Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BCG Matrix
BCG Matrix
Uploaded by
Krupa VagalOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BCG Matrix
BCG Matrix
Uploaded by
Krupa VagalCopyright:
Available Formats
BCG Matrix
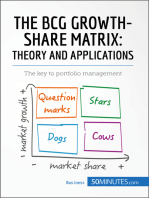
The Boston Consulting Group (BCG) is a management consulting firm founded by Harvard Business School alum Bruce Henderson in 1963. The growth-share matrix is a chart created by group in 1970 to help corporation analyze their business units or product lines, and decide where to allocate cash. It was popular for two decades, and is still used as an analytical tool. To use the chart, corporate analysts would plot a scatter graph of their business units, ranking their relative market shares and the growth rates of their respective industries. This led to a categorization of four different types of businesses:
Cash cows: Units with high market share in a slow-growing industry. These units typically generate cash in excess of the amount of cash needed to maintain the business. They are regarded as staid and boring, in a "mature" market, and every corporation would be thrilled to own as many as possible. They are to be "milked" continuously with as little investment as possible, since such investment would be wasted in an industry with low growth.
Dogs: More charitably called pets, units with low market share in a mature, slow-growing industry. These units typically "break even", generating barely enough cash to maintain the business's market share. Though owning a break-even unit provides the social benefit of providing jobs and possible synergies that assist other business units, from an accounting point of view such a unit is worthless, not generating cash for the company. They depress a profitable company's return on assets ratio, used by many investors to judge how well a company is being managed. Dogs, it is thought, should be sold off.
Question marks: Units with low market share in a fast-growing industry. Such business units require large amounts of cash to grow their market share. The corporate goal must be to grow the business to become a star. Otherwise, when the industry matures and growth slows, the unit will fall down into the dog's category.
Stars Units: with a high market share in a fastgrowing industry. The hope is that stars become the next cash cows. Sustaining the business unit's market leadership may require extra cash, but this is worthwhile if that's what it takes for the unit to remain a leader. When growth slows, stars become cash cows if they have been able to maintain their category leadership. As a particular industry matures and its growth slows, all business units become either cash cows or dogs.
The overall goal of this ranking was to help corporate analysts decide which of their business units to fund, and how much; and which units to sell. Managers were supposed to gain perspective from this analysis that allowed them to plan with confidence to use money generated by the cash cows to fund the stars and, possibly, the question marks. As the BCG stated in 1970: Only a diversified company with a balanced portfolio can use its strengths to truly capitalize on its growth opportunities. The balanced portfolio has: Stars whose high share and high growth assure the future; Cash cows that supply funds for that future growth; and Question marks to be converted into stars with the added funds.
Relative market share The reason for choosing relative market share, rather than just profits, is that it carries more information than just cash flow. It shows where the brand is positioned against its main competitors, and indicates where it might be likely to go in the future. It can also show what type of marketing activities might be expected to be effective. Market Growth Rate = Industry sales this year Industry Sales last year.
Limitations 1. Viewing every business as a star, cash cow, dog, or question mark is overly simplistic. 2. Many businesses fall right in the middle of the BCG matrix and thus are not easily classified. 3. The BCG matrix does not reflect whether or not various divisions or their industries are growing over time. 4. Other variables besides relative market share position and industry growth rate in sales are important in making strategic decisions about various divisions.
The BCG matrix is an important matrix regarding strategy adopted by firm. Still this matrix concern four strategy first growth or build strategy enhance market share), second is hold strategy (hold existing position), third Harvesting strategy (no further growth or select other opportunity), fourth is diversity (sell out the part of business).
