Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Esophageal Web Final
Esophageal Web Final
Uploaded by
adilCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- CLILDocument14 pagesCLILcarlos alberto100% (2)
- Thierry Bardini. Junkware. The Essential Junkiness of Our Culture and BiologyDocument298 pagesThierry Bardini. Junkware. The Essential Junkiness of Our Culture and BiologyJulieta Yelin100% (1)
- Lab 08 Oracle Access Management - Access Manager 11G R2 Ps3 2 Legged Mobile OauthDocument39 pagesLab 08 Oracle Access Management - Access Manager 11G R2 Ps3 2 Legged Mobile OauthAshutosh NichatNo ratings yet
- Short Questions FMDocument21 pagesShort Questions FMsultanrana100% (1)
- Test Bank On GI PathologyDocument14 pagesTest Bank On GI PathologySeff CausapinNo ratings yet
- Gastro RobbinsDocument68 pagesGastro RobbinsAndrea PescosolidoNo ratings yet
- Diseases of The Esophagus DR Lapuz MCDDocument6 pagesDiseases of The Esophagus DR Lapuz MCDMiguel Cuevas Dolot100% (1)
- Pathology PracticalDocument20 pagesPathology Practicalisaungureanu88.iuNo ratings yet
- 5 Patho 1 - Lut - Dr. MesinaDocument11 pages5 Patho 1 - Lut - Dr. MesinaRobert Francis DikioNo ratings yet
- Srs Esophagus & Stomach: PathologyDocument4 pagesSrs Esophagus & Stomach: PathologyyayayanizaNo ratings yet
- The Appendix FinalDocument62 pagesThe Appendix FinalLajel S. LachicaNo ratings yet
- Benign Disease of The Esophagus PDFDocument4 pagesBenign Disease of The Esophagus PDFSpecialNameNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Congenital Genitourinary AbnormalitiesDocument4 pagesChapter 3 Congenital Genitourinary AbnormalitiesRem AlfelorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Congenital Genitourinary AbnormalitiesDocument4 pagesChapter 3 Congenital Genitourinary AbnormalitiesRemelou Garchitorena AlfelorNo ratings yet
- Sidhu 2002Document3 pagesSidhu 2002Yacine Tarik AizelNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Ultrasonographyin Small AnimalsDocument10 pagesAbdominal Ultrasonographyin Small AnimalsAna Clara SevasteNo ratings yet
- Digestive System AnatomyDocument3 pagesDigestive System AnatomyJo Marchianne PigarNo ratings yet
- 6.5 Small IntestineDocument6 pages6.5 Small IntestineRahimShah RahimNo ratings yet
- Approaches To Esophageal SuturesDocument7 pagesApproaches To Esophageal Suturestaner_soysurenNo ratings yet
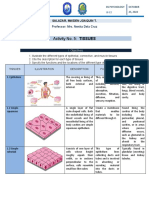
- ZOO 1 SALAZAR ACT 5 TISSUES (Repaired)Document8 pagesZOO 1 SALAZAR ACT 5 TISSUES (Repaired)TORRES, EFRAIM MATTHEW S.No ratings yet
- Belizario ParasitologyDocument66 pagesBelizario Parasitologyangela tanteoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Bohn NodulesDocument3 pagesClinical Bohn NodulesMARIA KARINA HERNANDEZ PEREZNo ratings yet
- Validation Si and Li - 2016bDocument3 pagesValidation Si and Li - 2016byayayanizaNo ratings yet
- Pathology B - Gastrointestinal Tract (Esguerra, 2015) PDFDocument18 pagesPathology B - Gastrointestinal Tract (Esguerra, 2015) PDFJem QuintoNo ratings yet
- Pathology B - Gastrointestinal Tract (Esguerra, 2015)Document18 pagesPathology B - Gastrointestinal Tract (Esguerra, 2015)Ars MoriendiNo ratings yet
- Gi Tract Disorders (Infant)Document8 pagesGi Tract Disorders (Infant)Nicole Faylogna AgullanaNo ratings yet
- AMOEBIASISDocument11 pagesAMOEBIASISsrini9047No ratings yet
- Agenesis Atresia Fistula: Mechanical ObstructionDocument13 pagesAgenesis Atresia Fistula: Mechanical Obstructionnge257No ratings yet
