Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Location of Single Holes (GD&T)
Location of Single Holes (GD&T)
Uploaded by
Kishor kumar Bhatia0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
130 views9 pagesThe document discusses coordinate tolerancing for single holes. It provides the measuring principle for coordinate tolerancing which involves a correction value formula to account for part thickness and distance from the indicator. The document also lists advantages of coordinate tolerancing such as being simple, permitting direct measurements, and not requiring special gauges or calculations. Disadvantages listed include resulting in square tolerance zones and being more difficult to assess clearances between mating features.
Original Description:
Geometrical Dimensioning & Tolerancing (GD&T), Design documentation, Mechanical Engineering
Original Title
Location of Single Holes ( GD&T)
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses coordinate tolerancing for single holes. It provides the measuring principle for coordinate tolerancing which involves a correction value formula to account for part thickness and distance from the indicator. The document also lists advantages of coordinate tolerancing such as being simple, permitting direct measurements, and not requiring special gauges or calculations. Disadvantages listed include resulting in square tolerance zones and being more difficult to assess clearances between mating features.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
130 views9 pagesLocation of Single Holes (GD&T)
Location of Single Holes (GD&T)
Uploaded by
Kishor kumar BhatiaThe document discusses coordinate tolerancing for single holes. It provides the measuring principle for coordinate tolerancing which involves a correction value formula to account for part thickness and distance from the indicator. The document also lists advantages of coordinate tolerancing such as being simple, permitting direct measurements, and not requiring special gauges or calculations. Disadvantages listed include resulting in square tolerance zones and being more difficult to assess clearances between mating features.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
You are on page 1of 9
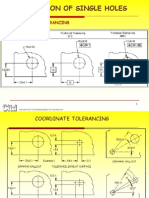
LOCATION OF SINGLE HOLES (GD&T)
Training By Kishor Bhatia
LOCATION OF SINGLE HOLES
COORDINATE TOLERANCING
COORDINATE TOLERANCING
COORDINATE TOLERANCING
COORDINATE TOLERANCING
MEASURING PRINCIPLE
C = ( R2 - R1 ) a / ( 2a + b )
C = correction value, R1 = low indicator reading, R2 = high indicator reading,
= distance between the part and the center of the dial indicator, b =part thickness,
The corrected readings are then R1 + C and R2 C
6
MEASURING COORDINATE DIMENSIONS
COORD. TOL. ADVANTAGES
Simple and easy to understand and commonly used method. Permits direct measurements with standard instruments. Does not require special gauges and calculations.
COORD. TOL. DISADVANTAGES
- Results in square or rectangular tolerance zone. - Results in un desirable accumulation in chain dimensioning. - More difficult to asses clearances between mating features. - Does not correspond to the control exercised by fixed functional gauges.
You might also like
- Asset 2022-23 Class 5 MathsDocument19 pagesAsset 2022-23 Class 5 MathsKishor kumar Bhatia100% (1)
- Imo Class 5 2022-23 Set-B Level-1Document8 pagesImo Class 5 2022-23 Set-B Level-1Kishor kumar BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Full Report - Group 2Document45 pagesFull Report - Group 2Saya Walid Chinta100% (2)
- Location of Single HolesDocument8 pagesLocation of Single HolesKumar ChowdaryNo ratings yet
- GEODESY-unittwoDocument42 pagesGEODESY-unittwoyenewabera8No ratings yet
- Chap 1-1Document53 pagesChap 1-1hudarusliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1B The Displacement of Boundary MarksDocument33 pagesChapter 1B The Displacement of Boundary MarksNaqibDarwishNo ratings yet
- KTS Quick GuideDocument19 pagesKTS Quick GuideF GIAΚNo ratings yet
- L3 Leveling PDFDocument33 pagesL3 Leveling PDFAinur NasuhaNo ratings yet
- Triangulation Resection 2011Document4 pagesTriangulation Resection 2011Leo NovanNo ratings yet
- GD&TDocument5 pagesGD&Travindra_2011No ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International ExaminationsDocument5 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International ExaminationsHubbak KhanNo ratings yet
