Professional Documents
Culture Documents
English Phonetics 3
English Phonetics 3
Uploaded by
Mohd Zulkhairi AbdullahCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- 99 Pounds - ScoreDocument5 pages99 Pounds - Scoreduane8wagnerNo ratings yet
- Jali-Jali Full ScoreDocument14 pagesJali-Jali Full ScoreGloria Dorothy Rolanda100% (2)
- Kortlandt Beekes ArmeniacaDocument247 pagesKortlandt Beekes ArmeniacaAlexander Nikolaev100% (1)
- Завдання для самостійної роботи з Фонетики 1 курсDocument4 pagesЗавдання для самостійної роботи з Фонетики 1 курсIvanka ShumykNo ratings yet
- Aspects of Connected SpeechDocument32 pagesAspects of Connected SpeechBrendon Jikal100% (2)
- 14 Aspects of Connected SpeechDocument23 pages14 Aspects of Connected Speechammaranas100% (1)
- Phonological Rules: LING101 September 24, 2009Document10 pagesPhonological Rules: LING101 September 24, 2009Francesca GiannottaNo ratings yet
- Task 1Document7 pagesTask 1YUSRI BIN KIPLI MoeNo ratings yet
- English Week 1-4 NotesDocument15 pagesEnglish Week 1-4 Notesfizasm33No ratings yet
- Features of Connected SpeechDocument6 pagesFeatures of Connected Speechdenieb1311No ratings yet
- Modifications of Consonants in Connected SpeechDocument11 pagesModifications of Consonants in Connected Speechelshen mamedovNo ratings yet
- Types of Articulatory ProcessesDocument4 pagesTypes of Articulatory ProcessesDiahNo ratings yet
- A. Assimilatory Processes A. Consonant Assimilates Vowel FeaturesDocument4 pagesA. Assimilatory Processes A. Consonant Assimilates Vowel FeaturesTheywa DeNo ratings yet
- Phonology - PPT With Cover Page v2Document49 pagesPhonology - PPT With Cover Page v2BAH TiarNo ratings yet
- Linguistics NotesDocument5 pagesLinguistics NotesDexter LoughNo ratings yet
- English Phonology: 1 Semester 2021 Dr. Eman AlhusaiyanDocument28 pagesEnglish Phonology: 1 Semester 2021 Dr. Eman AlhusaiyanDr.Eman LinguisticsNo ratings yet
- Rhythm &intonationDocument16 pagesRhythm &intonationAnshuman TripathiNo ratings yet
- Connected SpeechDocument66 pagesConnected Speechandrewcook33332No ratings yet
- Week7 Phonological RulesDocument20 pagesWeek7 Phonological Rules6469yhkmtjNo ratings yet
- Phonetics and PhonologyDocument19 pagesPhonetics and PhonologyjayzebraNo ratings yet
- Rules On Subject Verb AgreementDocument20 pagesRules On Subject Verb AgreementMarife BumatayNo ratings yet
- Dr. Riceli C. Mendoza University of Southern Mindanao PhilippinesDocument17 pagesDr. Riceli C. Mendoza University of Southern Mindanao PhilippinesJose Luis Gatillon SotoNo ratings yet
- Phonology: The Sound Patterns of Language: 01:615:201 Introduction To Linguistic Theory Adam SzczegielniakDocument50 pagesPhonology: The Sound Patterns of Language: 01:615:201 Introduction To Linguistic Theory Adam SzczegielniakRahayu Ratu AzizahNo ratings yet
- PhonologyDocument48 pagesPhonologyCaryll BaylonNo ratings yet
- Grammar SchoolDocument21 pagesGrammar SchoolNebojša KrmpotNo ratings yet
- Phonology - PPT RemovedDocument42 pagesPhonology - PPT RemovedTommyNo ratings yet
- Aspects of Connected Speech: TE10003! The Phonology of EnglishDocument15 pagesAspects of Connected Speech: TE10003! The Phonology of EnglishDherick RaleighNo ratings yet
- Cantonese PhonologyDocument9 pagesCantonese PhonologyJorge Guerrero100% (1)
- Phonological Processes Sem1Document23 pagesPhonological Processes Sem1sadiyatariq496No ratings yet
- Connected SpeechDocument6 pagesConnected SpeechValentina CandurinNo ratings yet
- Connected Speech: Communication.... Chat... Talk... Sing..Document16 pagesConnected Speech: Communication.... Chat... Talk... Sing..Dilrabo KoshevaNo ratings yet
