Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Requirement Verbs
Requirement Verbs
Uploaded by
Drzvvk ZxjkkOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Requirement Verbs
Requirement Verbs
Uploaded by
Drzvvk ZxjkkCopyright:
Available Formats
Student Guidance Notes
Guide 14
September 2004
Verbs, learning outcomes and syllabus content general guidance notes for students on how to read and interpret the 2005 syllabus
This guide explains how you should interpret the detail of the 2005 syllabus, and how you should plan your study. It also contains a series of frequently asked questions relating to this guide, some of which were asked at the recent lecturers conference. If you have any further queries relating to this guide, please contact CIMA Student Services department on + 44 (0)208 849 2404, or email your query to cima.contact@cimaglobal.com
October 2004
Reading the syllabus
Each topic within the syllabus contains a list of learning outcomes, which should be read in conjunction with the knowledge content for the syllabus. A learning outcome has two main purposes: to define the skill or ability that a well-prepared candidate should be able to exhibit in the examination; to demonstrate the approach likely to be taken by examiners in examination questions. The learning outcomes are part of a hierarchy of learning objectives. The verbs used at the beginning of each learning outcome relate to a specific learning objective e.g. Evaluate alternative approaches to budgeting. The verb evaluate indicates a high level learning objective. Because learning objectives are hierarchical, it is expected that at this level, students will have knowledge of different budgeting systems and methodologies and be able to apply them. A list of the learning objectives and the verbs, that appear in the syllabus learning outcomes and examinations, follows:
October 2004
Learning Objective Verbs Used
1 Knowledge What you are expected to know. 2 Comprehension What you are expected to understand. List State Define Describe Distinguish Explain Identify Illustrate Apply Calculate/ compute Demonstrate Prepare Reconcile Solve Tabulate Analyse Categorise Compare and contrast Construct Discuss Interpret Produce Advise Evaluate Recommend
Definition
Make a list of Express, fully or clearly, the details of/facts of Give the exact meaning of Communicate the key features of Highlight the differences between Make clear or intelligible/State the meaning of Recognise, establish or select after consideration Use an example to describe or explain something Put to practical use Ascertain or reckon mathematically Prove with certainty or to exhibit by practical means Make or get ready for use Make or prove consistent/compatible Find an answer to Arrange in a table Examine in detail the structure of Place into a defined class or division Show the similarities and/or differences between Build up or compile Examine in detail by argument Translate into intelligible or familiar terms Create or bring into existence Counsel, inform or notify Appraise or assess the value of Advise on a course of action
3 Application How you are expected to apply your knowledge.
4 Analysis How you are expected to analyse the detail of what you have learned.
5 Evaluation How you are expected to use your learning to evaluate, make decisions or recommendations.
When studying, you should first note the learning outcome(s) relating to the topic. You need to develop skills relating to that topic up to, but not exceeding, the level in the hierarchy at which the verb(s) are placed. Every examination question will use one or other of the verbs from the hierarchy. Examiners will not use a verb in a question requirement that comes from a higher level than that of the verb in the learning outcome being tested. The syllabus content is simply a suggestion of topic areas you should cover, in order to be able to satisfy the learning outcomes. It is the learning outcomes that are examined, not the syllabus content.
