Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gagandeep Garg ME-IT13-602
Gagandeep Garg ME-IT13-602
Uploaded by
Pawan Kumar ThakurCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Lamp Making TiffanyDocument61 pagesLamp Making Tiffanypepitagrillos100% (3)
- Microwave Communication SystemDocument93 pagesMicrowave Communication SystemMark Bryan Hermida Cruz100% (2)
- Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) Control: Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of TechnologyDocument115 pagesElectrostatic Discharge (ESD) Control: Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technologyrhap_0925060No ratings yet
- Airbus vs. Boeing NotesDocument4 pagesAirbus vs. Boeing NotesEsteban AguirreNo ratings yet
- Compressor Fundamentals, Performance CurvesDocument69 pagesCompressor Fundamentals, Performance Curvesใบบอนสิชล100% (5)
- Diversity TechniquesDocument37 pagesDiversity TechniquessoumyaNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Diversity TechniqueDocument25 pagesPresentation On Diversity TechniqueRanjeet pratap singh bhadoriyaNo ratings yet
- Micro and Macro DiversityDocument46 pagesMicro and Macro DiversityNandhini PNo ratings yet
- Diversity TechniquesDocument52 pagesDiversity Techniquesthanammaha09No ratings yet
- GSM Network Basics: Transmission PlanningDocument4 pagesGSM Network Basics: Transmission PlanningSameer SulemanNo ratings yet
- Antenna Diversity: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument5 pagesAntenna Diversity: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediawashkouletNo ratings yet
- Types of DiversityDocument3 pagesTypes of DiversityKADUNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9: Diversity: Chapter 7 - Equalization, Diversity, and CodingDocument33 pagesLecture 9: Diversity: Chapter 7 - Equalization, Diversity, and CodingShakeel AminNo ratings yet
- EC8652: Wireless Communication Department of ECE: Unit IvDocument38 pagesEC8652: Wireless Communication Department of ECE: Unit IvAbhijeet RaghuwanshiNo ratings yet
- Mobile Computing - Wireless TransmissionDocument48 pagesMobile Computing - Wireless Transmissionashkash nikeNo ratings yet
- 1st Half - Module 4Document87 pages1st Half - Module 4SampNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis of Spread Spectrum System (Direct Sequence) Over Fading Channel Models - and Multi-Carrier CDMADocument18 pagesPerformance Analysis of Spread Spectrum System (Direct Sequence) Over Fading Channel Models - and Multi-Carrier CDMAMounesh PanchalNo ratings yet
- Diversity Schemes and Combining TechniquesDocument36 pagesDiversity Schemes and Combining TechniquesMd. Golam Sarwar JoyNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Microwave & Satellite Technologies-1Document55 pagesFundamentals of Microwave & Satellite Technologies-1Rodric PeterNo ratings yet
- ECT402 WirelessCommunication Module4 Part1Document69 pagesECT402 WirelessCommunication Module4 Part1u2001170No ratings yet
- Multiplexing - Definition - Types of Multiplexing: FDM, WDM, TDMDocument14 pagesMultiplexing - Definition - Types of Multiplexing: FDM, WDM, TDMYohannis DanielNo ratings yet
- Diversity - in - Wireless - SystemsDocument2 pagesDiversity - in - Wireless - SystemsJ HARSHA YADAVNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Diversity in Wireless Communication BY Sani-e-Zehra Rizvi STD 13748Document38 pagesAn Overview of Diversity in Wireless Communication BY Sani-e-Zehra Rizvi STD 13748Waqar AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two: Introduction To Channel ModelingDocument7 pagesChapter Two: Introduction To Channel Modelinggashawbeza tayeNo ratings yet