- ORAL II - ALLPHONES - CONSONANTS and VOWELSDocument36 pagesORAL II - ALLPHONES - CONSONANTS and VOWELSMaría M MalakNo ratings yet
- Focus in MalagasyDocument22 pagesFocus in Malagasyalexandreq100% (1)
- Assimilation (Change)Document11 pagesAssimilation (Change)Patrícia Argôlo RosaNo ratings yet
- النحو المقارنDocument148 pagesالنحو المقارنAhmedAl-agwedNo ratings yet
- Phonology 3 PDFDocument64 pagesPhonology 3 PDFLingua Academy-club LacNo ratings yet
- Phonics RulesDocument18 pagesPhonics RulesAisy Astarina100% (1)
- The - R - SoundDocument8 pagesThe - R - SoundAgustina AcostaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Classification of Sound UnitsDocument14 pagesLecture 2 - Classification of Sound UnitsDaniel CNo ratings yet
- Assimilation: Is A Process of Alteration of Speech Sounds As A Result of WhichDocument16 pagesAssimilation: Is A Process of Alteration of Speech Sounds As A Result of Whichapi-283816739No ratings yet
- Phonetic Rules VowelsDocument3 pagesPhonetic Rules Vowelsyoussof2008No ratings yet
- PHONOLOGYDocument65 pagesPHONOLOGYcristinesilvaNo ratings yet
- Aspects of Connected SpeechDocument9 pagesAspects of Connected SpeechIosif StalinNo ratings yet
- Connected SpeechDocument7 pagesConnected SpeechMaria Eugenia GlosnickiNo ratings yet
- 9 Place Assimilation & Types of AssimilationDocument16 pages9 Place Assimilation & Types of AssimilationAngelline NyittiNo ratings yet
- Third StageDocument10 pagesThird StageSara N AhmadNo ratings yet
- Features of Connected SpeechDocument30 pagesFeatures of Connected SpeechJoselyn Wrande Sanhueza100% (2)
- Connected Speech BookletDocument32 pagesConnected Speech BookletNELCNo ratings yet
- English and Kazakh Phonemes and Their Allophones: Done by Bagzhan Uais, Aya21-3MDocument20 pagesEnglish and Kazakh Phonemes and Their Allophones: Done by Bagzhan Uais, Aya21-3MBagzhanNo ratings yet
- PHONOLOGY The Sound Patterns of Language 1Document36 pagesPHONOLOGY The Sound Patterns of Language 1Jeannette DeguinonNo ratings yet
- Phonology 17Document104 pagesPhonology 17farhan ramadhanNo ratings yet
- Types of Allophones and Their UsesDocument9 pagesTypes of Allophones and Their UsesDanielGonzálezZambrano83% (6)
- Nouns & AdjDocument4 pagesNouns & AdjНаталія АтласNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 and Chapter 7 - MorphologyDocument14 pagesChapter 6 and Chapter 7 - MorphologyEspe PascualNo ratings yet
- Ngữ âm - âm vị - CONSONANT 1's reviewDocument4 pagesNgữ âm - âm vị - CONSONANT 1's review2357080026No ratings yet
- Lecture 9. Phonological ProcessesDocument4 pagesLecture 9. Phonological Processesbe creativeNo ratings yet
- ÔN TẬP NGỮ ÂM - ÂM VỊ HỌC - LÝ THUYẾTDocument8 pagesÔN TẬP NGỮ ÂM - ÂM VỊ HỌC - LÝ THUYẾTTrà Nguyễn HươngNo ratings yet
- Conjugation: Write, Wrote, Written (Marking byDocument4 pagesConjugation: Write, Wrote, Written (Marking byNylilav Enish Lagdamen NimbraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document13 pagesChapter 7linh nguyenNo ratings yet
- MORPHOLOGY (Morphs, Allomorph, Grammatical and Phonological Conditioning)Document17 pagesMORPHOLOGY (Morphs, Allomorph, Grammatical and Phonological Conditioning)Sergio Felix CuratacaniNo ratings yet
- Seminar (2) ГотовоDocument5 pagesSeminar (2) ГотовоЯна ГержанNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: English VowelsDocument13 pagesUnit 3: English VowelsRachma Gupita100% (2)
- No Nama Tandatangan Kehadiran Catatan: Pendaftaran Peserta Beyblade Alpha One Center (Tamparuli)Document3 pagesNo Nama Tandatangan Kehadiran Catatan: Pendaftaran Peserta Beyblade Alpha One Center (Tamparuli)Mohd Zulkhairi AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Pace Race: Marathon, 1/2 Marathon, 10K & 5K Customizable, Printable Pace BandsDocument3 pagesPace Race: Marathon, 1/2 Marathon, 10K & 5K Customizable, Printable Pace BandsMohd Zulkhairi AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Inovasi PBS Eng Y2 01Document1 pageInovasi PBS Eng Y2 01Mohd Zulkhairi AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Cycle 2Document1 pageCycle 2Mohd Zulkhairi AbdullahNo ratings yet
