Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter - 15 Rural Devlopment
Chapter - 15 Rural Devlopment
Uploaded by
JuiÇý ßitëCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- ECCD ChecklistDocument3 pagesECCD ChecklistLorelyn Buscagan Elivera83% (6)
- Rural DevelopmentDocument29 pagesRural DevelopmentBhaskar Bhushan86% (7)
- Approaches To Economic DevelopmentDocument13 pagesApproaches To Economic DevelopmentPricia Abella100% (1)
- Josefina B. Bitonio, DPA: MPA 213 Management of Rural and Urban DevelopmentDocument44 pagesJosefina B. Bitonio, DPA: MPA 213 Management of Rural and Urban DevelopmentRonnie CampoNo ratings yet
- Rural DevelopmentDocument12 pagesRural DevelopmenttriratnacomNo ratings yet
- Rural Development - Concept and Strategies PDFDocument10 pagesRural Development - Concept and Strategies PDFashoo awasthiNo ratings yet
- Free Internet Access ProgramDocument2 pagesFree Internet Access Programnut_crackreNo ratings yet
- Media and Gender Monitor 24Document20 pagesMedia and Gender Monitor 24AMARC - Association mondiale des radiodiffuseurs communautairesNo ratings yet
- Lucena City Awarded As One of Best Lgus With Community-Based Drug Rehabilitation PracticesDocument2 pagesLucena City Awarded As One of Best Lgus With Community-Based Drug Rehabilitation PracticesCriselda Cabangon DavidNo ratings yet
- RRA and PRADocument7 pagesRRA and PRAYeasin ArafatNo ratings yet
- RapidsDocument6 pagesRapidsJeffrey Constantino PatacsilNo ratings yet
- Business Ethics - PPT NewDocument18 pagesBusiness Ethics - PPT New01712154645No ratings yet
- Republic Act No. 6713Document38 pagesRepublic Act No. 6713Ramon AvanceñaNo ratings yet
- Core Periphery (Regional Planning)Document6 pagesCore Periphery (Regional Planning)mrkkenflo80% (5)
- 20212C1 MOR 49 12 FinalPaper OLIVERDocument68 pages20212C1 MOR 49 12 FinalPaper OLIVERJoshua OliverNo ratings yet
- Povert Allevation ProgrammesDocument11 pagesPovert Allevation ProgrammesPreetha BalajiNo ratings yet
- Contingent ValuationDocument31 pagesContingent ValuationTNo ratings yet
- Distribution of IPs in The Philippines and Patterns of Social Org. - 1560846301Document5 pagesDistribution of IPs in The Philippines and Patterns of Social Org. - 1560846301Nicole Angela Ban-egNo ratings yet
- Group Activity: Competitive Analysis and Opportunities in The Marketplace of CoconutDocument3 pagesGroup Activity: Competitive Analysis and Opportunities in The Marketplace of CoconutVance UrsulumNo ratings yet
- 2020 KMME SyllabusDocument14 pages2020 KMME SyllabusNikko Rey Amoguis Mainit100% (1)
- Dao 2009-16 - 143Document2 pagesDao 2009-16 - 143denr lpddNo ratings yet
- Urban Ecology and Sustainability: by Atif Nauman (University of Gujrat)Document22 pagesUrban Ecology and Sustainability: by Atif Nauman (University of Gujrat)Camlon KhajarNo ratings yet
- Charter Change: Federalism in The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesCharter Change: Federalism in The PhilippinesPamela CabelloNo ratings yet
- The Community Mortgage ProgramDocument18 pagesThe Community Mortgage ProgramSeth Anthony CubillasNo ratings yet
- 4-Classifications of GovernmentDocument23 pages4-Classifications of GovernmentCherie DiazNo ratings yet
- Philippine Irrigation History & DevelopmentDocument11 pagesPhilippine Irrigation History & DevelopmentSheena ButacNo ratings yet
- Rural and Urban Development MeaningDocument13 pagesRural and Urban Development Meaningteddy jr AnfoneNo ratings yet
- Onu FSDR - 2022Document208 pagesOnu FSDR - 2022sofiabloemNo ratings yet
- PWDS in Rural PhilippinesDocument145 pagesPWDS in Rural PhilippinesSan TyNo ratings yet
- Role of Science and Technology To Industry, Agriculture, Fishery and CommerceDocument8 pagesRole of Science and Technology To Industry, Agriculture, Fishery and CommerceTrixiaNo ratings yet
- Nicole T. Aretaño 2BSA4 Assign#8 OPEMAN-18 Assignment#8 QuestionsDocument3 pagesNicole T. Aretaño 2BSA4 Assign#8 OPEMAN-18 Assignment#8 Questionsnicolearetano417No ratings yet