- CNS Unit-IDocument62 pagesCNS Unit-IRadha RaniNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet1Document63 pagesTutorial Sheet1Yash AwasthiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11 - Large Scale Propagation ModelDocument20 pagesLecture 11 - Large Scale Propagation ModelSANJIDA AKTERNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Wireless Fading ChannelsDocument15 pagesCharacteristics of Wireless Fading ChannelsKasini venthan manikandanathanNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Small Scale FadingDocument43 pagesChapter Two Small Scale FadingGuta MekesaNo ratings yet
- WC - Unit - IvDocument38 pagesWC - Unit - IvJayakumar JkNo ratings yet
- Diversity Scheme - Wikipedi.Document2 pagesDiversity Scheme - Wikipedi.Shiva prasadNo ratings yet
- MCCDocument8 pagesMCCsauravNo ratings yet
- Unit II Possible Questions With AnswersDocument19 pagesUnit II Possible Questions With AnswersNithish.V.J.No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Part 1Document40 pagesChapter 3 Part 1Behailu AsmareNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Wireless TransmissionsDocument51 pagesChapter 2 Wireless TransmissionsMuhammad Zakrya KhanNo ratings yet
- MCC-Assignment 1Document4 pagesMCC-Assignment 1Saif ChogleNo ratings yet
- EX NO: 01 Wireless Channel Simulation Including Fading and Doppler Effects 05-11-20 AimDocument5 pagesEX NO: 01 Wireless Channel Simulation Including Fading and Doppler Effects 05-11-20 AimKamal Cruz LeNo ratings yet
- 3 - Diversity Protection SwitchingDocument20 pages3 - Diversity Protection SwitchingMarkNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CDMADocument105 pagesIntroduction To CDMADev Nath MondalNo ratings yet
- LF - bt1006 - E01 - 0 Lte Ofdm Principle 32Document29 pagesLF - bt1006 - E01 - 0 Lte Ofdm Principle 32Camilo Bazan HerediaNo ratings yet
- MCC-Assignment 1-12c027Document5 pagesMCC-Assignment 1-12c027Saif ChogleNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Co Channel IntereferenceDocument36 pagesUnit 3 Co Channel IntereferenceHarshaPuttaguntaNo ratings yet
- Check The Correct StatementDocument2 pagesCheck The Correct StatementAya MohamedNo ratings yet
- Multiplexing and ModulationDocument16 pagesMultiplexing and ModulationanuchinjithNo ratings yet
- Unit - 3: 1. Diversity Gain. Diversity Gain Is The Increase in Signal-To-Interference Ratio Due ToDocument1 pageUnit - 3: 1. Diversity Gain. Diversity Gain Is The Increase in Signal-To-Interference Ratio Due ToS.J Angelin PraveenaNo ratings yet
- CDMA ConceptDocument38 pagesCDMA ConceptsumitgoraiNo ratings yet
- Slides 4Document91 pagesSlides 4Ala AwoudaNo ratings yet
- ECT402 WirelessCommunication Module2Document108 pagesECT402 WirelessCommunication Module2u2001170No ratings yet
- Channel Models and Mitigation PDFDocument73 pagesChannel Models and Mitigation PDFkiraethio21No ratings yet
- Unit 4 Spread Spectrum and Ultiple Ccess TechniqueDocument26 pagesUnit 4 Spread Spectrum and Ultiple Ccess TechniqueThasleema BanuNo ratings yet
- What Is Channel EstimationDocument15 pagesWhat Is Channel EstimationShubham GuptaNo ratings yet
- Module 19: WDM ComponentsDocument9 pagesModule 19: WDM ComponentsARCHIT SUNDLINo ratings yet
- Analysis of Chromatic Scattering in 2 8 Channel at 4 10 Gbps at Various DistancesDocument5 pagesAnalysis of Chromatic Scattering in 2 8 Channel at 4 10 Gbps at Various DistanceswahbaabassNo ratings yet
