Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lateral Earth Pressure
Lateral Earth Pressure
Uploaded by
Laura HernandezCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- ASHRAE Standards ListDocument9 pagesASHRAE Standards ListRahul DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Design of FoundationsDocument3 pagesConceptual Design of FoundationsJames AswaNo ratings yet
- Soil ClassificationDocument21 pagesSoil Classificationamira husseinNo ratings yet
- Coulomb Theory For Retaining WallDocument11 pagesCoulomb Theory For Retaining WallTahir Ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Fema-440 - Improvement of Nonlinear Static Seismic Analysis ProceduresDocument392 pagesFema-440 - Improvement of Nonlinear Static Seismic Analysis ProceduresVlad VladNo ratings yet
- Total and Effective StressDocument3 pagesTotal and Effective Stressmortaza7094100% (3)
- Soil Mechanics Analysis Pressure Distribution: Learning Objectives: 1. Determine Pressure Distribution For Applied LoadsDocument11 pagesSoil Mechanics Analysis Pressure Distribution: Learning Objectives: 1. Determine Pressure Distribution For Applied LoadsShafiullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Flood Modelling PDFDocument12 pagesFlood Modelling PDFShashika IreshNo ratings yet
- PowerPoint P, ResentationDocument3 pagesPowerPoint P, ResentationlaNo ratings yet
- Soil Classification PDFDocument11 pagesSoil Classification PDFSivadol VongmongkolNo ratings yet
- Stability AnalysisDocument7 pagesStability AnalysisyasirjurabaNo ratings yet
- Penjelasan Slide PPT Liquefaction of SoilDocument14 pagesPenjelasan Slide PPT Liquefaction of Soilbasri kamaruddinNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Shallow Foundation-Bearing Capacity 2Document43 pagesLesson 1 Shallow Foundation-Bearing Capacity 2Ridho Putra PurnomoNo ratings yet
- Design PDFDocument260 pagesDesign PDFPrf El-SakhawyNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Structure Supported On Elastic FoundationDocument6 pagesAnalysis of Structure Supported On Elastic Foundationtaosye100% (2)
- CE 632 Earth PressureDocument18 pagesCE 632 Earth PressureBala Sutharshan100% (1)
- FractureDocument18 pagesFractureNAGARAJUNo ratings yet
- Fresh Kills ParkDocument18 pagesFresh Kills Parkheya16No ratings yet
- Ce 423-Foundation Engineering: Bearing Capacity of Shallow FootingsDocument28 pagesCe 423-Foundation Engineering: Bearing Capacity of Shallow FootingsMin Min II100% (1)
- Vs30 Correlations UC DavisDocument38 pagesVs30 Correlations UC Davisbasum matNo ratings yet
- Engineering Properties of Soils and Materials PermeabilityDocument8 pagesEngineering Properties of Soils and Materials PermeabilitySridevi GudaNo ratings yet
- Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering: Suresh R. Dash, Subhamoy Bhattacharya, Anthony BlakeboroughDocument8 pagesSoil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering: Suresh R. Dash, Subhamoy Bhattacharya, Anthony Blakeboroughuchiha894354No ratings yet
- 2.2 Grain Size Distribution: Sieve AnalysisDocument20 pages2.2 Grain Size Distribution: Sieve AnalysisYen Ling NgNo ratings yet
- Settlement CalculationDocument9 pagesSettlement CalculationIthihas SeventyoneNo ratings yet
- FootingsDocument56 pagesFootingskKhalid YousafNo ratings yet
- 03 - Stability of SlopesDocument26 pages03 - Stability of SlopesAndreea CălinNo ratings yet
- Terzaghi's Bearing CapacityDocument3 pagesTerzaghi's Bearing CapacityMd. Mohit HasanNo ratings yet
- LECTURE - FoundationsDocument6 pagesLECTURE - FoundationsFazelah YakubNo ratings yet