- Calabanga ProjectDocument45 pagesCalabanga ProjectEdgar SalomonNo ratings yet
- PYDPDocument55 pagesPYDP9sbwyxhnvfNo ratings yet
- Rural DevelopmentDocument19 pagesRural Developmentvikramgarg1991No ratings yet
- Comprehensive Agrarian Reform Program or RA 6657Document12 pagesComprehensive Agrarian Reform Program or RA 6657Anonymous ngDib0L2No ratings yet
- Urban GovernanceDocument2 pagesUrban GovernanceSarthak MehraNo ratings yet
- Market SegmentationDocument22 pagesMarket SegmentationCh RajkamalNo ratings yet
- Tourism Entrepreneurial Opportunities in SikkimDocument14 pagesTourism Entrepreneurial Opportunities in SikkimDebasish Batabyal100% (2)
- A Study On One Village One Product Project - Seminar24Document9 pagesA Study On One Village One Product Project - Seminar24ferdianNo ratings yet
- Business Communication FNLDocument122 pagesBusiness Communication FNLLemma Deme ResearcherNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Theories and Concepts in Rural DevelopmentDocument37 pagesLecture 1 Theories and Concepts in Rural Developmentalogngo100% (4)
- Capacity BuildingDocument12 pagesCapacity BuildingDavid Sz100% (1)
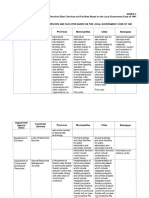
- ANNEX C Matrix of Devolved Basic Services and Facilities Based On LGC 1991Document9 pagesANNEX C Matrix of Devolved Basic Services and Facilities Based On LGC 1991Badeth AblaoNo ratings yet
- A Case Study On Rural EntrepreneurshipDocument15 pagesA Case Study On Rural Entrepreneurshipabhilashravishankar100% (9)
- Needs Wants and Demands: Marketing ConceptDocument4 pagesNeeds Wants and Demands: Marketing Conceptlyka resurreccionNo ratings yet
- Rural Development - ConceptsDocument10 pagesRural Development - Conceptsujjwal kumar 2106No ratings yet
- 1987 Philippine ConstitutionDocument36 pages1987 Philippine ConstitutionSanny Jean Rosa-utNo ratings yet
- Sri Lanka Policies Towards Urban Development Vision Strategy and Initiatives UDADocument30 pagesSri Lanka Policies Towards Urban Development Vision Strategy and Initiatives UDAADBGADNo ratings yet
- The Recruitment, Selection and RetentionDocument28 pagesThe Recruitment, Selection and RetentionFaidin NurNo ratings yet
- Agencies Found Inside The Municipal City Hall: Iceliza G. Santos Arc-2204Document6 pagesAgencies Found Inside The Municipal City Hall: Iceliza G. Santos Arc-2204Neil Carlo OcampoNo ratings yet
- Administrative Culture and Political ChaDocument13 pagesAdministrative Culture and Political ChaMarivic PenarubiaNo ratings yet
- Importance of Rural and Urban Development - 15 SlidesDocument16 pagesImportance of Rural and Urban Development - 15 SlidesMafe Angela OrejolaNo ratings yet
- Causes and Effects of UrbanizationDocument9 pagesCauses and Effects of UrbanizationHIRA SHABBIR100% (2)
- Economic & Market AppraisalDocument69 pagesEconomic & Market AppraisalSandeep Kumar SahaNo ratings yet
- Rural Marketing ImportanceDocument3 pagesRural Marketing Importanceoindrila dasguptaNo ratings yet
- Human ActsDocument4 pagesHuman ActsOr Terzulum lawrenceNo ratings yet
- Distribution Indigenous Peoples and IpraDocument32 pagesDistribution Indigenous Peoples and IpraXzyl Dawn SingsonNo ratings yet
- Econ Bohol CMPDocument2 pagesEcon Bohol CMPLiezl AloNo ratings yet
- Sustainability Reporting of Telecommunications Companies: Evidence From The PhilippinesDocument12 pagesSustainability Reporting of Telecommunications Companies: Evidence From The PhilippinescupcakeNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 RURAL DEVELOPMENT-2-6Document5 pagesUnit 1 RURAL DEVELOPMENT-2-6thedragonwarrior26No ratings yet
- Lecture 12. Concepts, Connotations, PoliciesDocument8 pagesLecture 12. Concepts, Connotations, PoliciessbbNo ratings yet
- Grade9 SyllabusDocument12 pagesGrade9 Syllabusjameshajiyavudeen001No ratings yet