- Modelling of WCDMA Base Station Signal in Multipath EnvironmentDocument7 pagesModelling of WCDMA Base Station Signal in Multipath EnvironmentInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Principle of DiversityDocument17 pagesPrinciple of DiversityJhosua AsbornNo ratings yet
- Dense Wavelength Division MultiplexingDocument22 pagesDense Wavelength Division Multiplexingsvt4bhosaleNo ratings yet
- FADING Unit 2Document8 pagesFADING Unit 2TisthaNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument13 pagesAssignmentSumaiya Sadia BristyNo ratings yet
- Chap. 3 Transmission Media 1Document11 pagesChap. 3 Transmission Media 1chaa2014No ratings yet
- WCN Notes-MergedDocument173 pagesWCN Notes-MergedYamini BollineniNo ratings yet
- (M4 POWERPOINT) MicrowaveDocument162 pages(M4 POWERPOINT) MicrowaveLanceDavidNo ratings yet
- Wireless Transmission and ServicesDocument41 pagesWireless Transmission and ServicesJigish DesaiNo ratings yet
- CISA Exam - Testing Concept-Network Physical Media (Fiber Optic/ UTP/STP/Co-axial) (Domain-4)From EverandCISA Exam - Testing Concept-Network Physical Media (Fiber Optic/ UTP/STP/Co-axial) (Domain-4)No ratings yet
- Data Interpretation On Questionnaire of Market Potential Study of Kotler InsuranceDocument10 pagesData Interpretation On Questionnaire of Market Potential Study of Kotler InsurancePawan Kumar ThakurNo ratings yet
- 9th - Song of The RainDocument19 pages9th - Song of The RainPawan Kumar Thakur67% (3)
- Green Computing ReportDocument28 pagesGreen Computing ReportPawan Kumar ThakurNo ratings yet
- Panjab University, Chandigarh: Press ReleaseDocument1 pagePanjab University, Chandigarh: Press ReleasePawan Kumar ThakurNo ratings yet
- Villa For Sale Ectlt KV 3brd ChandigarhDocument12 pagesVilla For Sale Ectlt KV 3brd ChandigarhPawan Kumar ThakurNo ratings yet
- MMX Unit 1Document33 pagesMMX Unit 1Pawan Kumar ThakurNo ratings yet
- Hadamard Transform: Nisha (612) Pawan (613) Rachita NagpalDocument9 pagesHadamard Transform: Nisha (612) Pawan (613) Rachita NagpalPawan Kumar ThakurNo ratings yet
- Research Area: Software Engineering SummaryDocument1 pageResearch Area: Software Engineering SummaryPawan Kumar ThakurNo ratings yet
- The H.263 Video Coding StandardDocument4 pagesThe H.263 Video Coding StandardPawan Kumar ThakurNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Kavita Kumari Roll No. MEIT13-06 2 Sem. M.E. (Information Technology)Document17 pagesPresented By: Kavita Kumari Roll No. MEIT13-06 2 Sem. M.E. (Information Technology)Pawan Kumar ThakurNo ratings yet
- Website On PBGDocument12 pagesWebsite On PBGPawan Kumar ThakurNo ratings yet
- Video and AnimationDocument14 pagesVideo and AnimationPawan Kumar ThakurNo ratings yet
- Computer Based Animation: Presented ByDocument14 pagesComputer Based Animation: Presented ByPawan Kumar ThakurNo ratings yet
- C3.0 Multiple Access TechniquesDocument6 pagesC3.0 Multiple Access TechniquesPawan Kumar ThakurNo ratings yet
- HandoffDocument17 pagesHandoffPawan Kumar ThakurNo ratings yet
- Customer Service Department: Komatsu Utility Europe Pag. 1 Di 24 WETT001304Document24 pagesCustomer Service Department: Komatsu Utility Europe Pag. 1 Di 24 WETT001304juanito100% (1)
- Pack SizeDocument9 pagesPack SizeMuhammad AfzalNo ratings yet
- SSA Assignment 01Document2 pagesSSA Assignment 01Isma MasoodNo ratings yet
- KPP 2020Document1 pageKPP 2020Dino BajloNo ratings yet
- Ford KNC Suspension enDocument1 pageFord KNC Suspension enpandiyarajmechNo ratings yet
- DPR of Vishwakarma Yojana Phase 3 - Kothe VillageDocument46 pagesDPR of Vishwakarma Yojana Phase 3 - Kothe VillageNayanKankadiyaNo ratings yet
