the tank circuit is in phase with the generated oscillations. PROCEDURE: 1. connections are made as per circuit diagram. 2. Connect CRO output terminals and observe the waveform. 3. Calculate practically the frequency of oscillations by using the expression f = 1 / T ( T= Time period of the waveform) 4. Repeat the above steps 2,3 for different values of L, and note down the practically values of oscillations of the collpitts oscillator. 5. Compare the values of oscillations both theoritically and practically.
OBSERVATIONS: Inductance ( mH ) Theoretical Frequency ( Hz ) Practical Frequency ( Hz )
MODELWAVEFORM:
PRECAUTIONS: 1. The connections should be correct. 2. Transistor terminals should be identified properly. 3. Readings should be taken without parallalox error.
RESULT: Frequency of oscillations of colpitts oscillator is measured practically and campared with theoritical values . VIVA QUESTIONS: 1. What are the applications of LC oscillators? 2. What type of feedback is used in oscillators? 3. What is the expression for the frequency of oscillations of colpitts oscillator? 4. Is an oscillator DC to AC converter? 5. What is the loop gain and loop phase shift of an oscillator? 6. How does colpitts differ from Hartley? 7. Which pair in circuit forms stabilizing circuit? 8. What is the function of input and output capacitor? 9. What is the condition for sustained oscillations in this oscillator? 10. Output capacitor acts as a?
You might also like
- Secret Banker's ManualDocument75 pagesSecret Banker's Manualncwazzy100% (6)
- Expt 6 - Colpitts Oscillator (2020)Document4 pagesExpt 6 - Colpitts Oscillator (2020)samarthNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - OscillatorsDocument31 pagesChapter 2 - OscillatorsAbdul Qawie Jumaan100% (1)
- EE2203-Electronic Device and Circuits Question BankDocument11 pagesEE2203-Electronic Device and Circuits Question BankAnbarasan Annamalai100% (1)
- Assignment 2 - BarCo Corp - A2020Document6 pagesAssignment 2 - BarCo Corp - A2020farmina shaikhNo ratings yet
- Sage X3 - User Guide - SE - Reports - Common Data-US000Document108 pagesSage X3 - User Guide - SE - Reports - Common Data-US000caplusinc100% (1)
- OscillatorsDocument4 pagesOscillatorsShankar HNo ratings yet
- 5 Hartely OscillatorDocument4 pages5 Hartely OscillatordamasNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 2 (Oscillator) - ModifiedDocument58 pagesTOPIC 2 (Oscillator) - ModifiedAR de SouzaNo ratings yet
- Simulation MultipleerDocument15 pagesSimulation MultipleerFrancesco De FlorenceNo ratings yet
- 2 3 OscillatorsDocument32 pages2 3 Oscillatorsrobiah zakariaNo ratings yet
- Oscillator ManualDocument22 pagesOscillator ManualckooipgNo ratings yet
- Exp (4) - RF OscillatorsDocument12 pagesExp (4) - RF OscillatorsTony SopranoNo ratings yet
- Hartley and Colpitt - S OscillatorDocument7 pagesHartley and Colpitt - S OscillatorT BlackNo ratings yet
- 7 Hartly & Collpit PDFDocument13 pages7 Hartly & Collpit PDFengineerluv100% (1)
- Expt 7 - Hartley Oscillator (2020)Document4 pagesExpt 7 - Hartley Oscillator (2020)samarthNo ratings yet
- RF Sine Wave OscillatorsDocument3 pagesRF Sine Wave Oscillatorsmohammed229No ratings yet
- Unit-Ii - Oscillators Two Marks Question & AnswerDocument4 pagesUnit-Ii - Oscillators Two Marks Question & Answerpriyadarshini212007No ratings yet
- Lab 2 ICSDocument16 pagesLab 2 ICSIrfan HaiderNo ratings yet
- RF OSCILLATORS: Colpitts Oscillator Communication Lab تلااصتلاا ر بتخمDocument8 pagesRF OSCILLATORS: Colpitts Oscillator Communication Lab تلااصتلاا ر بتخمAliNo ratings yet
- 2.0 Oscillators 2.0 Oscillators: Linear DC Power Supply and Various Types Linear DC Power Supply and Various TypesDocument47 pages2.0 Oscillators 2.0 Oscillators: Linear DC Power Supply and Various Types Linear DC Power Supply and Various TypesSadrina MahamudNo ratings yet
- Oscillator PDFDocument4 pagesOscillator PDFJoshua DuffyNo ratings yet