- The Use of L1 in English Language Teaching (2019) PDFDocument22 pagesThe Use of L1 in English Language Teaching (2019) PDFOscar LunaNo ratings yet
- Barisal University Result 2013-14 (Kha Unit)Document7 pagesBarisal University Result 2013-14 (Kha Unit)Amader BarisalNo ratings yet
- Three Minute Thesis RulesDocument4 pagesThree Minute Thesis RulesLindsey Sais100% (2)
- RA-095630 - PROFESSIONAL TEACHER - Elementary - CAUAYAN, ISABELA - 10-2022Document37 pagesRA-095630 - PROFESSIONAL TEACHER - Elementary - CAUAYAN, ISABELA - 10-2022Liean Gumaru Angui-BodolloNo ratings yet
- Valedictory Address: Ug Pan-Research Hala Na Kay Kinahanglan Namu". We Are Always Seeking For Money To OurDocument4 pagesValedictory Address: Ug Pan-Research Hala Na Kay Kinahanglan Namu". We Are Always Seeking For Money To OurBuyingying Kang Duay SuayNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson PlanBernadeth Casidsid BuroNo ratings yet
- Perspectives of Human Resource DevelopmentDocument25 pagesPerspectives of Human Resource DevelopmentJashen Jhann GabitanoNo ratings yet
- Type Appearance CauseDocument18 pagesType Appearance CauseTasbir AbirNo ratings yet
- 2020 NAAB Conditions For AccreditationDocument15 pages2020 NAAB Conditions For AccreditationSally AlaslamiNo ratings yet
- Respect, Responsibility, and RegardDocument8 pagesRespect, Responsibility, and RegardHeather BTNo ratings yet
- Professional Teacher - Secondary (Science)Document21 pagesProfessional Teacher - Secondary (Science)PRC BaguioNo ratings yet
- The Dignity of The Human PersonDocument38 pagesThe Dignity of The Human Personcamillusong1560No ratings yet
- Dancing The Balkans in The UK or A Being PDFDocument13 pagesDancing The Balkans in The UK or A Being PDFTainá LouvenNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh Agricultural University ThesisDocument8 pagesBangladesh Agricultural University Thesisdnnvbpvh100% (2)
- Mild/Moderate Lesson Plan FormatDocument6 pagesMild/Moderate Lesson Plan Formatapi-510352498No ratings yet
- Biomimicry Learning As Inspiration For Product Design Innovation in Industrial Revolution 4.0Document18 pagesBiomimicry Learning As Inspiration For Product Design Innovation in Industrial Revolution 4.0Muhammad Syarief GirsangNo ratings yet
- 7 4 1 Lesson PlanDocument6 pages7 4 1 Lesson Planapi-279610929No ratings yet
- ThebullyofthenetDocument6 pagesThebullyofthenetapi-249396922No ratings yet
- PowerPrep Solutions Test 2 Answer KeyDocument1 pagePowerPrep Solutions Test 2 Answer KeyProgramming with broNo ratings yet
- 2015 Healthy Kids Colorado SurveyDocument22 pages2015 Healthy Kids Colorado SurveyMichael_Lee_RobertsNo ratings yet
- Proposed University of CaloocanDocument54 pagesProposed University of CaloocanKenneth RomeroNo ratings yet
- Education Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesEducation Lesson Planitskenzy10No ratings yet
- Carpentry Module 6 Grade 9 10 q2Document16 pagesCarpentry Module 6 Grade 9 10 q2Em Israel Jr.100% (2)
- Gender and Society LESSON 9: Representation of Women in Media and Masculinity and FemininityDocument6 pagesGender and Society LESSON 9: Representation of Women in Media and Masculinity and FemininityCamille AdarnaNo ratings yet
- D Epartment of Education: R Epublic of The P HilippinesDocument3 pagesD Epartment of Education: R Epublic of The P HilippinesNIMFA PADILLANo ratings yet
- 4 - Information Seeking and Acquisition Are Key Components of Inform PDFDocument28 pages4 - Information Seeking and Acquisition Are Key Components of Inform PDFUwaisNo ratings yet
- 1516S1 CCN2014 Food Hygiene Individual AssignmentDocument7 pages1516S1 CCN2014 Food Hygiene Individual AssignmentPoon Wai Shing AesonNo ratings yet
- Director School Admissions Enrollment in Chicago IL Resume Peter PaulettiDocument1 pageDirector School Admissions Enrollment in Chicago IL Resume Peter PaulettiPeterPaulettiNo ratings yet
Chapter - 15 Rural Devlopment
Chapter - 15 Rural Devlopment
Uploaded by
