Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Time For Replication, Transcription Time For Cell Division: No Gene Expression
Time For Replication, Transcription Time For Cell Division: No Gene Expression
Uploaded by
ibanitescuOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Time For Replication, Transcription Time For Cell Division: No Gene Expression
Time For Replication, Transcription Time For Cell Division: No Gene Expression
Uploaded by
ibanitescuCopyright:
Available Formats
Time for cell division: no gene expression
Time for replication, transcription
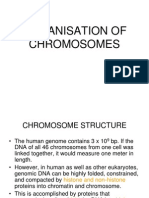
Chromosomes contain the genetic material Genes are physically located within the chromosomes Chromosomes are composed of DNA and proteins Primary function of genetic material is to store needed information
Typical chromosome contains a single, linear, double-stranded DNA molecule DNA must be folded and packaged Chromatin is the DNA-protein complex making up chromosomes
Chromatin is the combination of DNA and proteins found in eukaryotic chromosomes. Proteins in chromatin are:
histones: small, positively charged non-histone proteins: transcription factors, enzymes
Packaging of DNA with proteins leads to compacted structure, which facilitates fitting the DNA into the nucleus
Stains darkly (highly condensed) Repetitive sequences Replicates later in the cell cycle Little or no recombination Transcriptionally repressive: silences gene expression
Stains lightly (decondensed) Single copy sequences (genes) Replicates early in the cell cycle Recombines Transcriptionally active: permissive for gene expression
How do you fit approximately 2 meters (human diploid nucleus) into a space that averages maybe 5 millionths of a meter wide? How do you replicate, repair and transcribe tightly packaged DNA?
Diameter of nucleus = 5-10 mm DNA must be packaged to protect it, but must still be accessible to allow gene expression and cellular responsiveness
1. 2. 3. 4.
Nucleosome (11 nm) Solenoid (30 nm) Loops (300 nm) Coiled loops (700 nm)
5.
Metaphase chromosome (1400 nm)
Level 1: nucleosome formation
Level 2: 30 nm fiber
Level 3: Nuclear scaffolding
Level 4: Mitotic (metaphase) chromosome
Nucleosomes are formed by winding about 200 base pairs of the DNA duplex around a core of histone proteins. The histone core is made of:
2 2 2 2 molecules molecules molecules molecules histone histone histone histone H2A H2B H3 H4
Another histone, H1, binds outside the core.
string on a bead for obvious reasons Linker can vary (8-114bp or more) Compaction ratio is approx 7 fold
30 nm fiber is coil of nucleosomes with 6/turn
A 30 nm diameter chromatin fiber
The zig-zag model, H1 histone has a role in contraction of nucleosomes Compaction ratio approx 100 fold
The 30nm fiber is organized to loops that can be opened up individually
300 nm coiled chromatin fibers radial loops
Form a structural scaffolding to which loops of chromatin are attached nuclear matrix (or chromosome scaffold) 2 scaffold proteins are found (Non histones proteins) 30-nm fibers interact with the nuclear matrix Compacts 30-nm fiber by participating in the formation of radial loop domains Anchored to nuclear matrix
Haploid genom: 2 m
1. Total lenght of mitotic chromosome is:180 mm
You might also like
- LS 107 - Midterm 1 Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesLS 107 - Midterm 1 Cheat SheetAudrie L.No ratings yet