- Grid1 - MIGUEL GRAU - GR1S - Input DataDocument2 pagesGrid1 - MIGUEL GRAU - GR1S - Input DataCarlos CastilloNo ratings yet
- Boarding Pass Bangkok PDFDocument4 pagesBoarding Pass Bangkok PDFLink KhoNo ratings yet
- Unipoint Controller - MAN0638 - V7 - 01 - 11 - EMEAIDocument24 pagesUnipoint Controller - MAN0638 - V7 - 01 - 11 - EMEAIΓιώργος ΚόρδαςNo ratings yet
- Control Panels IEC Norms EC Directives en-USDocument336 pagesControl Panels IEC Norms EC Directives en-USreeawsNo ratings yet
- Enterprise Mobility 8-5 Deployment GuideDocument560 pagesEnterprise Mobility 8-5 Deployment GuideAbhay BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Exploded Views and Parts ListDocument23 pagesExploded Views and Parts ListhughdempseyNo ratings yet
- ATON1Document42 pagesATON1Firdauz Rahmat100% (1)
- Fin TubesDocument4 pagesFin TubesBhanu K PrakashNo ratings yet
- 406MHz Sarsat Beacon Tester BrochureDocument2 pages406MHz Sarsat Beacon Tester Brochuretangocanh80No ratings yet
- No 4 Major SubwaysDocument2 pagesNo 4 Major SubwaysAndiKhaerin0% (1)
- Technical Data SOLO Transfer BIO-GRINDER HUNGRYGIANT2022Document4 pagesTechnical Data SOLO Transfer BIO-GRINDER HUNGRYGIANT2022Oscar AguirreNo ratings yet
- LeafletsDocument2 pagesLeafletsAmir FarajiNo ratings yet
- Polystyrene Beehives Key Facts Bee Hive SuppliesDocument3 pagesPolystyrene Beehives Key Facts Bee Hive Suppliesabuye aberaNo ratings yet
- Cement Bond LogDocument62 pagesCement Bond Logbinod_sunu100% (2)
- Motor Tracker Peugeot - 8-Valve Engine Description PDFDocument23 pagesMotor Tracker Peugeot - 8-Valve Engine Description PDFKISKACNo ratings yet
- Mazagon Dock LTDDocument12 pagesMazagon Dock LTDroy thomasNo ratings yet
- Manual SPECFEM2DDocument60 pagesManual SPECFEM2DAmorntep JirasakjamroonsriNo ratings yet
- MSA VMW PP PresentationDocument65 pagesMSA VMW PP PresentationplasmapeteNo ratings yet
- EEE G613 Advanced DSP - Lab Experiment 2: CientDocument2 pagesEEE G613 Advanced DSP - Lab Experiment 2: CientAYUSH KUMAR CHOWDHURYNo ratings yet
- hnc-21M-Operation Guide-V3.3 PDFDocument123 pageshnc-21M-Operation Guide-V3.3 PDFKev MoralesNo ratings yet
Gagandeep Garg ME-IT13-602
Gagandeep Garg ME-IT13-602
Uploaded by
Pawan Kumar ThakurOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gagandeep Garg ME-IT13-602
Gagandeep Garg ME-IT13-602
Uploaded by
Pawan Kumar ThakurCopyright:
Available Formats
Gagandeep Garg ME-IT13-602
If
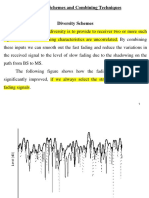
a fading radio signal is received through only one channel, then in a deep fade, the signal could be lost, and there is nothing that can be done.
It
can result in a loss of signal power without reducing the power of the noise. This signal loss can be over some or all of the signal bandwidth. Various Mitigation Techniques are: Diversity Schemes Channel Equalization Rake receiver
Diversity Schemes
A diversity scheme refers to a method for improving the reliability of a message signal by utilizing two or more communication channels with different characteristics . Exploits random nature of radio propagation by finding independent paths . They minimize fading effects since deep fade seldom occurs during same time interval on two or more paths simultaneously.
Types of Diversity Schemes
Macroscopic Diversity:
Combine two or more long-term lognormal signals obtained via independent fading paths received at two or more different antennas at different base station. Select base station which is not shadowed Combine two or more short-term Rayleigh signals obtained via independent fading paths received at two or more different antennas at same costie. It exploits the rapidly changing signal.