- Ajcr 2010 1 6Document3 pagesAjcr 2010 1 6Muhammad Bilal MirzaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Other NematodesDocument7 pagesLesson 5 Other Nematodesshairene PiaNo ratings yet
- Folds of Peritoneum: Abdomen and PelvisDocument100 pagesFolds of Peritoneum: Abdomen and PelvissrisakthiNo ratings yet
- Cirugia Peds Fund TeoricosDocument12 pagesCirugia Peds Fund Teoricos[JC]No ratings yet
- Pediatric GI RadiologyDocument6 pagesPediatric GI Radiologysarguss14No ratings yet
- Clinical Approach To A Patient With Dysphagia: Medicine UpdateDocument3 pagesClinical Approach To A Patient With Dysphagia: Medicine UpdateAnonymous XFDJfsGviNo ratings yet
- Benign Esophageal Tumors: Esophagoscopy and Endoscopic Esophageal UltrasoundDocument7 pagesBenign Esophageal Tumors: Esophagoscopy and Endoscopic Esophageal UltrasoundYacine Tarik AizelNo ratings yet
- Canine and Feline Mega EsophagusDocument10 pagesCanine and Feline Mega Esophagustaner_soysurenNo ratings yet
- Dysphagia: Ethan A. Mezoff, MDDocument5 pagesDysphagia: Ethan A. Mezoff, MDYenny FramelaNo ratings yet
- Fasciolopsis Buski - An Overview - ScienceDirect TopicsDocument13 pagesFasciolopsis Buski - An Overview - ScienceDirect TopicsRadeat GetiyeNo ratings yet
- 09c6 PDFDocument8 pages09c6 PDFlusitania IkengNo ratings yet
- A Rare Case of Fatal Bowel Obstruction Secondary To A Colonic BezoarDocument3 pagesA Rare Case of Fatal Bowel Obstruction Secondary To A Colonic BezoarLannydchandraNo ratings yet
- Git Trans-Oral Cavity To StomachDocument6 pagesGit Trans-Oral Cavity To StomachHanako Sasaki AranillaNo ratings yet
- Intestinal ObstructionDocument70 pagesIntestinal ObstructionosNo ratings yet
- Tubal Assessment and TuBAL SURGERYDocument15 pagesTubal Assessment and TuBAL SURGERYRyan IlhamNo ratings yet
- 'Aliah's GIT & HB Systems1Document39 pages'Aliah's GIT & HB Systems1Luqman Al-Bashir FauziNo ratings yet
- Digestive System LecDocument13 pagesDigestive System LecMikaella ViadorNo ratings yet
- NCM107 PediatricsDocument11 pagesNCM107 PediatricsKM PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Management of Velopharyngeal DysfunctionDocument8 pagesDiagnosis and Management of Velopharyngeal Dysfunctiondrgurpal74No ratings yet
- Git Radiology and ImagingDocument4 pagesGit Radiology and Imagingoddone_outNo ratings yet
- Kleitsch 1958Document6 pagesKleitsch 1958CojocariNo ratings yet
- RLQ PainDocument20 pagesRLQ PainBEATRICE SOPHIA PARMANo ratings yet
- Jurnal Inter OrganDocument8 pagesJurnal Inter Organdyah sekar pratiwiNo ratings yet
- PathologyDocument8 pagesPathologyJemimah Tomarong DespabeladeroNo ratings yet
- Mini Review: Current Concepts in The Management of Anterior Urethral StricturesDocument8 pagesMini Review: Current Concepts in The Management of Anterior Urethral StricturesDwi WiraNo ratings yet
- Imaging Intestinal ObstructionDocument5 pagesImaging Intestinal Obstructionludiegues752No ratings yet
- Imaging of AbdominalDocument15 pagesImaging of AbdominalSpecialNameNo ratings yet
- Necrotizing Enterocolitis: Pathology and PathogenesisDocument3 pagesNecrotizing Enterocolitis: Pathology and PathogenesisJemarey DeramaNo ratings yet
- Block Vii Module 1 Cheat Sheet PDFDocument32 pagesBlock Vii Module 1 Cheat Sheet PDFMark FuerteNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Management of Esophageal Rings and WebsDocument4 pagesDiagnosis and Management of Esophageal Rings and WebsIt's MeNo ratings yet