- Mark OF THE BEASTDocument183 pagesMark OF THE BEASTgrb123xb123100% (2)
- Nucleus PresentationDocument46 pagesNucleus PresentationArun Ravi100% (1)
- Unit 3. The NucleusDocument130 pagesUnit 3. The NucleusArio AhmadieNo ratings yet
- Structure and Organization of ChromatinDocument11 pagesStructure and Organization of Chromatincassidy conchaNo ratings yet
- Chromatin Structure and Histones Code - CCBDocument44 pagesChromatin Structure and Histones Code - CCBhafssa BachirNo ratings yet
- 2 Genetics Lecture - DNA PackagingDocument45 pages2 Genetics Lecture - DNA PackagingAMIRA HELAYELNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic, Prokaryotic and Viral Genome OrganisationDocument17 pagesEukaryotic, Prokaryotic and Viral Genome OrganisationAman KhanNo ratings yet
- Advance Genetics: THE Complexity of Eukaryotic GenomeDocument9 pagesAdvance Genetics: THE Complexity of Eukaryotic Genomecassidy conchaNo ratings yet
- 03 NucleusDocument11 pages03 NucleusRadon WilsonNo ratings yet
- Organisation of Eukaryotic ChromosomesDocument48 pagesOrganisation of Eukaryotic Chromosomesstevensb05591% (23)
- DNA PackagingDocument25 pagesDNA PackagingHoor Ul Ain Rounaq100% (1)
- Organisation of ChromosomesDocument2 pagesOrganisation of Chromosomesstevensb055No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Cell Bio NotesDocument18 pagesChapter 5 Cell Bio NotesJenny100% (1)
- Chromosome Chromati PackegingDocument16 pagesChromosome Chromati Packegingseenu mohapatraNo ratings yet
- Materi Minggu 6Document44 pagesMateri Minggu 6HafizahNo ratings yet
- Molecular BiologyDocument61 pagesMolecular BiologyRaghuvar TiwaryNo ratings yet
- MB1 Nucleus and ChromosomesDocument48 pagesMB1 Nucleus and Chromosomesfaezeh zare karizakNo ratings yet
- Molecular Genetics Chapter 8Document49 pagesMolecular Genetics Chapter 8byunus88No ratings yet
- BTN222-L2-DNA and Genome STR-2019Document43 pagesBTN222-L2-DNA and Genome STR-2019rafiya IsmailNo ratings yet
- ChromosomesDocument39 pagesChromosomesSuresh Kannan100% (1)
- Nucleic Acids: NucleoproteinsDocument332 pagesNucleic Acids: NucleoproteinsazeemNo ratings yet
- Cellular BiologyDocument31 pagesCellular BiologyKhang NguyenNo ratings yet
- Molecular BiologyB SC Biochemistry SEM IIIDocument61 pagesMolecular BiologyB SC Biochemistry SEM IIINnleinomNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Dna OrgDocument14 pagesEukaryotic Dna Orgrimpp100% (1)
- DNA PackagingDocument3 pagesDNA Packagingyourneeds.meNo ratings yet
- Lecture No. 3: Packaging of DNA Into ChromatinDocument20 pagesLecture No. 3: Packaging of DNA Into ChromatinIqra ArshadNo ratings yet
- Chromosome Organization: AkamandalDocument24 pagesChromosome Organization: AkamandalnaomiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - DNA Structure and OrganizationDocument33 pagesChapter 9 - DNA Structure and OrganizationIka BakarNo ratings yet
- 2nd Week - Genome Organization and DNA ReplicationDocument76 pages2nd Week - Genome Organization and DNA ReplicationyazicigaamzeNo ratings yet
- Organisation of Genomes - Eukaryotes: Non-Dividing Cells Dividing CellsDocument17 pagesOrganisation of Genomes - Eukaryotes: Non-Dividing Cells Dividing CellsTimothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- Block 1 Ebrahim Moola Mol MedDocument88 pagesBlock 1 Ebrahim Moola Mol MedMatsiri ImmanuelNo ratings yet
