Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Other Construction Projects
Other Construction Projects
Uploaded by
ambipathiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Other Construction Projects
Other Construction Projects
Uploaded by
ambipathiCopyright:
Available Formats
Other Construction Projects
Chapter 18
Highways (Pg 383)
Flexible Roadway Sub grade (Packed Soil) Sub base (Sand or gravel) Pavement (Asphalt Layer.
Rigid Roadway Sub grade (Packed Soil) Sub base (Sand or Gravel) Steel Bars Pavement (Concrete)
Substructure of Bridges
Abutments -are the supports at the end of the bridge. Piers Vertical structural supports placed between abutments in longer bridges Span The distance between each pier is called a span. Piles A solid base that the piers rest on.
Piles
7 Types of Bridges
Beam Bridge Arch Bridge Truss Bridge Cantilever Bridge Suspension Bridge Cable-Stayed Bridge Movable Bridge.
Beam Bridge
Piers support beams that support spans of reinforced concrete slabs. This is the most frequently used type of bridge because it is normally least expensive.
Arch Bridge
The load of the bridge is transferred along the arch to the abutments or piers at the end of the arch.
Truss Bridge
Trusses may be used above or below the roadway to support the bridge.
Cantilever Bridge
Beams called cantilevers extend from each end of the bridge. They are connected by a section called a suspended span.
Suspension Bridge
These have two tall towers that support main cables that run the entire length of the bridge.
Cable-Stayed Bridge
These are similar to suspension bridges except the cables are connected directly to the roadway.
Movable Bridge
These bridges are designed so that a portion of the roadway can be moved to allow large water vessels to pass underneath.
Dams
A dam is a structure that is placed across a river to control or block the flow of water. A reservoir is a lake in which water is stored for use. Dams may be made of earth, concrete, steel, masonry, or wood.
Dams
Embankment blocks the flow of water. Outlet Works used to control the flow of water through or around the dam. Spillway acts as a safety valve that allows excess water to bypass the dam when it becomes too full. Cofferdams Temporary watertight walls.
Canals
Irrigation Canals Carries water from a place where water is plentiful to another place where water is needed. Navigation Canals Connects two bodies of water. Construction of a canal requires earth moving. Navigation canals may also require the construction of locks if the two waterways being connected are at different elevations. A lock is an enclosed part of the canal that is equipped with a gate.
Canal Lock
Three Types of Tunnels
Earth are constructed in soil or sand. These are hazardous to build because soil can be unstable. Immersed pre-manufactured sections are floated to the tunnel site. The sections are connected. Rock blasting away material or by using a giant boring machine. Conveyors carry out rock and the tunnels are formed.
Pipelines
Are an efficient way to transport products such as crude oil, refined petroleum, and natural gas. Most pipelines are buried underground.
Air-Supported Structure
There is no frame or load-bearing wall to support the roof. Air pressure supplied by a fan supports the walls and the roof.
Review
Surveying, earthmoving, and paving are used to build roads and highways. Types of bridges included beam, arch, truss, cantilever, suspension, cable stayed, and movable Dams provide a dependable water supply, help control flooding, and provide hydroelectricity.
Review
Canals are built for navigation or irrigation and may require locks. The three main types of tunnels are earth, immersed, and rock. Most pipelines are buried underground, with only the pumping stations above ground. Air-supported structures consist of a structural membrane supported by air pressure.
