Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Moment of Area
Moment of Area
Uploaded by
Mahesh PrasadOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Moment of Area
Moment of Area
Uploaded by
Mahesh PrasadCopyright:
Available Formats
2E4: SOLIDS & STRUCTURES
Lecture 8
Dr. Bidisha Ghosh
Notes:
http://www.tcd.ie/civileng/Staff/Bidisha.Ghosh/
Solids & Structures
Properties of Sections
Cross-sections of beams:
Cross-Sections of other structural or machine
elements:
To find out stress or deformation we need to know about the
geometric properties of these sections!
Centroid
Centroid is the geometric centre which represents a
point in the plane about which the area of the cross-
section is equally distributed.
Centre of gravity for a body is a point which locates
the gravity or weight of the body.
Centroid and CG are same for homogeneous
material.
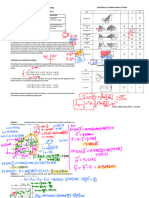
Moment of Area
dA
A
dA
}
This is called the First Moment of Area
An important concept to find out centroid.
The limits of the integration are decided based on the
dimensions (end points) of the area under consideration.
x y
A A
Q ydA Q xdA = =
} }
Take a infinitesimally small area (dA)
in the shaded area (area under
consideration).
Moment of this area about the point O,
Moment of the entire shaded area
about the point O can be by summing
over all such small dA areas or by,
First moment of area about x-axis or
y-axis,
Calculating position of centroid
The centroid of the entire shaded area (set of areas dA) is
the point C with respect to which the sum of the rst
moments of the dA areas is equal to zero.
The centroid is the point dening the geometric center of
system or of an object.
y
x
A A
Q
Q
x ydA y xdA
A A
= = = =
} }
Centroid of a Triangle
Composite areas
When a composite area is considered as an
assemblage of n elementary areas, the resultant
moment about any axis is the algebraic sum of the
moments of the component areas.
Therefore the centroid of a composite area is located
by,
i i i i
i i
Ax A y
x y
A A
= =
Centroid of an L-Shaped Area
Centroid of an L-Shaped Area
Moments of Inertia
MOI is a measure of the resistance to changes to its
rotation. It is the inertia of a rotating body with respect to its
rotation. The moment of inertia plays much the same role
in rotational dynamics as mass does in linear dynamics.
It is the second moment of area,
Radius of gyration, (the distance at which the entire area
can be assumed to be distributed for calculation of MOI)
y
x
x y
I
I
r r
A A
= =
2 2
x y
A A
I y dA I x dA = =
} }
Can you write a
matlab/excel code to
calculate moment of
inertia?
Moments of Inertia of a rectangle
2 2
2 2
2
2 2
2
2
2
3 3 2
2
=
=
3 12
x
A
A
d b
d b
d
d
d
d
I y dA y dxdy
y dx dy
y bdy
y bd
b
= =
(
(
=
(
(
=
(
} }}
} }
}
Polar Moment of Inertia
This is the moment of inertia of a plane area about an
axis perpendicular to the area.
0 x y
J I I = +
Parallel Axis Theorem
The parallel-axis theorem relates the moment of
inertia of an area with respect to any axis to the
moment of inertia around a parallel axis through the
centroid.