- Foundation Analysis and Design 1 PDFDocument48 pagesFoundation Analysis and Design 1 PDFagpsimoes100% (1)
- Calculation of Shallow FoundationsDocument262 pagesCalculation of Shallow Foundationssujan95100% (1)
- RollerDocument4 pagesRollerkapola100% (1)
- LicuefaciónDocument8 pagesLicuefaciónDaisy FloresNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Capacity Base On Field TestDocument61 pages2.2 Capacity Base On Field TestRadifan HalifNo ratings yet
- Rectangular Beam AnalysisDocument5 pagesRectangular Beam AnalysisheshamNo ratings yet
- Cut & Fill ApplicationDocument20 pagesCut & Fill ApplicationTABIBI11No ratings yet
- Sheet Pile WallDocument61 pagesSheet Pile WallShayan AbagnaleNo ratings yet
- 1) Deep FoundationsDocument30 pages1) Deep FoundationsmehtabhumikaaNo ratings yet
- Bearing CapacityDocument13 pagesBearing CapacityankitraginiNo ratings yet
- Pile DesignDocument13 pagesPile DesignMohafisto SofistoNo ratings yet
- Pile Problem 1Document3 pagesPile Problem 1ReemALMousawiNo ratings yet
- Figure 2-1: Ditch Conduit 2-2: Positive Projecting Conduit Figure 2-3: Negative Projective ConduitDocument1 pageFigure 2-1: Ditch Conduit 2-2: Positive Projecting Conduit Figure 2-3: Negative Projective ConduithisoyounghiNo ratings yet
- 978 3 319 57777 7 - 23 PDFDocument8 pages978 3 319 57777 7 - 23 PDFAhmedHossainNo ratings yet
- Cantilever Retaining Wall AnalysisDocument7 pagesCantilever Retaining Wall AnalysisnhulugallaNo ratings yet
- 05 Circular FailureDocument16 pages05 Circular FailureMuhammed AmmachandyNo ratings yet
- Braced Cuts (Excavations)Document6 pagesBraced Cuts (Excavations)Rajeev KusugalNo ratings yet
- Unit-IV Shallow FoundationsDocument64 pagesUnit-IV Shallow FoundationsRaju KINGNo ratings yet
- Lateral Earth PressureDocument15 pagesLateral Earth PressureLingeswarran NumbikannuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (Seepage Through Dams)Document6 pagesChapter 1 (Seepage Through Dams)Mark Lorenz DiolataNo ratings yet
- Shallow Foundation Design 2: SettlementDocument32 pagesShallow Foundation Design 2: SettlementPhanna MongNo ratings yet
- Dealing With Gypsum Karst Problem Hazard Environment Issues and PlanningDocument12 pagesDealing With Gypsum Karst Problem Hazard Environment Issues and PlanningTito Poerwo100% (1)
- Lecture20 Drilled ShaftsDocument57 pagesLecture20 Drilled ShaftsAsia WardNo ratings yet
- Combined Axial and Bending Design R0 2017.12.02Document35 pagesCombined Axial and Bending Design R0 2017.12.02RoxanneDequinaNo ratings yet
- Pile Foundations Part-1Document42 pagesPile Foundations Part-1mohanty_anantakumar6332No ratings yet
- Towards A Unified Soil Mechanics Theory: The Use of Effective Stresses in Unsaturated Soils, Revised EditionFrom EverandTowards A Unified Soil Mechanics Theory: The Use of Effective Stresses in Unsaturated Soils, Revised EditionNo ratings yet
- Lateral Earth PressureDocument7 pagesLateral Earth PressureShafiullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Effective StressDocument97 pagesChapter 3 Effective Stressanon_917763370No ratings yet
- Comprehensive Step by Step Calculations For Retaining Wall Analysis Are Provided BelowDocument15 pagesComprehensive Step by Step Calculations For Retaining Wall Analysis Are Provided BelowLakshmiWijayasiriNo ratings yet
- Shallow Foundation Analysis and DesignDocument74 pagesShallow Foundation Analysis and Designofadol830No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument42 pagesUntitledShafkat SaminNo ratings yet
