Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 1 Classification of Mo
Chapter 1 Classification of Mo
Uploaded by
Faizaltul DianiCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Gentile's Taxonomy of Motor SkillsDocument1 pageGentile's Taxonomy of Motor Skillslionelxxl100% (1)
- The Burden of Visual Truth: The Role of Photojournalism in Mediating RealityDocument43 pagesThe Burden of Visual Truth: The Role of Photojournalism in Mediating RealityVictor Andrade0% (2)
- Pe 101 Module 2 Physical FitnessDocument20 pagesPe 101 Module 2 Physical FitnessMISSY BETH VILLONESNo ratings yet
- Spec Pe 09 Movement Education Module 1Document12 pagesSpec Pe 09 Movement Education Module 1Joas Refil100% (1)
- Basic Concepts of Applied Motor Learning and Performance: GROUP 2 - Presenter Name: CALICDAN, PIADocument44 pagesBasic Concepts of Applied Motor Learning and Performance: GROUP 2 - Presenter Name: CALICDAN, PIAPia Mae Zenith Calicdan100% (1)
- 1styear Principles of Motor Module 2Document13 pages1styear Principles of Motor Module 2Zedy Gulles100% (4)
- Different Types of TournamentsDocument4 pagesDifferent Types of TournamentsKurk DaugdaugNo ratings yet
- Personality and Sports: Prepared By: Janine Bisenio-BetchaydaDocument44 pagesPersonality and Sports: Prepared By: Janine Bisenio-BetchaydaJanine BisenioNo ratings yet
- ARTS1Document5 pagesARTS1Alphonse Rossaint Sambrano0% (1)
- Project Team Building, Conflict NegotiationDocument47 pagesProject Team Building, Conflict NegotiationChan Hy100% (1)
- D Zurilla - Goldfried, 1971Document20 pagesD Zurilla - Goldfried, 1971PaolaNo ratings yet
- Classification of Motor Skills 1st Lecture PDFDocument15 pagesClassification of Motor Skills 1st Lecture PDFVictor PetcuNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Motor Learning and Motor PerformanceDocument10 pagesLesson 1 Motor Learning and Motor PerformanceMarkanthony BaguioNo ratings yet
- One Dimension Motor Skill Classification SystemsDocument3 pagesOne Dimension Motor Skill Classification SystemsVincent Jay LatorzaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Motor AbilitiesDocument18 pagesChapter 3 Motor AbilitiesRoszalina InaNo ratings yet
- History of Athletics and The Track & FieldDocument12 pagesHistory of Athletics and The Track & FieldDiana Rose L. BautistaNo ratings yet
- Foundation-of-Active-Lifestyle PeDocument12 pagesFoundation-of-Active-Lifestyle PeMathew Batan100% (1)
- Appliedmotorlearning PPT No.1Document13 pagesAppliedmotorlearning PPT No.1Jojo JojoNo ratings yet
- Ontemporary Issues in P.E and SportsDocument13 pagesOntemporary Issues in P.E and SportsJudy Ann TumaraoNo ratings yet
- The History of AthleticsDocument59 pagesThe History of AthleticsLev Mazed SulioNo ratings yet
- 2week 2 Movement Eucation Movement Education Framework ConceptDocument17 pages2week 2 Movement Eucation Movement Education Framework ConceptMartin Paul Embile GabitoNo ratings yet
- Basic P.E Rhythmic ActvityDocument17 pagesBasic P.E Rhythmic ActvityJay R BayaniNo ratings yet
- Pe 3 Syllabus - GymnasticsDocument7 pagesPe 3 Syllabus - GymnasticsLOUISE DOROTHY PARAISO100% (1)
- Panigas - PE603-TRENDS-AND-ISSUES-IN-PHYSICAL-EDUCATIONDocument7 pagesPanigas - PE603-TRENDS-AND-ISSUES-IN-PHYSICAL-EDUCATIONracmaNo ratings yet
- PE LET Individual Dual and Combative Sports With Out TOSDocument28 pagesPE LET Individual Dual and Combative Sports With Out TOSGerald Mapalo Factor67% (3)
- Department of Teacher Education: Gpe 1 - Course SyllabusDocument14 pagesDepartment of Teacher Education: Gpe 1 - Course SyllabusJaymar Reponte100% (1)