JuiÇý ßitëOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter - 15 Rural Devlopment
Chapter - 15 Rural Devlopment
Uploaded by
JuiÇý ßitëCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter - 15
RURAL DEVELOPMENT
RURAL DEVELOPMENT CONCEPT AND MEANING
A vast majority of people in the world live in rural area and as such, rural development assumes global importance. In the Asian context ,development primarily means rural development ,since most of the people live in rural communities. Among the Asian countries ,India is primarily a rural country with 70 percent of the total population still living in villages. Rural people wield overwhelming influence on social, economic and political activities in India .thus in the Indian context development primarily means rural development only.
Important elements identified in ANKERS definition
There
should be full utilization of the available physical and human resource in the rural areas with functional linkage. Development of agriculture and allied activities is necessary. There should be again the development of rural industries. It should aim at higher income and better living conditions of rural population and
World banks definition consists three important elements Rural
development should be viewed as a process of raising the capacity of the rural people to control their environment i.e. social, economic, cultural and political. Rural development as a process should continuously raise the capacity of the rural people to influence their total environment ,enabling them to become initiators and controllers of change in their environment rather than being merely the passive objects of external manipulation and control.
World banks definition consists three important elements 3.rural development must result in a wider distribution of benefit accruing from technical development and the participation of weaker section of the rural population in the process of development. MICHAEL TODARO1. Improvements in levels of living, including employment, education, health,and nutrition housing and a variety of social services.
MICHAEL TODARO2.decreasing inequality in the distribution of rural incomes and in rural urban balances in incomes and economic opportunities. 3.increasing the capacity of the rural sector to sustain and accelerate the pace of these improvements.
Integrated rural development
R.krishnaswamy
rightly views that rural development involves several categories of integration i.e. spatial integration. Integration of economic development with social development ,integration of total area approach and target group approach. Integration of credit with technical services ,integration of human resource development with manpower needs by dovetailing education and training programme with anticipated manpower needs.
Integrated rural development
Rural
development has assumed a considerable significance throughout the planning era. The early development schemes such as community development programmes, intensive agriculture district programme ,intensive agriculture area programme, drought prone area programme,command area development program all have aimed at rural development. Rural development therefore is now rightly viewed as a strategy designed to improve the socio economic conditions of the rural poor.
Important features of rural economy and rural society
Rural areas are described as underdeveloped or backward as per captia real income is low in rural areas as compared to that in urban areas. The Indian planning commission defined underdeveloped as which is characterized by the co-existence, in greater or or lesser degree of unutilized and underutilized manpower on the one hand and the of unexploited natural resources on the other. Owing to inadequate capital resources and lack of skill and technology, different resources in the rural areas remain unutilized or underutilized leading to backwardness of rural development.
