Professional Documents
Culture Documents
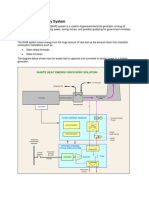
Waste Heat Recovery System
Waste Heat Recovery System
Uploaded by
Asrar UddinOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Waste Heat Recovery System
Waste Heat Recovery System
Uploaded by
Asrar UddinCopyright:
Available Formats
-BY Mohd Asrar Uddin Soheb
Introduction
Waste heat is heat, which is generated in a process by way of fuel combustion or chemical reaction, and then dumped into the environment even though it could still be reused for some useful and economic purpose.
Energy Flow without Waste heat recovery
Energy Flow with Waste heat recovery
Fuel
Fuel
Heat generation (boilers, heaters)
Heat generation (boilers, heaters)
Process
Process
Cooling
Cooling
Surroundings (rivers, air, etc.)
Surroundings (rivers, air, etc.)
Waste Source & Quality
S.No 1. 2. 3. Source Heat in flue gases. Heat in vapour streams. Convective and radiant heat lost from exterior of equipment. Quality The higher the temperature, the greater the potential value for heat recovery. As above but when condensed, latent heat also recoverable. Low grade if collected may be used for space heating or air preheats.
4.
5.
Heat losses in cooling water.
Heat losses in providing chilled water or in the disposal of chilled water Heat stored in products leaving the process Heat in gaseous and liquid effluents leaving process.
Low grade useful gains if heat is exchanged with incoming fresh water.
a) High grade if it can be utilized to reduce demand for refrigeration. b) Low grade if refrigeration unit used as a form of heat pump. Quality depends upon temperature. Poor if heavily contaminated and thus requiring alloy heat exchanger.
6. 7.
Benefits of 'waste heat recovery' can be broadly classified in two categories:
Direct Benefits: Recovery of waste heat has a direct effect on the efficiency of the process. This is reflected by reduction in the utility consumption & costs, and process cost. Indirect Benefits: a) Reduction in pollution
b) Reduction in equipment sizes
c) Reduction in auxiliary energy consumption
Recuperators In a recuperator, heat exchange takes place between the flue gases and the air through metallic or ceramic walls. Duct or tubes carry the air for combustion to be pre-heated, the other side contains the waste heat stream.
Metallic Radiation Recuperator
Convective Recuperator
Convective Radiative Recuperator
Heat Wheels It is a sizable porous disk, fabricated with material having a fairly high heat capacity, which rotates between two side-byside ducts: one a cold gas duct, the other a hot gas duct. The axis of the disk is located parallel to, and on the partition between, the two ducts. As the disk slowly rotates, sensible heat (moisture that contains latent heat) is transferred to the disk by the hot air and, as the disk rotates, from the disk to the cold air. The overall efficiency of sensible heat transfer for this kind of regenerator can be as high as 85 percent. Heat wheels have been built as large as 21 meters in diameter with air capacities up to 1130 m3 / min.
Eight ways to profit from waste heat
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
Save Fuel Generate Electricity Sell Heat and Electricity Reduce Cooling needs Reduce Capital Investment Cost 6. Increase Production 7. Reduce Greenhouse gas emission 8. Transform The Energy
The major components contributing to the annual savings are Coal and water. Capital Cost can be reduced. Reduces the emission of Harmful gases. Maintenance cost can be reduced.
QUERIES ??