- Lesson 2 The Measurement of Motor PerformanceDocument67 pagesLesson 2 The Measurement of Motor PerformanceDrift AlvinNo ratings yet
- Basic Movement PatternsDocument3 pagesBasic Movement Patterns1234567werNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3: Exercise Variables and PrinciplesDocument31 pagesLESSON 3: Exercise Variables and PrinciplesCapulong Kimberly100% (1)
- Volleyball Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesVolleyball Lesson PlanJunela Maimai Suclatan0% (1)
- Introduction To Physical EducationDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Physical EducationLOVELYJEANBALBERO VALLESERA100% (1)
- FLS Mjpe 205 Physiology of Exercise and Physical ActivityDocument11 pagesFLS Mjpe 205 Physiology of Exercise and Physical ActivitySantos Jewel100% (1)
- Name of Student: JURILLA MARK KC B. Course: BPED 2A Address: Purok: Gumamela Brgy. Binubuhan, Bago City Teacher: MS - MIA BALISTADocument14 pagesName of Student: JURILLA MARK KC B. Course: BPED 2A Address: Purok: Gumamela Brgy. Binubuhan, Bago City Teacher: MS - MIA BALISTAMark Barbo Jurilla100% (1)
- Unit1 Fitness and Wellness For AllDocument7 pagesUnit1 Fitness and Wellness For AllJames Andrei LeonidaNo ratings yet
- Propose Module PEd 103Document14 pagesPropose Module PEd 103Destiny Rose TabucaoNo ratings yet
- FITT & Training PrinciplesDocument33 pagesFITT & Training Principlescsarimah csarimahNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Principles of MotorDocument25 pagesModule 5 Principles of Motorzedy gullesNo ratings yet
- 6 Pillars of Ethics and SportsmanshipDocument6 pages6 Pillars of Ethics and SportsmanshipZan Retsiger100% (1)
- Prelim Term Lesson Physical EducationDocument6 pagesPrelim Term Lesson Physical EducationChris Angelo TorillosNo ratings yet
- 005a Movement ConceptsDocument2 pages005a Movement ConceptsMalej Đào KyblNo ratings yet
- 3 Pe Unit 1 Sports OfficiatingDocument31 pages3 Pe Unit 1 Sports OfficiatingCharmaine Ramos0% (1)
- College of Saint John Paul (Ii) Arts and SciencesDocument17 pagesCollege of Saint John Paul (Ii) Arts and SciencesKoolecarla BernardoNo ratings yet
- The 7 Principles of Exercise and Sport Training: IndividualityDocument2 pagesThe 7 Principles of Exercise and Sport Training: IndividualityTah IehNo ratings yet
- Team Sports: Volleyball: ObjectivesDocument24 pagesTeam Sports: Volleyball: ObjectivesKei EvaristoNo ratings yet
- Elements of BiomechanicsDocument4 pagesElements of Biomechanicsnikita100% (1)
- Skill ClassificationDocument4 pagesSkill ClassificationAhmad KhuwarizmyNo ratings yet
- Methods of TrainingDocument26 pagesMethods of TrainingDavid Johnson50% (2)
- Sociological Foundations of Physical EduDocument15 pagesSociological Foundations of Physical EduIsabelle Grace LosabiaNo ratings yet
- Basketball DiscussionDocument34 pagesBasketball DiscussionJadeal28No ratings yet
- Historical Development of Physical EducaDocument37 pagesHistorical Development of Physical EducaMark Johnson San JuanNo ratings yet
- Philosophy of P.EDocument2 pagesPhilosophy of P.EArchan Dom ReyesNo ratings yet
- Department of Teacher Education: BPE 222 - Course SyllabusDocument11 pagesDepartment of Teacher Education: BPE 222 - Course SyllabusEric Pascual Indie100% (1)
- TRAD - DANCES - Final ExamDocument4 pagesTRAD - DANCES - Final ExamJvnRodz P GmlmNo ratings yet
- Pem4 Principles of Motor Control and Learning of Exercise, Sports and DanceDocument23 pagesPem4 Principles of Motor Control and Learning of Exercise, Sports and DanceNelissa Pearl Coloma100% (2)