2 2
( ) =
x x y
A
I y y dA I Ad = + +
}
Moment of Inertia of an I-beam
You might also like
- Urea Unit Process BookDocument144 pagesUrea Unit Process BookAnonymous mUVpgT7No ratings yet
- RippleTankSE Key PDFDocument10 pagesRippleTankSE Key PDFYesi Setyo Ningrum100% (1)
- ME 101: Engineering Mechanics: Rajib Kumar BhattacharjyaDocument48 pagesME 101: Engineering Mechanics: Rajib Kumar BhattacharjyaudayaeroNo ratings yet
- Static and Kinetic Friction: ComputerDocument6 pagesStatic and Kinetic Friction: ComputerbobpleaseNo ratings yet
- Design of Retaining Wall: 10 M Height 1.0Document30 pagesDesign of Retaining Wall: 10 M Height 1.0Executive Engineer DesignNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Sectional Properties PresentationDocument14 pagesLesson 2 Sectional Properties PresentationTashNo ratings yet
- Concentrated Forces:: Unit IV Distributed ForcesDocument11 pagesConcentrated Forces:: Unit IV Distributed Forcesbpal1970No ratings yet
- Chapter 06 Mechanics of Engineering by HCMUTDocument55 pagesChapter 06 Mechanics of Engineering by HCMUTB NamNo ratings yet
- Sectional Properties PresentationDocument12 pagesSectional Properties PresentationJohan PienaarNo ratings yet
- Centroid SDocument50 pagesCentroid SAnu ParameswaranNo ratings yet
- Properties of Surfaces (Centre of Gravity & Moment of Inertia)Document48 pagesProperties of Surfaces (Centre of Gravity & Moment of Inertia)Tauseef100% (1)
- SRB Session5 CentroidsMomentofINERTIADocument4 pagesSRB Session5 CentroidsMomentofINERTIAFullo Flores MarviloneNo ratings yet
- Properties of AreasDocument20 pagesProperties of AreasroyNo ratings yet
- Section Properties and BendingDocument18 pagesSection Properties and BendingAmr El SaeedNo ratings yet
- U3 Moment of Interia Introduction and NumericalsDocument41 pagesU3 Moment of Interia Introduction and NumericalsShreyas RavichandranNo ratings yet
- شابتر 6Document36 pagesشابتر 6Feras ArafatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 06Document55 pagesChapter 06Bảo Tín TrầnNo ratings yet
- Distributed Forces Centroids and C of GravityDocument55 pagesDistributed Forces Centroids and C of GravityTuhafeni HailekaNo ratings yet
- Module 7 - Chapter 7Document17 pagesModule 7 - Chapter 7tenderNo ratings yet
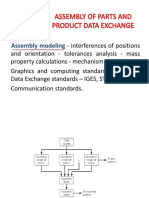
- Unit V Assembly of Parts and Product Data ExchangeDocument104 pagesUnit V Assembly of Parts and Product Data Exchangepalaniappan_pandian100% (1)
- Mass PropertiesDocument17 pagesMass Propertiespalaniappan_pandianNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9-Center of Gravity and Centroids-OdatDocument74 pagesChapter 9-Center of Gravity and Centroids-OdatMohammed Al-OdatNo ratings yet
- University Institute of Engineering Academic Unit 3Document38 pagesUniversity Institute of Engineering Academic Unit 3Vinoth Rouge RockersNo ratings yet
- Moment of Inertia PDFDocument18 pagesMoment of Inertia PDFBernalyn ManaogNo ratings yet
- EG-262 Section PropertiesDocument38 pagesEG-262 Section PropertiesAmr El SaeedNo ratings yet
- 03 - Moment of Inertia - Formulas, MOI of Objects (Solved Examples)Document18 pages03 - Moment of Inertia - Formulas, MOI of Objects (Solved Examples)upfaupNo ratings yet
- Moment Inertia PDFDocument18 pagesMoment Inertia PDFSameOldHatNo ratings yet
- Chapter NineDocument15 pagesChapter Niness1322No ratings yet
- Unit 3: Lecture Notes On CentroidDocument4 pagesUnit 3: Lecture Notes On CentroidMohammed FurqanNo ratings yet
- CH 6Document7 pagesCH 6GadisaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3.a (CG Centroid)Document21 pagesChapter 3.a (CG Centroid)LogarithemNo ratings yet