Microscopic diversity:
Macroscopic Diversity
Long term fading occurs in shadow region and causes average power to drop over a long period of time. Macroscopic diversity defeats shadowing by using transmitted and received basestation signals at two different geographical sites. These signals can be used to determine which site is better for communication.
Site B hill
Shadow section For site A
hill For site B Site A Avg. power of signal at two sites Pra=mA(x), Prb=mB(x)
mA(x) & mB(x) are log-normal distributed means. Cell A is selected if mA(x) > mB(x)
Microscopic diversity
Used when two or more uncorelated short-term corelated Rayleigh signals are received with identical long term fading i.e. all signal-paths have to follow same geographical path. Different fading-signals are received from different antennas at same antenna site. Various diversity schemes are 1. Frequency diversity 2. Time diversity 3. Space diversity 4. Polarization diversity
Frequency diversity
Two mobile radio signals separated by two carrier frequencies far apart will be independent. It is implemented by transmitting information on more than one carrier frequency. If the frequency separation > coherence bandwidth then channel will be uncorrelated thus will experience different fades. As two or more different frequencies experience different fading, at least one will have strong signal.
Frequency diversity (contd..)
OFDM modulation and access technique exploits frequency diversity. Frequency diversity consumes extra bandwidth.
Time diversity
Time diversity reception techniques are applicable to the transmission of digital data. Transmission in which signals representing the same information are sent over the same channel at different times. Use coding and interleaving (it breaks the memory of the channel, not all bits of the codeword are likely to fall into a deep fade) It consumes extra transmission time
Time diversity (Contd..)
Delay between replicas > coherence time Produce uncorrelated channels
Thank You!!!
You might also like
- Lamp Making TiffanyDocument61 pagesLamp Making Tiffanypepitagrillos100% (3)
- Microwave Communication SystemDocument93 pagesMicrowave Communication SystemMark Bryan Hermida Cruz100% (2)
- Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) Control: Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of TechnologyDocument115 pagesElectrostatic Discharge (ESD) Control: Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technologyrhap_0925060No ratings yet
- Airbus vs. Boeing NotesDocument4 pagesAirbus vs. Boeing NotesEsteban AguirreNo ratings yet
- Compressor Fundamentals, Performance CurvesDocument69 pagesCompressor Fundamentals, Performance Curvesใบบอนสิชล100% (5)
- Diversity TechniquesDocument37 pagesDiversity TechniquessoumyaNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Diversity TechniqueDocument25 pagesPresentation On Diversity TechniqueRanjeet pratap singh bhadoriyaNo ratings yet
- Micro and Macro DiversityDocument46 pagesMicro and Macro DiversityNandhini PNo ratings yet
- Diversity TechniquesDocument52 pagesDiversity Techniquesthanammaha09No ratings yet
- GSM Network Basics: Transmission PlanningDocument4 pagesGSM Network Basics: Transmission PlanningSameer SulemanNo ratings yet
- Antenna Diversity: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument5 pagesAntenna Diversity: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediawashkouletNo ratings yet
- Types of DiversityDocument3 pagesTypes of DiversityKADUNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9: Diversity: Chapter 7 - Equalization, Diversity, and CodingDocument33 pagesLecture 9: Diversity: Chapter 7 - Equalization, Diversity, and CodingShakeel AminNo ratings yet