You might also like
- The Contemporary World SyllabusDocument10 pagesThe Contemporary World SyllabusDGDelfin83% (18)
- Oil Palm Processing in NigeriaDocument14 pagesOil Palm Processing in NigeriaEDWARD100% (1)
- Atlanta Business Email List - V1Document4 pagesAtlanta Business Email List - V1Tom Harris0% (1)
- Growth Share MatrixDocument2 pagesGrowth Share MatrixPankaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Portfolio AnalysisDocument36 pagesPortfolio Analysissalman200867100% (2)
- The BCG Growth-Share Matrix: Theory and Applications: The key to portfolio managementFrom EverandThe BCG Growth-Share Matrix: Theory and Applications: The key to portfolio managementRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- 02 - Intro To TechnopreneurshipDocument18 pages02 - Intro To TechnopreneurshipJoyce Millares100% (2)
- BCG MatrixDocument3 pagesBCG MatrixMAHENDRA SHIVAJI DHENAKNo ratings yet
- BCG Matrix: Product Life CycleDocument10 pagesBCG Matrix: Product Life CycleiamgyanuNo ratings yet
- BCG Growth-Share MatrixDocument2 pagesBCG Growth-Share Matrixmanojdiman943No ratings yet
- Boston Consulting GroupDocument5 pagesBoston Consulting GroupTalk 2meNo ratings yet
- BCG GE Hofner EtcDocument14 pagesBCG GE Hofner EtcVikasNo ratings yet
- BCG MatrixDocument12 pagesBCG Matrixsplusk100% (6)
- BCG Matrix: Surya.H 121901042 Strategic ManagementDocument3 pagesBCG Matrix: Surya.H 121901042 Strategic ManagementCrazy MechonsNo ratings yet
- BCG MatrixDocument4 pagesBCG MatrixRahul AgarwalNo ratings yet
- BCG MatrixDocument19 pagesBCG MatrixRishab MehtaNo ratings yet
- Understanding The BCG Model Limitations / Problems of BCG ModelDocument13 pagesUnderstanding The BCG Model Limitations / Problems of BCG Modelshovit singhNo ratings yet
- The BCG MatrixDocument3 pagesThe BCG MatrixMalini PaulNo ratings yet
- MM - What Is A BCG MatrixDocument6 pagesMM - What Is A BCG MatrixAnonymous NhOj4NNo ratings yet
- BCG ItcDocument92 pagesBCG Itcprachii09No ratings yet
- BCG MatrixDocument2 pagesBCG Matrixsukhiromana0No ratings yet
- BCG MatrixDocument12 pagesBCG MatrixRajesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Boston Consulting Group (BCG) MatrixDocument14 pagesBoston Consulting Group (BCG) MatrixMutahar Hayat100% (1)
- Boston Consulting GroupDocument3 pagesBoston Consulting GroupPuran SinghNo ratings yet
- The BCG GrowthDocument3 pagesThe BCG GrowthKhuram ShahzadNo ratings yet
- BCG Matrix (Boston Consulting Group)Document12 pagesBCG Matrix (Boston Consulting Group)Talha AhmedNo ratings yet
- BCG MatrixDocument8 pagesBCG MatrixShagun ShekharNo ratings yet
- Competitive Position: Relative Market Share. One of The Dimensions Used To EvaluateDocument3 pagesCompetitive Position: Relative Market Share. One of The Dimensions Used To EvaluateAjay Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- BCG Notes FinalDocument10 pagesBCG Notes FinalHarsora UrvilNo ratings yet
- MM Ansoff & BCG MatrixDocument31 pagesMM Ansoff & BCG MatrixAshirbad NayakNo ratings yet
- Boston Consulting Group (BCG) MatrixDocument11 pagesBoston Consulting Group (BCG) MatrixAnjali AnjaliNo ratings yet
- Tata DataDocument2 pagesTata DataRoshan KumarNo ratings yet
- The BCG Growth-Share MatrixDocument5 pagesThe BCG Growth-Share MatrixShoury AnandNo ratings yet
- BCG Matrix 1Document4 pagesBCG Matrix 1Rahiq AhmedNo ratings yet