THANK YOU
You might also like
- Table 1 Guide To Ventilation Ranges (Ach) and Component VelocitiesDocument1 pageTable 1 Guide To Ventilation Ranges (Ach) and Component VelocitiesNiong DavidNo ratings yet
- Economizers Operating and Maintenance PracticesDocument0 pagesEconomizers Operating and Maintenance PracticespariskosNo ratings yet
- Chimedza W: Boiler Blowdown Heat Recovery ProjectDocument34 pagesChimedza W: Boiler Blowdown Heat Recovery ProjectBlessed ZiyambeNo ratings yet
- Conditioning and Distribution of Compressed AirDocument19 pagesConditioning and Distribution of Compressed AirKCNo ratings yet
- Waste Heat RecoveryDocument20 pagesWaste Heat RecoveryAMIT PRAJAPATINo ratings yet
- Waste Heat RecoveryDocument17 pagesWaste Heat Recoverynayan100% (2)
- Waste Heat Recovery Technologies and Applications: ART-203 Group No:04Document17 pagesWaste Heat Recovery Technologies and Applications: ART-203 Group No:04Sazid ZamanNo ratings yet
- WEAST HEAT RECOVERY Heating Purpose For Woldia University CaftiriaDocument10 pagesWEAST HEAT RECOVERY Heating Purpose For Woldia University CaftiriaMisge ChekoleNo ratings yet
- WASTE HEAT RECOVERY (HRSG) PerformanceDocument17 pagesWASTE HEAT RECOVERY (HRSG) PerformanceEjaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Design, Fabrication and Performance Analysis of Vapor Absorption Refrigeration System Powered by Solar Using NanofluidDocument5 pagesDesign, Fabrication and Performance Analysis of Vapor Absorption Refrigeration System Powered by Solar Using NanofluidchilakaprakashNo ratings yet
- CondenserDocument44 pagesCondenserNeil John CatapangNo ratings yet
- Air Cooled CondenserDocument7 pagesAir Cooled Condensermoreds1983No ratings yet
- Power Plant-1Document32 pagesPower Plant-1marlito100% (1)
- Waste Heat Recovery FactsheetDocument2 pagesWaste Heat Recovery FactsheetMajid JafariNo ratings yet
- Heat RecoveryDocument2 pagesHeat RecoveryRohmat SetiawanNo ratings yet
- 2 ERG 401 2015 Energy Performance Analysis of BOILERDocument57 pages2 ERG 401 2015 Energy Performance Analysis of BOILERnaveenNo ratings yet
- Comparing Boiler Efficiency Calculation MethodsDocument21 pagesComparing Boiler Efficiency Calculation Methodsวรศิษฐ์ อ๋องNo ratings yet
- Calculation The Loads For Water Cooling SystemDocument15 pagesCalculation The Loads For Water Cooling SystemmassomieNo ratings yet
- C.O.P Derivation and Thermodynamic Calculation of Ammonia-Water Vapor Absorption Refrigeration System-2 PDFDocument10 pagesC.O.P Derivation and Thermodynamic Calculation of Ammonia-Water Vapor Absorption Refrigeration System-2 PDFErGiteshAroraNo ratings yet
- Solar Roofs: A Huge Stride Towards Sustainable Development: I M Dharmadasa and P. PallawelaDocument6 pagesSolar Roofs: A Huge Stride Towards Sustainable Development: I M Dharmadasa and P. PallawelaDejana NeznamNo ratings yet
- F Advanced Heller System Technical 2005 Good OneDocument53 pagesF Advanced Heller System Technical 2005 Good Onesubru1980No ratings yet
- Soot Deposits and Fires in Exhaust Gas BoilersDocument21 pagesSoot Deposits and Fires in Exhaust Gas BoilersJose G. CastilloNo ratings yet
- Waste Heat Recovery 1311947494Document2 pagesWaste Heat Recovery 1311947494Cem AlpaslanNo ratings yet
- Dry Cooling SystemDocument53 pagesDry Cooling Systemxlxjrv50% (2)
- Selection Criteria For DampersDocument4 pagesSelection Criteria For Dampersmarlon168No ratings yet
- 34 Boiler AccessoriesDocument21 pages34 Boiler AccessoriesSwaraj TodankarNo ratings yet