- Topic 4Document26 pagesTopic 4HCNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Effective StressDocument18 pagesLecture 4 Effective StressAdi Fikri Sidi83% (6)
- Retaining Wall DesignDocument15 pagesRetaining Wall DesignFarhan IqbalNo ratings yet
- Pread Ootings: Emo To Esigners ArchDocument5 pagesPread Ootings: Emo To Esigners ArchLaura HernandezNo ratings yet
- 01 ENB371 Tutorial Week 12 Pile Foundations 2Document6 pages01 ENB371 Tutorial Week 12 Pile Foundations 2Laura HernandezNo ratings yet
- Design of Residential Footings Built On Expansive Soil Using Probabilistic MethodsDocument6 pagesDesign of Residential Footings Built On Expansive Soil Using Probabilistic MethodsLaura HernandezNo ratings yet
- Soils and The Environment: Soil Scientists (And Most Ordinary People)Document26 pagesSoils and The Environment: Soil Scientists (And Most Ordinary People)Laura HernandezNo ratings yet
- Mathcad Beams DesignDocument6 pagesMathcad Beams DesignCristian A. O. SalazarNo ratings yet
- Foundation Analysis and Design: Michael Valley, P.EDocument0 pagesFoundation Analysis and Design: Michael Valley, P.ELaura HernandezNo ratings yet
- Design Basis and Economic Aspects of Different Types of Retaining WallsDocument18 pagesDesign Basis and Economic Aspects of Different Types of Retaining WallsLaura HernandezNo ratings yet
- JEC+Prog+ +Combined+Rectangular+FootingDocument6 pagesJEC+Prog+ +Combined+Rectangular+FootingLaura HernandezNo ratings yet
- TDP 2 - Soils Eng. Soil Properties 1Document14 pagesTDP 2 - Soils Eng. Soil Properties 1Laura HernandezNo ratings yet
- Diseño Trapezoidal PDFDocument7 pagesDiseño Trapezoidal PDFLaura HernandezNo ratings yet
- 1 Stress III MohrDocument30 pages1 Stress III MohrLaura HernandezNo ratings yet
- Compressibility Factor Rev 1aDocument5 pagesCompressibility Factor Rev 1aPanner2009No ratings yet
- Standard Specification For Wrought Tltanium.8 Alumlnum-. Vanadium ELI (Extra Low Interstitial) Alloy (R&6401) Tor Surgicallmpl8nt Applications1Document3 pagesStandard Specification For Wrought Tltanium.8 Alumlnum-. Vanadium ELI (Extra Low Interstitial) Alloy (R&6401) Tor Surgicallmpl8nt Applications1Ignacio Hiram M RoqueNo ratings yet
- Us8748666 PDFDocument10 pagesUs8748666 PDFJuan CampeonNo ratings yet
- Boundary Conditions PDFDocument30 pagesBoundary Conditions PDFSairRamNo ratings yet
- Gcse : H O (L) H (Aq) + OH (Aq)Document9 pagesGcse : H O (L) H (Aq) + OH (Aq)Takudzwa ChademanaNo ratings yet
- CHEG 342 Solutions ManualDocument213 pagesCHEG 342 Solutions ManualChaitanya SheopurkarNo ratings yet
- Peigao Duan, Xiujun Bai, Yuping Xu, Aiyun Zhang, Feng Wang, Lei Zhang, Juan MiaoDocument9 pagesPeigao Duan, Xiujun Bai, Yuping Xu, Aiyun Zhang, Feng Wang, Lei Zhang, Juan MiaoyemresimsekNo ratings yet
- Flashcards - 5.1 Forces and Their Interactions - AQA Physics GCSE-7Document35 pagesFlashcards - 5.1 Forces and Their Interactions - AQA Physics GCSE-7wagnerleandroNo ratings yet
- Temperature Trouble Shootings and Maintance of WS-100Document8 pagesTemperature Trouble Shootings and Maintance of WS-100Mohamad Niko BSTINo ratings yet
- DLP AbbreviationDocument8 pagesDLP AbbreviationTrecita BacoNo ratings yet
- 04 Estructura Atomica-2011Document85 pages04 Estructura Atomica-2011FranciscoTestaNo ratings yet
- Wiki Quantum MechanicsDocument182 pagesWiki Quantum MechanicsArmandNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical EngineeringDocument3 pagesGeotechnical EngineeringYawer HussainNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Basic ConceptsDocument16 pagesThermodynamics Basic Conceptschincha chuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Bonding General ConceptsDocument79 pagesChapter 8 Bonding General Conceptsabd jaf100% (1)