- Electronic Circuits Circuits Circuits LTPC 0 0 3 Unit I Feedback Amplifiers 9Document12 pagesElectronic Circuits Circuits Circuits LTPC 0 0 3 Unit I Feedback Amplifiers 9helenseelanNo ratings yet
- Oscillator BasicsDocument22 pagesOscillator BasicsAnandu UdayakumarNo ratings yet
- ColpittsDocument8 pagesColpittsRavi Teja100% (1)
- Shreyash Bhimanwar 111907050 EntcDocument10 pagesShreyash Bhimanwar 111907050 EntcshreyashNo ratings yet
- Colpitts OscillatorDocument17 pagesColpitts Oscillatorjerricalday100% (2)
- Dis 2020 Chap 2 Oscillator EssayDocument7 pagesDis 2020 Chap 2 Oscillator EssayHAIQAL ZAMRYNo ratings yet
- Types of Oscillator CircuitsDocument10 pagesTypes of Oscillator CircuitsSam XingxnNo ratings yet
- Astable Multivibrator: Non Linear Applications:-A) Astable Multivibrator B) Mono Stable MultivibratorDocument15 pagesAstable Multivibrator: Non Linear Applications:-A) Astable Multivibrator B) Mono Stable MultivibratorFarhan AkhterNo ratings yet
- Analog Mini Project: Topic: Hartley OscillatorDocument4 pagesAnalog Mini Project: Topic: Hartley OscillatorMananRajputNo ratings yet
- Tutorial On Hartley and Colpitts Oscillator CircuitsDocument7 pagesTutorial On Hartley and Colpitts Oscillator CircuitsKhushbu SavaliyaNo ratings yet
- RF OscillatorsDocument11 pagesRF OscillatorsMohammad Irani0% (1)
- Hartley OscillatorDocument4 pagesHartley OscillatorManjot KaurNo ratings yet
- Astable Multi Vibrator: Prior To The Lab SessionDocument5 pagesAstable Multi Vibrator: Prior To The Lab SessionRiya Saluja100% (1)
- EEE 2104 Lab Report 07Document6 pagesEEE 2104 Lab Report 07shohim603No ratings yet
- Colpitts OscillatorDocument11 pagesColpitts Oscillatordinesh189No ratings yet
- ELE324 Oscillators L3 V2Document55 pagesELE324 Oscillators L3 V2Eduar MhangoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Tuned OscillatorsDocument25 pagesLesson 3 Tuned OscillatorsOdoch HerbertNo ratings yet
- OscillatorsDocument26 pagesOscillatorsjoeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Ee 301Document58 pagesChapter 2 Ee 301PrevenaManiamNo ratings yet
- Multisim OscillatorDocument5 pagesMultisim OscillatorJack bowmanNo ratings yet
- 23ECE185 Simulation Exp3 HalfWaveRectifierDocument1 page23ECE185 Simulation Exp3 HalfWaveRectifierridhubaranNo ratings yet
- RF Oscillators: Experiment 1Document11 pagesRF Oscillators: Experiment 1Emil Eugene DomingoNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.2: Colpitt OscillatorDocument3 pagesExperiment No.2: Colpitt OscillatorBhadresh Renuka50% (2)
- Heartly OscillatorDocument10 pagesHeartly OscillatorMr. Kumar AilaboinaNo ratings yet
- Capacitors and Time-Dependent Signals: ConceptDocument6 pagesCapacitors and Time-Dependent Signals: ConceptsriNo ratings yet
- Microwave Viva QuestionsDocument28 pagesMicrowave Viva Questionsqwerty100% (2)
- Oscillator We Looked at in The Previous Tutorial. Just Like The Hartley Oscillator, The TunedDocument6 pagesOscillator We Looked at in The Previous Tutorial. Just Like The Hartley Oscillator, The TunedXercxis Buendia MolanoNo ratings yet
- Oscillators Module 02Document20 pagesOscillators Module 02ervaishu5342100% (1)
- Experimeni 1: Ohjective - of The ExheimeniDocument9 pagesExperimeni 1: Ohjective - of The Exheimenisv234No ratings yet
- Colpitts OscillatorDocument4 pagesColpitts OscillatorAnimesh Bhanja100% (1)
- WEin Bridge OscillatorDocument3 pagesWEin Bridge OscillatorManjot KaurNo ratings yet
- Satyam College of Engineering and Technology, Aralvoimozhi Ece Iv-Semester Revision Questions Electronic Circuits Ii 2 Mark Questions Revision IDocument4 pagesSatyam College of Engineering and Technology, Aralvoimozhi Ece Iv-Semester Revision Questions Electronic Circuits Ii 2 Mark Questions Revision ISaranya MohanNo ratings yet
- Analog Mini Project Group2Document21 pagesAnalog Mini Project Group2Threefold CordNo ratings yet
- Oscillators: What Is Meant by Oscillator?Document5 pagesOscillators: What Is Meant by Oscillator?Ghulam MurtazaNo ratings yet