- EC8652: Wireless Communication Department of ECE: Unit IvDocument38 pagesEC8652: Wireless Communication Department of ECE: Unit IvAbhijeet RaghuwanshiNo ratings yet
- Mobile Computing - Wireless TransmissionDocument48 pagesMobile Computing - Wireless Transmissionashkash nikeNo ratings yet
- 1st Half - Module 4Document87 pages1st Half - Module 4SampNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis of Spread Spectrum System (Direct Sequence) Over Fading Channel Models - and Multi-Carrier CDMADocument18 pagesPerformance Analysis of Spread Spectrum System (Direct Sequence) Over Fading Channel Models - and Multi-Carrier CDMAMounesh PanchalNo ratings yet
- Diversity Schemes and Combining TechniquesDocument36 pagesDiversity Schemes and Combining TechniquesMd. Golam Sarwar JoyNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Microwave & Satellite Technologies-1Document55 pagesFundamentals of Microwave & Satellite Technologies-1Rodric PeterNo ratings yet
- ECT402 WirelessCommunication Module4 Part1Document69 pagesECT402 WirelessCommunication Module4 Part1u2001170No ratings yet
- Multiplexing - Definition - Types of Multiplexing: FDM, WDM, TDMDocument14 pagesMultiplexing - Definition - Types of Multiplexing: FDM, WDM, TDMYohannis DanielNo ratings yet
- Diversity - in - Wireless - SystemsDocument2 pagesDiversity - in - Wireless - SystemsJ HARSHA YADAVNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Diversity in Wireless Communication BY Sani-e-Zehra Rizvi STD 13748Document38 pagesAn Overview of Diversity in Wireless Communication BY Sani-e-Zehra Rizvi STD 13748Waqar AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two: Introduction To Channel ModelingDocument7 pagesChapter Two: Introduction To Channel Modelinggashawbeza tayeNo ratings yet
- CNS Unit-IDocument62 pagesCNS Unit-IRadha RaniNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet1Document63 pagesTutorial Sheet1Yash AwasthiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11 - Large Scale Propagation ModelDocument20 pagesLecture 11 - Large Scale Propagation ModelSANJIDA AKTERNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Wireless Fading ChannelsDocument15 pagesCharacteristics of Wireless Fading ChannelsKasini venthan manikandanathanNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Small Scale FadingDocument43 pagesChapter Two Small Scale FadingGuta MekesaNo ratings yet
- WC - Unit - IvDocument38 pagesWC - Unit - IvJayakumar JkNo ratings yet
- Diversity Scheme - Wikipedi.Document2 pagesDiversity Scheme - Wikipedi.Shiva prasadNo ratings yet
- MCCDocument8 pagesMCCsauravNo ratings yet
- Unit II Possible Questions With AnswersDocument19 pagesUnit II Possible Questions With AnswersNithish.V.J.No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Part 1Document40 pagesChapter 3 Part 1Behailu AsmareNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Wireless TransmissionsDocument51 pagesChapter 2 Wireless TransmissionsMuhammad Zakrya KhanNo ratings yet
- MCC-Assignment 1Document4 pagesMCC-Assignment 1Saif ChogleNo ratings yet
- EX NO: 01 Wireless Channel Simulation Including Fading and Doppler Effects 05-11-20 AimDocument5 pagesEX NO: 01 Wireless Channel Simulation Including Fading and Doppler Effects 05-11-20 AimKamal Cruz LeNo ratings yet
- 3 - Diversity Protection SwitchingDocument20 pages3 - Diversity Protection SwitchingMarkNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CDMADocument105 pagesIntroduction To CDMADev Nath MondalNo ratings yet
- LF - bt1006 - E01 - 0 Lte Ofdm Principle 32Document29 pagesLF - bt1006 - E01 - 0 Lte Ofdm Principle 32Camilo Bazan HerediaNo ratings yet