- OIL REMOVAL USING DURIAN PEEL WASTES EFFECT OF ADSORBENT CONDITION MJIT Volume 1 No 1 56 61Document6 pagesOIL REMOVAL USING DURIAN PEEL WASTES EFFECT OF ADSORBENT CONDITION MJIT Volume 1 No 1 56 61Russel AloceljaNo ratings yet
- ENCHighlightsDocument60 pagesENCHighlightsUtpal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Language Arts Subject For Middle School - 8th Grade - Vocabulary Skills by SlidesgoDocument61 pagesLanguage Arts Subject For Middle School - 8th Grade - Vocabulary Skills by SlidesgoLilik Ali MahfudNo ratings yet
- Ch-3-A-2 Acids Bases and SaltsDocument32 pagesCh-3-A-2 Acids Bases and Saltsarnavpatel138No ratings yet
- Application Drugs of Abuse GC Mass Spectrometry 5994 1012en AgilentDocument16 pagesApplication Drugs of Abuse GC Mass Spectrometry 5994 1012en AgilentMauricio SilvestriNo ratings yet
- MSDS AquasaltDocument8 pagesMSDS Aquasaltemilio zeaNo ratings yet
- Effects of Particle Size and Its Distribution On Specific Cake Resistance During Rice Wine Microfiltration PDFDocument6 pagesEffects of Particle Size and Its Distribution On Specific Cake Resistance During Rice Wine Microfiltration PDFAlexRiveraNo ratings yet
- Medidor Vortex Vapor Modelo Prowirl l200Document103 pagesMedidor Vortex Vapor Modelo Prowirl l200mizzioNo ratings yet
- Momentum and CollisionsDocument13 pagesMomentum and CollisionsImran TabakovićNo ratings yet
- Acrodisc Syringe Filters Chemical Compatibility GuideDocument36 pagesAcrodisc Syringe Filters Chemical Compatibility GuideNermeen ElmelegaeNo ratings yet
- InorganicDocument105 pagesInorganicKishan Gupta100% (6)
- 1 Type of Flow: 1.1 Wider SectionDocument3 pages1 Type of Flow: 1.1 Wider SectionBrendan LimNo ratings yet
- George E. Totten, Lavern D. Wedeven, James R. Dickey, and Michael Anderson, Editors - Bench Testing of Industrial Fluid Lubrication and Wear Properties Used inDocument338 pagesGeorge E. Totten, Lavern D. Wedeven, James R. Dickey, and Michael Anderson, Editors - Bench Testing of Industrial Fluid Lubrication and Wear Properties Used inAbderrahim AbarayNo ratings yet
- Physic Supplymentary Guess Paper 2023Document1 pagePhysic Supplymentary Guess Paper 2023Muhammad Umer Farooq NadeemNo ratings yet
Lateral Earth Pressure
Lateral Earth Pressure
Uploaded by
Laura HernandezOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lateral Earth Pressure
Lateral Earth Pressure
Uploaded by
Laura HernandezCopyright:
Available Formats
Soil mechanics Lateral earth pressure
References: 1. Budhu, Muni, D. Soil Mechanics & Foundations. New York; John Wiley & Sons, Inc, 2000. 2. Schroeder, W.L., Dickenson, S.E, Warrington, Don, C. Soils in Construction. Fifth Edition. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey; Prentice Hall, 2004.
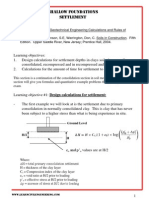
Learning objectives: 1. The effective stress Principle 2. Differences of Effective and Total stress. The Lateral Earth Pressure or Horizontal Pressure(stress):
- Once you find the vertical stress (), it is relatively simple to calculate the lateral earth pressure for the soil. - The key concept to understand is that the vertical pressure in soil is different than the horizontal pressure. This is different than water, in which the vertical pressure and horizontal pressure is the same. - In soil the lateral Earth pressure is equal to the effective vertical stress () times a earth The density of thetype block = (lbs/cf) pressure coefficient (K). This coefficient depends on the soil and where the soil is allowed to move.