October 2004
You might also like
- Let Us Understand What Kirkpatrick's Model IsDocument26 pagesLet Us Understand What Kirkpatrick's Model IsFlora found100% (9)
- Theory PosterDocument2 pagesTheory PosterSonja LueNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Principles and Practice of AssessmentDocument6 pagesUnderstanding The Principles and Practice of Assessmentapi-265013545No ratings yet
- Written Test Guide CoC 1 and CoC 2Document11 pagesWritten Test Guide CoC 1 and CoC 2Jesus Placedes100% (8)
- 60 PillarsDocument62 pages60 PillarsGerardChan100% (7)
- Information LegalizationDocument4 pagesInformation LegalizationDrzvvk ZxjkkNo ratings yet
- General Knowledge TIG 2ndedition DOE031910 PDFDocument55 pagesGeneral Knowledge TIG 2ndedition DOE031910 PDFAmina Bešić Klepo100% (1)
- How To Create A Table of SpecificationsDocument59 pagesHow To Create A Table of SpecificationsSherry Mae Armada74% (23)
- Lesson 5 - Construction of Written TestDocument33 pagesLesson 5 - Construction of Written TestAndrea Lastaman100% (9)
- ASSESSMENT IN LEARNING Module 4Document13 pagesASSESSMENT IN LEARNING Module 4Liezel Alquiza100% (2)
- Outcomes Based Education (OBE) SeminarDocument49 pagesOutcomes Based Education (OBE) SeminarRaymark D. Llagas100% (6)
- Meeting the Assessment Requirements of the Award in Education and TrainingFrom EverandMeeting the Assessment Requirements of the Award in Education and TrainingNo ratings yet
- What Is Effective Questioning? Effective Questioning Is A Key Tool in Assessment For Learning Strategies andDocument14 pagesWhat Is Effective Questioning? Effective Questioning Is A Key Tool in Assessment For Learning Strategies andJennifer AquinoNo ratings yet
- Piloting Is A Crucial Stage of Materials DevelopmentDocument5 pagesPiloting Is A Crucial Stage of Materials Developmentchapagain_yNo ratings yet
- Guide14 Verbs Learningoutcomes SyllabuscontentDocument3 pagesGuide14 Verbs Learningoutcomes SyllabuscontentGurpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- EDUC 4 Lesson 5Document13 pagesEDUC 4 Lesson 5Ray Lorenz OrtegaNo ratings yet
- The Aligned CurriculumDocument14 pagesThe Aligned CurriculumMuhammad Ramdhan PurnamaNo ratings yet
- AO1 Knowledge and Understanding Exercises and ActivitiesDocument9 pagesAO1 Knowledge and Understanding Exercises and ActivitiesshujaitbukhariNo ratings yet
- Learning Taxonomy: Using Outcomes To Design Achievement TestDocument49 pagesLearning Taxonomy: Using Outcomes To Design Achievement TestSarah AndersonNo ratings yet
- Guidance On Command Words Used in Learning Outcomes and Question Papers DIPLOMA v2 Sept15 (010915 Rew) 179201551521 - NoRestrictionDocument6 pagesGuidance On Command Words Used in Learning Outcomes and Question Papers DIPLOMA v2 Sept15 (010915 Rew) 179201551521 - NoRestrictionAli MohdNo ratings yet
- Teaching GuideDocument53 pagesTeaching GuideDarrenNaelgasNo ratings yet
- Assessment Concepts For Web 14 Apr 2014Document6 pagesAssessment Concepts For Web 14 Apr 2014Bernard ChanNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 10 The Art of Preparing Examinations/Test QuestionsDocument27 pagesActivity No. 10 The Art of Preparing Examinations/Test QuestionsGuinivere C. MorilesNo ratings yet
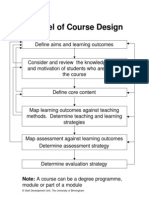
- A Model For Course Design by BHAM UniversityDocument4 pagesA Model For Course Design by BHAM UniversityLupita Rodríguez BulnesNo ratings yet
- LearningoutcomesDocument4 pagesLearningoutcomesapi-267948590No ratings yet
- ST Mary Mackillop Unit Plan User GuideDocument2 pagesST Mary Mackillop Unit Plan User Guideapi-320230014No ratings yet
- Implementing Performance-Based-Assessment in The EFL ClassroomDocument5 pagesImplementing Performance-Based-Assessment in The EFL ClassroomNana EdoNo ratings yet
- FS 5 - Activity 6 On Scoring RibricsDocument10 pagesFS 5 - Activity 6 On Scoring RibricsGlydel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- LessonPlanRubric PDFDocument4 pagesLessonPlanRubric PDFLeonard FinezNo ratings yet