- Basic Swimming Lesson 1 - Introduction To SwimmingDocument53 pagesBasic Swimming Lesson 1 - Introduction To SwimmingKurt Izen OrtegaNo ratings yet
- College of Education: Course Syllabus in Foundations of Physical ActivitiesDocument6 pagesCollege of Education: Course Syllabus in Foundations of Physical ActivitiesCamille Ann Faigao FamisanNo ratings yet
- Movement Competency Training Module No. 14Document3 pagesMovement Competency Training Module No. 14Jhon Keneth NamiasNo ratings yet
- Arousal, Stress and Anxiety in SportsDocument33 pagesArousal, Stress and Anxiety in SportsJC CambriNo ratings yet
- Recommended Level or Amount of Physical Acivity To Maintain Good Health?Document15 pagesRecommended Level or Amount of Physical Acivity To Maintain Good Health?incognitoNo ratings yet
- Components of Physical Fitnes: Health Related Fitness ComponentsDocument3 pagesComponents of Physical Fitnes: Health Related Fitness ComponentsAnn Lei YusonNo ratings yet
- Physiology Movement 52Document25 pagesPhysiology Movement 52Jay Lure BaguioNo ratings yet
- Pathfit 2 Presentation - PPTX 3Document68 pagesPathfit 2 Presentation - PPTX 3Kimberly Pascua ArizNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Classification of Motor Skills v2Document12 pagesLesson 1 Classification of Motor Skills v2Drift AlvinNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Classification of Motor SkillsDocument54 pagesLesson 1 Classification of Motor SkillsDrift AlvinNo ratings yet
- EssaS TopicS With AnswersDocument677 pagesEssaS TopicS With AnswersSaiswareeNo ratings yet
- Character Analysis OrganizersDocument6 pagesCharacter Analysis OrganizersnellytusiimeNo ratings yet
- Impact of Social Media On Emotional Health of The Senior Highschool JAM (AutoRecovered)Document21 pagesImpact of Social Media On Emotional Health of The Senior Highschool JAM (AutoRecovered)Jasmin CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Day 5 YukiDocument1 pageLesson Plan Day 5 Yukiapi-303126816No ratings yet
- Annotated Bibliography 1 For Mse RedoDocument2 pagesAnnotated Bibliography 1 For Mse Redoapi-533483656No ratings yet
- Review of Related Literature SampleDocument6 pagesReview of Related Literature Samplegago kaNo ratings yet
- MurrayDocument31 pagesMurrayayeshaNo ratings yet
- Reverse Your Break Up - 15 Ways To Win Your Ex BackDocument11 pagesReverse Your Break Up - 15 Ways To Win Your Ex Backfyou@hotmail.co.nzNo ratings yet
- Jurnal 4Document16 pagesJurnal 4Suryo UtomoNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting DevelopmentDocument38 pagesFactors Affecting DevelopmentMariel Jane Mendoza - DucotNo ratings yet
- Google Classroom As A Tool For Active LearningDocument7 pagesGoogle Classroom As A Tool For Active LearningIkhram JohariNo ratings yet
- Assignment Mass Media PDFDocument4 pagesAssignment Mass Media PDFHamza HuzefaNo ratings yet
- A Brief History of Mental Health CareDocument3 pagesA Brief History of Mental Health Carexiang jinNo ratings yet
- THANH NGA NGUYEN ThesisDocument229 pagesTHANH NGA NGUYEN ThesisThu NguyenNo ratings yet
- Anthropocentrism and Ecocentrism: The Quest For A New WorldviewDocument7 pagesAnthropocentrism and Ecocentrism: The Quest For A New Worldviewyghj21No ratings yet
- Dap PaperDocument6 pagesDap Paperapi-539933367No ratings yet
- A. Community OrganizationDocument11 pagesA. Community OrganizationCymbeline Siena-MartinezNo ratings yet
- Velazquez-Guest SpeakerDocument4 pagesVelazquez-Guest Speakerapi-318497518No ratings yet
- Diana's DisappointmentDocument2 pagesDiana's Disappointmentasdftfddrd xyrxryNo ratings yet
