Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Transmission Media: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Transmission Media: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Uploaded by
Omer ArshadCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- AWEUD n258 DataSheetDocument2 pagesAWEUD n258 DataSheettalox0% (1)
- Radar Cheat SheetDocument12 pagesRadar Cheat SheetEng-Sa'di Y. Tamimi100% (1)
- Forouzan chp7Document31 pagesForouzan chp7Aniket MehtaNo ratings yet
- Transmission Media: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004Document31 pagesTransmission Media: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004Keyur MahantNo ratings yet
- Transmission Media: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004Document31 pagesTransmission Media: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004Ralph Jayson SilangNo ratings yet
- Radio Over Fiber & WCDMADocument33 pagesRadio Over Fiber & WCDMASyed Shahzaib RazaNo ratings yet
- CH - 02 - 2 Transmissional MediaDocument37 pagesCH - 02 - 2 Transmissional MediascorpionNo ratings yet
- Radio Over Fiber TechnologyDocument46 pagesRadio Over Fiber TechnologySyed Shahzaib RazaNo ratings yet
- MWC2013 Backhaul ReportDocument16 pagesMWC2013 Backhaul ReportMarko BileNo ratings yet
- Wang 2020 IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 790 012014Document9 pagesWang 2020 IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 790 012014Malik Talha SaadNo ratings yet
- Deployment of 5G Network For Efficient Spectrum Utilization in Alakahia, Rivers StateDocument10 pagesDeployment of 5G Network For Efficient Spectrum Utilization in Alakahia, Rivers StateMustafa NyazNo ratings yet
- 5G Over-The-Air Performance Measurement: and Evaluation Using Fieldfox Handheld AnalyzersDocument18 pages5G Over-The-Air Performance Measurement: and Evaluation Using Fieldfox Handheld AnalyzersHuicheng YuNo ratings yet
- SDRs For Mmwave in 5G TechnologyDocument5 pagesSDRs For Mmwave in 5G TechnologyArun KumarNo ratings yet
- 5G Over-the-Air Performance Measurement and Evaluation Using FieldFox Handheld AnalyzersDocument15 pages5G Over-the-Air Performance Measurement and Evaluation Using FieldFox Handheld AnalyzerschristiancandidoNo ratings yet
- Beamforming For 5G MM Wave Networks at Quadrature Baseband and RF Using OFDM SignalinDocument8 pagesBeamforming For 5G MM Wave Networks at Quadrature Baseband and RF Using OFDM SignalinInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- 5G Over-the-Air PerformanceDocument15 pages5G Over-the-Air PerformanceMarian VerdeNo ratings yet
- New Final Doc 1Document13 pagesNew Final Doc 1Akhilesh UppulaNo ratings yet
- Telecom SpectrumDocument6 pagesTelecom SpectrumNikhil MunjalNo ratings yet
- 7 Millimeter Wave Antenna Design For 5G ApplicationsDocument18 pages7 Millimeter Wave Antenna Design For 5G ApplicationsDjelloul AISSAOUINo ratings yet
- 3G Overview: ZTE University TD&W&PCS BSS Course TeamDocument42 pages3G Overview: ZTE University TD&W&PCS BSS Course TeamshishirNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis of Physical Layer of Wimax System Using SimulinkDocument5 pagesPerformance Analysis of Physical Layer of Wimax System Using SimulinkKurt Mk-JimNo ratings yet
- The Next Wireless Wave Is A Millimeter Wave: August 2007Document13 pagesThe Next Wireless Wave Is A Millimeter Wave: August 2007Nguyen Binh DuongNo ratings yet
- JEEE 3485 FinalDocument14 pagesJEEE 3485 Finalwotangoabush80No ratings yet
- Deployment of Mobile WimaxDocument6 pagesDeployment of Mobile WimaxsaintdevilzNo ratings yet
- A CDL-Based Channel Model With Dual-Polarized Antennas For 5G MIMO Systems in Rural Remote AreasDocument14 pagesA CDL-Based Channel Model With Dual-Polarized Antennas For 5G MIMO Systems in Rural Remote AreaspruxmanNo ratings yet
- DroneeDocument11 pagesDroneePedro VillarroelNo ratings yet