- UNIT 3 Teaching&LearningDocument18 pagesUNIT 3 Teaching&LearningwankamisahNo ratings yet
- Guidelines On Writing Learning OutcomesDocument4 pagesGuidelines On Writing Learning OutcomesSuriaRAsaiNo ratings yet
- Acc201 Unisa ModuleDocument330 pagesAcc201 Unisa ModuleElton Jones MusasiwaNo ratings yet
- Unpacking Learning CompetenciesDocument5 pagesUnpacking Learning CompetenciesThis is a GarbageNo ratings yet
- m2 ObjectiveDocument4 pagesm2 ObjectiveHải Trà NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Profed 06 Lesson 5Document5 pagesProfed 06 Lesson 5Marvin CariagaNo ratings yet
- Lopezangel Chapter 6Document18 pagesLopezangel Chapter 6Mary Annalie Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- vt59.2708 21323560432 - 2329076630610927 - 3882378228468079699 - N.pdfprogram Course and Intended Learning OuDocument23 pagesvt59.2708 21323560432 - 2329076630610927 - 3882378228468079699 - N.pdfprogram Course and Intended Learning OuAllyza Mae AgravanteNo ratings yet
- Handbook For Outcomes Assessment Using Learning Goals and ObjectivesDocument14 pagesHandbook For Outcomes Assessment Using Learning Goals and ObjectivesHofstraUniversityNo ratings yet
- Professional Development Portfolio GuideDocument14 pagesProfessional Development Portfolio GuideRicardo Sage2 HarrisNo ratings yet
- Writing Learning Objectives PDFDocument9 pagesWriting Learning Objectives PDFrinku100% (1)
- Relationship Between Reliability and ValidityDocument2 pagesRelationship Between Reliability and ValidityYasmeen NazNo ratings yet
- Scoring RubricsDocument14 pagesScoring RubricsTopacio Manlaput100% (1)
- IDocument5 pagesIIrene Quimson100% (6)
- 8602, Assignment 1Document13 pages8602, Assignment 1Abdul WajidNo ratings yet
- Preparing Examination Questions (Essays) : Ideas To Help Ensure That The Question(s) Are Marked ObjectivelyDocument3 pagesPreparing Examination Questions (Essays) : Ideas To Help Ensure That The Question(s) Are Marked ObjectivelyradugaNo ratings yet
- Asl 1 - RubricsDocument18 pagesAsl 1 - RubricsNhalyn Torres AquinoNo ratings yet
- Out Based PrinciplesDocument13 pagesOut Based PrinciplesJaenelyn AlquizarNo ratings yet
- Education Is Not Preparation For Life, Education Is Life Itself.Document37 pagesEducation Is Not Preparation For Life, Education Is Life Itself.Murphy Red100% (1)
- Guidance On Command Words Used in Learning Outcomes and Question Papers - Diploma QualificationsDocument25 pagesGuidance On Command Words Used in Learning Outcomes and Question Papers - Diploma QualificationsIndermohan MehtaNo ratings yet
- FS 2 PPT 2-1Document19 pagesFS 2 PPT 2-1Nikki RebidenNo ratings yet
- WEEK 5 WORKSHEET - Standardized TestingDocument8 pagesWEEK 5 WORKSHEET - Standardized Testing5pc4465zgsNo ratings yet
- Assessemnt of Learning Module 5Document3 pagesAssessemnt of Learning Module 5Katrina ClariñoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Construction of Written TestDocument47 pagesLesson 5 Construction of Written TestearnestjoyqtjacintoNo ratings yet
- Command Words GuidelinesDocument25 pagesCommand Words Guidelinesആദിത്യ ആകാശ്No ratings yet
- Mac4863 2021 TL 502 0 BDocument16 pagesMac4863 2021 TL 502 0 BItumeleng KekanaNo ratings yet
- Elective-2-Activity-5 (Output)Document4 pagesElective-2-Activity-5 (Output)Rosemarie GaringNo ratings yet
- WWP Evel 50 Sept 2011 DraftDocument10 pagesWWP Evel 50 Sept 2011 Drafta.blytheNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER IV - Lesson IDocument11 pagesCHAPTER IV - Lesson IAngelica Macalalad100% (2)
- Written and Oral TestDocument18 pagesWritten and Oral TestDaniel Bermillo100% (4)
- Managing Professional Development 1Document7 pagesManaging Professional Development 1Shyamini ChandranNo ratings yet
- Teaching MathDocument84 pagesTeaching MathKaren Ocon EstelaNo ratings yet