Important features of rural economy and rural society
The main features of rural sector or rural economy in India are Greater dependence on agriculture. Large scale underdevelopment and unemployment. Poor income and indebtness. Capital deficiency.
Important features of rural economy and rural society
The main features of rural sector or rural economy in India are Low level of technology and poor extension facilities. Low level of productivity. Lack of infrastructure. Lack of basic amenities of life. Averse to population limitation. Social and cultural factors.
Scope of rural development
Developing
social consciousness. Collective decision making and collective action. Dedicated village leadership. Use of science. Development of agriculture and allied sectors. Provision of subsidiary. Development of cottage and village industries.
Interdependence between rural and urban sectors
Rural development cannot be planned and achieved in isolation ,for the overall development of India both rural and urban development become necessary. Rural development is a comprehensive programme of activities that include agriculture growth, development of village industries ,development of housing for the poor, planning for public health, family planning, and child care, and health care for livestock, education, like provision of adult education including functional literacy, development of rural transport and communication. The interdependence between rural and urban sectors clearly shows the development of both is necessary for mutual good and overall development of the country.
Important strategies of rural development
Small farmers development agency. Marginal farmers and agricultural labor
development agency. Cash scheme for rural development. Drought prone area programme (DPAP). Development of tribal areas. Minimum need programme. Development of desert area programme (DDA). Village development programme. Training of rural youth for self employment.
Important strategies of rural development
national rural development programme. (NRDP). Rural landless employment gurantee programme. Development of women and children. Council for advancement of peoples action and rural technology. Jawahar rojgar yozna. Scheme for rural artisian. Employment insurance scheme. National social asistance programme. Rural group life insurance scheme. Jawahar gram samridhi yojana.
Rural water supply and sanitation
Water supply and sanitation is a critical determinant of public health outcomes, particularly in low and lower middle income countries. The government of India supplements the drinking water supply scheme of the states by providing financial asistance under the accelerated rural water supply programme (ARWSP). The entire programme (ARWSP) was given a mission approach when the technology mission on drinking water management, called the national drinking water mission (NDWM) was introduced in 1986 and now renamed as rajiv Gandhi national drinking water mission.
Rural water supply and sanitation
The prime objectives of the mission are To ensure coverage f all rural habitations, especially to reach the unreached with an access to safe drinking water. To ensure sustainibility of the system and sources. and To tackle the water quality problems in the affected habitations.
Rural developments scope
Women
and child development. Scheduled castes development. Scheduled tribes development. Minorities development. Welfare and development of persons with disabilities. Social defence sector. Challenges and outlook.
Rural development :a critical analysis
Despite
making a spectacular progress in various fields, India faces poverty, unemployment, ignorance and socio-economic inequality. New economic forces are bringing with them new opportunities for development and for contributing to nation building . More than 70 percent of our people live in villages and 80 percent of our poor live in rural population.
Rural development :a critical analysis
poverty ,hunger and health care represent some of the major challenges before rural India. Acute poverty ,indebt ness, and illiteracy are among the factors that have combined to compel many farmers to take their own lives. Addressing unemployment in the rural area is crucial to improving the economic conditions of the people. No one should be permitted to misuse the resources or benefit from the distress of the rural poor.