- Ce150 Steel 3 Determination of Section Properties of Structural ShapesDocument8 pagesCe150 Steel 3 Determination of Section Properties of Structural ShapesJerico Pineda BolesaNo ratings yet
- Application of IntegralDocument21 pagesApplication of IntegralTRIATMOJO ARYANTO WIYONO 2019No ratings yet
- Lecture Sheet 5 - Centroid & Moment of InertiaDocument49 pagesLecture Sheet 5 - Centroid & Moment of InertiaNafin Afnan100% (1)
- Neo Neet 11 p1 Phy H Motion in 1d s08Document67 pagesNeo Neet 11 p1 Phy H Motion in 1d s08gecbchebbecbebvebNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Statics: Yousif J. BasDocument25 pagesEngineering Mechanics Statics: Yousif J. Basalnd azadNo ratings yet
- CH 5Document7 pagesCH 5GadisaNo ratings yet
- Obafemi Awolowo University, Ile-Ife Department of Civil EngineeringDocument24 pagesObafemi Awolowo University, Ile-Ife Department of Civil EngineeringChibuike CharlesNo ratings yet
- 3d Printed Composite Body Illustrating Area and Mass Moment of Inertia With Mohr S Circle and Pole MethodDocument17 pages3d Printed Composite Body Illustrating Area and Mass Moment of Inertia With Mohr S Circle and Pole MethodhdahmaniNo ratings yet
- Moment InertiaDocument18 pagesMoment InertiaHamka HidayahNo ratings yet
- CE 5001 Structural Steel Design Lecture 02Document41 pagesCE 5001 Structural Steel Design Lecture 02Oshada AttygalleNo ratings yet
- APPLICATION 6 Moment of InertiaDocument44 pagesAPPLICATION 6 Moment of InertiaAnais RosalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10: Moments of InertiaDocument13 pagesChapter 10: Moments of InertiaDr. Pankaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture #19: Moments of InertiaDocument19 pagesLecture #19: Moments of InertiaAfiqah ZainuddinNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Advanced Structural Mechanics (Presentation) Author Antonio PalermoDocument78 pagesIntroduction To Advanced Structural Mechanics (Presentation) Author Antonio PalermoJoshua NicholasNo ratings yet
- Moment of InertiaDocument27 pagesMoment of InertiaPinca JoshuaNo ratings yet
- VDB 1023 Engineering Mechanics: Geometric Properties of Area and Solids Part I - Center of Gravity, CentroidDocument28 pagesVDB 1023 Engineering Mechanics: Geometric Properties of Area and Solids Part I - Center of Gravity, CentroidwengsungNo ratings yet
- First and Second Moment of AreaDocument26 pagesFirst and Second Moment of AreaAswinNo ratings yet
- Centroids & Moment of InertiaDocument8 pagesCentroids & Moment of InertiaGADDCNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Moments of InertiaDocument20 pagesChapter 6 - Moments of InertiaLetshego Itumeleng MoahloliNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 7 and 8 Centroids and InertiaDocument61 pagesCHAPTER 7 and 8 Centroids and InertiaDavid MurphyNo ratings yet
- Centroid + MOI (Students)Document39 pagesCentroid + MOI (Students)Usman HafeezNo ratings yet
- Momen InersiaDocument13 pagesMomen InersiaHendra DoankNo ratings yet
- Mechanics I (Statics) Ch-5Document23 pagesMechanics I (Statics) Ch-5Miki AscaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Cross-Sectional Properties of Structural MembersDocument13 pagesChapter 6: Cross-Sectional Properties of Structural MembersWint Thu HtunNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Area Moments of InertiaDocument10 pagesChapter 6 - Area Moments of InertiaCaleb fikaduNo ratings yet
- 1 - Properties of Plane AreasDocument24 pages1 - Properties of Plane AreasEng Ahmed Abdullah (Engineer)No ratings yet
- Centroids PDFDocument13 pagesCentroids PDFNerinel CoronadoNo ratings yet
- Moments of InertiaDocument18 pagesMoments of InertiazaihahNo ratings yet