- Rubrics: Useful Assessment ToolsDocument3 pagesRubrics: Useful Assessment ToolsRose Dumayac100% (1)
- Lesson 3 and 4 Report EditedDocument39 pagesLesson 3 and 4 Report EditedMark Adrian MartinezNo ratings yet
- MaeDocument6 pagesMaeAnaMae Asuncion De LunaNo ratings yet
- How to Practice Before Exams: A Comprehensive Guide to Mastering Study Techniques, Time Management, and Stress Relief for Exam SuccessFrom EverandHow to Practice Before Exams: A Comprehensive Guide to Mastering Study Techniques, Time Management, and Stress Relief for Exam SuccessNo ratings yet
- Monetizing Clients On TwitterDocument3 pagesMonetizing Clients On TwitterDrzvvk ZxjkkNo ratings yet
- Espresso Final Menu - Edit - V9Document13 pagesEspresso Final Menu - Edit - V9Drzvvk ZxjkkNo ratings yet
- PSWR FactsheetDocument4 pagesPSWR FactsheetDrzvvk ZxjkkNo ratings yet
- Bursery - Westminster Immigration Services ProposalDocument10 pagesBursery - Westminster Immigration Services ProposalDrzvvk ZxjkkNo ratings yet
- Sensitivity AnalysisDocument2 pagesSensitivity AnalysisDrzvvk Zxjkk100% (1)
- English Power Point OthelloDocument8 pagesEnglish Power Point Othellomlear23No ratings yet
- Hamlet - Body Biography ProjectDocument4 pagesHamlet - Body Biography ProjectHairam ShafiqNo ratings yet
- Categorization of CompetenciesDocument3 pagesCategorization of CompetenciesAditi Ameya KirtaneNo ratings yet
- Dalton's Form 1Document85 pagesDalton's Form 1Qingsong CaiNo ratings yet
- 3 MusketeersDocument2 pages3 MusketeersAngelu Pu-odNo ratings yet
- Gestalt TherapyDocument2 pagesGestalt TherapyjessicaNo ratings yet
- Dangers of MeditationDocument6 pagesDangers of MeditationsainandanreddyNo ratings yet
- Welcome Address GraduationDocument5 pagesWelcome Address GraduationCharles OkonkwoNo ratings yet
- занятие 1 интервьюDocument2 pagesзанятие 1 интервьюLurina NataliiaNo ratings yet
- 10 Subtest A: Making Inferences: Social Language Development Test - ElementaryDocument5 pages10 Subtest A: Making Inferences: Social Language Development Test - ElementaryCamila VergaraNo ratings yet
- Ss1 Family Planning EssayDocument1 pageSs1 Family Planning EssayIrish BarcelonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Research MethodologyDocument3 pagesChapter 1 Research MethodologyLalaliliNo ratings yet
- Negotiation Between Government and The Teachers Association: Negotiation Strategy Paper - Alternate Dispute ResolutionDocument3 pagesNegotiation Between Government and The Teachers Association: Negotiation Strategy Paper - Alternate Dispute ResolutionLoukya PabbathiNo ratings yet
- 11 Pjir Volume Articles June 2013 Arabic أسئلة حائرةDocument119 pages11 Pjir Volume Articles June 2013 Arabic أسئلة حائرةInamUlHaqGhaziNo ratings yet
- Đề Thi Tuyển Sinh Chuyen Anh Sp 2015Document6 pagesĐề Thi Tuyển Sinh Chuyen Anh Sp 2015Quân VũNo ratings yet
- Part 1 - Disunity To UnityDocument4 pagesPart 1 - Disunity To UnityjackNo ratings yet
- Employee Satisfaction of Hotel Industry - A Case Study of The GranDocument53 pagesEmployee Satisfaction of Hotel Industry - A Case Study of The GranParth PatelNo ratings yet
- Session 1 CB Offline 20 RevDocument24 pagesSession 1 CB Offline 20 Revmichael100% (1)
- Contemporary WorldBSOADocument10 pagesContemporary WorldBSOAReniva Nescelle MariaNo ratings yet
- Grammar - Pho's Move and StepDocument4 pagesGrammar - Pho's Move and StepMarchella NANo ratings yet
- Enchanted I Fall WithDocument47 pagesEnchanted I Fall WithNishithivi VNo ratings yet
- Final Practicial ResearchDocument9 pagesFinal Practicial ResearchMark VirgilNo ratings yet
- Ethics Reflection PaperDocument7 pagesEthics Reflection PaperDavid Bacon100% (1)
- Robot Relationships Student WorksheetDocument5 pagesRobot Relationships Student WorksheetGeorgina VegaNo ratings yet
- SCENARIOSDocument3 pagesSCENARIOSCharmaine Gorge DangsiNo ratings yet
- A Level Drama Coursework EdexcelDocument9 pagesA Level Drama Coursework Edexcelirugqgajd100% (2)