- ENGCOY, WM. M1 Lesson 2Document11 pagesENGCOY, WM. M1 Lesson 2ansaf100% (1)
- Carol C Choo, Roger C Ho - Clinical Psychology Casebook Across The Lifespan-Springer Singapore (2019)Document100 pagesCarol C Choo, Roger C Ho - Clinical Psychology Casebook Across The Lifespan-Springer Singapore (2019)Yein Oh100% (1)
- Meanings, Preferences, and Power Among Men Having Sex With Men in ManilaDocument21 pagesMeanings, Preferences, and Power Among Men Having Sex With Men in ManilaJoo XanderNo ratings yet
- Interview Evaluation FormDocument2 pagesInterview Evaluation FormIdorenyin AnkohNo ratings yet
- Abhidhamma Chart Cetasika Mental FactorsDocument2 pagesAbhidhamma Chart Cetasika Mental FactorsCalvin Sweatsa Lot0% (1)
- La Paz National High SchoolDocument19 pagesLa Paz National High SchoolBon Ivan FirmezaNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Self Module 1Document4 pagesUnderstanding The Self Module 1Billie MatchocaNo ratings yet
Chapter 1 Classification of Mo
Chapter 1 Classification of Mo
Uploaded by
Faizaltul DianiOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 1 Classification of Mo
Chapter 1 Classification of Mo
Uploaded by
Faizaltul DianiCopyright:
Available Formats
.
Chapter 1
The Classification of Motor Skills
Concept: Motor skills can be classified into general categories
The Study of Motor Skills: Motor Learning, Control, and Development
Motor skills require body, head,
and/or limb movement to achieve its goal Motor learning involves the study of:
Acquisition of new skills Performance enhancement of well-learned skills Reacquisition of skills following injury, disease, etc.
The study of motor skills:(cont.)
Motor control involves the study of:
How the neuromuscular system functions to enable coordinated movement
While learning a new skill While performing a well-learned skill
Motor development involves the study of:
Human development from infancy to old age
Issues related to either motor learning or motor control
University of Delaware Motor-Control Research
Christopher Knight
Development of upper limb proprioceptive accuracy in children and adolescents
Daniel J. Goble a, Colleen A. Lewis a,b, Edward A. Hurvitz b, Susan H. Brown
Terms Related to Motor Skills: Skills, Actions, and Movement
Skills - Tasks or activities that have specific goals to achieve (action goals) Motor skills vs. cognitive skills Actions Term often used as synonymous with the term motor skills Movements Behavioral characteristics of a specific limb or a combination of limbs
One-Dimension Classification Systems
Categorize skills according to one common characteristic Divided into two categories, each representing extreme ends of a continuum
One-Dimension Classification Systems, contd
Three motor skill classifications that use onedimension approaches [see Figure 1.2]:
1. Size of primary musculature required 2. Specificity of where actions begin or end 3. Stability of the environment context
1. Size of Primary Musculature Required
The benefit of a continuum approach to skill classification
Some motor skills involve both types to achieve the action goal and would be located between the two points
2. Specificity of Where Actions Begin or End
Two main categories:
Discrete motor skills - specified beginning and end points, usually require a simple movement
e.g. flipping a light switch
Continuous motor skills - arbitrary beginning and end points; usually involve repetitive movements
e.g. steering a car
Combination category: Serial motor skills
Involve a continuous series of discrete skills
e.g. shifting gears in a stick shift automobile