- BER AND PAPR ANALYSIS OF 8X8 MIMO OFDM SYSTEM - USING SLM TECHNIQUE - Thesis - M.Tech PDFDocument82 pagesBER AND PAPR ANALYSIS OF 8X8 MIMO OFDM SYSTEM - USING SLM TECHNIQUE - Thesis - M.Tech PDFabdul.azeezNo ratings yet
- ctngc1015 PDFDocument5 pagesctngc1015 PDFAhmed Salah MohmedNo ratings yet
- 3G Over SatelliteDocument6 pages3G Over Satellitegamer08No ratings yet
- Metering Article Dec06Document3 pagesMetering Article Dec06SujokoTeeNo ratings yet
- Use of C-Band Spectrum For Mobile Broadband in Cities: London and ShenzhenDocument32 pagesUse of C-Band Spectrum For Mobile Broadband in Cities: London and ShenzhenArsalan Badar WastiNo ratings yet
- Propagation Channel Characterization For PDFDocument6 pagesPropagation Channel Characterization For PDFDrAbdallah NasserNo ratings yet
- Modulation Formats For Beyond-100Gbps Ethernet Optical Links - A Review of ResearchDocument4 pagesModulation Formats For Beyond-100Gbps Ethernet Optical Links - A Review of ResearchVijay JanyaniNo ratings yet
- White Paper: A Comparison of Two Fourth Generation Technologies: Wimax and 3Gpp-LteDocument3 pagesWhite Paper: A Comparison of Two Fourth Generation Technologies: Wimax and 3Gpp-LteMuhammad Bilal JunaidNo ratings yet
- Table of ContentsDocument1 pageTable of ContentsphotonicsmattNo ratings yet
- Dimensioning GSM/GPRS Networks For Circuit-And Packet-Switched ServicesDocument6 pagesDimensioning GSM/GPRS Networks For Circuit-And Packet-Switched ServicesKhandker Md SayerNo ratings yet
- Dimensioning of GPRS NetworkDocument6 pagesDimensioning of GPRS NetworkShefrin MohamedNo ratings yet
- 5G For Broadcasters - New Opportunities For Distribution and ContentDocument12 pages5G For Broadcasters - New Opportunities For Distribution and Contentander20xNo ratings yet
- TelecommunicationDocument1 pageTelecommunicationarvindranganathanNo ratings yet
- Re-Assignment of 3G Spectrum and The Spectrum Utilisation FeeDocument5 pagesRe-Assignment of 3G Spectrum and The Spectrum Utilisation Feewilly cNo ratings yet
- Wireless Evolution With 4G Technologies: Prof. D. U. Adokar, Priti J. RajputDocument11 pagesWireless Evolution With 4G Technologies: Prof. D. U. Adokar, Priti J. RajputNebiye SolomonNo ratings yet
- 1 20080902 - A-MAS-3i - For - Enhanced - HSDPA - Data - Rates PDFDocument11 pages1 20080902 - A-MAS-3i - For - Enhanced - HSDPA - Data - Rates PDFMohammad Abdullah Al MamunNo ratings yet
- Selection of Voip Codecs For Different Networks Based On Qos AnalysisDocument7 pagesSelection of Voip Codecs For Different Networks Based On Qos Analysiswaty5340No ratings yet
- Evolution of Mobile Technology and Business Models: Su-En TanDocument19 pagesEvolution of Mobile Technology and Business Models: Su-En Tanszi1979No ratings yet
- Sensors: Experimental Demonstration of Mmwave Vehicle-To-Vehicle Communications Using Ieee 802.11adDocument22 pagesSensors: Experimental Demonstration of Mmwave Vehicle-To-Vehicle Communications Using Ieee 802.11adlaeeeqNo ratings yet
- Interference Problem Between ZigBee and PDFDocument6 pagesInterference Problem Between ZigBee and PDFghadeer alkhodrNo ratings yet
- WiMax Vs 3G Mobile CommunicationDocument24 pagesWiMax Vs 3G Mobile CommunicationMohammed Hanafy AliNo ratings yet
- BSNLDocument112 pagesBSNLishu_sood6789100% (1)
- Mid Band Spectrum and The Co Existence With Radio AltimetersDocument33 pagesMid Band Spectrum and The Co Existence With Radio AltimetersYo AcaNo ratings yet
- 5G BeamformingDocument88 pages5G BeamformingMahamod IsmailNo ratings yet
- 4G & 5G Technologies: ResearchDocument7 pages4G & 5G Technologies: Researchusama darNo ratings yet
- Lawful Interception For 3G Networks White Paper: November, 2005 Aqsacom Document No. 040450Document23 pagesLawful Interception For 3G Networks White Paper: November, 2005 Aqsacom Document No. 040450imranq_3No ratings yet
- 5G Semiconductor Test WP enDocument37 pages5G Semiconductor Test WP enGeoffrey AlleyneNo ratings yet