- Gastroenterology:: Motility Disorders of Esophagus, GERDDocument46 pagesGastroenterology:: Motility Disorders of Esophagus, GERDPatricia May CruzNo ratings yet
- 2 - Intestinal Obstruction. IntussusceptionDocument27 pages2 - Intestinal Obstruction. IntussusceptionNaimenur KorkmazNo ratings yet
- UNCDCYSTDocument5 pagesUNCDCYSTeviltohuntNo ratings yet
- Appendix DuplicationDocument3 pagesAppendix DuplicationMario TrejoNo ratings yet
- Esophageal & Hepato CA Half PDFDocument6 pagesEsophageal & Hepato CA Half PDFhtt.pNo ratings yet
- Treatise on the Anatomy and Physiology of the Mucous Membranes: With Illustrative Pathological ObservationsFrom EverandTreatise on the Anatomy and Physiology of the Mucous Membranes: With Illustrative Pathological ObservationsNo ratings yet
- Sarah Phillips: Dually Certified K-6 Teacher Contact Professional ProfileDocument2 pagesSarah Phillips: Dually Certified K-6 Teacher Contact Professional Profileapi-420172483No ratings yet
- Assignment On InflationDocument7 pagesAssignment On InflationKhalid Mahmood100% (4)
- Asem0909 PDFDocument14 pagesAsem0909 PDFTROY2ARCHILLESNo ratings yet
- Job Mismatch in The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesJob Mismatch in The Philippinesjovelyn c. aronNo ratings yet
- MPS-blank Template Production SchedulingDocument8 pagesMPS-blank Template Production SchedulingSaesaeNo ratings yet
- Write The Days in The Correct OrderDocument7 pagesWrite The Days in The Correct OrderRuth Yánez PadillaNo ratings yet
- Michelangelo Research Paper OutlineDocument4 pagesMichelangelo Research Paper Outlinecampsxek100% (1)
- Clock Arithmetic Aptitude Question With AnswersDocument4 pagesClock Arithmetic Aptitude Question With AnswersOpt TutorNo ratings yet
- Ocr A-Level History Coursework DeadlineDocument8 pagesOcr A-Level History Coursework Deadlinelozuzimobow3100% (2)
- Bloodborne Top-Tier Farmable Gem ChalicesDocument2 pagesBloodborne Top-Tier Farmable Gem ChalicesJose MedinaNo ratings yet
- "Analysis of Marketing Strategies of Nestle Maggi: Winter ReportDocument51 pages"Analysis of Marketing Strategies of Nestle Maggi: Winter ReportAnonymous PbMgeIvKNo ratings yet
- IELTS MASTER - IELTS Reading Test 3Document1 pageIELTS MASTER - IELTS Reading Test 3poon isaacNo ratings yet
- TEP Course FileDocument22 pagesTEP Course FilemohsinpakistanNo ratings yet
- Research Design MBA MK02 UNIT IIDocument15 pagesResearch Design MBA MK02 UNIT IIAmit Kumar100% (3)
- Towards A Meta-Theory of Accounting Information SystemsDocument15 pagesTowards A Meta-Theory of Accounting Information SystemsAhmed KhalafNo ratings yet
- Superstar Stamina How To Get Hard and Stay Hard GET YOUR BODY INTO SHAPE SO YOU'LL LOVE ITDocument78 pagesSuperstar Stamina How To Get Hard and Stay Hard GET YOUR BODY INTO SHAPE SO YOU'LL LOVE ITdominique marshallNo ratings yet
- EUROKLAV-29VS+ ManualDocument58 pagesEUROKLAV-29VS+ ManualpagulahaNo ratings yet
- Hapter 10 BistikDocument2 pagesHapter 10 BistikAhmad Rofi100% (1)
- Presentation Class InglishDocument16 pagesPresentation Class Inglishmiralis gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Grumpy Bear: Some Questions ..Document2 pagesGrumpy Bear: Some Questions ..Mike BNo ratings yet