3. Stability of the Environmental Context
Two main concepts:
Closed motor skills involve a stationary supporting surface, object, and/or other people; performer determines when to begin the action
e.g. picking up a cup while seated at a table
Open motor skill involve supporting surface, object, and/or other people in motion; environment features determines when to begin the action
e.g. catching a thrown ball
A Two-Dimension Classification System
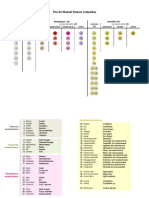
Gentiles Taxonomy of Motor Skills
(Table 1.1)
Taxonomy - A classification system organized according to relationships among the component characteristics of what is being classified
Gentiles Two-Dimensions Taxonomy, contd
Two-dimensions of the taxonomy:
1.Environmental context 2.Function of the action
1.Environmental context
Two characteristics Regulatory conditions
Characteristics of environment that control the movement characteristics of an action
Intertrial variability
Whether the regulatory conditions are the same or different from one performance attempt to another
Gentiles Two-Dimensions Taxonomy, contd
2. Function of the action Two characteristics Body orientation
Does the skill require the person to move from one location to another or to stay in the same location
body stability, - maintain same location body transport change location (actively or passively)
Object manipulation
Summary of the 2 Dimensions
4 characteristics can describe any motor skill:
2 Environmental context characteristics
1. Are the regulatory conditions stationary or in motion? 2. Do the regulatory conditions change from trial to trial?
2 Action function characteristics
1. Does the action goal require maintaining the body in the same location or transporting the body from one place to another? 2. Is an object manipulated?
The 16 Skill Categories
The interaction of the four environmental context characteristics and the four action function characteristics creates 16 skill categories Table 1.1 shows Gentiles original presentation of the taxonomy along with two examples of skill in each category
Characteristics of Gentiles Taxonomy
Each category puts different demands on the performer Skill complexity basis for taxonomy organization
From simplest [#1A] diagonally to most complex [#4D]
Complexity increases when a motor skill involves one or more of the following:
Open environment Trial-to-trial variability Object to manipulate Body transport
Practical Uses of Gentiles Taxonomy
Guide for evaluating motor performance capabilities, limitations, and deficiencies Systematic basis for selecting progressions of functionally appropriate activities to
increase performance capabilities overcome performance deficiencies
Chart persons progress developing a profile of competencies
You might also like
- Gentile's Taxonomy of Motor SkillsDocument1 pageGentile's Taxonomy of Motor Skillslionelxxl100% (1)
- The Burden of Visual Truth: The Role of Photojournalism in Mediating RealityDocument43 pagesThe Burden of Visual Truth: The Role of Photojournalism in Mediating RealityVictor Andrade0% (2)
- Pe 101 Module 2 Physical FitnessDocument20 pagesPe 101 Module 2 Physical FitnessMISSY BETH VILLONESNo ratings yet
- Spec Pe 09 Movement Education Module 1Document12 pagesSpec Pe 09 Movement Education Module 1Joas Refil100% (1)
- Basic Concepts of Applied Motor Learning and Performance: GROUP 2 - Presenter Name: CALICDAN, PIADocument44 pagesBasic Concepts of Applied Motor Learning and Performance: GROUP 2 - Presenter Name: CALICDAN, PIAPia Mae Zenith Calicdan100% (1)
