Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pemeriksaan Radiologi Thorax
Pemeriksaan Radiologi Thorax
Uploaded by
bamboomanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pemeriksaan Radiologi Thorax
Pemeriksaan Radiologi Thorax
Uploaded by
bamboomanCopyright:
Available Formats
Raymond Adiwicaksana
Chest X-Ray CT-scan USG
Foto PA Foto AP Foto lateral kiri Posisi lain
Top lordotic Recumbency Oblique Lateral decubitus Expirasi maksimal
Faktor kondisi
Kondisi pulmo Kondisi costae
Faktor inspirasi cukup
Cukupo Kurang
Posisi sesuai
Errect supine
Simetris
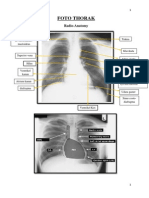
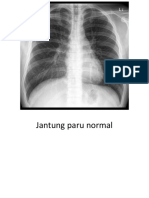
1. pulmo 2. hilum 3.jantung 4.mediastinum 5. diafragma 6. sudut costofrenik 7. trakea 8. tulang 9.jaringan lunak 10. area dibawah diafragma
Untuk mengukur jantung Mendeteksi pembesaran jantung CTR adalah perbandingan diameter transversal jantung dengan diameter transversal rongga thorax Ratio normal
50%, untuk asia 55% 60% pada neonatus
Kelemahan
Tidak bisa dipakai pada orang dengan letak jantung mendatar atau vertikal Orang dengan pericardium penuh lemak
Rumus
CTR = (a+b)/(c1+c2)
A chest computed tomography (to-MOG-ra-fee) scan, or chest CT scan, is a painless, noninvasive test. It creates precise pictures of the structures in your chest, such as your lungs. "Noninvasive" means that no surgery is done and no instruments are inserted into your body.
Lung imaging test Computed axial tomography (CAT) scan Helical CT scan (another name for spiral CT scan)
The chest CT scan can: Provide more detailed pictures of your lungs and other chest structures than a standard chest x ray Find the exact location of a tumor or other problem Show something that isn't visible on a chest x ray
Indikasi
Emboli paru Emfisema Hipertensi pulmonal Ca paru Sesak nafas dan sakit dada yang tidak diketahui sebabnya
Pemeriksaan ini tidak spesifik Kontraindikasi
Hipoksia berat dan kelainan jantung bawaan
Isotop
99m Tc makrokoloid sebesar 2mCi intravena, memancarkan sinar gamma dengan energi 140keV
Tidak perlu persiapan Pemeriksaan
Siapkan preparat radiofarmaka Suntikkan perlahan sementara penderita ispirasi beberapa kali dalam posisi tidur terlentang Scanning paru dengan kamera gamma pada empat posisi depan, belakang, sisi kanan, dan kiri
Interpretasi
Myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI) offers a method of visualizing blood flow to the heart by injection of a radioactive cardiac-specific tracer, ie, a cardiac imaging isotope. This improves the diagnostic accuracy of a cardiovascular stress test MPI offers the additional advantage of estimating left ventricular function.
Find the cause of unexplained chest pain or chest pain brought on by exercise. Check for the location and amount of damage caused by a heart attack. Identify coronary artery disease (CAD). Check to see that the heart is getting enough blood after heart surgery or angioplasty. Identify a congenital heart defect
1.Calcium-score screening heart scan 2.Coronary CT angiography (CTA) 3.Total body CT scan
Reasons for the procedure A chest ultrasound may used to assess
the presence of excess fluid in the pleural space or other areas of the chest, especially when the amount of fluid is small. useful to determine the type of fluid, exudate (seen in inflammatory, cancerous, or infectious conditions) or transudate (fluid that has leaked from blood or lymph vessels for various reasons). It can also be used to evaluate the heart and its valves. When used for this purpose, the procedure is called an echocardiogram.
Chest ultrasound may be performed to guide a needle during thoracentesis (puncture of the chest wall for the removal of fluids) or biopsy. to assess the movement of the diaphragm.
- john hopkins hospital -
absence of radiation, better portability, real-time imaging, the ability to perform dynamic imaging.
