Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 21 - A Turbulent Decade 21-1: Postwar Troubles: Demobilization - The Shift From A Wartime To A Peacetime Footing
Chapter 21 - A Turbulent Decade 21-1: Postwar Troubles: Demobilization - The Shift From A Wartime To A Peacetime Footing
Uploaded by
Ben LiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 21 - A Turbulent Decade 21-1: Postwar Troubles: Demobilization - The Shift From A Wartime To A Peacetime Footing
Chapter 21 - A Turbulent Decade 21-1: Postwar Troubles: Demobilization - The Shift From A Wartime To A Peacetime Footing
Uploaded by
Ben LiCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 21 A Turbulent Decade 21-1: Postwar Troubles
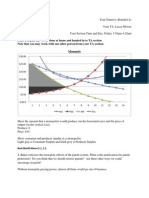
Demobilization the shift from a wartime to a peacetime footing Four million soldiers returned to civilian life Women were urged to give up jobs to make room for returning veterans. The same patriotism which induced women to enter industry during the war should induce them to vacate their positions, - NY Labor Federation Women were forced out by men Women work force fell in 1920 to what it was in 1910 Demand for goods out-spaced supply Prices soared until cost of goods and services in 1920 was about twice that of 1914 1920-1921 Recession struct and prices fell Demobilization was a factor government canceled more than $2 Billion in war contracts Factories cut back production and laid off workers 1921 10% of labor force were unemployed Farm crisis benefited from wartime markets Dep. Of Agriculture, wheat dropped from 2.16 to less than a dollar American farms lost ownership of their land 1919 unions called more than 3600 strikes First strike
1. January 1919 2. 35,000 shipyard workers 3. Seattle, Washington 4. Demanded higher wages and shorter workday 5. Within two weeks, 110 local unions voted to join the workers in a general strike 6. Began on February 6, 10 am. 7. 60,000 workers left their job. Seattle newspapers blamed immigrants calling them muddle-headed foreigners and riffraff from europe intent on terrorizing the community
Mayor Ole Hanson the strike as the work of Bolsheviks and called in troops to prevent unrest public pressure = no more strike The Boston Strike
1. September 1919 2. Boston Police formed a union to seek better pay and working conditions 3. Edwin Curtis refused to recognize the union fired 19 officers for engaging in union activities 4. 75% of police went on strike 5. Journalist William Allen White described strike 6. Governor Calvin Coolidge called in state militia to restore order 7. Newspapers denounced strikes as agents of Lenin and the strike as a Bolshevist nightmare 8. Curtis hired unemployed veterans The Steel Strike 1. September 1919 2. 365,000 steelworkers 3. Demanded recognition of their union and protesting low wages and long working hours. 4. Almost shut down the steel industry 5. Portrayed foreign workers as radicals and called on loyal Americans to return to work 6. Bosses brought in African Americans and Mexicans as replacement workers and hired armed thugs to attack the strikers 7. Strikers were jailed, beaten, or shot 8. January 9, 1920 canceled the strike Red Scare A period of anti-Communist hysteria Communists controlled many women's organizations Women's International League for Peace and Freedom Walter Lippmann Journalist The Palmer Raids
1. 1919 2. Rash of bomb scares 3. April, alert postal clerks discovered 36 bombs in the mail addressed to such prominent citizens as John D. Rockefeller, Supreme Court justice Oliver Wendell Holmes, and Postmaster General Albert Burleson
4. Attorney General A. Mitchell Palmer's house was damaged, died in blast 5. newspapers called a few free treatments in the electric chair. 6. Palmer launched an anti-Red crusade
You might also like