- Ice Plant Trainer (TD-03) : DescriptionDocument2 pagesIce Plant Trainer (TD-03) : DescriptionAshish VermaNo ratings yet
- Cooling Tower PowerPointDocument12 pagesCooling Tower PowerPointHaerNo ratings yet
- A Review To Optimize The Heat Transfer Rate and Increase The Efficiency of The Cooling TowerDocument6 pagesA Review To Optimize The Heat Transfer Rate and Increase The Efficiency of The Cooling TowerEditor IJRITCCNo ratings yet
- Air Cooled Condenser - Kratki OpisDocument47 pagesAir Cooled Condenser - Kratki Opisbaca88No ratings yet
- Boiler Structure and Principle (English)Document28 pagesBoiler Structure and Principle (English)Engr ImranNo ratings yet
- Cooling With Absorption ChillerDocument12 pagesCooling With Absorption ChillerTofanBNo ratings yet
- Basics of Steam GenerationDocument15 pagesBasics of Steam GenerationsvkatkarNo ratings yet
- Balance Point of Compressor and Capillary TubeDocument13 pagesBalance Point of Compressor and Capillary TubeMonojit KonarNo ratings yet
- Basic Parts of A BoilerDocument9 pagesBasic Parts of A Boilermessi107No ratings yet
- NTPC (National Thermal Power Corporation) Sipat Mechanical Vocational Training Report 4-Haxxo24 I IDocument44 pagesNTPC (National Thermal Power Corporation) Sipat Mechanical Vocational Training Report 4-Haxxo24 I Ihaxxo24No ratings yet
- Thermo Heat PumpDocument15 pagesThermo Heat PumpAkshay BhadangeNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting Guide 1Document4 pagesTroubleshooting Guide 1Cindy GallosNo ratings yet
- Design of Air IDocument5 pagesDesign of Air IInvedeNo ratings yet
- Design 2-Pass Shell and Tube Heat ExchangerDocument20 pagesDesign 2-Pass Shell and Tube Heat Exchangerazib100% (1)
- Mechanical Engineering Project - Thermal Power Plant Study - WWW - Amie.nbcafe - inDocument24 pagesMechanical Engineering Project - Thermal Power Plant Study - WWW - Amie.nbcafe - inbtdoss72100% (1)
- Evaporator Fan DesignDocument39 pagesEvaporator Fan DesignAnand PatelNo ratings yet
- Brochure Air Cooled CondenserDocument8 pagesBrochure Air Cooled CondenserFathur Rahman Handoko100% (1)
- Bottle Blow Down AnalysisDocument45 pagesBottle Blow Down AnalysisDoctorOberman100% (2)
- Cooling Tower Efficiency and ApproachDocument8 pagesCooling Tower Efficiency and Approachjeevitha jeeviNo ratings yet
- Biogas Boiler: Thermal Efficiency: Biogas Has A Lower Calorific Value Than Natural Gas, andDocument2 pagesBiogas Boiler: Thermal Efficiency: Biogas Has A Lower Calorific Value Than Natural Gas, andLeonardo GalardoNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Generator PDFDocument8 pagesOxygen Generator PDFAndres Rojas100% (1)
- Absorption Future PDFDocument12 pagesAbsorption Future PDFVaidyanathan KS100% (1)
- DieselPower PlantDocument12 pagesDieselPower PlantJC ElarmoNo ratings yet
- Thermax Double Effect Direct Fired BrochureDocument24 pagesThermax Double Effect Direct Fired BrochurePushpak Radadiya100% (1)
- 3 Experience and Case Studies 12.5.05Document3 pages3 Experience and Case Studies 12.5.05Sikander Girgoukar100% (1)
- IT10 BrochureDocument5 pagesIT10 BrochureMarlon Pierre de Haas100% (1)
- PET PlantDocument66 pagesPET PlantAri BinukoNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 2 (Waste Heat Recovery)Document4 pagesAssignment - 2 (Waste Heat Recovery)Akmal Hafeez Muhammad HafeezNo ratings yet
- Cara Menentukan Ukuran Steam TrapDocument5 pagesCara Menentukan Ukuran Steam TraprafiradityaNo ratings yet
- Thermal Energy ManagementDocument66 pagesThermal Energy ManagementKAZI SIAMUL ISLAMNo ratings yet
- Waste Heat Recovery NDocument28 pagesWaste Heat Recovery NranveerNo ratings yet