- Gigabit Wireless Communications Using Mm-Wave CircuitsDocument39 pagesGigabit Wireless Communications Using Mm-Wave Circuitsjamessabraham2No ratings yet
- Eurofins E E Wireless News Update in Nov 1701282787Document6 pagesEurofins E E Wireless News Update in Nov 1701282787rohitnanwaniNo ratings yet
- Study of 3G TechnologyDocument7 pagesStudy of 3G TechnologyPooja Bidwai ShirpewarNo ratings yet
- 12 Spectrum - 5G Mobile and Wireless Communications TechnologyDocument15 pages12 Spectrum - 5G Mobile and Wireless Communications TechnologySornagopal VijayaraghavanNo ratings yet
- 5G: New Air Interface and Radio Access Virtualization: Huawei White Paper Ȕ April 2015Document11 pages5G: New Air Interface and Radio Access Virtualization: Huawei White Paper Ȕ April 2015Anonymous EmLpNr6No ratings yet
- 01 Overview of Broadband CommunicationsDocument51 pages01 Overview of Broadband CommunicationsAimNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Network Planning and Optimisation 2G/3G/4G: Evolution to 5GFrom EverandFundamentals of Network Planning and Optimisation 2G/3G/4G: Evolution to 5GNo ratings yet
- Optical Fiber Telecommunications Volume VIB: Systems and NetworksFrom EverandOptical Fiber Telecommunications Volume VIB: Systems and NetworksNo ratings yet
- Mushaf by Nimra AhmadDocument493 pagesMushaf by Nimra AhmadOmer Arshad100% (6)
- Led Highbay Light-hbl50-200w-03-Ta-spec-A1 - PhlipsDocument4 pagesLed Highbay Light-hbl50-200w-03-Ta-spec-A1 - PhlipsOmer ArshadNo ratings yet
- ENGIN112 L5: Boolean Algebra September 12, 2003Document18 pagesENGIN112 L5: Boolean Algebra September 12, 2003Omer ArshadNo ratings yet
- Network Devices: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004Document20 pagesNetwork Devices: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004Omer ArshadNo ratings yet
- Binary Adders and Subtractors: ENGIN112 L14: Binary Adder Subtractor October 3, 2003Document16 pagesBinary Adders and Subtractors: ENGIN112 L14: Binary Adder Subtractor October 3, 2003Omer ArshadNo ratings yet
- Computer-Aided Engineering Drawing: 1. Getting StartedDocument36 pagesComputer-Aided Engineering Drawing: 1. Getting StartedOmer ArshadNo ratings yet
- Huawei Improve SDSRDocument9 pagesHuawei Improve SDSRAhmadArwani88No ratings yet
- Ch1-Handover Strategies in GSM - ModDocument41 pagesCh1-Handover Strategies in GSM - ModSoha FarhatNo ratings yet
- Integrated Circuits Lab: Experiment #3 Low Pass and High Pass Filters I ObjectivesDocument9 pagesIntegrated Circuits Lab: Experiment #3 Low Pass and High Pass Filters I Objectivesanimesh pariharNo ratings yet
- Amphenol 5964300GDocument5 pagesAmphenol 5964300Gklamar5No ratings yet
- Data Sheet: Performance-Optimized 802.11ac Dual-Radio 3x3:3 Access PointDocument6 pagesData Sheet: Performance-Optimized 802.11ac Dual-Radio 3x3:3 Access PointKléber Cruz SánchezNo ratings yet
- GSM Optimization and TroubleshootingDocument109 pagesGSM Optimization and TroubleshootingRockman CoolNo ratings yet
- UV1316Document20 pagesUV1316andrei8411No ratings yet
- Fitch - The-Superheterodyne-BookDocument70 pagesFitch - The-Superheterodyne-BookmplennaNo ratings yet
- Microwave Devices Directional Coupler and Isolator: E. Cinthuriya - Me - Communication EngineeringDocument23 pagesMicrowave Devices Directional Coupler and Isolator: E. Cinthuriya - Me - Communication EngineeringShwetaNo ratings yet
- Power Line Carrier: CommunicationDocument66 pagesPower Line Carrier: Communicationmani_2010nairNo ratings yet
- Ckt-Odv065r14b17k-B DS 0-0-1Document2 pagesCkt-Odv065r14b17k-B DS 0-0-1АлександрNo ratings yet
- DF-A0134 Version 1.1Document2 pagesDF-A0134 Version 1.1Mostafa hdghNo ratings yet
- CEPT Novice 1Document26 pagesCEPT Novice 1Ster RncNo ratings yet
- 80M VerticalDocument3 pages80M Verticalmuli100% (1)
- Meraki Datasheet Antenna Sector 14dbi EsDocument1 pageMeraki Datasheet Antenna Sector 14dbi EsDamaso OspinoNo ratings yet