- Lateral Earth Pressure (H) = K * v -The three different types of coefficients are below; with there most used formulas to calculate the earth pressure coefficient. - Ka = tan2 (45 /2) = (1 sin ) / (1 + sin ) Ka is known as active
earth pressure coefficient - Kp = tan2 (45 + /2) = (1 sin ) / (1 - sin ) Kp is known as passive earth pressure coefficient - KO = 1 sin (for sands) KO is known as at rest earth pressure coefficient - Ka < KO < Kp Kp = 1 / Ka
- = angle of internal friction
- Also important to note: The total force per unit length of the wall, Po, is equal to the area of the pressure diagram, which is;
- Po (lbs/ft) = Ko H2 (for a dry soil)
www.learncivilengineering.com
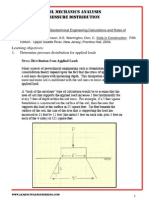
Example: Determine the active lateral earth pressure on the frictionless wall shown in the below figure. Strategy: The lateral earth pressure coefficients can only be applied to the effective stresses. You need to calculate the vertical effective stress, apply Ka, and then add the pore water pressure.
12 ft
sat = 140 lbs / cf = 30o
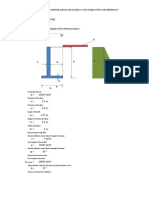
Step 1: Calculate Ka. - Ka = tan2 (45 /2) = (1 sin ) / (1 + sin ) = 1/3 Step 2: Calculate the vertical effective stress. - = u - = sat h = 140 lbs/cf x 12 ft = 1680 lbs/sf - u = w h = 62.4 lbs/cf x 12ft = 749 lbs /sf - = 1680 749 = 931 lbs/sf Step 3: Calculate the lateral effective stress. - H = Ka x \ = .333 x 931 lbs/sf = 310 lbs/sf Step 4: Sketch the lateral earth pressure distributions.
12 ft
sat = 140 lbs / cf = 30o
310 lbs/sf From soil
749 lbs/sf Hydrostatic
www.learncivilengineering.com
You might also like
- ASHRAE Standards ListDocument9 pagesASHRAE Standards ListRahul DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Design of FoundationsDocument3 pagesConceptual Design of FoundationsJames AswaNo ratings yet
- Soil ClassificationDocument21 pagesSoil Classificationamira husseinNo ratings yet
- Coulomb Theory For Retaining WallDocument11 pagesCoulomb Theory For Retaining WallTahir Ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Fema-440 - Improvement of Nonlinear Static Seismic Analysis ProceduresDocument392 pagesFema-440 - Improvement of Nonlinear Static Seismic Analysis ProceduresVlad VladNo ratings yet
- Total and Effective StressDocument3 pagesTotal and Effective Stressmortaza7094100% (3)
- Soil Mechanics Analysis Pressure Distribution: Learning Objectives: 1. Determine Pressure Distribution For Applied LoadsDocument11 pagesSoil Mechanics Analysis Pressure Distribution: Learning Objectives: 1. Determine Pressure Distribution For Applied LoadsShafiullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Flood Modelling PDFDocument12 pagesFlood Modelling PDFShashika IreshNo ratings yet
- PowerPoint P, ResentationDocument3 pagesPowerPoint P, ResentationlaNo ratings yet
- Soil Classification PDFDocument11 pagesSoil Classification PDFSivadol VongmongkolNo ratings yet
- Stability AnalysisDocument7 pagesStability AnalysisyasirjurabaNo ratings yet
- Penjelasan Slide PPT Liquefaction of SoilDocument14 pagesPenjelasan Slide PPT Liquefaction of Soilbasri kamaruddinNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Shallow Foundation-Bearing Capacity 2Document43 pagesLesson 1 Shallow Foundation-Bearing Capacity 2Ridho Putra PurnomoNo ratings yet
- Design PDFDocument260 pagesDesign PDFPrf El-SakhawyNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Structure Supported On Elastic FoundationDocument6 pagesAnalysis of Structure Supported On Elastic Foundationtaosye100% (2)
- CE 632 Earth PressureDocument18 pagesCE 632 Earth PressureBala Sutharshan100% (1)