- Genetics Seminars 1-3Document289 pagesGenetics Seminars 1-3Мөнхгэрэл ГанбатNo ratings yet
- SGKDSJHKDJHDocument1 pageSGKDSJHKDJHapi-296833859No ratings yet
- UNIT IV-Genome OrganizationDocument119 pagesUNIT IV-Genome OrganizationLakshya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Dna StructureDocument67 pagesDna Structurespitzmark2030No ratings yet
- The Nucleus: Genome (Genetic Information) in Eukaryotic Cells, So It Is ResponsibleDocument9 pagesThe Nucleus: Genome (Genetic Information) in Eukaryotic Cells, So It Is ResponsibleAbbas TalibNo ratings yet
- 2 NucleusDocument19 pages2 NucleusYuu Ayu'k LifestarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document34 pagesChapter 1Nurarief AffendyNo ratings yet
- H2 Biology - Notes On Organisation and Control of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic GenomesDocument15 pagesH2 Biology - Notes On Organisation and Control of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic GenomesSefLRho100% (5)
- TM-04 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Chromosome Structure (Genap 2016-2017)Document32 pagesTM-04 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Chromosome Structure (Genap 2016-2017)Fiy Jannatin AliyahNo ratings yet
- DNA Packaging by Enamul HaqueDocument27 pagesDNA Packaging by Enamul HaqueEnamul Haque100% (1)
- 07 NucleusDocument4 pages07 NucleusUday JangaleNo ratings yet
- Nucleus and ChromosomesDocument43 pagesNucleus and Chromosomesapi-19916399No ratings yet
- Molecular BiologyDocument73 pagesMolecular BiologyRapada, Rowelyn S.No ratings yet
- 6 Cytology Nucleus 1Document35 pages6 Cytology Nucleus 1SamNo ratings yet
- Neuclic Acid and Protein SynthesisDocument21 pagesNeuclic Acid and Protein SynthesisPradyut BiswasNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes Unit 3Document27 pagesBiology Notes Unit 3Ralph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- Interphasic NucleusDocument21 pagesInterphasic Nucleushamahamahama3No ratings yet
- Genome Organization and ControlDocument32 pagesGenome Organization and Controllmiguel92100% (1)
- NucleusDocument2 pagesNucleuslinhNo ratings yet
- Chromosomes: 10.1 Viral GenomesDocument6 pagesChromosomes: 10.1 Viral GenomesMaeLkz BaldadoNo ratings yet
- Histone Proteins, The Nucleosome and Chromatin Structure - 9Document44 pagesHistone Proteins, The Nucleosome and Chromatin Structure - 9REMYAREMA31No ratings yet
- Cell Nucleus, Mitochondrium, Peroxysome: Viktoria Vereczki, M.D., PH.DDocument47 pagesCell Nucleus, Mitochondrium, Peroxysome: Viktoria Vereczki, M.D., PH.D20SMB24 - ShafanaNo ratings yet
- DNA PackagingDocument25 pagesDNA PackagingChamara ChathurangaNo ratings yet
- Organisation and Control of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic GenomeDocument8 pagesOrganisation and Control of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic GenomeNicholas OwNo ratings yet
- Pengepakan Kromosm: Syamsu RijalDocument31 pagesPengepakan Kromosm: Syamsu RijalLIEBERKHUNNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Chromosomes and Human GenomeDocument19 pages6.1 Chromosomes and Human GenomeSergej ElekNo ratings yet
- Dwi Dutha Arie Sampurna XII A 5 / 08Document18 pagesDwi Dutha Arie Sampurna XII A 5 / 08Dwi Duta AriNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 (06) WebsiteDocument27 pagesLecture 3 (06) Websiteeri512457No ratings yet