- 1styear Principles of Motor Module 2Document13 pages1styear Principles of Motor Module 2Zedy Gulles100% (4)
- Different Types of TournamentsDocument4 pagesDifferent Types of TournamentsKurk DaugdaugNo ratings yet
- Personality and Sports: Prepared By: Janine Bisenio-BetchaydaDocument44 pagesPersonality and Sports: Prepared By: Janine Bisenio-BetchaydaJanine BisenioNo ratings yet
- ARTS1Document5 pagesARTS1Alphonse Rossaint Sambrano0% (1)
- Project Team Building, Conflict NegotiationDocument47 pagesProject Team Building, Conflict NegotiationChan Hy100% (1)
- D Zurilla - Goldfried, 1971Document20 pagesD Zurilla - Goldfried, 1971PaolaNo ratings yet
- Classification of Motor Skills 1st Lecture PDFDocument15 pagesClassification of Motor Skills 1st Lecture PDFVictor PetcuNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Motor Learning and Motor PerformanceDocument10 pagesLesson 1 Motor Learning and Motor PerformanceMarkanthony BaguioNo ratings yet
- One Dimension Motor Skill Classification SystemsDocument3 pagesOne Dimension Motor Skill Classification SystemsVincent Jay LatorzaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Motor AbilitiesDocument18 pagesChapter 3 Motor AbilitiesRoszalina InaNo ratings yet
- History of Athletics and The Track & FieldDocument12 pagesHistory of Athletics and The Track & FieldDiana Rose L. BautistaNo ratings yet
- Foundation-of-Active-Lifestyle PeDocument12 pagesFoundation-of-Active-Lifestyle PeMathew Batan100% (1)
- Appliedmotorlearning PPT No.1Document13 pagesAppliedmotorlearning PPT No.1Jojo JojoNo ratings yet
- Ontemporary Issues in P.E and SportsDocument13 pagesOntemporary Issues in P.E and SportsJudy Ann TumaraoNo ratings yet
- The History of AthleticsDocument59 pagesThe History of AthleticsLev Mazed SulioNo ratings yet
- 2week 2 Movement Eucation Movement Education Framework ConceptDocument17 pages2week 2 Movement Eucation Movement Education Framework ConceptMartin Paul Embile GabitoNo ratings yet
- Basic P.E Rhythmic ActvityDocument17 pagesBasic P.E Rhythmic ActvityJay R BayaniNo ratings yet
- Pe 3 Syllabus - GymnasticsDocument7 pagesPe 3 Syllabus - GymnasticsLOUISE DOROTHY PARAISO100% (1)
- Panigas - PE603-TRENDS-AND-ISSUES-IN-PHYSICAL-EDUCATIONDocument7 pagesPanigas - PE603-TRENDS-AND-ISSUES-IN-PHYSICAL-EDUCATIONracmaNo ratings yet
- PE LET Individual Dual and Combative Sports With Out TOSDocument28 pagesPE LET Individual Dual and Combative Sports With Out TOSGerald Mapalo Factor67% (3)
- Department of Teacher Education: Gpe 1 - Course SyllabusDocument14 pagesDepartment of Teacher Education: Gpe 1 - Course SyllabusJaymar Reponte100% (1)
- Lesson 2 The Measurement of Motor PerformanceDocument67 pagesLesson 2 The Measurement of Motor PerformanceDrift AlvinNo ratings yet
- Basic Movement PatternsDocument3 pagesBasic Movement Patterns1234567werNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3: Exercise Variables and PrinciplesDocument31 pagesLESSON 3: Exercise Variables and PrinciplesCapulong Kimberly100% (1)
- Volleyball Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesVolleyball Lesson PlanJunela Maimai Suclatan0% (1)
- Introduction To Physical EducationDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Physical EducationLOVELYJEANBALBERO VALLESERA100% (1)
- FLS Mjpe 205 Physiology of Exercise and Physical ActivityDocument11 pagesFLS Mjpe 205 Physiology of Exercise and Physical ActivitySantos Jewel100% (1)