- FSK ResearchDocument42 pagesFSK Researchمهيمن الابراهيميNo ratings yet
- Wideband Microstrip AntennasDocument181 pagesWideband Microstrip AntennasSimona DanNo ratings yet
- 2G System ReportDocument188 pages2G System ReportchinmaypareekNo ratings yet
- Product Specifications Product Specifications: Vhlpx3 VHLPX3 - 13 13 - 1WH/A 1WH/ADocument5 pagesProduct Specifications Product Specifications: Vhlpx3 VHLPX3 - 13 13 - 1WH/A 1WH/ACj LlemosNo ratings yet
- DX-690-960-65-15i-M: Antenna SpecificationsDocument2 pagesDX-690-960-65-15i-M: Antenna SpecificationsАлександрNo ratings yet
- WP Designed Speed 802.11nDocument56 pagesWP Designed Speed 802.11nzizo1921No ratings yet
- Data Sheet MDI-910 ClassA - enDocument2 pagesData Sheet MDI-910 ClassA - enDeleter DoraNo ratings yet
- Huawei Bts 3900 Series ConfigurationDocument5 pagesHuawei Bts 3900 Series ConfigurationminoothwinNo ratings yet
- RADAR SystemDocument5 pagesRADAR SystemPrathamesh ShelarNo ratings yet
- Level Variability of Radio Signals Propagating Through Fire Experimental Measurements and Results PDFDocument8 pagesLevel Variability of Radio Signals Propagating Through Fire Experimental Measurements and Results PDFStefânia SousaNo ratings yet
- Study of Pattern Generator and Its UseDocument55 pagesStudy of Pattern Generator and Its UseesesesNo ratings yet
- 11-Element Yagi Antenna 146 ... 174 MHZ Vertical / Horizontal PolarizationDocument1 page11-Element Yagi Antenna 146 ... 174 MHZ Vertical / Horizontal PolarizationMauricio PerdomoNo ratings yet
Transmission Media: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Transmission Media: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Uploaded by
Omer ArshadOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Transmission Media: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Transmission Media: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Uploaded by
Omer ArshadCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 7
Transmission Media
McGraw-Hill The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
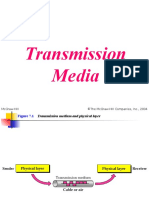
Figure 7.1
Transmission medium and physical layer
McGraw-Hill
The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Figure 7.2
Classes of transmission media
McGraw-Hill
The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
7.1 Guided Media
Twisted-Pair Cable
Coaxial Cable Fiber-Optic Cable
McGraw-Hill
The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Figure 7.3
Twisted-pair cable
McGraw-Hill
The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Figure 7.4
UTP and STP
McGraw-Hill
The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Table 7.1 Categories of unshielded twisted-pair cables
Category Bandwidth Data Rate Digital/Analog Use
1
2
very low
< 2 MHz
< 100 kbps
2 Mbps
Analog
Analog/digital
Telephone
T-1 lines
3
4 5 6 (draft) 7 (draft)
16 MHz
20 MHz 100 MHz 200 MHz 600 MHz
10 Mbps
20 Mbps 100 Mbps 200 Mbps 600 Mbps
Digital
Digital Digital Digital Digital
LANs
LANs LANs LANs LANs
McGraw-Hill
The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Figure 7.5
UTP connector
McGraw-Hill
The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Figure 7.6
UTP performance
McGraw-Hill
The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Figure 7.7
Coaxial cable
McGraw-Hill
The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Table 7.2 Categories of coaxial cables
Category
RG-59 RG-58 RG-11
Impedance
75 W 50 W 50 W
Use
Cable TV Thin Ethernet Thick Ethernet
McGraw-Hill
The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Figure 7.8
BNC connectors
McGraw-Hill
The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Figure 7.9
Coaxial cable performance
McGraw-Hill
The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Figure 7.10
Bending of light ray
McGraw-Hill
The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Figure 7.11 Optical fiber