- Waste Heat RecoveryDocument4 pagesWaste Heat RecoveryMudasar JavedNo ratings yet
- Co Generation Unit 4Document52 pagesCo Generation Unit 4Johnson Johnson100% (2)
- Waste Heat RecoveryDocument37 pagesWaste Heat Recoveryommech2020No ratings yet
- T PembakaranDocument34 pagesT Pembakarandimas setyawanNo ratings yet
- 20220615-Chiller Stage TransitionsDocument5 pages20220615-Chiller Stage TransitionspratheeshNo ratings yet
- Spec-Monobloc 20221118Document1 pageSpec-Monobloc 20221118Anonymous LDJnXeNo ratings yet
- Crac Specification For CUCDocument12 pagesCrac Specification For CUCLi LiuNo ratings yet
- Hitachi Centrifugal ChillersDocument8 pagesHitachi Centrifugal ChillersAlejandro Lopez FidalgoNo ratings yet
- PP2 - Advance HVAC Course OEA - 1Document49 pagesPP2 - Advance HVAC Course OEA - 1Bassel El Sayed AliNo ratings yet
- Inverter Ducted UnitsDocument2 pagesInverter Ducted UnitsAnonymous ynJByUsNo ratings yet
- Pack Calculation Pro ManualDocument94 pagesPack Calculation Pro ManualramonluhrNo ratings yet
- System Description HVACDocument22 pagesSystem Description HVACmikko intalNo ratings yet
- Johnson 2017 PDFDocument240 pagesJohnson 2017 PDFbk2 dingoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 9 - BMS and Hvac SystemsDocument2 pagesAssignment 9 - BMS and Hvac SystemsvipulNo ratings yet
- AAF - ChevroNet - Filters CatalogueDocument2 pagesAAF - ChevroNet - Filters CatalogueSAGL100% (1)
- Units: Wall Mounted "Monoblock" Units For Outdoor Installations Cold Rooms Process Cooling Distribution CentersDocument3 pagesUnits: Wall Mounted "Monoblock" Units For Outdoor Installations Cold Rooms Process Cooling Distribution Centersmr_3647839No ratings yet
- Variable Air Volume SystemsDocument11 pagesVariable Air Volume SystemsApoorvaNo ratings yet
- Achievement Chart of Rac SerivicingDocument1 pageAchievement Chart of Rac SerivicingJonas AustriaNo ratings yet
- Hydronic System: J.IlangumaranDocument17 pagesHydronic System: J.Ilangumaranapi-25999517100% (1)
- Heating Ventilation & Air ConditioningDocument16 pagesHeating Ventilation & Air Conditioningsuman chandNo ratings yet
- Chiller Daily ChecklistDocument1 pageChiller Daily ChecklistamuronegaduNo ratings yet
- BOQ HVAC-Ginger ManesarDocument4 pagesBOQ HVAC-Ginger Manesarmascotengineers100% (1)
- Multi Pressure Vapour Compression Refrigeration SystemDocument11 pagesMulti Pressure Vapour Compression Refrigeration SystemDeepakNo ratings yet
- DHW Usage Factor Demographic Characteristics Occupancy: Entering Water Temp Faucet Delivery Temp Delta TDocument6 pagesDHW Usage Factor Demographic Characteristics Occupancy: Entering Water Temp Faucet Delivery Temp Delta Tmech_sahilNo ratings yet
- Carrier 30GTN PDDocument38 pagesCarrier 30GTN PDBudhi HermawanNo ratings yet
- 4 23Document3 pages4 23Anonymous iSsmdcNo ratings yet
- Hvac P.g.diplomaDocument5 pagesHvac P.g.diplomaSuthan SelvarajNo ratings yet
- 2014 Modern Hydronic System Designs Hts AshraeDocument41 pages2014 Modern Hydronic System Designs Hts AshraeNagarjun ReddyNo ratings yet
- Ashrae 90 - 1Document85 pagesAshrae 90 - 1Qaz ZaqNo ratings yet
- Air Condition BoqDocument2 pagesAir Condition BoqAndrew Awad AdlyNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration: U U W Q Du W QDocument20 pagesRefrigeration: U U W Q Du W QVandyck Mensah EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- HVAC ThesisDocument87 pagesHVAC ThesisAnonymous 3v1z9lNo ratings yet
- Calculation SheetDocument4 pagesCalculation SheetAhmed KhattabNo ratings yet