- Name of Student: JURILLA MARK KC B. Course: BPED 2A Address: Purok: Gumamela Brgy. Binubuhan, Bago City Teacher: MS - MIA BALISTADocument14 pagesName of Student: JURILLA MARK KC B. Course: BPED 2A Address: Purok: Gumamela Brgy. Binubuhan, Bago City Teacher: MS - MIA BALISTAMark Barbo Jurilla100% (1)
- Unit1 Fitness and Wellness For AllDocument7 pagesUnit1 Fitness and Wellness For AllJames Andrei LeonidaNo ratings yet
- Propose Module PEd 103Document14 pagesPropose Module PEd 103Destiny Rose TabucaoNo ratings yet
- FITT & Training PrinciplesDocument33 pagesFITT & Training Principlescsarimah csarimahNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Principles of MotorDocument25 pagesModule 5 Principles of Motorzedy gullesNo ratings yet
- 6 Pillars of Ethics and SportsmanshipDocument6 pages6 Pillars of Ethics and SportsmanshipZan Retsiger100% (1)
- Prelim Term Lesson Physical EducationDocument6 pagesPrelim Term Lesson Physical EducationChris Angelo TorillosNo ratings yet
- 005a Movement ConceptsDocument2 pages005a Movement ConceptsMalej Đào KyblNo ratings yet
- 3 Pe Unit 1 Sports OfficiatingDocument31 pages3 Pe Unit 1 Sports OfficiatingCharmaine Ramos0% (1)
- College of Saint John Paul (Ii) Arts and SciencesDocument17 pagesCollege of Saint John Paul (Ii) Arts and SciencesKoolecarla BernardoNo ratings yet
- The 7 Principles of Exercise and Sport Training: IndividualityDocument2 pagesThe 7 Principles of Exercise and Sport Training: IndividualityTah IehNo ratings yet
- Team Sports: Volleyball: ObjectivesDocument24 pagesTeam Sports: Volleyball: ObjectivesKei EvaristoNo ratings yet
- Elements of BiomechanicsDocument4 pagesElements of Biomechanicsnikita100% (1)
- Skill ClassificationDocument4 pagesSkill ClassificationAhmad KhuwarizmyNo ratings yet
- Methods of TrainingDocument26 pagesMethods of TrainingDavid Johnson50% (2)
- Sociological Foundations of Physical EduDocument15 pagesSociological Foundations of Physical EduIsabelle Grace LosabiaNo ratings yet
- Basketball DiscussionDocument34 pagesBasketball DiscussionJadeal28No ratings yet
- Historical Development of Physical EducaDocument37 pagesHistorical Development of Physical EducaMark Johnson San JuanNo ratings yet
- Philosophy of P.EDocument2 pagesPhilosophy of P.EArchan Dom ReyesNo ratings yet
- Department of Teacher Education: BPE 222 - Course SyllabusDocument11 pagesDepartment of Teacher Education: BPE 222 - Course SyllabusEric Pascual Indie100% (1)
- TRAD - DANCES - Final ExamDocument4 pagesTRAD - DANCES - Final ExamJvnRodz P GmlmNo ratings yet
- Pem4 Principles of Motor Control and Learning of Exercise, Sports and DanceDocument23 pagesPem4 Principles of Motor Control and Learning of Exercise, Sports and DanceNelissa Pearl Coloma100% (2)
- Basic Swimming Lesson 1 - Introduction To SwimmingDocument53 pagesBasic Swimming Lesson 1 - Introduction To SwimmingKurt Izen OrtegaNo ratings yet
- College of Education: Course Syllabus in Foundations of Physical ActivitiesDocument6 pagesCollege of Education: Course Syllabus in Foundations of Physical ActivitiesCamille Ann Faigao FamisanNo ratings yet
- Movement Competency Training Module No. 14Document3 pagesMovement Competency Training Module No. 14Jhon Keneth NamiasNo ratings yet
- Arousal, Stress and Anxiety in SportsDocument33 pagesArousal, Stress and Anxiety in SportsJC CambriNo ratings yet
- Recommended Level or Amount of Physical Acivity To Maintain Good Health?Document15 pagesRecommended Level or Amount of Physical Acivity To Maintain Good Health?incognitoNo ratings yet
- Components of Physical Fitnes: Health Related Fitness ComponentsDocument3 pagesComponents of Physical Fitnes: Health Related Fitness ComponentsAnn Lei YusonNo ratings yet