McGraw-Hill
The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Figure 7.12
Propagation modes
McGraw-Hill
The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Figure 7.13
Modes
McGraw-Hill
The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Table 7.3 Fiber types
Type 50/125 62.5/125 100/125 7/125 Core 50 62.5 100 7 Cladding 125 125 125 125 Mode Multimode, graded-index Multimode, graded-index Multimode, graded-index Single-mode
McGraw-Hill
The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Figure 7.14
Fiber construction
McGraw-Hill
The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Figure 7.15
Fiber-optic cable connectors
McGraw-Hill
The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Figure 7.16
Optical fiber performance
McGraw-Hill
The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
7.2 Unguided Media: Wireless
Radio Waves
Microwaves Infrared
McGraw-Hill
The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Figure 7.17
Electromagnetic spectrum for wireless communication
McGraw-Hill
The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Figure 7.18
Propagation methods
McGraw-Hill
The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Table 7.4 Bands
Band VLF LF MF HF VHF UHF SHF EHF Range 330 KHz 30300 KHz 300 KHz3 MHz 330 MHz 30300 MHz 300 MHz3 GHz 330 GHz 30300 GHz Propagation Ground Ground Sky Sky Application Long-range radio navigation Radio beacons and navigational locators AM radio Citizens band (CB), ship/aircraft communication
Sky and line-of-sight
Line-of-sight Line-of-sight Line-of-sight
VHF TV, FM radio
UHF TV, cellular phones, paging, satellite Satellite communication Long-range radio navigation
McGraw-Hill
The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Figure 7.19
Wireless transmission waves
McGraw-Hill
The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Figure 7.20
Omnidirectional antennas
McGraw-Hill
The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Note: Radio waves are used for multicast communications, such as radio and television, and paging systems.
McGraw-Hill
The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Figure 7.21
Unidirectional antennas
McGraw-Hill
The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Note: Microwaves are used for unicast communication such as cellular telephones, satellite networks, and wireless LANs.
McGraw-Hill
The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Note: Infrared signals can be used for shortrange communication in a closed area using line-of-sight propagation.
McGraw-Hill
The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
You might also like
- AWEUD n258 DataSheetDocument2 pagesAWEUD n258 DataSheettalox0% (1)
- Radar Cheat SheetDocument12 pagesRadar Cheat SheetEng-Sa'di Y. Tamimi100% (1)
- Forouzan chp7Document31 pagesForouzan chp7Aniket MehtaNo ratings yet
- Transmission Media: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004Document31 pagesTransmission Media: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004Keyur MahantNo ratings yet
- Transmission Media: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004Document31 pagesTransmission Media: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004Ralph Jayson SilangNo ratings yet
- Radio Over Fiber & WCDMADocument33 pagesRadio Over Fiber & WCDMASyed Shahzaib RazaNo ratings yet
- CH - 02 - 2 Transmissional MediaDocument37 pagesCH - 02 - 2 Transmissional MediascorpionNo ratings yet
- Radio Over Fiber TechnologyDocument46 pagesRadio Over Fiber TechnologySyed Shahzaib RazaNo ratings yet
- MWC2013 Backhaul ReportDocument16 pagesMWC2013 Backhaul ReportMarko BileNo ratings yet
- Wang 2020 IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 790 012014Document9 pagesWang 2020 IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 790 012014Malik Talha SaadNo ratings yet