You might also like
- ECCD ChecklistDocument3 pagesECCD ChecklistLorelyn Buscagan Elivera83% (6)
- Rural DevelopmentDocument29 pagesRural DevelopmentBhaskar Bhushan86% (7)
- Approaches To Economic DevelopmentDocument13 pagesApproaches To Economic DevelopmentPricia Abella100% (1)
- Josefina B. Bitonio, DPA: MPA 213 Management of Rural and Urban DevelopmentDocument44 pagesJosefina B. Bitonio, DPA: MPA 213 Management of Rural and Urban DevelopmentRonnie CampoNo ratings yet
- Rural DevelopmentDocument12 pagesRural DevelopmenttriratnacomNo ratings yet
- Rural Development - Concept and Strategies PDFDocument10 pagesRural Development - Concept and Strategies PDFashoo awasthiNo ratings yet
- Free Internet Access ProgramDocument2 pagesFree Internet Access Programnut_crackreNo ratings yet
- Media and Gender Monitor 24Document20 pagesMedia and Gender Monitor 24AMARC - Association mondiale des radiodiffuseurs communautairesNo ratings yet
- Lucena City Awarded As One of Best Lgus With Community-Based Drug Rehabilitation PracticesDocument2 pagesLucena City Awarded As One of Best Lgus With Community-Based Drug Rehabilitation PracticesCriselda Cabangon DavidNo ratings yet
- RRA and PRADocument7 pagesRRA and PRAYeasin ArafatNo ratings yet
- RapidsDocument6 pagesRapidsJeffrey Constantino PatacsilNo ratings yet
- Business Ethics - PPT NewDocument18 pagesBusiness Ethics - PPT New01712154645No ratings yet
- Republic Act No. 6713Document38 pagesRepublic Act No. 6713Ramon AvanceñaNo ratings yet
- Core Periphery (Regional Planning)Document6 pagesCore Periphery (Regional Planning)mrkkenflo80% (5)
- 20212C1 MOR 49 12 FinalPaper OLIVERDocument68 pages20212C1 MOR 49 12 FinalPaper OLIVERJoshua OliverNo ratings yet
- Povert Allevation ProgrammesDocument11 pagesPovert Allevation ProgrammesPreetha BalajiNo ratings yet
- Contingent ValuationDocument31 pagesContingent ValuationTNo ratings yet
- Distribution of IPs in The Philippines and Patterns of Social Org. - 1560846301Document5 pagesDistribution of IPs in The Philippines and Patterns of Social Org. - 1560846301Nicole Angela Ban-egNo ratings yet
- Group Activity: Competitive Analysis and Opportunities in The Marketplace of CoconutDocument3 pagesGroup Activity: Competitive Analysis and Opportunities in The Marketplace of CoconutVance UrsulumNo ratings yet
- 2020 KMME SyllabusDocument14 pages2020 KMME SyllabusNikko Rey Amoguis Mainit100% (1)
- Dao 2009-16 - 143Document2 pagesDao 2009-16 - 143denr lpddNo ratings yet
- Urban Ecology and Sustainability: by Atif Nauman (University of Gujrat)Document22 pagesUrban Ecology and Sustainability: by Atif Nauman (University of Gujrat)Camlon KhajarNo ratings yet
- Charter Change: Federalism in The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesCharter Change: Federalism in The PhilippinesPamela CabelloNo ratings yet
- The Community Mortgage ProgramDocument18 pagesThe Community Mortgage ProgramSeth Anthony CubillasNo ratings yet
- 4-Classifications of GovernmentDocument23 pages4-Classifications of GovernmentCherie DiazNo ratings yet
- Philippine Irrigation History & DevelopmentDocument11 pagesPhilippine Irrigation History & DevelopmentSheena ButacNo ratings yet
- Rural and Urban Development MeaningDocument13 pagesRural and Urban Development Meaningteddy jr AnfoneNo ratings yet
- Onu FSDR - 2022Document208 pagesOnu FSDR - 2022sofiabloemNo ratings yet
- PWDS in Rural PhilippinesDocument145 pagesPWDS in Rural PhilippinesSan TyNo ratings yet
- Role of Science and Technology To Industry, Agriculture, Fishery and CommerceDocument8 pagesRole of Science and Technology To Industry, Agriculture, Fishery and CommerceTrixiaNo ratings yet
- Nicole T. Aretaño 2BSA4 Assign#8 OPEMAN-18 Assignment#8 QuestionsDocument3 pagesNicole T. Aretaño 2BSA4 Assign#8 OPEMAN-18 Assignment#8 Questionsnicolearetano417No ratings yet