- Civil Disturbance ManagementDocument43 pagesCivil Disturbance ManagementVon Datz85% (33)
- Readers TheaterDocument7 pagesReaders Theaterapi-334295481100% (1)
- USA 1919-41 Notes RemyDocument33 pagesUSA 1919-41 Notes RemyBryan NgoNo ratings yet
- Theories of Peace and ConflictDocument19 pagesTheories of Peace and ConflictTAOHEEDNo ratings yet
- 19th Century English LiteratureDocument58 pages19th Century English LiteraturemilkoviciusNo ratings yet
- Untitled PresentationDocument8 pagesUntitled Presentationapi-308086787No ratings yet
- 1920-30 American History RevisionDocument3 pages1920-30 American History RevisionFikayo AdeyemiNo ratings yet
- The Aftermath of The Great WarDocument32 pagesThe Aftermath of The Great Warcharlotte_kelly3898No ratings yet
- 1920s Revision PresDocument8 pages1920s Revision Presmxl1ymayNo ratings yet
- 1910 SDocument20 pages1910 SLA-ABCFNo ratings yet
- 1920s Alt. ReadingDocument8 pages1920s Alt. ReadingmochsNo ratings yet
- Lecture ch24Document40 pagesLecture ch24api-171412573No ratings yet
- History Part 2Document24 pagesHistory Part 2Galuh JgsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 - World War I 20-3: The War at HomeDocument3 pagesChapter 20 - World War I 20-3: The War at HomeBen LiNo ratings yet
- 20-1 Americans Struggle With Postwar IssuesDocument11 pages20-1 Americans Struggle With Postwar Issuesi like reviews100% (1)
- 20th CenturyDocument16 pages20th CenturyAfricaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Notes 28-31Document7 pagesChapter Notes 28-31Drew SherwoodNo ratings yet
- America in World War II Homefront Reading Passage-1Document4 pagesAmerica in World War II Homefront Reading Passage-1DERRICK FRIERSONNo ratings yet
- America's History America: A Concise History: Eighth Edition Sixth EditionDocument27 pagesAmerica's History America: A Concise History: Eighth Edition Sixth EditionHenry ChaoNo ratings yet
- World War 1 and Roaring 20sDocument22 pagesWorld War 1 and Roaring 20sapi-355176482100% (1)
- L2 PlanchronoDocument11 pagesL2 PlanchronoThafath KhellatNo ratings yet
- APUSH Ch. 14 NotesDocument5 pagesAPUSH Ch. 14 NotesKelsey YoungNo ratings yet
- CH 3 - The TwentiesDocument15 pagesCH 3 - The TwentiesSenorita Brewster100% (1)
- The Red Scare of 1920Document2 pagesThe Red Scare of 1920Vinnie MarzanoNo ratings yet
- Racial Tensions and Economic DeclineDocument22 pagesRacial Tensions and Economic DeclineChristian JonesNo ratings yet
- 7 6 - American Economic HistoryDocument42 pages7 6 - American Economic Historyapi-235395204No ratings yet
- The Gilded Age 1877-1900: Key Individuals and Terms FromDocument16 pagesThe Gilded Age 1877-1900: Key Individuals and Terms FromRocket FireNo ratings yet
- Grade-9 Russian Revolution NotesDocument3 pagesGrade-9 Russian Revolution Notesgadesowjanya7No ratings yet
- APUSH Chapter 32 NotesDocument5 pagesAPUSH Chapter 32 NotesphthysyllysmNo ratings yet
- Sem1 US History EOC Review PPTDocument176 pagesSem1 US History EOC Review PPTJaila MormanNo ratings yet
- Midterm EssayDocument6 pagesMidterm EssayJonas WipfNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Socialism in Europe and The Russian Revolution (Handout)Document8 pagesChapter 2 Socialism in Europe and The Russian Revolution (Handout)KIRANJOT KAURNo ratings yet
- Apush Study Guide ReviewDocument20 pagesApush Study Guide ReviewKatie ChoNo ratings yet
- 20TH&21ST CenturyDocument16 pages20TH&21ST CenturyPaula Sánchez SuárezNo ratings yet
- Post War Prosperity:: Lecture1: Politics in 1920s - 1929 SDocument9 pagesPost War Prosperity:: Lecture1: Politics in 1920s - 1929 SIkramNo ratings yet
- Nick II and LeninDocument58 pagesNick II and LeninSol Ines PerezNo ratings yet
- APUSH Chapter 31 NotesDocument6 pagesAPUSH Chapter 31 NotesphthysyllysmNo ratings yet