- BCG & Ansoff - ModelDocument9 pagesBCG & Ansoff - ModelMd Shahnawaz IslamNo ratings yet
- BCG MatrixDocument10 pagesBCG MatrixNeeraj TripathiNo ratings yet
- BCG Matrix: The Growth Share Matrix Was Created in 1968 by BCG's Founder, Bruce HendersonDocument4 pagesBCG Matrix: The Growth Share Matrix Was Created in 1968 by BCG's Founder, Bruce HendersonRuhul Amin Rasel100% (1)
- Final Theory - Marketing STRGDocument81 pagesFinal Theory - Marketing STRGkartkgala123No ratings yet
- Boston Consulting Group (BCG) Matrix Is A Four Celled Matrix Developed by BCG, USA. It IsDocument2 pagesBoston Consulting Group (BCG) Matrix Is A Four Celled Matrix Developed by BCG, USA. It IsShakib Ahmed Emon 0389No ratings yet
- BCG MatrixDocument12 pagesBCG MatrixA.Rahman SalahNo ratings yet
- Growth Share Matrix - Boston Consulting Group's Strategic ToolDocument10 pagesGrowth Share Matrix - Boston Consulting Group's Strategic ToolMuhd Ridho BaihaqueNo ratings yet
- BCG MatrixDocument7 pagesBCG MatrixRa babNo ratings yet
- Growth-Share Matrix: ChartDocument5 pagesGrowth-Share Matrix: ChartRenissa LewisNo ratings yet
- BCG MatrixDocument2 pagesBCG Matrixdip_g_007No ratings yet
- BCG Matrix and GE 9 Cell PlaningDocument5 pagesBCG Matrix and GE 9 Cell PlaningAmit Vasantbhai50% (2)
- Bruce Henderson: Boston Consulting Group (BCG) MATRIX Is Developed by Consulting Group in The Early 1970'SDocument17 pagesBruce Henderson: Boston Consulting Group (BCG) MATRIX Is Developed by Consulting Group in The Early 1970'SfahadfiazNo ratings yet
- The BCG MatrixDocument6 pagesThe BCG MatrixGuest HouseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 BCG MatrixDocument5 pagesChapter 7 BCG Matriximranpathan30No ratings yet
- BCG Matrix: Presented byDocument10 pagesBCG Matrix: Presented by2285 Rishika VaidyaNo ratings yet
- BCG GrowthDocument7 pagesBCG GrowthchienNo ratings yet
- BCG MatrixDocument17 pagesBCG Matrixchinmay manjrekarNo ratings yet
- BCG Matrix Assignment 1Document7 pagesBCG Matrix Assignment 1Raja AbdullahNo ratings yet
- BCG Matrix: Boston Consulting GroupDocument10 pagesBCG Matrix: Boston Consulting GroupKatha GandhiNo ratings yet
- Product StrategyDocument19 pagesProduct Strategyshivam sharmaNo ratings yet
- BCG Matrix SWOT Analysis and Porter ModeDocument12 pagesBCG Matrix SWOT Analysis and Porter ModeamiNo ratings yet
- BCG MatrixDocument11 pagesBCG MatrixVishakha GuptaNo ratings yet
- BCG MatrixDocument19 pagesBCG MatrixvittamsettyNo ratings yet
- BCG MatrixDocument6 pagesBCG MatrixSpandana AchantaNo ratings yet
- Boston Consulting Group MatrixDocument20 pagesBoston Consulting Group MatrixReema Mamtani100% (1)
- How to Make Money in Stocks: A Successful Strategy for Prosperous and Challenging TimesFrom EverandHow to Make Money in Stocks: A Successful Strategy for Prosperous and Challenging TimesNo ratings yet
- DIVIDEND INVESTING: Maximizing Returns while Minimizing Risk through Selective Stock Selection and Diversification (2023 Guide for Beginners)From EverandDIVIDEND INVESTING: Maximizing Returns while Minimizing Risk through Selective Stock Selection and Diversification (2023 Guide for Beginners)No ratings yet
- 2 TQMDocument1 page2 TQMKrupa VagalNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Financial StatementsDocument15 pagesAnalysis of Financial StatementsKrupa VagalNo ratings yet