- Calabanga ProjectDocument45 pagesCalabanga ProjectEdgar SalomonNo ratings yet
- PYDPDocument55 pagesPYDP9sbwyxhnvfNo ratings yet
- Rural DevelopmentDocument19 pagesRural Developmentvikramgarg1991No ratings yet
- Comprehensive Agrarian Reform Program or RA 6657Document12 pagesComprehensive Agrarian Reform Program or RA 6657Anonymous ngDib0L2No ratings yet
- Urban GovernanceDocument2 pagesUrban GovernanceSarthak MehraNo ratings yet
- Market SegmentationDocument22 pagesMarket SegmentationCh RajkamalNo ratings yet
- Tourism Entrepreneurial Opportunities in SikkimDocument14 pagesTourism Entrepreneurial Opportunities in SikkimDebasish Batabyal100% (2)
- A Study On One Village One Product Project - Seminar24Document9 pagesA Study On One Village One Product Project - Seminar24ferdianNo ratings yet
- Business Communication FNLDocument122 pagesBusiness Communication FNLLemma Deme ResearcherNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Theories and Concepts in Rural DevelopmentDocument37 pagesLecture 1 Theories and Concepts in Rural Developmentalogngo100% (4)
- Capacity BuildingDocument12 pagesCapacity BuildingDavid Sz100% (1)
- ANNEX C Matrix of Devolved Basic Services and Facilities Based On LGC 1991Document9 pagesANNEX C Matrix of Devolved Basic Services and Facilities Based On LGC 1991Badeth AblaoNo ratings yet
- A Case Study On Rural EntrepreneurshipDocument15 pagesA Case Study On Rural Entrepreneurshipabhilashravishankar100% (9)
- Needs Wants and Demands: Marketing ConceptDocument4 pagesNeeds Wants and Demands: Marketing Conceptlyka resurreccionNo ratings yet
- Rural Development - ConceptsDocument10 pagesRural Development - Conceptsujjwal kumar 2106No ratings yet
- 1987 Philippine ConstitutionDocument36 pages1987 Philippine ConstitutionSanny Jean Rosa-utNo ratings yet
- Sri Lanka Policies Towards Urban Development Vision Strategy and Initiatives UDADocument30 pagesSri Lanka Policies Towards Urban Development Vision Strategy and Initiatives UDAADBGADNo ratings yet
- The Recruitment, Selection and RetentionDocument28 pagesThe Recruitment, Selection and RetentionFaidin NurNo ratings yet
- Agencies Found Inside The Municipal City Hall: Iceliza G. Santos Arc-2204Document6 pagesAgencies Found Inside The Municipal City Hall: Iceliza G. Santos Arc-2204Neil Carlo OcampoNo ratings yet
- Administrative Culture and Political ChaDocument13 pagesAdministrative Culture and Political ChaMarivic PenarubiaNo ratings yet
- Importance of Rural and Urban Development - 15 SlidesDocument16 pagesImportance of Rural and Urban Development - 15 SlidesMafe Angela OrejolaNo ratings yet
- Causes and Effects of UrbanizationDocument9 pagesCauses and Effects of UrbanizationHIRA SHABBIR100% (2)
- Economic & Market AppraisalDocument69 pagesEconomic & Market AppraisalSandeep Kumar SahaNo ratings yet
- Rural Marketing ImportanceDocument3 pagesRural Marketing Importanceoindrila dasguptaNo ratings yet
- Human ActsDocument4 pagesHuman ActsOr Terzulum lawrenceNo ratings yet
- Distribution Indigenous Peoples and IpraDocument32 pagesDistribution Indigenous Peoples and IpraXzyl Dawn SingsonNo ratings yet
- Econ Bohol CMPDocument2 pagesEcon Bohol CMPLiezl AloNo ratings yet
- Sustainability Reporting of Telecommunications Companies: Evidence From The PhilippinesDocument12 pagesSustainability Reporting of Telecommunications Companies: Evidence From The PhilippinescupcakeNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 RURAL DEVELOPMENT-2-6Document5 pagesUnit 1 RURAL DEVELOPMENT-2-6thedragonwarrior26No ratings yet
- Lecture 12. Concepts, Connotations, PoliciesDocument8 pagesLecture 12. Concepts, Connotations, PoliciessbbNo ratings yet
- Grade9 SyllabusDocument12 pagesGrade9 Syllabusjameshajiyavudeen001No ratings yet