- History Midterm Study PacketDocument33 pagesHistory Midterm Study PacketscreamcreamvanillaNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 American HistoryDocument30 pagesUnit 9 American HistoryKhiết Tâm Thánh GiaNo ratings yet
- 1 Interwar Period 1Document34 pages1 Interwar Period 1Raymond NuvalNo ratings yet
- Politics of The 1920sDocument27 pagesPolitics of The 1920sAshraf ShawkyNo ratings yet
- Paris HistoryDocument106 pagesParis HistoryJose SanchezNo ratings yet
- Usa HistoryDocument58 pagesUsa HistoryJose SanchezNo ratings yet
- Roaring 20sDocument75 pagesRoaring 20sJAggie57No ratings yet
- Great DepressionDocument24 pagesGreat Depressionapi-301503837No ratings yet
- The North and The South:The American Civil War: by Yamil HannaDocument16 pagesThe North and The South:The American Civil War: by Yamil HannaOscar Enrique Mendoza GuerraNo ratings yet
- Compromise of 1850: Gold Rush in CaliforniaDocument5 pagesCompromise of 1850: Gold Rush in Californiaapi-121634514No ratings yet
- US History for Kids 1877-1914 - Political, Economic & Social Life | 19th - 20th Century US History | 6th Grade Social StudiesFrom EverandUS History for Kids 1877-1914 - Political, Economic & Social Life | 19th - 20th Century US History | 6th Grade Social StudiesNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 KAPLAN Original OUTLINE Ethan Yakhin Period 4 3/19/13Document12 pagesCHAPTER 6 KAPLAN Original OUTLINE Ethan Yakhin Period 4 3/19/13api-210462176No ratings yet
- Exam Form 2Document23 pagesExam Form 2Didi Gump EddieNo ratings yet
- CH 4 - The ThirtiesDocument14 pagesCH 4 - The ThirtiesSenorita BrewsterNo ratings yet
- CHC2D0 Grade 10 History NotesDocument9 pagesCHC2D0 Grade 10 History Notesxo_michellee_xoNo ratings yet
- The American Colonies Declare IndependenceDocument28 pagesThe American Colonies Declare IndependenceAlexandru BardașNo ratings yet
- Section B Depression and The New DealDocument42 pagesSection B Depression and The New DealtlyskivnNo ratings yet
- Radical America - Vol 9 No 4& 5 - 1974 - August OctoberDocument220 pagesRadical America - Vol 9 No 4& 5 - 1974 - August OctoberIsaacSilverNo ratings yet
- Great Depression NotesDocument6 pagesGreat Depression NotespomtartNo ratings yet
- USA 1919-1941 Revision NotesDocument12 pagesUSA 1919-1941 Revision NotesJosé António CorreiaNo ratings yet
- Independence 1Document28 pagesIndependence 1api-234908816No ratings yet
- The Roaring TwentiesDocument28 pagesThe Roaring TwentiesmissseesNo ratings yet
- Class Notes of The American Civil War 23-24Document3 pagesClass Notes of The American Civil War 23-24rudra samadhiyaNo ratings yet
- The Roaring 20 USA, 1919-1929: RevisionDocument42 pagesThe Roaring 20 USA, 1919-1929: RevisionSuzannochkaAstvatsaturianNo ratings yet
- 1920's America Knowledge For GCSEDocument4 pages1920's America Knowledge For GCSEMeyalioNo ratings yet
- APUSH Crosswords U7 - U8Document7 pagesAPUSH Crosswords U7 - U8MaryEK1No ratings yet
- CHinese WorksheetDocument6 pagesCHinese WorksheetBen LiNo ratings yet
- BTS I Need U PDFDocument4 pagesBTS I Need U PDFBen LiNo ratings yet
- BIO 2514 Student Information Fall 2015asdDocument2 pagesBIO 2514 Student Information Fall 2015asdBen LiNo ratings yet
- Final Fantasy XV - HellfireDocument16 pagesFinal Fantasy XV - HellfireBen LiNo ratings yet
- Final Fantasy XV - HellfireDocument16 pagesFinal Fantasy XV - HellfireBen LiNo ratings yet
- Class 14, Quiz 12: To Be Done at Home and Handed in To TA Section Note That You May Work With One Other Person From Your TA Section. MonopolyDocument1 pageClass 14, Quiz 12: To Be Done at Home and Handed in To TA Section Note That You May Work With One Other Person From Your TA Section. MonopolyBen LiNo ratings yet
- Projectfinaljb: Steinway Grand Piano 144Document4 pagesProjectfinaljb: Steinway Grand Piano 144Ben LiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 - World War I 20-3: The War at HomeDocument3 pagesChapter 20 - World War I 20-3: The War at HomeBen LiNo ratings yet