- Gene Editing, Epigenetic, Cloning and TherapyFrom EverandGene Editing, Epigenetic, Cloning and TherapyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Andreea-Balteanu MASc ThesisDocument75 pagesAndreea-Balteanu MASc ThesisibanitescuNo ratings yet
- Video TimingController v6.1 LogiCORE IP Pg016 - V - TCDocument89 pagesVideo TimingController v6.1 LogiCORE IP Pg016 - V - TCibanitescuNo ratings yet
- AHCI and RAID On HP Compaq Elite 8000, 8100, 8200, and 8300 Business PCsDocument29 pagesAHCI and RAID On HP Compaq Elite 8000, 8100, 8200, and 8300 Business PCsibanitescuNo ratings yet
- 2.4GHz - Inverted F AntennaDocument15 pages2.4GHz - Inverted F AntennasinnmleeNo ratings yet
- Finding Food in Iron and Bronze Age EraDocument9 pagesFinding Food in Iron and Bronze Age EraibanitescuNo ratings yet
- UEFIBIOS ToolsForHPbusinessdesktopsDocument4 pagesUEFIBIOS ToolsForHPbusinessdesktopsibanitescuNo ratings yet
- Texas Instruments VCO LMX248x Evaluation Board User's Guide Snau137aDocument36 pagesTexas Instruments VCO LMX248x Evaluation Board User's Guide Snau137aibanitescuNo ratings yet
- Frequency Multiplier Chirper Swept Frequency Multiplication (SFM) CDR - Pdfs-Indexed-620 - 1Document8 pagesFrequency Multiplier Chirper Swept Frequency Multiplication (SFM) CDR - Pdfs-Indexed-620 - 1ibanitescuNo ratings yet
- Adf PLL Ev Adf4355 3sd1z - Ug 873Document18 pagesAdf PLL Ev Adf4355 3sd1z - Ug 873ibanitescuNo ratings yet
- STMicro Low Cost PCB Antenna For 2.4GHz Radio Meander Design Application Note AN3359Document28 pagesSTMicro Low Cost PCB Antenna For 2.4GHz Radio Meander Design Application Note AN3359ibanitescu100% (1)
- Texas Instruments VCO LMX248x Evaluation Board User's Guide Snau137aDocument36 pagesTexas Instruments VCO LMX248x Evaluation Board User's Guide Snau137aibanitescuNo ratings yet
- LTCC Front-End Integration For D-Band Applications (110-170 GHZ)Document2 pagesLTCC Front-End Integration For D-Band Applications (110-170 GHZ)ibanitescuNo ratings yet
- Frequency Multiplier Chirper Swept Frequency Multiplication (SFM) CDR - Pdfs-Indexed-620 - 1Document8 pagesFrequency Multiplier Chirper Swept Frequency Multiplication (SFM) CDR - Pdfs-Indexed-620 - 1ibanitescuNo ratings yet
- Adl 5801Document40 pagesAdl 5801ibanitescuNo ratings yet
- Adf PLL High Performance Integrated 24 GHZ FMCW Radar Transceiver ChipsetDocument4 pagesAdf PLL High Performance Integrated 24 GHZ FMCW Radar Transceiver ChipsetibanitescuNo ratings yet
- Adf PLL Adf 4351 Adl5801 CN0239Document6 pagesAdf PLL Adf 4351 Adl5801 CN0239ibanitescuNo ratings yet
- Microwave Power Dividers - Wilkinson Unequal Power DivDocument1 pageMicrowave Power Dividers - Wilkinson Unequal Power DivibanitescuNo ratings yet
- Adf PLL Adf4159 Ad8065 Opamp CN0302Document5 pagesAdf PLL Adf4159 Ad8065 Opamp CN0302ibanitescuNo ratings yet
- A Linearization Method For A Uwb Vco-Based Chirp Generator Compensation Gomezgarciaalvestegui - Ku - 0099m - 11930 - Data - 1Document145 pagesA Linearization Method For A Uwb Vco-Based Chirp Generator Compensation Gomezgarciaalvestegui - Ku - 0099m - 11930 - Data - 1ibanitescuNo ratings yet
- Adf4355 3Document34 pagesAdf4355 3ibanitescuNo ratings yet
- ADF4159Document36 pagesADF4159ibanitescuNo ratings yet
- Cracking The Code of Life-8Document2 pagesCracking The Code of Life-8api-239029430No ratings yet