- Astable Multivibrator ExperimentDocument5 pagesAstable Multivibrator ExperimentShivakumar goud100% (1)
- Experiment No.1: Hartley OscillatorDocument3 pagesExperiment No.1: Hartley OscillatorBhadresh RenukaNo ratings yet
- Mohammed SadiqDocument2 pagesMohammed Sadiqmohammed229No ratings yet
- 4 Ece - 15.4.13 (Mod)Document2 pages4 Ece - 15.4.13 (Mod)BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Kl-23008 Block CDocument6 pagesKl-23008 Block CShammoutNo ratings yet
- Mazen Salem Baabdullah: Sales Director - Business Development ManagementDocument2 pagesMazen Salem Baabdullah: Sales Director - Business Development ManagementmazNo ratings yet
- Tsimakis A. A Pattern For Refactoring Detectors DiplomaThesisDocument44 pagesTsimakis A. A Pattern For Refactoring Detectors DiplomaThesisvandroutsouNo ratings yet
- Nar Ont 1 GbpsDocument49 pagesNar Ont 1 GbpsCatalin StoicescuNo ratings yet
- April 14, 2013: Minutes of The 2nd Session of The 20th Directorate of The XU-CSG For S.Y. 2013-2014Document8 pagesApril 14, 2013: Minutes of The 2nd Session of The 20th Directorate of The XU-CSG For S.Y. 2013-2014Harold John LaborteNo ratings yet
- ARLIGHT Industrial Lighting FixturesDocument16 pagesARLIGHT Industrial Lighting FixturesAnonymous WHvG48t8gsNo ratings yet
- Business Plan: Entrepreneurship ProjectDocument29 pagesBusiness Plan: Entrepreneurship ProjectÃpõõrv ShãrmãNo ratings yet
- Municipality of Sibutad: Members of The Municipal Development Council PresentDocument2 pagesMunicipality of Sibutad: Members of The Municipal Development Council PresentMaria LeeNo ratings yet
- Traditional Conjoint Workfile XLSTATDocument80 pagesTraditional Conjoint Workfile XLSTATSaurabh SinghNo ratings yet
- Direction Finding PresentationDocument35 pagesDirection Finding PresentationFoolraserNo ratings yet
- Logistics RegressionDocument56 pagesLogistics RegressionAlaguraja AlaguNo ratings yet
- 2 Design of Machine Elements MechDocument2 pages2 Design of Machine Elements MechSachi DhanandamNo ratings yet
- I On16 EngineerDocument68 pagesI On16 EngineerjamesmathiesonNo ratings yet
- Book 1Document219 pagesBook 1Ardi AnsyahNo ratings yet
- Toolbox Talks: Forklift FatalitiesDocument1 pageToolbox Talks: Forklift Fatalitiesserdar yücelNo ratings yet
- Iso TTR 18931 2001 (E)Document14 pagesIso TTR 18931 2001 (E)marco9991No ratings yet
- M3 Users GuideDocument5 pagesM3 Users GuideAnonymous G1iPoNOKNo ratings yet
- Nigerian Electricity Regulatory Commission: Eligible Customer Regulations 2017 Regulation No. Nerc-R-111Document30 pagesNigerian Electricity Regulatory Commission: Eligible Customer Regulations 2017 Regulation No. Nerc-R-111olisamc_628730283No ratings yet
- Peer Graded Assignments 1-3 Full VersionDocument7 pagesPeer Graded Assignments 1-3 Full VersionMihail100% (1)
- David Aguilar ResumeDocument1 pageDavid Aguilar ResumeDavidAguilarNo ratings yet
- Lex Yacc TutorialDocument38 pagesLex Yacc TutorialAbhijit DasNo ratings yet
- CV May 2020 - Karen DavidgeDocument7 pagesCV May 2020 - Karen Davidgeapi-490357188No ratings yet
- 1460-Article Text-95682-1-10-20220428Document18 pages1460-Article Text-95682-1-10-20220428AQILAH ADLA MazayaNo ratings yet
- Leadership - Pob NotesDocument11 pagesLeadership - Pob NoteschloeniabNo ratings yet
- (SVPDC) Learning Continuity Plan 2021-2022Document54 pages(SVPDC) Learning Continuity Plan 2021-2022Sir GilbertNo ratings yet
- Exhibitors Briefing (12-05-23)Document43 pagesExhibitors Briefing (12-05-23)John SantosNo ratings yet
- National Council of Examiners For Engineering and Surveying NCEESDocument182 pagesNational Council of Examiners For Engineering and Surveying NCEESbaranakinbingolNo ratings yet
- Leeder Et Al (2017) Cold Water Immersion and Recovery From Strenuous Exercise. A Meta AnalysisDocument9 pagesLeeder Et Al (2017) Cold Water Immersion and Recovery From Strenuous Exercise. A Meta AnalysisNg Hui HwaNo ratings yet