You might also like
- Suspension Bridge ReportDocument36 pagesSuspension Bridge ReportRam Pathak50% (6)
- Design of Bridges NotesDocument48 pagesDesign of Bridges Notesrahatul bashir100% (2)
- Methods of Analysis and Design of Boxbeams - Maisall, RollDocument2 pagesMethods of Analysis and Design of Boxbeams - Maisall, RollkolnabNo ratings yet
- R C C Bridge Design PDFDocument65 pagesR C C Bridge Design PDFshaik sadik100% (1)
- Bridge Engineering ReviewerDocument13 pagesBridge Engineering ReviewerChristine JoyNo ratings yet
- BridgeDocument9 pagesBridgeMuhammad Tajammul KhalidNo ratings yet
- Culverts: Submitted To-Mr - Vikas Srivastava SIRDocument25 pagesCulverts: Submitted To-Mr - Vikas Srivastava SIRsarthak mishraNo ratings yet
- Construction of Dam (Case Study)Document57 pagesConstruction of Dam (Case Study)Vivek YadavNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic TermsDocument5 pagesHydraulic TermsJuan FierroNo ratings yet
- Materials For Culvert ConstructionDocument4 pagesMaterials For Culvert ConstructionDeekshit Reddy100% (1)
- Suspension BridgesDocument5 pagesSuspension BridgesEng. Amodhya VikumshanNo ratings yet
- University of GondarDocument171 pagesUniversity of Gondaralamrew siyoum80% (5)
- Classification of BridgesDocument36 pagesClassification of BridgesNongthombam Tompok Singh-34No ratings yet
- Bridge ConstructionDocument33 pagesBridge ConstructionVivekChaudhary100% (3)
- BridgesDocument4 pagesBridgesRonit ChariNo ratings yet
- Suspension BridgeDocument39 pagesSuspension Bridgeayushj100% (2)
- Suspension Bridge: A Project Seminar ReportDocument30 pagesSuspension Bridge: A Project Seminar ReportayushjNo ratings yet
- Bridge EngineeringDocument16 pagesBridge EngineeringJoson Anquillano Villegas100% (1)
- Collet Photographs of Different Types of Bridges and Tunnels Frome SiteDocument18 pagesCollet Photographs of Different Types of Bridges and Tunnels Frome SiteHarish Patil100% (3)
- Suspension BridgeDocument30 pagesSuspension BridgeakashNo ratings yet
- Bridges: Structure Span Body of Water Valley RoadDocument19 pagesBridges: Structure Span Body of Water Valley RoadpandiyanNo ratings yet
- Cable Stayed BridgeDocument27 pagesCable Stayed BridgeRushabh Jain100% (1)
- GEOLOGY For ENGG - BridgesAssignmentDocument4 pagesGEOLOGY For ENGG - BridgesAssignmentIrish Sophia OlimpoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 B Bridge ConstructionDocument36 pagesLecture 9 B Bridge ConstructionramNo ratings yet
- Research 7Document3 pagesResearch 7jacobsimon navarroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document3 pagesChapter 1shaik saifulla lNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Suspension BridgeDocument48 pagesSeminar On Suspension Bridgeharinandan18100% (1)
- ChapterDocument7 pagesChapterAbdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- 1-Introduction To BridgesDocument94 pages1-Introduction To BridgesMANUPRIYA MANUPRIYANo ratings yet
- A Bridge Is A Structure Providing Passage Over An Obstacle Without Closing The Way BeneathDocument16 pagesA Bridge Is A Structure Providing Passage Over An Obstacle Without Closing The Way Beneathsaqib mujtaba100% (1)
- Constructon A DamDocument14 pagesConstructon A DamYusf RwandzyNo ratings yet
- Auxillo Ulo Week1-3Document8 pagesAuxillo Ulo Week1-3JOYLYN CRIS AUXILLONo ratings yet
- Type of BridgesDocument7 pagesType of BridgesAnesa SarkicNo ratings yet
- Types of BridgesDocument16 pagesTypes of Bridgesnil sutarNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report On Suspension Bridge: Submitted By:-Ashis Kumar Jain 0601220299, 7 SemDocument25 pagesSeminar Report On Suspension Bridge: Submitted By:-Ashis Kumar Jain 0601220299, 7 SemLawrence ConananNo ratings yet