- Benefits of EDTA Chelation Therapy in Arterioscler PDFDocument11 pagesBenefits of EDTA Chelation Therapy in Arterioscler PDFNéstor Mata RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Sales Rep. / Sales ManagerDocument3 pagesSales Rep. / Sales Managerapi-121455688No ratings yet
- A Comparative Study On Selected Fitness Components of 13-19 Years Female Basketball and Volleyball PlayersDocument11 pagesA Comparative Study On Selected Fitness Components of 13-19 Years Female Basketball and Volleyball PlayersAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNo ratings yet
- Campbell Biology 12th Edition SummaryDocument6 pagesCampbell Biology 12th Edition Summaryprincesje05No ratings yet
- 2 UMTS Radio Interface Physical LayerDocument56 pages2 UMTS Radio Interface Physical LayerKuldeep KashyapNo ratings yet
- Nephrotic Syndrome: By: Yeni Ayu Prihastuti Moderator: DR. Dr. Hani Susianti, SP - PK (K)Document42 pagesNephrotic Syndrome: By: Yeni Ayu Prihastuti Moderator: DR. Dr. Hani Susianti, SP - PK (K)yeniNo ratings yet
Esophageal Web Final
Esophageal Web Final
Uploaded by
adilOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Esophageal Web Final
Esophageal Web Final
Uploaded by
adilCopyright:
Available Formats
ABSTRACT
DISCUSSION
Esophageal webs are thin membranes located in the
Rings and webs are the most common structural
middle or upper esophagus. They are mainly observed
abnormalities in the esophagus. The terminology,
in the Plummer Vinson syndrome which is associated
pathogenesis, and treatment of these esophageal
with iron deficiency anemia. Its main symptoms are
lesions remain controversial. Esophageal rings usually
pain and difficulty in swallowing (odynophagia).
exist as a single lesion but can be multiple several
Esophageal webs are associated with bullous diseases names have been coined for when multiple rings are
(such as epidermolysis bullosa, pemphigus and bullous found in the esophagus, including multiple esophageal
pemphigoid) with graft versus host diseases involving rings or webs, congenital esophageal stenosis, ringed
the esophagus and with celiac diseases. esophagus, corrugated esophagus, and feline
A case of esophageal web is hereby presented esophagus.
manifesting as secondary candidial infection in 60 An esophageal web is a thin (2-3 mm), eccentric,
years old female with history of Dysphagia. smooth extension of normal esophageal tissue
consisting of mucosa and sub mucosa that can occur
INTRODUCTION
anywhere along the length of the esophagus but
Esophageal webs are thin 2-3mm membranes of
typically is located in the anterior postcricoid area of
normal esophageal tissue consisting of mucosa and sub
the proximal esophagus
mucosa. They can be congenital or acquired.
The pathophysiology of esophageal rings and webs is
Congenital webs commonly appear in the middle and
controversial. Several theories have been proposed for
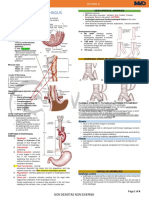
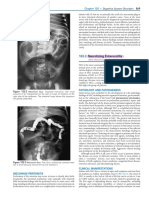
a) Barium swallow examination revealed esophageal web with
inferior third of esophagus and they are more likely to
associated narrowing and mucosal irregularity in the lower the formation of esophageal webs and rings. These
be circumferential with a central or eccentric orifice.
cervical and upper thoracic esophagus resembling neoplastic include etiologies related to congenital origin, iron
Acquired webs are much more common than congenital
lesion deficiency, development, inflammation, and
webs and typically appear in the cervical area (post-
autoimmunity.