- FractureDocument18 pagesFractureNAGARAJUNo ratings yet
- Fresh Kills ParkDocument18 pagesFresh Kills Parkheya16No ratings yet
- Ce 423-Foundation Engineering: Bearing Capacity of Shallow FootingsDocument28 pagesCe 423-Foundation Engineering: Bearing Capacity of Shallow FootingsMin Min II100% (1)
- Vs30 Correlations UC DavisDocument38 pagesVs30 Correlations UC Davisbasum matNo ratings yet
- Engineering Properties of Soils and Materials PermeabilityDocument8 pagesEngineering Properties of Soils and Materials PermeabilitySridevi GudaNo ratings yet
- Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering: Suresh R. Dash, Subhamoy Bhattacharya, Anthony BlakeboroughDocument8 pagesSoil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering: Suresh R. Dash, Subhamoy Bhattacharya, Anthony Blakeboroughuchiha894354No ratings yet
- 2.2 Grain Size Distribution: Sieve AnalysisDocument20 pages2.2 Grain Size Distribution: Sieve AnalysisYen Ling NgNo ratings yet
- Settlement CalculationDocument9 pagesSettlement CalculationIthihas SeventyoneNo ratings yet
- FootingsDocument56 pagesFootingskKhalid YousafNo ratings yet
- 03 - Stability of SlopesDocument26 pages03 - Stability of SlopesAndreea CălinNo ratings yet
- Terzaghi's Bearing CapacityDocument3 pagesTerzaghi's Bearing CapacityMd. Mohit HasanNo ratings yet
- LECTURE - FoundationsDocument6 pagesLECTURE - FoundationsFazelah YakubNo ratings yet
- Foundation Analysis and Design 1 PDFDocument48 pagesFoundation Analysis and Design 1 PDFagpsimoes100% (1)
- Calculation of Shallow FoundationsDocument262 pagesCalculation of Shallow Foundationssujan95100% (1)
- RollerDocument4 pagesRollerkapola100% (1)
- LicuefaciónDocument8 pagesLicuefaciónDaisy FloresNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Capacity Base On Field TestDocument61 pages2.2 Capacity Base On Field TestRadifan HalifNo ratings yet
- Rectangular Beam AnalysisDocument5 pagesRectangular Beam AnalysisheshamNo ratings yet
- Cut & Fill ApplicationDocument20 pagesCut & Fill ApplicationTABIBI11No ratings yet
- Sheet Pile WallDocument61 pagesSheet Pile WallShayan AbagnaleNo ratings yet
- 1) Deep FoundationsDocument30 pages1) Deep FoundationsmehtabhumikaaNo ratings yet
- Bearing CapacityDocument13 pagesBearing CapacityankitraginiNo ratings yet
- Pile DesignDocument13 pagesPile DesignMohafisto SofistoNo ratings yet
- Pile Problem 1Document3 pagesPile Problem 1ReemALMousawiNo ratings yet
- Figure 2-1: Ditch Conduit 2-2: Positive Projecting Conduit Figure 2-3: Negative Projective ConduitDocument1 pageFigure 2-1: Ditch Conduit 2-2: Positive Projecting Conduit Figure 2-3: Negative Projective ConduithisoyounghiNo ratings yet
- 978 3 319 57777 7 - 23 PDFDocument8 pages978 3 319 57777 7 - 23 PDFAhmedHossainNo ratings yet
- Cantilever Retaining Wall AnalysisDocument7 pagesCantilever Retaining Wall AnalysisnhulugallaNo ratings yet
- 05 Circular FailureDocument16 pages05 Circular FailureMuhammed AmmachandyNo ratings yet
- Braced Cuts (Excavations)Document6 pagesBraced Cuts (Excavations)Rajeev KusugalNo ratings yet
- Unit-IV Shallow FoundationsDocument64 pagesUnit-IV Shallow FoundationsRaju KINGNo ratings yet
- Lateral Earth PressureDocument15 pagesLateral Earth PressureLingeswarran NumbikannuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (Seepage Through Dams)Document6 pagesChapter 1 (Seepage Through Dams)Mark Lorenz DiolataNo ratings yet
- Shallow Foundation Design 2: SettlementDocument32 pagesShallow Foundation Design 2: SettlementPhanna MongNo ratings yet
- Dealing With Gypsum Karst Problem Hazard Environment Issues and PlanningDocument12 pagesDealing With Gypsum Karst Problem Hazard Environment Issues and PlanningTito Poerwo100% (1)