- MSC Sums Solution (MBA)Document24 pagesMSC Sums Solution (MBA)prashantsmartie100% (3)
- Apple Inc.: Less Is MoreDocument56 pagesApple Inc.: Less Is MoreKrupa VagalNo ratings yet
- AVIATIONDocument20 pagesAVIATIONKrupa VagalNo ratings yet
- Week 14 Ellen Moore CaseDocument9 pagesWeek 14 Ellen Moore Casegr4ng3No ratings yet
- TUGAS KELOMPOK 1-MANAJEMEN Transportasi Dan PergudanganDocument25 pagesTUGAS KELOMPOK 1-MANAJEMEN Transportasi Dan PergudanganMedika SihombingNo ratings yet
- Final Examination - Spring 2020 - KeyDocument2 pagesFinal Examination - Spring 2020 - Keytung tranNo ratings yet
- Economics of Strategy: Sixth EditionDocument63 pagesEconomics of Strategy: Sixth EditionRichardNicoArdyantoNo ratings yet
- Economics (PLE) at Singapore Management University. I Write To You To Submit My Application For An InternshipDocument2 pagesEconomics (PLE) at Singapore Management University. I Write To You To Submit My Application For An InternshipchiahaoguangNo ratings yet
- SGS.G20 5.SewMachines - DurexDocument27 pagesSGS.G20 5.SewMachines - DurexDuy AnhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 04Document8 pagesChapter 04Mominul MominNo ratings yet
- Las: Trends, Network, and Critical Thinking Module 5Document4 pagesLas: Trends, Network, and Critical Thinking Module 5hatdognamalakiNo ratings yet
- Or2 Case StudyDocument7 pagesOr2 Case StudyJulius TamayoNo ratings yet
- POM (406) IntroductionDocument2 pagesPOM (406) IntroductionFaryal MasoodNo ratings yet
- 2021 August BOLTDocument77 pages2021 August BOLTShraiya ManhasNo ratings yet
- Normative Analyses of Investment Incentive in EthiopiaDocument6 pagesNormative Analyses of Investment Incentive in EthiopiaBelay MekuanintNo ratings yet
- Credit Management: Hagos MirachDocument115 pagesCredit Management: Hagos Mirachዝምታ ተሻለNo ratings yet
- Graham Number and Warren Buffett PortfolioDocument2 pagesGraham Number and Warren Buffett PortfoliobogatishankarNo ratings yet
- Vora Case Group 9Document10 pagesVora Case Group 9Abhi_The_RockstarNo ratings yet
- Case Study On SBIDocument18 pagesCase Study On SBIRashika SaxenaNo ratings yet
- PBR GSBDocument2 pagesPBR GSBDanica GeneralaNo ratings yet
- DBR 253 2018 Retail Banking Trends PredictionsDocument106 pagesDBR 253 2018 Retail Banking Trends PredictionsDuy Nguyen Ho ThienNo ratings yet
- Tax Process QuestionnaireDocument4 pagesTax Process QuestionnaireRodney LabayNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Agrarian Reform ProgramDocument44 pagesComprehensive Agrarian Reform ProgramMark Angelo S. EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Logistic Coord CV - Melly DiredjaDocument2 pagesLogistic Coord CV - Melly DiredjaDavid BarimbingNo ratings yet
- Positions Currently Available at Amatola Water BoardDocument1 pagePositions Currently Available at Amatola Water BoardDispatchLIVENo ratings yet
- Financial Analyst in NYC NY Resume Jasmin JarquioDocument2 pagesFinancial Analyst in NYC NY Resume Jasmin JarquioJasminJarquioNo ratings yet
- Memorandum of Understanding (M O U)Document4 pagesMemorandum of Understanding (M O U)Supreeth SANo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction To CryptocurrencyDocument19 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To CryptocurrencyVA CreationsNo ratings yet
- Accgr12ssipsessions12 15ln2013book3Document40 pagesAccgr12ssipsessions12 15ln2013book3Cecilia MwaleNo ratings yet