- Deployment of 5G Network For Efficient Spectrum Utilization in Alakahia, Rivers StateDocument10 pagesDeployment of 5G Network For Efficient Spectrum Utilization in Alakahia, Rivers StateMustafa NyazNo ratings yet
- 5G Over-The-Air Performance Measurement: and Evaluation Using Fieldfox Handheld AnalyzersDocument18 pages5G Over-The-Air Performance Measurement: and Evaluation Using Fieldfox Handheld AnalyzersHuicheng YuNo ratings yet
- SDRs For Mmwave in 5G TechnologyDocument5 pagesSDRs For Mmwave in 5G TechnologyArun KumarNo ratings yet
- 5G Over-the-Air Performance Measurement and Evaluation Using FieldFox Handheld AnalyzersDocument15 pages5G Over-the-Air Performance Measurement and Evaluation Using FieldFox Handheld AnalyzerschristiancandidoNo ratings yet
- Beamforming For 5G MM Wave Networks at Quadrature Baseband and RF Using OFDM SignalinDocument8 pagesBeamforming For 5G MM Wave Networks at Quadrature Baseband and RF Using OFDM SignalinInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- 5G Over-the-Air PerformanceDocument15 pages5G Over-the-Air PerformanceMarian VerdeNo ratings yet
- New Final Doc 1Document13 pagesNew Final Doc 1Akhilesh UppulaNo ratings yet
- Telecom SpectrumDocument6 pagesTelecom SpectrumNikhil MunjalNo ratings yet
- 7 Millimeter Wave Antenna Design For 5G ApplicationsDocument18 pages7 Millimeter Wave Antenna Design For 5G ApplicationsDjelloul AISSAOUINo ratings yet
- 3G Overview: ZTE University TD&W&PCS BSS Course TeamDocument42 pages3G Overview: ZTE University TD&W&PCS BSS Course TeamshishirNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis of Physical Layer of Wimax System Using SimulinkDocument5 pagesPerformance Analysis of Physical Layer of Wimax System Using SimulinkKurt Mk-JimNo ratings yet
- The Next Wireless Wave Is A Millimeter Wave: August 2007Document13 pagesThe Next Wireless Wave Is A Millimeter Wave: August 2007Nguyen Binh DuongNo ratings yet
- JEEE 3485 FinalDocument14 pagesJEEE 3485 Finalwotangoabush80No ratings yet
- Deployment of Mobile WimaxDocument6 pagesDeployment of Mobile WimaxsaintdevilzNo ratings yet
- A CDL-Based Channel Model With Dual-Polarized Antennas For 5G MIMO Systems in Rural Remote AreasDocument14 pagesA CDL-Based Channel Model With Dual-Polarized Antennas For 5G MIMO Systems in Rural Remote AreaspruxmanNo ratings yet
- DroneeDocument11 pagesDroneePedro VillarroelNo ratings yet
- BER AND PAPR ANALYSIS OF 8X8 MIMO OFDM SYSTEM - USING SLM TECHNIQUE - Thesis - M.Tech PDFDocument82 pagesBER AND PAPR ANALYSIS OF 8X8 MIMO OFDM SYSTEM - USING SLM TECHNIQUE - Thesis - M.Tech PDFabdul.azeezNo ratings yet
- ctngc1015 PDFDocument5 pagesctngc1015 PDFAhmed Salah MohmedNo ratings yet
- 3G Over SatelliteDocument6 pages3G Over Satellitegamer08No ratings yet
- Metering Article Dec06Document3 pagesMetering Article Dec06SujokoTeeNo ratings yet
- Use of C-Band Spectrum For Mobile Broadband in Cities: London and ShenzhenDocument32 pagesUse of C-Band Spectrum For Mobile Broadband in Cities: London and ShenzhenArsalan Badar WastiNo ratings yet
- Propagation Channel Characterization For PDFDocument6 pagesPropagation Channel Characterization For PDFDrAbdallah NasserNo ratings yet
- Modulation Formats For Beyond-100Gbps Ethernet Optical Links - A Review of ResearchDocument4 pagesModulation Formats For Beyond-100Gbps Ethernet Optical Links - A Review of ResearchVijay JanyaniNo ratings yet
- White Paper: A Comparison of Two Fourth Generation Technologies: Wimax and 3Gpp-LteDocument3 pagesWhite Paper: A Comparison of Two Fourth Generation Technologies: Wimax and 3Gpp-LteMuhammad Bilal JunaidNo ratings yet
- Table of ContentsDocument1 pageTable of ContentsphotonicsmattNo ratings yet
- Dimensioning GSM/GPRS Networks For Circuit-And Packet-Switched ServicesDocument6 pagesDimensioning GSM/GPRS Networks For Circuit-And Packet-Switched ServicesKhandker Md SayerNo ratings yet
- Dimensioning of GPRS NetworkDocument6 pagesDimensioning of GPRS NetworkShefrin MohamedNo ratings yet