- Lecture20 Drilled ShaftsDocument57 pagesLecture20 Drilled ShaftsAsia WardNo ratings yet
- Combined Axial and Bending Design R0 2017.12.02Document35 pagesCombined Axial and Bending Design R0 2017.12.02RoxanneDequinaNo ratings yet
- Pile Foundations Part-1Document42 pagesPile Foundations Part-1mohanty_anantakumar6332No ratings yet
- Towards A Unified Soil Mechanics Theory: The Use of Effective Stresses in Unsaturated Soils, Revised EditionFrom EverandTowards A Unified Soil Mechanics Theory: The Use of Effective Stresses in Unsaturated Soils, Revised EditionNo ratings yet
- Lateral Earth PressureDocument7 pagesLateral Earth PressureShafiullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Effective StressDocument97 pagesChapter 3 Effective Stressanon_917763370No ratings yet
- Comprehensive Step by Step Calculations For Retaining Wall Analysis Are Provided BelowDocument15 pagesComprehensive Step by Step Calculations For Retaining Wall Analysis Are Provided BelowLakshmiWijayasiriNo ratings yet
- Shallow Foundation Analysis and DesignDocument74 pagesShallow Foundation Analysis and Designofadol830No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument42 pagesUntitledShafkat SaminNo ratings yet
- Topic 4Document26 pagesTopic 4HCNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Effective StressDocument18 pagesLecture 4 Effective StressAdi Fikri Sidi83% (6)
- Retaining Wall DesignDocument15 pagesRetaining Wall DesignFarhan IqbalNo ratings yet
- Pread Ootings: Emo To Esigners ArchDocument5 pagesPread Ootings: Emo To Esigners ArchLaura HernandezNo ratings yet
- 01 ENB371 Tutorial Week 12 Pile Foundations 2Document6 pages01 ENB371 Tutorial Week 12 Pile Foundations 2Laura HernandezNo ratings yet
- Design of Residential Footings Built On Expansive Soil Using Probabilistic MethodsDocument6 pagesDesign of Residential Footings Built On Expansive Soil Using Probabilistic MethodsLaura HernandezNo ratings yet
- Soils and The Environment: Soil Scientists (And Most Ordinary People)Document26 pagesSoils and The Environment: Soil Scientists (And Most Ordinary People)Laura HernandezNo ratings yet
- Mathcad Beams DesignDocument6 pagesMathcad Beams DesignCristian A. O. SalazarNo ratings yet
- Foundation Analysis and Design: Michael Valley, P.EDocument0 pagesFoundation Analysis and Design: Michael Valley, P.ELaura HernandezNo ratings yet
- Design Basis and Economic Aspects of Different Types of Retaining WallsDocument18 pagesDesign Basis and Economic Aspects of Different Types of Retaining WallsLaura HernandezNo ratings yet
- JEC+Prog+ +Combined+Rectangular+FootingDocument6 pagesJEC+Prog+ +Combined+Rectangular+FootingLaura HernandezNo ratings yet
- TDP 2 - Soils Eng. Soil Properties 1Document14 pagesTDP 2 - Soils Eng. Soil Properties 1Laura HernandezNo ratings yet
- Diseño Trapezoidal PDFDocument7 pagesDiseño Trapezoidal PDFLaura HernandezNo ratings yet
- 1 Stress III MohrDocument30 pages1 Stress III MohrLaura HernandezNo ratings yet
- Compressibility Factor Rev 1aDocument5 pagesCompressibility Factor Rev 1aPanner2009No ratings yet
- Standard Specification For Wrought Tltanium.8 Alumlnum-. Vanadium ELI (Extra Low Interstitial) Alloy (R&6401) Tor Surgicallmpl8nt Applications1Document3 pagesStandard Specification For Wrought Tltanium.8 Alumlnum-. Vanadium ELI (Extra Low Interstitial) Alloy (R&6401) Tor Surgicallmpl8nt Applications1Ignacio Hiram M RoqueNo ratings yet
- Us8748666 PDFDocument10 pagesUs8748666 PDFJuan CampeonNo ratings yet
- Boundary Conditions PDFDocument30 pagesBoundary Conditions PDFSairRamNo ratings yet