- Plasmids 101 Ebook Ed4 1 AddgeneDocument226 pagesPlasmids 101 Ebook Ed4 1 Addgenemustafa gökçenNo ratings yet
- 8610 Assignment 1 Ali Faizur RehmanDocument13 pages8610 Assignment 1 Ali Faizur RehmanAli Faizur RehmanNo ratings yet
- UT Dallas Syllabus For Biol2311.501 05f Taught by John Burr (Burr)Document2 pagesUT Dallas Syllabus For Biol2311.501 05f Taught by John Burr (Burr)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupNo ratings yet
- Advanced Placement College Biology Course SyllabusDocument13 pagesAdvanced Placement College Biology Course Syllabusapi-302885150No ratings yet
- Phase 1 Report - University of York - HEMP-30 Catalysing A Step Change in The ProductionDocument82 pagesPhase 1 Report - University of York - HEMP-30 Catalysing A Step Change in The Productionafriethiocarbon2023No ratings yet
- Cels191 Things To RememberDocument9 pagesCels191 Things To RememberMimi BoisterNo ratings yet
- IUMS2014, ProceedingDocument1,487 pagesIUMS2014, Proceedingamir-scribdNo ratings yet
- Guide To Unconventional Computing For MusicDocument290 pagesGuide To Unconventional Computing For MusicSonnenschein100% (5)
- Biology Vocabulary GlossaryDocument14 pagesBiology Vocabulary GlossaryElijah CastroNo ratings yet
- Yeast GeneticsDocument82 pagesYeast Geneticsbarak81470% (1)
- Question Text: Correct Mark 1.00 Out of 1.00Document22 pagesQuestion Text: Correct Mark 1.00 Out of 1.00Michalcova Realisan JezzaNo ratings yet
- BIOC15 Class 20 NotesDocument9 pagesBIOC15 Class 20 NotesCindy HouNo ratings yet
- Full Download PDF of (Ebook PDF) Evolution 3rd Edition by Futuyma, Douglas All ChapterDocument43 pagesFull Download PDF of (Ebook PDF) Evolution 3rd Edition by Futuyma, Douglas All Chapterdjuradilim100% (13)
- DEVPSY Reviewer - Chapters 1-6Document19 pagesDEVPSY Reviewer - Chapters 1-6Hannah MondillaNo ratings yet
- Biol 103 01 (F16)Document4 pagesBiol 103 01 (F16)bebbuwebbu100% (1)
- Reproduction and HeredityDocument3 pagesReproduction and Heredityapi-240418818No ratings yet
- ScienceWriting - DUKEDocument50 pagesScienceWriting - DUKEJéssica Almeida100% (1)
- CentoCancer® Comprehensive With Genes 1Document5 pagesCentoCancer® Comprehensive With Genes 1Muhammad Nabeel IlyasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 PDFDocument142 pagesChapter 1 PDFnhegdeNo ratings yet
- 15 Mulangi2012Planta2364Document13 pages15 Mulangi2012Planta2364Roulina ManjorangNo ratings yet
- MICROBIOLOGY - Microbial Taxonomy, Cell Structure and Bacterial Metabolism, Growth & GeneticsDocument16 pagesMICROBIOLOGY - Microbial Taxonomy, Cell Structure and Bacterial Metabolism, Growth & GeneticsRobie LeañoNo ratings yet
- Genetics and HeredityDocument32 pagesGenetics and HeredityJohn Emmanuel RamosNo ratings yet
- Trivial Pursuit - QuestionsDocument6 pagesTrivial Pursuit - Questionsapi-219485794No ratings yet
- Essentials of Understanding Psychology 11th Edition Feldman Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesEssentials of Understanding Psychology 11th Edition Feldman Solutions Manualprise.attone.itur100% (31)
- Lecture - '3 - Molecular Genetics IDocument22 pagesLecture - '3 - Molecular Genetics I啦啦啦啦No ratings yet
- Dr. Shumaila Naz: EducationDocument3 pagesDr. Shumaila Naz: EducationUsman QureshiNo ratings yet
- Synopsis Biology AEODocument4 pagesSynopsis Biology AEOnoyNo ratings yet