- GD T-VolvoDocument112 pagesGD T-VolvoBESNo ratings yet
- Theodlite ResectionDocument31 pagesTheodlite ResectionRipzan xhtNo ratings yet
- 9702 PHYSICS: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2014 SeriesDocument4 pages9702 PHYSICS: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2014 Seriesojasvin seechurnNo ratings yet
- 2016 Winter Model Answer PaperDocument20 pages2016 Winter Model Answer PaperRocky JNo ratings yet
- Group 5 - Fieldwork 2 - B06Document5 pagesGroup 5 - Fieldwork 2 - B06Prince KJNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - FieldworkDocument73 pagesChapter 3 - FieldworkNur Fatin Are Tien100% (1)
- DKD-R - 4-2 Calibration of RoughnessDocument16 pagesDKD-R - 4-2 Calibration of RoughnessRafael GarzónNo ratings yet
- EXP-6-Measurement of Screw ParametersDocument2 pagesEXP-6-Measurement of Screw Parametersnavneetkpatil8409No ratings yet
- l4 Control Survey TraverseDocument23 pagesl4 Control Survey TraverseSerinaaNo ratings yet
- CE371 Survey25 26 Circular+CurvesDocument25 pagesCE371 Survey25 26 Circular+Curvesdaniel naoeNo ratings yet
- A Brief Introduction To The Measurement of Roundness and Spindle Error SeparationDocument12 pagesA Brief Introduction To The Measurement of Roundness and Spindle Error SeparationaralvoiNo ratings yet
- Ankit Yadav - 21103017 - Lab Report 4Document6 pagesAnkit Yadav - 21103017 - Lab Report 4Ankit YadavNo ratings yet
- June 2013 (v2) MS - Paper 5 CIE Physics A-LevelDocument4 pagesJune 2013 (v2) MS - Paper 5 CIE Physics A-Leveltcs440734No ratings yet
- Concentricity and Coaxiality: The Institute For Enhancement of TechnologyDocument12 pagesConcentricity and Coaxiality: The Institute For Enhancement of TechnologyMukesh DepthsNo ratings yet
- Levelling ReportDocument13 pagesLevelling Reportwanyy100% (4)
- Unit 10 Module 22Document10 pagesUnit 10 Module 22Dracov PendonNo ratings yet
- Alignment Procedure PDocument8 pagesAlignment Procedure PvinothenergyNo ratings yet
- 9709 Mathematics: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2011 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersDocument6 pages9709 Mathematics: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2011 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersInayat UllahNo ratings yet
- Field Work 1 LEVELLINGDocument17 pagesField Work 1 LEVELLINGurlallaaNo ratings yet
- Product Specification Dimensioning and TolerancingDocument64 pagesProduct Specification Dimensioning and TolerancingilroscioNo ratings yet
- gss150 ReportDocument6 pagesgss150 ReportFatihah AswaniNo ratings yet
- Topographic Survey Specification For Urban Projects-4Document51 pagesTopographic Survey Specification For Urban Projects-4JUJANo ratings yet
- 1.5 PaintsDocument65 pages1.5 Paintsprakashbudha8848No ratings yet
- Geometrical Dimenstioning and ToleranceDocument82 pagesGeometrical Dimenstioning and ToleranceSreedhar PugalendhiNo ratings yet
- 2019 Summer Model Answer Paper (Msbte Study Resources)Document12 pages2019 Summer Model Answer Paper (Msbte Study Resources)Prajwal gamerNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Fundamentals of SurveyingDocument38 pagesLesson 2 - Fundamentals of SurveyingScott AlephNo ratings yet
- Gde 333 Homework 1 (Rev)Document31 pagesGde 333 Homework 1 (Rev)Kyla CerialesNo ratings yet
- Survey Notes 2Document71 pagesSurvey Notes 2uppanapallichandu0No ratings yet
- fw3 Ce121Document17 pagesfw3 Ce121Jun-jun PaleroNo ratings yet
- 22H51A05Q6 MathwdDocument4 pages22H51A05Q6 MathwdHarshini mNo ratings yet
- Field Work No. 1 Incremental Chord and Deflection Angle MethodDocument6 pagesField Work No. 1 Incremental Chord and Deflection Angle MethodElline FernandoNo ratings yet
- PDF 20230731 022616 0000Document10 pagesPDF 20230731 022616 0000godwinayamga123No ratings yet
- 9702 PHYSICS: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2008 Question PaperDocument3 pages9702 PHYSICS: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2008 Question Papermeiling_1993No ratings yet
- 9702 s14 Ms 52 PDFDocument5 pages9702 s14 Ms 52 PDFIntikhab AlamNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Part 1Document20 pagesUnit 2 Part 1Akram AliNo ratings yet
- June 2016 Mark Scheme 51Document4 pagesJune 2016 Mark Scheme 51manyikapanashe715No ratings yet