Cricoid).
b) CT Scan showed circumferential narrowing of the proximal The true prevalence of esophageal rings and webs is
Esophageal webs are more common in whites and in unknown. In patients with dysphagia, esophageal webs
esophagus
women with a ratio of 2:1. can be found in 5-15% by barium radiography. Rings
CASE REPORT and webs have been identified in all age cohorts.
Patients do not typically become symptomatic until
A 60 years old Female patient presented with six-
after the age of 40
month history of progressive Dysphagia. It was more
Alarming symptoms that are not consistent with
for solids than liquids, episodic in nature with varying
esophageal rings are progressive dysphagia, weight
interval of freedom from symptoms. She also reported
loss, and anemia.
with weakness, fatigue, tachycardia and palpable
The association between iron deficiency and
thyroid gland. She also had significant weight loss.
esophageal webs is controversial. Chisholm and Jacobs
IMAGING STUDIES supported this association in 2 case series of 72 and
Ultra sound thyroid revealed multiple nodules in both 63 patients. However, a careful epidemiologic study by
the lobes. Findings were consistent of multi nodular Elwood failed to show a correlation between iron
goiter. Barium swallow showed segment of irregular deficiency and cervical esophageal webs. Less
narrowing at C7, D1 and D2 level. Mucosa appeared REFERENCES controversy is found between iron deficiency and
eroded and ulceration was seen at this level. Shelf like 3.Burdick JS, Venu RP, Hogan WJ: Cutting the defiant lower esophageal ring. Gastrointest Endosc 1993 Sep-Oct; dysphagia without webs. Iron deficiency clearly can
39(5): 616-9[Medline].
indentation seen at C6-7 level. After the barium study 4.Chen MY, Ott DJ, Donati DL, et al: Correlation of lower esophageal mucosal ring and lower esophageal sphincter
pressure. Dig Dis Sci 1994 Apr; 39(4): 766-9[Medline].
precede dysphagia. Chisholm and Bredenkamp et al
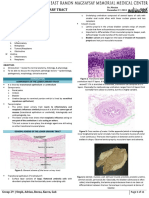
patient underwent Endoscopy twice and biopsy noted resolution of dysphagia but not webs after iron
7.Hirano I, Gilliam J, Goyal RK: Clinical and manometric features of the lower esophageal muscular ring. Am J
Gastroenterol 2000 Jan; 95(1): 43-9[Medline].
revealed diffuse infiltration by chronic inflammatory supplementation.
9.Hoover WB: The syndrome of anemia, glossitis, and dysphagia. N Engl J Med 1935; 213: 394-8.
cells. 2nd Biopsy confirmed that mucosal erosion and Barium swallow is the diagnostic test of choice and
ulceration was due to secondary candidial infection should be the initial test in patients with dysphagia.
You might also like
- CLILDocument14 pagesCLILcarlos alberto100% (2)
- Thierry Bardini. Junkware. The Essential Junkiness of Our Culture and BiologyDocument298 pagesThierry Bardini. Junkware. The Essential Junkiness of Our Culture and BiologyJulieta Yelin100% (1)
- Lab 08 Oracle Access Management - Access Manager 11G R2 Ps3 2 Legged Mobile OauthDocument39 pagesLab 08 Oracle Access Management - Access Manager 11G R2 Ps3 2 Legged Mobile OauthAshutosh NichatNo ratings yet
- Short Questions FMDocument21 pagesShort Questions FMsultanrana100% (1)
- Test Bank On GI PathologyDocument14 pagesTest Bank On GI PathologySeff CausapinNo ratings yet
- Gastro RobbinsDocument68 pagesGastro RobbinsAndrea PescosolidoNo ratings yet