Ultrasound examination of the pleura is more sensitive than a plain chest radiograph at detecting the presence of pleural fluid and differentiating pleural fluid from lung consolidation. Compared with computed tomography (CT), pleural ultrasound has a 95 percent sensitivity for detection of pleural disease in patients with a white out on plain chest radiograph, but is slightly less sensitive in detecting small amounts of fluid
Thoracic ultrasound is an operator dependent technology. Ultrasound is not as good as CT imaging for evaluation of the underlying lung parenchyma in the setting of complex pleural and lung parenchymal disease. Ultrasound guidance is not as good as guidance by CT imaging for complicated interventional procedures, such as empyema drainage with a pigtail catheter or biopsy of pleural masses.
Bedside detection of pleural fluid when the plain chest radiograph shows a white out Bedside detection of a pneumothorax Guidance for diagnostic and therapeutic thoracentesis Guidance for placement of thoracostomy tubes
There are many clinical indications for TUS but the most common is pleural effusion assessment. TUS can diagnose inoperable pleural metastases, allow safe day case pleural intervention, exclude significant pleural pathology not visible on CXR, triage further investigation.
- British Medical journal-
You might also like
- Ujian Ilmu BedahDocument140 pagesUjian Ilmu BedahNurulita CahyaniNo ratings yet
- 2.4.1.8 Pemeriksaan Radiologi Sistem PencernaanDocument108 pages2.4.1.8 Pemeriksaan Radiologi Sistem PencernaanAina AlmaaidahNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan Radiologi Tr. DigestivusDocument40 pagesPemeriksaan Radiologi Tr. DigestivusFadia DanniswaraNo ratings yet
- Dasar MRIDocument55 pagesDasar MRIWirdatul JannahNo ratings yet
- Radiologi Anak (Pediatri)Document77 pagesRadiologi Anak (Pediatri)Since Ivanna Rumbiak0% (1)
- Ringkasan RadiologiDocument58 pagesRingkasan RadiologigowindamijayaNo ratings yet
- Radiologi Pada THTDocument50 pagesRadiologi Pada THTRizky LumalessilNo ratings yet
- Segmen Paru Pada Gambaran CT ScanDocument3 pagesSegmen Paru Pada Gambaran CT ScanMin Wai HanNo ratings yet
- Proteksi RadiasiDocument4 pagesProteksi RadiasiAbbi Yanto ArtNo ratings yet
- SCHWARTE (Autosaved)Document27 pagesSCHWARTE (Autosaved)Diah AriesaNo ratings yet
- Bahan Ajar Teknik Radiografi 4Document58 pagesBahan Ajar Teknik Radiografi 4LuthfiAhmadNo ratings yet
- LAPORAN PRAKTIKUM VenografiDocument15 pagesLAPORAN PRAKTIKUM VenografifitriaNo ratings yet
- Bahan Kontras MediaDocument17 pagesBahan Kontras MediaRyanNo ratings yet
- Sanny - Fistulografi (42170137)Document24 pagesSanny - Fistulografi (42170137)joanneswitasannyNo ratings yet
- 37 - Gabungan Ujian Radiologi DR JustinDocument122 pages37 - Gabungan Ujian Radiologi DR JustinMeylisaGresiaNo ratings yet
- Buku RadiologiDocument5 pagesBuku RadiologiAisyiah Sarahdita SaidNo ratings yet
- Sortir Soal Ujian Radiologi Dea - 13 10 2016Document23 pagesSortir Soal Ujian Radiologi Dea - 13 10 2016LittleChenaNo ratings yet
- Trans PRKDocument23 pagesTrans PRKaymanalatasNo ratings yet
- Referat Bno IvpDocument15 pagesReferat Bno Ivpgusti yoga100% (1)
- Ringkasan Radiologi RongentDocument139 pagesRingkasan Radiologi RongentJan NahNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan Diagnostik Sistem PernafasanDocument28 pagesPemeriksaan Diagnostik Sistem PernafasanDewi AprilianiNo ratings yet