- BridgeDocument5 pagesBridgeVICCES ESTRADANo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document10 pagesAssignment 1Francis Jem ReyesNo ratings yet
- Suspension BridgeDocument32 pagesSuspension Bridgesai kiranNo ratings yet
- Engineering PDFDocument19 pagesEngineering PDFSheena FarinasNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgement: Kobe Danielle B. Jebulan CE-5ADocument19 pagesAcknowledgement: Kobe Danielle B. Jebulan CE-5ASheena FarinasNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Bridge EngineeringDocument46 pagesIntroduction To Bridge Engineering21-06580No ratings yet
- Bridge EngineeringDocument25 pagesBridge EngineeringAnubhav Chaudhary100% (1)
- 15 CV 741Document48 pages15 CV 741Suman NakarmiNo ratings yet
- Classification and Criteria For BridgesDocument23 pagesClassification and Criteria For BridgesEulecris MartinNo ratings yet
- ARCH BRIDGE-The Romans Built More Than 1,000 Stone Arch Bridges, Some of Which Still Survive, SuchDocument9 pagesARCH BRIDGE-The Romans Built More Than 1,000 Stone Arch Bridges, Some of Which Still Survive, SuchRenielle Mae Marquez VerdeNo ratings yet
- Ceng 7509. Bridge Engineering: Dr. John, Me, Mba, PHD, Ce, Mie, FivDocument80 pagesCeng 7509. Bridge Engineering: Dr. John, Me, Mba, PHD, Ce, Mie, FivTesfamichael Abathun100% (1)
- UNIT 3 - Bridge EnggDocument29 pagesUNIT 3 - Bridge EnggVishalNo ratings yet
- Harsh PresentationDocument13 pagesHarsh PresentationHARSH DAMAHENo ratings yet
- Suspension Bridge: Abstract: Bridge Is A Structure Built To Span Across A Valley, RoadDocument6 pagesSuspension Bridge: Abstract: Bridge Is A Structure Built To Span Across A Valley, RoadSheffy AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Bridge-EngineeringDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Bridge-EngineeringkiminyawaNo ratings yet
- Lecture of Civil EngineeringDocument52 pagesLecture of Civil EngineeringhassanNo ratings yet
- Course Outline: Amit Kumar Varma Geotechnical Engineer Department of RoadDocument5 pagesCourse Outline: Amit Kumar Varma Geotechnical Engineer Department of RoadVarma AmitNo ratings yet
- Bridge EngineeringDocument10 pagesBridge EngineeringLaeek PatelNo ratings yet
- Description Bridges: Descripción de Un PuentesDocument9 pagesDescription Bridges: Descripción de Un PuentesJennifer C RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Fixed or Movable BridgesDocument5 pagesFixed or Movable BridgesNur Fatmala100% (1)
- My Project Work RepDocument55 pagesMy Project Work Repshaik saifulla lNo ratings yet
- TP Proprement DiteDocument9 pagesTP Proprement DitejosuéNo ratings yet
- BRIDGESDocument14 pagesBRIDGEScollins rutoNo ratings yet
- Aashto:: Truss BridgeDocument5 pagesAashto:: Truss BridgeSajjad Amin AminNo ratings yet
- DamsDocument10 pagesDamsJosef OmuneNo ratings yet
- Building Landmarks - Bridges, Tunnels and Buildings - Architecture and Design | Children's Engineering BooksFrom EverandBuilding Landmarks - Bridges, Tunnels and Buildings - Architecture and Design | Children's Engineering BooksNo ratings yet
- Check List For The Confirmation of Ph.D. ScholarDocument1 pageCheck List For The Confirmation of Ph.D. ScholarambipathiNo ratings yet
- Civil Master Updated 31.12.14Document6 pagesCivil Master Updated 31.12.14ambipathiNo ratings yet
- Staff Duty List Model ExamDocument1 pageStaff Duty List Model ExamambipathiNo ratings yet
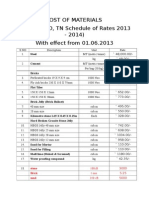
- Cost of MaterialsDocument2 pagesCost of MaterialsambipathiNo ratings yet
- Unit - 03Document21 pagesUnit - 03ambipathiNo ratings yet
- CE2405 Manual FinalDocument56 pagesCE2405 Manual Finalambipathi50% (2)
- Retest SCHDocument1 pageRetest SCHambipathiNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis II 2marksDocument17 pagesStructural Analysis II 2marksvik1510No ratings yet