- Gcse : H O (L) H (Aq) + OH (Aq)Document9 pagesGcse : H O (L) H (Aq) + OH (Aq)Takudzwa ChademanaNo ratings yet
- CHEG 342 Solutions ManualDocument213 pagesCHEG 342 Solutions ManualChaitanya SheopurkarNo ratings yet
- Peigao Duan, Xiujun Bai, Yuping Xu, Aiyun Zhang, Feng Wang, Lei Zhang, Juan MiaoDocument9 pagesPeigao Duan, Xiujun Bai, Yuping Xu, Aiyun Zhang, Feng Wang, Lei Zhang, Juan MiaoyemresimsekNo ratings yet
- Flashcards - 5.1 Forces and Their Interactions - AQA Physics GCSE-7Document35 pagesFlashcards - 5.1 Forces and Their Interactions - AQA Physics GCSE-7wagnerleandroNo ratings yet
- Temperature Trouble Shootings and Maintance of WS-100Document8 pagesTemperature Trouble Shootings and Maintance of WS-100Mohamad Niko BSTINo ratings yet
- DLP AbbreviationDocument8 pagesDLP AbbreviationTrecita BacoNo ratings yet
- 04 Estructura Atomica-2011Document85 pages04 Estructura Atomica-2011FranciscoTestaNo ratings yet
- Wiki Quantum MechanicsDocument182 pagesWiki Quantum MechanicsArmandNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical EngineeringDocument3 pagesGeotechnical EngineeringYawer HussainNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Basic ConceptsDocument16 pagesThermodynamics Basic Conceptschincha chuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Bonding General ConceptsDocument79 pagesChapter 8 Bonding General Conceptsabd jaf100% (1)
- OIL REMOVAL USING DURIAN PEEL WASTES EFFECT OF ADSORBENT CONDITION MJIT Volume 1 No 1 56 61Document6 pagesOIL REMOVAL USING DURIAN PEEL WASTES EFFECT OF ADSORBENT CONDITION MJIT Volume 1 No 1 56 61Russel AloceljaNo ratings yet
- ENCHighlightsDocument60 pagesENCHighlightsUtpal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Language Arts Subject For Middle School - 8th Grade - Vocabulary Skills by SlidesgoDocument61 pagesLanguage Arts Subject For Middle School - 8th Grade - Vocabulary Skills by SlidesgoLilik Ali MahfudNo ratings yet
- Ch-3-A-2 Acids Bases and SaltsDocument32 pagesCh-3-A-2 Acids Bases and Saltsarnavpatel138No ratings yet
- Application Drugs of Abuse GC Mass Spectrometry 5994 1012en AgilentDocument16 pagesApplication Drugs of Abuse GC Mass Spectrometry 5994 1012en AgilentMauricio SilvestriNo ratings yet
- MSDS AquasaltDocument8 pagesMSDS Aquasaltemilio zeaNo ratings yet
- Effects of Particle Size and Its Distribution On Specific Cake Resistance During Rice Wine Microfiltration PDFDocument6 pagesEffects of Particle Size and Its Distribution On Specific Cake Resistance During Rice Wine Microfiltration PDFAlexRiveraNo ratings yet
- Medidor Vortex Vapor Modelo Prowirl l200Document103 pagesMedidor Vortex Vapor Modelo Prowirl l200mizzioNo ratings yet
- Momentum and CollisionsDocument13 pagesMomentum and CollisionsImran TabakovićNo ratings yet
- Acrodisc Syringe Filters Chemical Compatibility GuideDocument36 pagesAcrodisc Syringe Filters Chemical Compatibility GuideNermeen ElmelegaeNo ratings yet
- InorganicDocument105 pagesInorganicKishan Gupta100% (6)
- 1 Type of Flow: 1.1 Wider SectionDocument3 pages1 Type of Flow: 1.1 Wider SectionBrendan LimNo ratings yet
- George E. Totten, Lavern D. Wedeven, James R. Dickey, and Michael Anderson, Editors - Bench Testing of Industrial Fluid Lubrication and Wear Properties Used inDocument338 pagesGeorge E. Totten, Lavern D. Wedeven, James R. Dickey, and Michael Anderson, Editors - Bench Testing of Industrial Fluid Lubrication and Wear Properties Used inAbderrahim AbarayNo ratings yet
- Physic Supplymentary Guess Paper 2023Document1 pagePhysic Supplymentary Guess Paper 2023Muhammad Umer Farooq NadeemNo ratings yet