- Centroids, Centre of Mass & Centres of GravityDocument42 pagesCentroids, Centre of Mass & Centres of GravityGray RagudosNo ratings yet
- Of Fluid Mechanics?: Problem Based Learning - 1Document2 pagesOf Fluid Mechanics?: Problem Based Learning - 1AliNo ratings yet
- Lect 32Document16 pagesLect 32Nicholas FeatherstonNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- The Alcoholysis Reaction of Isocyanates Giving Urethanes: Evidence For A Multimolecular MechanismDocument8 pagesThe Alcoholysis Reaction of Isocyanates Giving Urethanes: Evidence For A Multimolecular MechanismViviana TorresNo ratings yet
- Thrust Position, Differential Expansion, and Rod Position Monitor SpecificationsDocument1 pageThrust Position, Differential Expansion, and Rod Position Monitor SpecificationsTu PhamNo ratings yet
- Natural Perfume MaterialsDocument362 pagesNatural Perfume MaterialsAlan Miller100% (5)
- X Maths PaperDocument5 pagesX Maths Paperankurpapneja4100% (1)
- The Effects of Mass, Length, and Amplitude On The Period of A Simple PendulumDocument4 pagesThe Effects of Mass, Length, and Amplitude On The Period of A Simple PendulumVamp VampNo ratings yet
- 2381r 08Document74 pages2381r 08waltervillanNo ratings yet
- FRASER 1999 - What Are Discourse MarkersDocument22 pagesFRASER 1999 - What Are Discourse Markersrverano1983No ratings yet
- Penguard HB 2005 PDFDocument4 pagesPenguard HB 2005 PDFMuthuKumarNo ratings yet
- Altivar 312: Variable Speed Drives For Asynchronous Motors PROFIBUS DP Communication ManualDocument37 pagesAltivar 312: Variable Speed Drives For Asynchronous Motors PROFIBUS DP Communication ManualMarcos AldrovandiNo ratings yet
- Operation and Maintenance DamperDocument4 pagesOperation and Maintenance DamperBharatsinh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Bekesy Audiometry 1960Document13 pagesBekesy Audiometry 1960GermatojNo ratings yet
- Angle of Twist: Torsion II: 1Document4 pagesAngle of Twist: Torsion II: 1Anjana ENo ratings yet
- Makalah Astronomi (Bulan Fixx)Document28 pagesMakalah Astronomi (Bulan Fixx)PoniahNo ratings yet
- Full Text 01Document90 pagesFull Text 01Walid NASRINo ratings yet
- EEE121 - Electric Circuit AnalysisDocument13 pagesEEE121 - Electric Circuit Analysisrizwanspirit11No ratings yet
- 3.2 Mass Ma 4 KG Rests On Top of Mass MB 5kg That Rests On A FricDocument7 pages3.2 Mass Ma 4 KG Rests On Top of Mass MB 5kg That Rests On A Fricsoumengoswami10No ratings yet
- ZZ - Introduction To Lorentz Geometry Curves and Surfaces by Alexandre Lymberopoulos and Ivo Terek CoutoDocument351 pagesZZ - Introduction To Lorentz Geometry Curves and Surfaces by Alexandre Lymberopoulos and Ivo Terek Coutorajesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Bearing Capacity of Model Footings ON SandDocument47 pagesBearing Capacity of Model Footings ON SandAjayan VoNo ratings yet
- Level Measurement DevicesDocument1 pageLevel Measurement DevicesChem.EnggNo ratings yet
- Manual of Steel DesignDocument158 pagesManual of Steel DesignSyed Shoaib RazaNo ratings yet
- CE SubjectsDocument8 pagesCE SubjectsDavid Rhayzzon Gagarin PasionNo ratings yet
- AE Question PDFDocument12 pagesAE Question PDFAkhil SureshNo ratings yet
- DSV SVDocument1 pageDSV SVPUNITHA KUMARNo ratings yet
- SKYMARK C-Series Water-Cooled Self-Contained Units Catalog (1112)Document24 pagesSKYMARK C-Series Water-Cooled Self-Contained Units Catalog (1112)Carlos MelgarNo ratings yet
- A Dielectric Lens Antenna With Enhanced Aperture Efficiency For Industrial Radar ApplicationsDocument3 pagesA Dielectric Lens Antenna With Enhanced Aperture Efficiency For Industrial Radar ApplicationsacademicosNo ratings yet