- Department of Civil EngineeringDocument2 pagesDepartment of Civil EngineeringambipathiNo ratings yet
- Each Question Carry 14 MarksDocument2 pagesEach Question Carry 14 MarksambipathiNo ratings yet
- Deflection Monitoring of Prestressed Concrete Bridges Retrofitted by External Post-TensioningDocument8 pagesDeflection Monitoring of Prestressed Concrete Bridges Retrofitted by External Post-TensioningIndra MishraNo ratings yet
- Sado Full Paper FinalDocument8 pagesSado Full Paper Finalrax dearNo ratings yet
- Designing and Constructing Prestressed BridgesDocument235 pagesDesigning and Constructing Prestressed Bridgesjavier CondeNo ratings yet
- Reason Behind Failure of Central Hinge Bearings Modifications Proposed in The Central Hinge Bearings of The Mahatma Gandhi Setu in Patna by I.N. MishraDocument8 pagesReason Behind Failure of Central Hinge Bearings Modifications Proposed in The Central Hinge Bearings of The Mahatma Gandhi Setu in Patna by I.N. MishraIndra Nath MishraNo ratings yet
- Balanced Cantilever Construction of Precast Segmental Bridges - BridgeTechDocument8 pagesBalanced Cantilever Construction of Precast Segmental Bridges - BridgeTechSilvio CarrilloNo ratings yet
- (2022) Dywidag Form Traveller - KAR - 110722Document103 pages(2022) Dywidag Form Traveller - KAR - 110722Perentjana DjajaNo ratings yet
- Bridges-Lecture Notes PDFDocument49 pagesBridges-Lecture Notes PDFمحمدلحلوحNo ratings yet
- Minimizing Construction Problems in Segmentally Precast Box Girder Bridges PDFDocument285 pagesMinimizing Construction Problems in Segmentally Precast Box Girder Bridges PDFAditya PratamaNo ratings yet
- Iamhai Report of Balanced Cantilever BridgeDocument97 pagesIamhai Report of Balanced Cantilever BridgeAn PhạmNo ratings yet
- l2 BridgeDocument65 pagesl2 Bridge林诗莹No ratings yet
- Erd of Bridges and Concrete Dams: Dr. Saurabh ShiradhonkarDocument66 pagesErd of Bridges and Concrete Dams: Dr. Saurabh ShiradhonkarAnubhav ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Bridge Construction MethodsDocument107 pagesBridge Construction MethodsHendra Ginting75% (12)
- Semester: - 4 Name of Faculty: - Ms Chaya Zende. Topic: - Collect Photographs of Different Types of BridgesDocument9 pagesSemester: - 4 Name of Faculty: - Ms Chaya Zende. Topic: - Collect Photographs of Different Types of BridgesVT7VedNo ratings yet
- Irc Amendments Jan 2019Document31 pagesIrc Amendments Jan 2019Shaik Bademiya100% (2)
- Bridge Across Zuari River: A Boon To Goa: R. RamakrishnanDocument3 pagesBridge Across Zuari River: A Boon To Goa: R. RamakrishnansuheilbugsNo ratings yet
- Andaman MethodologyDocument10 pagesAndaman MethodologySK SwainNo ratings yet
- Developments in Bridge DesignDocument14 pagesDevelopments in Bridge DesignchandrasekarNo ratings yet
- Precast Segmental Box Girder Bridge ManualDocument122 pagesPrecast Segmental Box Girder Bridge ManualMohamed Talat Ramadan100% (4)
- Bridge EnggDocument29 pagesBridge EnggSuresh KomurajuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Design ConsiderationsDocument34 pagesChapter 4: Design ConsiderationsAnonymous b9fkTYfEoRNo ratings yet
- Ce 412Document99 pagesCe 412jules100% (2)
- Bridge Construction MethodsDocument34 pagesBridge Construction MethodsAbhishek KoulNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Part 1Document167 pagesUnit 5 Part 1Kaushal MehtaNo ratings yet
- Segmental Bridges Cost DataDocument8 pagesSegmental Bridges Cost DataShikhar SinghNo ratings yet
- Full Thesis PDFDocument89 pagesFull Thesis PDFKaushiki KambojNo ratings yet
- Corbel Hinge Box Girder ConcreteDocument18 pagesCorbel Hinge Box Girder ConcreteAdamNo ratings yet