- DBQ Organizer Template: The Documents (Use "Most") The "Relevant Outside Information"Document1 pageDBQ Organizer Template: The Documents (Use "Most") The "Relevant Outside Information"Ben LiNo ratings yet
- 1872 Cavite Mutiny Justine PalasigueDocument3 pages1872 Cavite Mutiny Justine PalasigueJustine PalasigueNo ratings yet
- French Revolution Final DraftDocument26 pagesFrench Revolution Final DraftDivya RounakNo ratings yet
- Pub - Riotous Assemblies Popular Protest in Hanoverian eDocument367 pagesPub - Riotous Assemblies Popular Protest in Hanoverian eBogdan ParoškiNo ratings yet
- Wolfi Landstreicher - Anonymous Autonomous Self Organization and Anarchist Intervention A Tension in PracticeDocument22 pagesWolfi Landstreicher - Anonymous Autonomous Self Organization and Anarchist Intervention A Tension in PracticeLuis MartinsNo ratings yet
- The 1930's in California - Final California Essay - AMST 395Document4 pagesThe 1930's in California - Final California Essay - AMST 395Andrew “Castaway” GroundNo ratings yet
- The Boxer UprisingDocument7 pagesThe Boxer UprisingFahad NahviNo ratings yet
- HIS-103 LEC-14: Agartala Conspiracy CaseDocument12 pagesHIS-103 LEC-14: Agartala Conspiracy CaseTaef Hossain 1531416630No ratings yet
- CH 16 - Collective Behavior and Social Change - NotesDocument83 pagesCH 16 - Collective Behavior and Social Change - Notesamnahbatool785No ratings yet
- Q2 Module 3 AP 1 Grade 7Document4 pagesQ2 Module 3 AP 1 Grade 7byahero3480% (10)
- Sakdal UprisingDocument2 pagesSakdal UprisingHarvin Julius LasqueroNo ratings yet
- Final Draft of Rogerian-Style ArgumentDocument9 pagesFinal Draft of Rogerian-Style Argumentapi-610212620No ratings yet
- Compare and Contrast The Causes of 1905 and February Revolutions in RussiaDocument2 pagesCompare and Contrast The Causes of 1905 and February Revolutions in RussiaMarta ReysnerNo ratings yet
- Buffalo Springfield Anthem of The SixtiesDocument2 pagesBuffalo Springfield Anthem of The SixtiesRoy WardenNo ratings yet
- Cópia de Inventário Unispanco OLDDocument5,597 pagesCópia de Inventário Unispanco OLDThiago Targino QuerozNo ratings yet
- Scions of Dorn BackgroundDocument2 pagesScions of Dorn BackgroundSteven UhlenbergNo ratings yet
- Greg Gutfeld Portland Mayor Learns Bitter Lesson of Appeasing AntifaDocument5 pagesGreg Gutfeld Portland Mayor Learns Bitter Lesson of Appeasing AntifaApollo WongNo ratings yet
- Dark Heresy Supplement) - TimelineDocument8 pagesDark Heresy Supplement) - TimelineJasper Chan100% (1)
- GERIZAL Compilation - Formative Assessment A2Document9 pagesGERIZAL Compilation - Formative Assessment A2Jan Gavin GoNo ratings yet
- The American Revolution - A Visual History - DK Publishing (DK Publishing, Smithsonian, 2016, 9781465446077, Eng) PDFDocument362 pagesThe American Revolution - A Visual History - DK Publishing (DK Publishing, Smithsonian, 2016, 9781465446077, Eng) PDFFrédéric Pili100% (3)
- Berlin UproarDocument2 pagesBerlin UproarHarvin IriawanNo ratings yet
- History of KoreaDocument9 pagesHistory of KoreaIncubusNo ratings yet
- Nguyễn Phúc ThuầnDocument2 pagesNguyễn Phúc ThuầnChristopher ServantNo ratings yet
- Barry K. Grant - American Cinema of The 1960s, Themes and Variations (2008)Document297 pagesBarry K. Grant - American Cinema of The 1960s, Themes and Variations (2008)Kornelia Piekut100% (7)
- Savage Worlds - The Thin Blue Line - Player's Guide PDFDocument85 pagesSavage Worlds - The Thin Blue Line - Player's Guide PDFDanDan_XPNo ratings yet
- Why Is There No Just Riot TheoryDocument44 pagesWhy Is There No Just Riot Theorybharan16No ratings yet
- Conquest and Foundation: History of The GothsDocument2 pagesConquest and Foundation: History of The GothsCorina Taraș-LunguNo ratings yet