- 5G For Broadcasters - New Opportunities For Distribution and ContentDocument12 pages5G For Broadcasters - New Opportunities For Distribution and Contentander20xNo ratings yet
- TelecommunicationDocument1 pageTelecommunicationarvindranganathanNo ratings yet
- Re-Assignment of 3G Spectrum and The Spectrum Utilisation FeeDocument5 pagesRe-Assignment of 3G Spectrum and The Spectrum Utilisation Feewilly cNo ratings yet
- Wireless Evolution With 4G Technologies: Prof. D. U. Adokar, Priti J. RajputDocument11 pagesWireless Evolution With 4G Technologies: Prof. D. U. Adokar, Priti J. RajputNebiye SolomonNo ratings yet
- 1 20080902 - A-MAS-3i - For - Enhanced - HSDPA - Data - Rates PDFDocument11 pages1 20080902 - A-MAS-3i - For - Enhanced - HSDPA - Data - Rates PDFMohammad Abdullah Al MamunNo ratings yet
- Selection of Voip Codecs For Different Networks Based On Qos AnalysisDocument7 pagesSelection of Voip Codecs For Different Networks Based On Qos Analysiswaty5340No ratings yet
- Evolution of Mobile Technology and Business Models: Su-En TanDocument19 pagesEvolution of Mobile Technology and Business Models: Su-En Tanszi1979No ratings yet
- Sensors: Experimental Demonstration of Mmwave Vehicle-To-Vehicle Communications Using Ieee 802.11adDocument22 pagesSensors: Experimental Demonstration of Mmwave Vehicle-To-Vehicle Communications Using Ieee 802.11adlaeeeqNo ratings yet
- Interference Problem Between ZigBee and PDFDocument6 pagesInterference Problem Between ZigBee and PDFghadeer alkhodrNo ratings yet
- WiMax Vs 3G Mobile CommunicationDocument24 pagesWiMax Vs 3G Mobile CommunicationMohammed Hanafy AliNo ratings yet
- BSNLDocument112 pagesBSNLishu_sood6789100% (1)
- Mid Band Spectrum and The Co Existence With Radio AltimetersDocument33 pagesMid Band Spectrum and The Co Existence With Radio AltimetersYo AcaNo ratings yet
- 5G BeamformingDocument88 pages5G BeamformingMahamod IsmailNo ratings yet
- 4G & 5G Technologies: ResearchDocument7 pages4G & 5G Technologies: Researchusama darNo ratings yet
- Lawful Interception For 3G Networks White Paper: November, 2005 Aqsacom Document No. 040450Document23 pagesLawful Interception For 3G Networks White Paper: November, 2005 Aqsacom Document No. 040450imranq_3No ratings yet
- 5G Semiconductor Test WP enDocument37 pages5G Semiconductor Test WP enGeoffrey AlleyneNo ratings yet
- Gigabit Wireless Communications Using Mm-Wave CircuitsDocument39 pagesGigabit Wireless Communications Using Mm-Wave Circuitsjamessabraham2No ratings yet
- Eurofins E E Wireless News Update in Nov 1701282787Document6 pagesEurofins E E Wireless News Update in Nov 1701282787rohitnanwaniNo ratings yet
- Study of 3G TechnologyDocument7 pagesStudy of 3G TechnologyPooja Bidwai ShirpewarNo ratings yet
- 12 Spectrum - 5G Mobile and Wireless Communications TechnologyDocument15 pages12 Spectrum - 5G Mobile and Wireless Communications TechnologySornagopal VijayaraghavanNo ratings yet
- 5G: New Air Interface and Radio Access Virtualization: Huawei White Paper Ȕ April 2015Document11 pages5G: New Air Interface and Radio Access Virtualization: Huawei White Paper Ȕ April 2015Anonymous EmLpNr6No ratings yet
- 01 Overview of Broadband CommunicationsDocument51 pages01 Overview of Broadband CommunicationsAimNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Network Planning and Optimisation 2G/3G/4G: Evolution to 5GFrom EverandFundamentals of Network Planning and Optimisation 2G/3G/4G: Evolution to 5GNo ratings yet
- Optical Fiber Telecommunications Volume VIB: Systems and NetworksFrom EverandOptical Fiber Telecommunications Volume VIB: Systems and NetworksNo ratings yet
- Mushaf by Nimra AhmadDocument493 pagesMushaf by Nimra AhmadOmer Arshad100% (6)
- Led Highbay Light-hbl50-200w-03-Ta-spec-A1 - PhlipsDocument4 pagesLed Highbay Light-hbl50-200w-03-Ta-spec-A1 - PhlipsOmer ArshadNo ratings yet