- MCC-Assignment 1-12c027Document5 pagesMCC-Assignment 1-12c027Saif ChogleNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Co Channel IntereferenceDocument36 pagesUnit 3 Co Channel IntereferenceHarshaPuttaguntaNo ratings yet
- Check The Correct StatementDocument2 pagesCheck The Correct StatementAya MohamedNo ratings yet
- Multiplexing and ModulationDocument16 pagesMultiplexing and ModulationanuchinjithNo ratings yet
- Unit - 3: 1. Diversity Gain. Diversity Gain Is The Increase in Signal-To-Interference Ratio Due ToDocument1 pageUnit - 3: 1. Diversity Gain. Diversity Gain Is The Increase in Signal-To-Interference Ratio Due ToS.J Angelin PraveenaNo ratings yet
- CDMA ConceptDocument38 pagesCDMA ConceptsumitgoraiNo ratings yet
- Slides 4Document91 pagesSlides 4Ala AwoudaNo ratings yet
- ECT402 WirelessCommunication Module2Document108 pagesECT402 WirelessCommunication Module2u2001170No ratings yet
- Channel Models and Mitigation PDFDocument73 pagesChannel Models and Mitigation PDFkiraethio21No ratings yet
- Unit 4 Spread Spectrum and Ultiple Ccess TechniqueDocument26 pagesUnit 4 Spread Spectrum and Ultiple Ccess TechniqueThasleema BanuNo ratings yet
- What Is Channel EstimationDocument15 pagesWhat Is Channel EstimationShubham GuptaNo ratings yet
- Module 19: WDM ComponentsDocument9 pagesModule 19: WDM ComponentsARCHIT SUNDLINo ratings yet
- Analysis of Chromatic Scattering in 2 8 Channel at 4 10 Gbps at Various DistancesDocument5 pagesAnalysis of Chromatic Scattering in 2 8 Channel at 4 10 Gbps at Various DistanceswahbaabassNo ratings yet
- Modelling of WCDMA Base Station Signal in Multipath EnvironmentDocument7 pagesModelling of WCDMA Base Station Signal in Multipath EnvironmentInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Principle of DiversityDocument17 pagesPrinciple of DiversityJhosua AsbornNo ratings yet
- Dense Wavelength Division MultiplexingDocument22 pagesDense Wavelength Division Multiplexingsvt4bhosaleNo ratings yet
- FADING Unit 2Document8 pagesFADING Unit 2TisthaNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument13 pagesAssignmentSumaiya Sadia BristyNo ratings yet
- Chap. 3 Transmission Media 1Document11 pagesChap. 3 Transmission Media 1chaa2014No ratings yet
- WCN Notes-MergedDocument173 pagesWCN Notes-MergedYamini BollineniNo ratings yet
- (M4 POWERPOINT) MicrowaveDocument162 pages(M4 POWERPOINT) MicrowaveLanceDavidNo ratings yet
- Wireless Transmission and ServicesDocument41 pagesWireless Transmission and ServicesJigish DesaiNo ratings yet
- CISA Exam - Testing Concept-Network Physical Media (Fiber Optic/ UTP/STP/Co-axial) (Domain-4)From EverandCISA Exam - Testing Concept-Network Physical Media (Fiber Optic/ UTP/STP/Co-axial) (Domain-4)No ratings yet
- Data Interpretation On Questionnaire of Market Potential Study of Kotler InsuranceDocument10 pagesData Interpretation On Questionnaire of Market Potential Study of Kotler InsurancePawan Kumar ThakurNo ratings yet
- 9th - Song of The RainDocument19 pages9th - Song of The RainPawan Kumar Thakur67% (3)
- Green Computing ReportDocument28 pagesGreen Computing ReportPawan Kumar ThakurNo ratings yet
- Panjab University, Chandigarh: Press ReleaseDocument1 pagePanjab University, Chandigarh: Press ReleasePawan Kumar ThakurNo ratings yet
- Villa For Sale Ectlt KV 3brd ChandigarhDocument12 pagesVilla For Sale Ectlt KV 3brd ChandigarhPawan Kumar ThakurNo ratings yet
- MMX Unit 1Document33 pagesMMX Unit 1Pawan Kumar ThakurNo ratings yet
- Hadamard Transform: Nisha (612) Pawan (613) Rachita NagpalDocument9 pagesHadamard Transform: Nisha (612) Pawan (613) Rachita NagpalPawan Kumar ThakurNo ratings yet