- Diseases of The Esophagus DR Lapuz MCDDocument6 pagesDiseases of The Esophagus DR Lapuz MCDMiguel Cuevas Dolot100% (1)
- Pathology PracticalDocument20 pagesPathology Practicalisaungureanu88.iuNo ratings yet
- 5 Patho 1 - Lut - Dr. MesinaDocument11 pages5 Patho 1 - Lut - Dr. MesinaRobert Francis DikioNo ratings yet
- Srs Esophagus & Stomach: PathologyDocument4 pagesSrs Esophagus & Stomach: PathologyyayayanizaNo ratings yet
- The Appendix FinalDocument62 pagesThe Appendix FinalLajel S. LachicaNo ratings yet
- Benign Disease of The Esophagus PDFDocument4 pagesBenign Disease of The Esophagus PDFSpecialNameNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Congenital Genitourinary AbnormalitiesDocument4 pagesChapter 3 Congenital Genitourinary AbnormalitiesRem AlfelorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Congenital Genitourinary AbnormalitiesDocument4 pagesChapter 3 Congenital Genitourinary AbnormalitiesRemelou Garchitorena AlfelorNo ratings yet
- Sidhu 2002Document3 pagesSidhu 2002Yacine Tarik AizelNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Ultrasonographyin Small AnimalsDocument10 pagesAbdominal Ultrasonographyin Small AnimalsAna Clara SevasteNo ratings yet
- Digestive System AnatomyDocument3 pagesDigestive System AnatomyJo Marchianne PigarNo ratings yet
- 6.5 Small IntestineDocument6 pages6.5 Small IntestineRahimShah RahimNo ratings yet
- Approaches To Esophageal SuturesDocument7 pagesApproaches To Esophageal Suturestaner_soysurenNo ratings yet
- ZOO 1 SALAZAR ACT 5 TISSUES (Repaired)Document8 pagesZOO 1 SALAZAR ACT 5 TISSUES (Repaired)TORRES, EFRAIM MATTHEW S.No ratings yet
- Belizario ParasitologyDocument66 pagesBelizario Parasitologyangela tanteoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Bohn NodulesDocument3 pagesClinical Bohn NodulesMARIA KARINA HERNANDEZ PEREZNo ratings yet
- Validation Si and Li - 2016bDocument3 pagesValidation Si and Li - 2016byayayanizaNo ratings yet
- Pathology B - Gastrointestinal Tract (Esguerra, 2015) PDFDocument18 pagesPathology B - Gastrointestinal Tract (Esguerra, 2015) PDFJem QuintoNo ratings yet
- Pathology B - Gastrointestinal Tract (Esguerra, 2015)Document18 pagesPathology B - Gastrointestinal Tract (Esguerra, 2015)Ars MoriendiNo ratings yet
- Gi Tract Disorders (Infant)Document8 pagesGi Tract Disorders (Infant)Nicole Faylogna AgullanaNo ratings yet
- AMOEBIASISDocument11 pagesAMOEBIASISsrini9047No ratings yet
- Agenesis Atresia Fistula: Mechanical ObstructionDocument13 pagesAgenesis Atresia Fistula: Mechanical Obstructionnge257No ratings yet
- Ajcr 2010 1 6Document3 pagesAjcr 2010 1 6Muhammad Bilal MirzaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Other NematodesDocument7 pagesLesson 5 Other Nematodesshairene PiaNo ratings yet
- Folds of Peritoneum: Abdomen and PelvisDocument100 pagesFolds of Peritoneum: Abdomen and PelvissrisakthiNo ratings yet
- Cirugia Peds Fund TeoricosDocument12 pagesCirugia Peds Fund Teoricos[JC]No ratings yet
- Pediatric GI RadiologyDocument6 pagesPediatric GI Radiologysarguss14No ratings yet
- Clinical Approach To A Patient With Dysphagia: Medicine UpdateDocument3 pagesClinical Approach To A Patient With Dysphagia: Medicine UpdateAnonymous XFDJfsGviNo ratings yet
- Benign Esophageal Tumors: Esophagoscopy and Endoscopic Esophageal UltrasoundDocument7 pagesBenign Esophageal Tumors: Esophagoscopy and Endoscopic Esophageal UltrasoundYacine Tarik AizelNo ratings yet