- Resusitasi Jantung Paru (Web1)Document14 pagesResusitasi Jantung Paru (Web1)SantiNo ratings yet
- Jenis Pemeriksaan RadiologiDocument1 pageJenis Pemeriksaan RadiologiTya Lupheluphe DiyaNo ratings yet
- ELS 7123EK AP Aortic Stenosis Patient Bro Asia Singles 120916 MalayDocument12 pagesELS 7123EK AP Aortic Stenosis Patient Bro Asia Singles 120916 MalayNur fitriNo ratings yet
- Tugas RadiologiDocument15 pagesTugas RadiologiDesti PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan Fizikal CVSDocument72 pagesPemeriksaan Fizikal CVSNaqib SakilaNo ratings yet
- Cardiac CatheterizationDocument9 pagesCardiac CatheterizationSarah EddiahNo ratings yet
- Analisis Jurnal SkriningDocument8 pagesAnalisis Jurnal SkriningRita Nur IsnainiNo ratings yet
- Panduan Asesmen PasienDocument55 pagesPanduan Asesmen PasienrorieNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan Usg, CTG, Rontgen KDKDocument25 pagesPemeriksaan Usg, CTG, Rontgen KDKMauwala HutikaNo ratings yet
- Juring RadiologiDocument30 pagesJuring Radiologiholy_miracleNo ratings yet
- None 26b090f4Document9 pagesNone 26b090f4Pratiwi Dewi Indah PakartiNo ratings yet
- Radiologi 1Document32 pagesRadiologi 1Anggita ChandraNo ratings yet
- CPR Odraslih 2015 - 2020Document56 pagesCPR Odraslih 2015 - 2020Stefan StojkovićNo ratings yet
- AppendectomyDocument11 pagesAppendectomyanon_25581207No ratings yet
- Jenis Tindakan Yang Memerlukan Persetujuan Tindakan MedisDocument11 pagesJenis Tindakan Yang Memerlukan Persetujuan Tindakan MedisYulia FebrianiNo ratings yet
- Ruptur EsofagusDocument21 pagesRuptur EsofagusIndra17No ratings yet
- UGIB (Surgical)Document16 pagesUGIB (Surgical)Domo kilingNo ratings yet
- Laporan Kasus Myoma UteriDocument7 pagesLaporan Kasus Myoma Uteriseptian71100% (1)
- Vent Riku Lo MegaliDocument10 pagesVent Riku Lo MegalidsNo ratings yet
- Lap AratomyDocument10 pagesLap AratomyEver GreenNo ratings yet
- Sindroma Vena CavaDocument6 pagesSindroma Vena CavaNur Farah HaniniNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan IVADocument8 pagesPemeriksaan IVACynthia Oktarisza100% (1)
- NeuroblastomaDocument16 pagesNeuroblastomaperdhana kusumaNo ratings yet
- Case Study EdDocument12 pagesCase Study EdFakaruzi RadzuanNo ratings yet
- Timektomi Pada TymomaDocument19 pagesTimektomi Pada TymomaTias DiahNo ratings yet
- Case ClerkDocument19 pagesCase Clerkmojakomoja100% (7)
- Laporan Kasus AnestesiDocument28 pagesLaporan Kasus AnestesiSepta Kristiyan TNo ratings yet
- LSCSDocument12 pagesLSCSHandra Equi NoqzNo ratings yet
- NOTULENSI-Pengkajian JantungDocument3 pagesNOTULENSI-Pengkajian JantungNunungNo ratings yet
- Presentation Kumpulan 6Document29 pagesPresentation Kumpulan 6haziqNo ratings yet
- Case Study Di Klinik OrthopedikDocument15 pagesCase Study Di Klinik OrthopedikFariz Masiong100% (8)
- Kanser ParuDocument5 pagesKanser ParuHAYATT_74No ratings yet
- AppendectomyDocument7 pagesAppendectomyMuhammad Sabiq Salman KatimanNo ratings yet
- DEFINISIDocument15 pagesDEFINISIZulkhairi ZawawiNo ratings yet
- Barah Paru ParuDocument9 pagesBarah Paru ParuNuos1975No ratings yet
- Anestesi Pada GeriatriDocument12 pagesAnestesi Pada GeriatriPuangkaNo ratings yet
- Makalah Usg GinjalDocument14 pagesMakalah Usg GinjalrizkaNo ratings yet
- Appendectomy Case Study Dewan BedahDocument9 pagesAppendectomy Case Study Dewan BedahKhairy IestNo ratings yet
- 2 Kecemasan ClerkingDocument15 pages2 Kecemasan ClerkingNur Amani Md YamanNo ratings yet