- Physiology Movement 52Document25 pagesPhysiology Movement 52Jay Lure BaguioNo ratings yet
- Pathfit 2 Presentation - PPTX 3Document68 pagesPathfit 2 Presentation - PPTX 3Kimberly Pascua ArizNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Classification of Motor Skills v2Document12 pagesLesson 1 Classification of Motor Skills v2Drift AlvinNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Classification of Motor SkillsDocument54 pagesLesson 1 Classification of Motor SkillsDrift AlvinNo ratings yet
- EssaS TopicS With AnswersDocument677 pagesEssaS TopicS With AnswersSaiswareeNo ratings yet
- Character Analysis OrganizersDocument6 pagesCharacter Analysis OrganizersnellytusiimeNo ratings yet
- Impact of Social Media On Emotional Health of The Senior Highschool JAM (AutoRecovered)Document21 pagesImpact of Social Media On Emotional Health of The Senior Highschool JAM (AutoRecovered)Jasmin CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Day 5 YukiDocument1 pageLesson Plan Day 5 Yukiapi-303126816No ratings yet
- Annotated Bibliography 1 For Mse RedoDocument2 pagesAnnotated Bibliography 1 For Mse Redoapi-533483656No ratings yet
- Review of Related Literature SampleDocument6 pagesReview of Related Literature Samplegago kaNo ratings yet
- MurrayDocument31 pagesMurrayayeshaNo ratings yet
- Reverse Your Break Up - 15 Ways To Win Your Ex BackDocument11 pagesReverse Your Break Up - 15 Ways To Win Your Ex Backfyou@hotmail.co.nzNo ratings yet
- Jurnal 4Document16 pagesJurnal 4Suryo UtomoNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting DevelopmentDocument38 pagesFactors Affecting DevelopmentMariel Jane Mendoza - DucotNo ratings yet
- Google Classroom As A Tool For Active LearningDocument7 pagesGoogle Classroom As A Tool For Active LearningIkhram JohariNo ratings yet
- Assignment Mass Media PDFDocument4 pagesAssignment Mass Media PDFHamza HuzefaNo ratings yet
- A Brief History of Mental Health CareDocument3 pagesA Brief History of Mental Health Carexiang jinNo ratings yet
- THANH NGA NGUYEN ThesisDocument229 pagesTHANH NGA NGUYEN ThesisThu NguyenNo ratings yet
- Anthropocentrism and Ecocentrism: The Quest For A New WorldviewDocument7 pagesAnthropocentrism and Ecocentrism: The Quest For A New Worldviewyghj21No ratings yet
- Dap PaperDocument6 pagesDap Paperapi-539933367No ratings yet
- A. Community OrganizationDocument11 pagesA. Community OrganizationCymbeline Siena-MartinezNo ratings yet
- Velazquez-Guest SpeakerDocument4 pagesVelazquez-Guest Speakerapi-318497518No ratings yet
- Diana's DisappointmentDocument2 pagesDiana's Disappointmentasdftfddrd xyrxryNo ratings yet
- ENGCOY, WM. M1 Lesson 2Document11 pagesENGCOY, WM. M1 Lesson 2ansaf100% (1)
- Carol C Choo, Roger C Ho - Clinical Psychology Casebook Across The Lifespan-Springer Singapore (2019)Document100 pagesCarol C Choo, Roger C Ho - Clinical Psychology Casebook Across The Lifespan-Springer Singapore (2019)Yein Oh100% (1)
- Meanings, Preferences, and Power Among Men Having Sex With Men in ManilaDocument21 pagesMeanings, Preferences, and Power Among Men Having Sex With Men in ManilaJoo XanderNo ratings yet
- Interview Evaluation FormDocument2 pagesInterview Evaluation FormIdorenyin AnkohNo ratings yet
- Abhidhamma Chart Cetasika Mental FactorsDocument2 pagesAbhidhamma Chart Cetasika Mental FactorsCalvin Sweatsa Lot0% (1)
- La Paz National High SchoolDocument19 pagesLa Paz National High SchoolBon Ivan FirmezaNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Self Module 1Document4 pagesUnderstanding The Self Module 1Billie MatchocaNo ratings yet