- Canine and Feline Mega EsophagusDocument10 pagesCanine and Feline Mega Esophagustaner_soysurenNo ratings yet
- Dysphagia: Ethan A. Mezoff, MDDocument5 pagesDysphagia: Ethan A. Mezoff, MDYenny FramelaNo ratings yet
- Fasciolopsis Buski - An Overview - ScienceDirect TopicsDocument13 pagesFasciolopsis Buski - An Overview - ScienceDirect TopicsRadeat GetiyeNo ratings yet
- 09c6 PDFDocument8 pages09c6 PDFlusitania IkengNo ratings yet
- A Rare Case of Fatal Bowel Obstruction Secondary To A Colonic BezoarDocument3 pagesA Rare Case of Fatal Bowel Obstruction Secondary To A Colonic BezoarLannydchandraNo ratings yet
- Git Trans-Oral Cavity To StomachDocument6 pagesGit Trans-Oral Cavity To StomachHanako Sasaki AranillaNo ratings yet
- Intestinal ObstructionDocument70 pagesIntestinal ObstructionosNo ratings yet
- Tubal Assessment and TuBAL SURGERYDocument15 pagesTubal Assessment and TuBAL SURGERYRyan IlhamNo ratings yet
- 'Aliah's GIT & HB Systems1Document39 pages'Aliah's GIT & HB Systems1Luqman Al-Bashir FauziNo ratings yet
- Digestive System LecDocument13 pagesDigestive System LecMikaella ViadorNo ratings yet
- NCM107 PediatricsDocument11 pagesNCM107 PediatricsKM PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Management of Velopharyngeal DysfunctionDocument8 pagesDiagnosis and Management of Velopharyngeal Dysfunctiondrgurpal74No ratings yet
- Git Radiology and ImagingDocument4 pagesGit Radiology and Imagingoddone_outNo ratings yet
- Kleitsch 1958Document6 pagesKleitsch 1958CojocariNo ratings yet
- RLQ PainDocument20 pagesRLQ PainBEATRICE SOPHIA PARMANo ratings yet
- Jurnal Inter OrganDocument8 pagesJurnal Inter Organdyah sekar pratiwiNo ratings yet
- PathologyDocument8 pagesPathologyJemimah Tomarong DespabeladeroNo ratings yet
- Mini Review: Current Concepts in The Management of Anterior Urethral StricturesDocument8 pagesMini Review: Current Concepts in The Management of Anterior Urethral StricturesDwi WiraNo ratings yet
- Imaging Intestinal ObstructionDocument5 pagesImaging Intestinal Obstructionludiegues752No ratings yet
- Imaging of AbdominalDocument15 pagesImaging of AbdominalSpecialNameNo ratings yet
- Necrotizing Enterocolitis: Pathology and PathogenesisDocument3 pagesNecrotizing Enterocolitis: Pathology and PathogenesisJemarey DeramaNo ratings yet
- Block Vii Module 1 Cheat Sheet PDFDocument32 pagesBlock Vii Module 1 Cheat Sheet PDFMark FuerteNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Management of Esophageal Rings and WebsDocument4 pagesDiagnosis and Management of Esophageal Rings and WebsIt's MeNo ratings yet
- Gastroenterology:: Motility Disorders of Esophagus, GERDDocument46 pagesGastroenterology:: Motility Disorders of Esophagus, GERDPatricia May CruzNo ratings yet
- 2 - Intestinal Obstruction. IntussusceptionDocument27 pages2 - Intestinal Obstruction. IntussusceptionNaimenur KorkmazNo ratings yet
- UNCDCYSTDocument5 pagesUNCDCYSTeviltohuntNo ratings yet
- Appendix DuplicationDocument3 pagesAppendix DuplicationMario TrejoNo ratings yet
- Esophageal & Hepato CA Half PDFDocument6 pagesEsophageal & Hepato CA Half PDFhtt.pNo ratings yet
- Treatise on the Anatomy and Physiology of the Mucous Membranes: With Illustrative Pathological ObservationsFrom EverandTreatise on the Anatomy and Physiology of the Mucous Membranes: With Illustrative Pathological ObservationsNo ratings yet