- The Use of L1 in English Language Teaching (2019) PDFDocument22 pagesThe Use of L1 in English Language Teaching (2019) PDFOscar LunaNo ratings yet
- Barisal University Result 2013-14 (Kha Unit)Document7 pagesBarisal University Result 2013-14 (Kha Unit)Amader BarisalNo ratings yet
- Three Minute Thesis RulesDocument4 pagesThree Minute Thesis RulesLindsey Sais100% (2)
- RA-095630 - PROFESSIONAL TEACHER - Elementary - CAUAYAN, ISABELA - 10-2022Document37 pagesRA-095630 - PROFESSIONAL TEACHER - Elementary - CAUAYAN, ISABELA - 10-2022Liean Gumaru Angui-BodolloNo ratings yet
- Valedictory Address: Ug Pan-Research Hala Na Kay Kinahanglan Namu". We Are Always Seeking For Money To OurDocument4 pagesValedictory Address: Ug Pan-Research Hala Na Kay Kinahanglan Namu". We Are Always Seeking For Money To OurBuyingying Kang Duay SuayNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson PlanBernadeth Casidsid BuroNo ratings yet
- Perspectives of Human Resource DevelopmentDocument25 pagesPerspectives of Human Resource DevelopmentJashen Jhann GabitanoNo ratings yet
- Type Appearance CauseDocument18 pagesType Appearance CauseTasbir AbirNo ratings yet
- 2020 NAAB Conditions For AccreditationDocument15 pages2020 NAAB Conditions For AccreditationSally AlaslamiNo ratings yet
- Respect, Responsibility, and RegardDocument8 pagesRespect, Responsibility, and RegardHeather BTNo ratings yet
- Professional Teacher - Secondary (Science)Document21 pagesProfessional Teacher - Secondary (Science)PRC BaguioNo ratings yet
- The Dignity of The Human PersonDocument38 pagesThe Dignity of The Human Personcamillusong1560No ratings yet
- Dancing The Balkans in The UK or A Being PDFDocument13 pagesDancing The Balkans in The UK or A Being PDFTainá LouvenNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh Agricultural University ThesisDocument8 pagesBangladesh Agricultural University Thesisdnnvbpvh100% (2)
- Mild/Moderate Lesson Plan FormatDocument6 pagesMild/Moderate Lesson Plan Formatapi-510352498No ratings yet
- Biomimicry Learning As Inspiration For Product Design Innovation in Industrial Revolution 4.0Document18 pagesBiomimicry Learning As Inspiration For Product Design Innovation in Industrial Revolution 4.0Muhammad Syarief GirsangNo ratings yet
- 7 4 1 Lesson PlanDocument6 pages7 4 1 Lesson Planapi-279610929No ratings yet
- ThebullyofthenetDocument6 pagesThebullyofthenetapi-249396922No ratings yet
- PowerPrep Solutions Test 2 Answer KeyDocument1 pagePowerPrep Solutions Test 2 Answer KeyProgramming with broNo ratings yet
- 2015 Healthy Kids Colorado SurveyDocument22 pages2015 Healthy Kids Colorado SurveyMichael_Lee_RobertsNo ratings yet
- Proposed University of CaloocanDocument54 pagesProposed University of CaloocanKenneth RomeroNo ratings yet
- Education Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesEducation Lesson Planitskenzy10No ratings yet
- Carpentry Module 6 Grade 9 10 q2Document16 pagesCarpentry Module 6 Grade 9 10 q2Em Israel Jr.100% (2)
- Gender and Society LESSON 9: Representation of Women in Media and Masculinity and FemininityDocument6 pagesGender and Society LESSON 9: Representation of Women in Media and Masculinity and FemininityCamille AdarnaNo ratings yet
- D Epartment of Education: R Epublic of The P HilippinesDocument3 pagesD Epartment of Education: R Epublic of The P HilippinesNIMFA PADILLANo ratings yet
- 4 - Information Seeking and Acquisition Are Key Components of Inform PDFDocument28 pages4 - Information Seeking and Acquisition Are Key Components of Inform PDFUwaisNo ratings yet
- 1516S1 CCN2014 Food Hygiene Individual AssignmentDocument7 pages1516S1 CCN2014 Food Hygiene Individual AssignmentPoon Wai Shing AesonNo ratings yet
- Director School Admissions Enrollment in Chicago IL Resume Peter PaulettiDocument1 pageDirector School Admissions Enrollment in Chicago IL Resume Peter PaulettiPeterPaulettiNo ratings yet