- Civil 3D, The ModernDocument60 pagesCivil 3D, The ModernCarlos Macedo CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- Standard Traverse ReportDocument22 pagesStandard Traverse ReportSITI AISYAH ALYA BT MOHD ISMAILNo ratings yet
- GROUP NO 05 Triangulation - Survey PresentationDocument9 pagesGROUP NO 05 Triangulation - Survey PresentationGERARD HAULENo ratings yet
- 9702 w11 Ms 53Document4 pages9702 w11 Ms 53Hubbak KhanNo ratings yet
- SGF212 - Theodolite Traverse-1Document31 pagesSGF212 - Theodolite Traverse-1Derrick AmeduNo ratings yet
- Ch-26 Miscellaneous of MetrologyDocument32 pagesCh-26 Miscellaneous of MetrologyManojNo ratings yet
- fw4 Ce121Document15 pagesfw4 Ce121Jun-jun Palero100% (1)
- Triangulation - Engineering SurveyingDocument30 pagesTriangulation - Engineering SurveyingWkNo ratings yet
- MARK SCHEME For The June 2005 Question Paper: University of Cambridge International ExaminationsDocument8 pagesMARK SCHEME For The June 2005 Question Paper: University of Cambridge International ExaminationsKhalid MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Metrology: Nri Institute of TechnologyDocument55 pagesMetrology: Nri Institute of TechnologySavantNo ratings yet
- Unit Ii Me16501 PDFDocument192 pagesUnit Ii Me16501 PDFSelva BabuNo ratings yet
- Class 6 Level 1 Imo 2020 Set ADocument7 pagesClass 6 Level 1 Imo 2020 Set AKishor kumar BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Class 6 Level 1 Imo 2022 Set BDocument8 pagesClass 6 Level 1 Imo 2022 Set BKishor kumar BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Class 6 Level 1 Imo 2021 Set BDocument8 pagesClass 6 Level 1 Imo 2021 Set BKishor kumar BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Class 6 Level 1 Imo 2020 Set BDocument7 pagesClass 6 Level 1 Imo 2020 Set BKishor kumar BhatiaNo ratings yet
- IMO Class 6 - 2023-24 Set ADocument8 pagesIMO Class 6 - 2023-24 Set AKishor kumar Bhatia100% (1)
- Asset 2022-23 Class 5 ScienceDocument16 pagesAsset 2022-23 Class 5 ScienceKishor kumar BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Class 6 Level 1 Imo 2018 Set ADocument7 pagesClass 6 Level 1 Imo 2018 Set AKishor kumar BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Suggestion To PM of India - Banking SectorDocument1 pageSuggestion To PM of India - Banking SectorKishor kumar BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Class 6 Level 1 Imo 2022 Set BDocument8 pagesClass 6 Level 1 Imo 2022 Set BKishor kumar BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Class 11th and 12th For School, Mains Level, IIT Advance & NEETDocument3 pagesChemistry Class 11th and 12th For School, Mains Level, IIT Advance & NEETKishor kumar BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Suggestion To PM of India 27 Personal-Information-PrivacyDocument3 pagesSuggestion To PM of India 27 Personal-Information-PrivacyKishor kumar BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Class 2 Imo Paper 2014 Set ADocument8 pagesClass 2 Imo Paper 2014 Set AKishor kumar BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Solution IMT-120 3Document8 pagesSolution IMT-120 3Kishor kumar BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Suggestion To PM of India 32 Post OfficeDocument4 pagesSuggestion To PM of India 32 Post OfficeKishor kumar BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Suggestion To PM of India 23-Banking-SectorDocument2 pagesSuggestion To PM of India 23-Banking-SectorKishor kumar BhatiaNo ratings yet
- DMRCDocument1 pageDMRCKishor kumar BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Geometrical Dimensioning & Tolerancing - Review of Indian StandardsDocument43 pagesGeometrical Dimensioning & Tolerancing - Review of Indian StandardsKishor kumar Bhatia100% (3)
- Geometrical Tolerancing (GD&T)Document12 pagesGeometrical Tolerancing (GD&T)Kishor kumar BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Advance English Language - LearningDocument114 pagesAdvance English Language - LearningKishor kumar Bhatia100% (2)
- Location of Miscellaneous Types - GD&TDocument9 pagesLocation of Miscellaneous Types - GD&TKishor kumar Bhatia100% (1)
- Pattern CastingDocument17 pagesPattern CastingKishor kumar Bhatia100% (1)
- Tolerance Accumulation and Analysis (GD&T)Document80 pagesTolerance Accumulation and Analysis (GD&T)Kishor kumar Bhatia50% (4)
- Coplanarity & Symmetry - GD&TDocument9 pagesCoplanarity & Symmetry - GD&TKishor kumar BhatiaNo ratings yet