- Sarah Phillips: Dually Certified K-6 Teacher Contact Professional ProfileDocument2 pagesSarah Phillips: Dually Certified K-6 Teacher Contact Professional Profileapi-420172483No ratings yet
- Assignment On InflationDocument7 pagesAssignment On InflationKhalid Mahmood100% (4)
- Asem0909 PDFDocument14 pagesAsem0909 PDFTROY2ARCHILLESNo ratings yet
- Job Mismatch in The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesJob Mismatch in The Philippinesjovelyn c. aronNo ratings yet
- MPS-blank Template Production SchedulingDocument8 pagesMPS-blank Template Production SchedulingSaesaeNo ratings yet
- Write The Days in The Correct OrderDocument7 pagesWrite The Days in The Correct OrderRuth Yánez PadillaNo ratings yet
- Michelangelo Research Paper OutlineDocument4 pagesMichelangelo Research Paper Outlinecampsxek100% (1)
- Clock Arithmetic Aptitude Question With AnswersDocument4 pagesClock Arithmetic Aptitude Question With AnswersOpt TutorNo ratings yet
- Ocr A-Level History Coursework DeadlineDocument8 pagesOcr A-Level History Coursework Deadlinelozuzimobow3100% (2)
- Bloodborne Top-Tier Farmable Gem ChalicesDocument2 pagesBloodborne Top-Tier Farmable Gem ChalicesJose MedinaNo ratings yet
- "Analysis of Marketing Strategies of Nestle Maggi: Winter ReportDocument51 pages"Analysis of Marketing Strategies of Nestle Maggi: Winter ReportAnonymous PbMgeIvKNo ratings yet
- IELTS MASTER - IELTS Reading Test 3Document1 pageIELTS MASTER - IELTS Reading Test 3poon isaacNo ratings yet
- TEP Course FileDocument22 pagesTEP Course FilemohsinpakistanNo ratings yet
- Research Design MBA MK02 UNIT IIDocument15 pagesResearch Design MBA MK02 UNIT IIAmit Kumar100% (3)
- Towards A Meta-Theory of Accounting Information SystemsDocument15 pagesTowards A Meta-Theory of Accounting Information SystemsAhmed KhalafNo ratings yet
- Superstar Stamina How To Get Hard and Stay Hard GET YOUR BODY INTO SHAPE SO YOU'LL LOVE ITDocument78 pagesSuperstar Stamina How To Get Hard and Stay Hard GET YOUR BODY INTO SHAPE SO YOU'LL LOVE ITdominique marshallNo ratings yet
- EUROKLAV-29VS+ ManualDocument58 pagesEUROKLAV-29VS+ ManualpagulahaNo ratings yet
- Hapter 10 BistikDocument2 pagesHapter 10 BistikAhmad Rofi100% (1)
- Presentation Class InglishDocument16 pagesPresentation Class Inglishmiralis gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Grumpy Bear: Some Questions ..Document2 pagesGrumpy Bear: Some Questions ..Mike BNo ratings yet
- Benefits of EDTA Chelation Therapy in Arterioscler PDFDocument11 pagesBenefits of EDTA Chelation Therapy in Arterioscler PDFNéstor Mata RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Sales Rep. / Sales ManagerDocument3 pagesSales Rep. / Sales Managerapi-121455688No ratings yet
- A Comparative Study On Selected Fitness Components of 13-19 Years Female Basketball and Volleyball PlayersDocument11 pagesA Comparative Study On Selected Fitness Components of 13-19 Years Female Basketball and Volleyball PlayersAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNo ratings yet
- Campbell Biology 12th Edition SummaryDocument6 pagesCampbell Biology 12th Edition Summaryprincesje05No ratings yet
- 2 UMTS Radio Interface Physical LayerDocument56 pages2 UMTS Radio Interface Physical LayerKuldeep KashyapNo ratings yet
- Nephrotic Syndrome: By: Yeni Ayu Prihastuti Moderator: DR. Dr. Hani Susianti, SP - PK (K)Document42 pagesNephrotic Syndrome: By: Yeni Ayu Prihastuti Moderator: DR. Dr. Hani Susianti, SP - PK (K)yeniNo ratings yet