- ENGIN112 L5: Boolean Algebra September 12, 2003Document18 pagesENGIN112 L5: Boolean Algebra September 12, 2003Omer ArshadNo ratings yet
- Network Devices: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004Document20 pagesNetwork Devices: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004Omer ArshadNo ratings yet
- Binary Adders and Subtractors: ENGIN112 L14: Binary Adder Subtractor October 3, 2003Document16 pagesBinary Adders and Subtractors: ENGIN112 L14: Binary Adder Subtractor October 3, 2003Omer ArshadNo ratings yet
- Computer-Aided Engineering Drawing: 1. Getting StartedDocument36 pagesComputer-Aided Engineering Drawing: 1. Getting StartedOmer ArshadNo ratings yet
- Huawei Improve SDSRDocument9 pagesHuawei Improve SDSRAhmadArwani88No ratings yet
- Ch1-Handover Strategies in GSM - ModDocument41 pagesCh1-Handover Strategies in GSM - ModSoha FarhatNo ratings yet
- Integrated Circuits Lab: Experiment #3 Low Pass and High Pass Filters I ObjectivesDocument9 pagesIntegrated Circuits Lab: Experiment #3 Low Pass and High Pass Filters I Objectivesanimesh pariharNo ratings yet
- Amphenol 5964300GDocument5 pagesAmphenol 5964300Gklamar5No ratings yet
- Data Sheet: Performance-Optimized 802.11ac Dual-Radio 3x3:3 Access PointDocument6 pagesData Sheet: Performance-Optimized 802.11ac Dual-Radio 3x3:3 Access PointKléber Cruz SánchezNo ratings yet
- GSM Optimization and TroubleshootingDocument109 pagesGSM Optimization and TroubleshootingRockman CoolNo ratings yet
- UV1316Document20 pagesUV1316andrei8411No ratings yet
- Fitch - The-Superheterodyne-BookDocument70 pagesFitch - The-Superheterodyne-BookmplennaNo ratings yet
- Microwave Devices Directional Coupler and Isolator: E. Cinthuriya - Me - Communication EngineeringDocument23 pagesMicrowave Devices Directional Coupler and Isolator: E. Cinthuriya - Me - Communication EngineeringShwetaNo ratings yet
- Power Line Carrier: CommunicationDocument66 pagesPower Line Carrier: Communicationmani_2010nairNo ratings yet
- Ckt-Odv065r14b17k-B DS 0-0-1Document2 pagesCkt-Odv065r14b17k-B DS 0-0-1АлександрNo ratings yet
- DF-A0134 Version 1.1Document2 pagesDF-A0134 Version 1.1Mostafa hdghNo ratings yet
- CEPT Novice 1Document26 pagesCEPT Novice 1Ster RncNo ratings yet
- 80M VerticalDocument3 pages80M Verticalmuli100% (1)
- Meraki Datasheet Antenna Sector 14dbi EsDocument1 pageMeraki Datasheet Antenna Sector 14dbi EsDamaso OspinoNo ratings yet
- FSK ResearchDocument42 pagesFSK Researchمهيمن الابراهيميNo ratings yet
- Wideband Microstrip AntennasDocument181 pagesWideband Microstrip AntennasSimona DanNo ratings yet
- 2G System ReportDocument188 pages2G System ReportchinmaypareekNo ratings yet
- Product Specifications Product Specifications: Vhlpx3 VHLPX3 - 13 13 - 1WH/A 1WH/ADocument5 pagesProduct Specifications Product Specifications: Vhlpx3 VHLPX3 - 13 13 - 1WH/A 1WH/ACj LlemosNo ratings yet
- DX-690-960-65-15i-M: Antenna SpecificationsDocument2 pagesDX-690-960-65-15i-M: Antenna SpecificationsАлександрNo ratings yet
- WP Designed Speed 802.11nDocument56 pagesWP Designed Speed 802.11nzizo1921No ratings yet
- Data Sheet MDI-910 ClassA - enDocument2 pagesData Sheet MDI-910 ClassA - enDeleter DoraNo ratings yet
- Huawei Bts 3900 Series ConfigurationDocument5 pagesHuawei Bts 3900 Series ConfigurationminoothwinNo ratings yet
- RADAR SystemDocument5 pagesRADAR SystemPrathamesh ShelarNo ratings yet
- Level Variability of Radio Signals Propagating Through Fire Experimental Measurements and Results PDFDocument8 pagesLevel Variability of Radio Signals Propagating Through Fire Experimental Measurements and Results PDFStefânia SousaNo ratings yet
- Study of Pattern Generator and Its UseDocument55 pagesStudy of Pattern Generator and Its UseesesesNo ratings yet
- 11-Element Yagi Antenna 146 ... 174 MHZ Vertical / Horizontal PolarizationDocument1 page11-Element Yagi Antenna 146 ... 174 MHZ Vertical / Horizontal PolarizationMauricio PerdomoNo ratings yet