- Research Area: Software Engineering SummaryDocument1 pageResearch Area: Software Engineering SummaryPawan Kumar ThakurNo ratings yet
- The H.263 Video Coding StandardDocument4 pagesThe H.263 Video Coding StandardPawan Kumar ThakurNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Kavita Kumari Roll No. MEIT13-06 2 Sem. M.E. (Information Technology)Document17 pagesPresented By: Kavita Kumari Roll No. MEIT13-06 2 Sem. M.E. (Information Technology)Pawan Kumar ThakurNo ratings yet
- Website On PBGDocument12 pagesWebsite On PBGPawan Kumar ThakurNo ratings yet
- Video and AnimationDocument14 pagesVideo and AnimationPawan Kumar ThakurNo ratings yet
- Computer Based Animation: Presented ByDocument14 pagesComputer Based Animation: Presented ByPawan Kumar ThakurNo ratings yet
- C3.0 Multiple Access TechniquesDocument6 pagesC3.0 Multiple Access TechniquesPawan Kumar ThakurNo ratings yet
- HandoffDocument17 pagesHandoffPawan Kumar ThakurNo ratings yet
- Customer Service Department: Komatsu Utility Europe Pag. 1 Di 24 WETT001304Document24 pagesCustomer Service Department: Komatsu Utility Europe Pag. 1 Di 24 WETT001304juanito100% (1)
- Pack SizeDocument9 pagesPack SizeMuhammad AfzalNo ratings yet
- SSA Assignment 01Document2 pagesSSA Assignment 01Isma MasoodNo ratings yet
- KPP 2020Document1 pageKPP 2020Dino BajloNo ratings yet
- Ford KNC Suspension enDocument1 pageFord KNC Suspension enpandiyarajmechNo ratings yet
- DPR of Vishwakarma Yojana Phase 3 - Kothe VillageDocument46 pagesDPR of Vishwakarma Yojana Phase 3 - Kothe VillageNayanKankadiyaNo ratings yet
- Grid1 - MIGUEL GRAU - GR1S - Input DataDocument2 pagesGrid1 - MIGUEL GRAU - GR1S - Input DataCarlos CastilloNo ratings yet
- Boarding Pass Bangkok PDFDocument4 pagesBoarding Pass Bangkok PDFLink KhoNo ratings yet
- Unipoint Controller - MAN0638 - V7 - 01 - 11 - EMEAIDocument24 pagesUnipoint Controller - MAN0638 - V7 - 01 - 11 - EMEAIΓιώργος ΚόρδαςNo ratings yet
- Control Panels IEC Norms EC Directives en-USDocument336 pagesControl Panels IEC Norms EC Directives en-USreeawsNo ratings yet
- Enterprise Mobility 8-5 Deployment GuideDocument560 pagesEnterprise Mobility 8-5 Deployment GuideAbhay BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Exploded Views and Parts ListDocument23 pagesExploded Views and Parts ListhughdempseyNo ratings yet
- ATON1Document42 pagesATON1Firdauz Rahmat100% (1)
- Fin TubesDocument4 pagesFin TubesBhanu K PrakashNo ratings yet
- 406MHz Sarsat Beacon Tester BrochureDocument2 pages406MHz Sarsat Beacon Tester Brochuretangocanh80No ratings yet
- No 4 Major SubwaysDocument2 pagesNo 4 Major SubwaysAndiKhaerin0% (1)
- Technical Data SOLO Transfer BIO-GRINDER HUNGRYGIANT2022Document4 pagesTechnical Data SOLO Transfer BIO-GRINDER HUNGRYGIANT2022Oscar AguirreNo ratings yet
- LeafletsDocument2 pagesLeafletsAmir FarajiNo ratings yet
- Polystyrene Beehives Key Facts Bee Hive SuppliesDocument3 pagesPolystyrene Beehives Key Facts Bee Hive Suppliesabuye aberaNo ratings yet
- Cement Bond LogDocument62 pagesCement Bond Logbinod_sunu100% (2)
- Motor Tracker Peugeot - 8-Valve Engine Description PDFDocument23 pagesMotor Tracker Peugeot - 8-Valve Engine Description PDFKISKACNo ratings yet
- Mazagon Dock LTDDocument12 pagesMazagon Dock LTDroy thomasNo ratings yet
- Manual SPECFEM2DDocument60 pagesManual SPECFEM2DAmorntep JirasakjamroonsriNo ratings yet
- MSA VMW PP PresentationDocument65 pagesMSA VMW PP PresentationplasmapeteNo ratings yet
- EEE G613 Advanced DSP - Lab Experiment 2: CientDocument2 pagesEEE G613 Advanced DSP - Lab Experiment 2: CientAYUSH KUMAR CHOWDHURYNo ratings yet
- hnc-21M-Operation Guide-V3.3 PDFDocument123 pageshnc-21M-Operation Guide-V3.3 PDFKev MoralesNo ratings yet