- New Doc 7Document1 pageNew Doc 7Mohd Zulkhairi AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Lampiran A SK Penimbawan Tuaran Sabah: Tahun 4Document2 pagesLampiran A SK Penimbawan Tuaran Sabah: Tahun 4Mohd Zulkhairi AbdullahNo ratings yet
- New Doc 6Document1 pageNew Doc 6Mohd Zulkhairi AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Bibliografi: Mechanic Module". Research Report - Vol 23, 9.955-967Document2 pagesBibliografi: Mechanic Module". Research Report - Vol 23, 9.955-967Mohd Zulkhairi AbdullahNo ratings yet
- New Doc 36Document1 pageNew Doc 36Mohd Zulkhairi AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Keputusan Analisis Data Dengan Menggunakan Ujian-T Sampel Bersandar Bagi HDocument2 pagesKeputusan Analisis Data Dengan Menggunakan Ujian-T Sampel Bersandar Bagi HMohd Zulkhairi AbdullahNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Introduction of The ResearchDocument43 pages1.0 Introduction of The ResearchMohd Zulkhairi AbdullahNo ratings yet
- TSL3133 AR Proposal RubricDocument10 pagesTSL3133 AR Proposal RubricMohd Zulkhairi AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Lampiran G Keputusan Analisis Diskriptif Soal Selidik Kajian SebenarDocument4 pagesLampiran G Keputusan Analisis Diskriptif Soal Selidik Kajian SebenarMohd Zulkhairi AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Module Edu 3105Document232 pagesModule Edu 3105Mohd Zulkhairi Abdullah50% (2)
- Module TSL 3107Document73 pagesModule TSL 3107Mohd Zulkhairi AbdullahNo ratings yet
- RPH BM RaskanDocument26 pagesRPH BM RaskanMohd Zulkhairi AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Upsr Model Test 1Document17 pagesUpsr Model Test 1Norhaslina Mohd NoorNo ratings yet
- Module Lga 3102Document123 pagesModule Lga 3102Mohd Zulkhairi AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Module TSL 3108Document96 pagesModule TSL 3108Mohd Zulkhairi Abdullah100% (2)
- English Phonetics and Phonology 6Document20 pagesEnglish Phonetics and Phonology 6Mohd Zulkhairi AbdullahNo ratings yet
- English Phonetics and Phonology 5Document18 pagesEnglish Phonetics and Phonology 5Mohd Zulkhairi AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Task 4 - Luisa Fernanda Godoy TorresDocument6 pagesTask 4 - Luisa Fernanda Godoy TorresLuisa Fernanda GodoyNo ratings yet
- Task 6-Oral-Production-ActivityDocument12 pagesTask 6-Oral-Production-ActivityIVONNE GARCIANo ratings yet
- 2nd Year PhoneticsDocument4 pages2nd Year Phoneticskhadidja bnh0% (1)
- Phonetic and Pronunciation ExerciseDocument3 pagesPhonetic and Pronunciation ExerciseThư ĐỗNo ratings yet
- Phonological Processes in Connected SpeechDocument7 pagesPhonological Processes in Connected Speechsara ciullaNo ratings yet
- Studies in Lycian and Carian Phonology ADocument30 pagesStudies in Lycian and Carian Phonology AMar AlexNo ratings yet
- Kakyo - Zeami's Fundamental Principles of Acting. Part ThreeDocument23 pagesKakyo - Zeami's Fundamental Principles of Acting. Part ThreeBru PereiraNo ratings yet
- Add On - CERTIFICATE COURSE IN SPOKEN ENGLISH FOR COMMUNICATION SKILLDocument5 pagesAdd On - CERTIFICATE COURSE IN SPOKEN ENGLISH FOR COMMUNICATION SKILLSimran KaurNo ratings yet
- Slovenačka FonologijaDocument4 pagesSlovenačka FonologijaHaris HadžibaščauševićNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 History of ELDocument7 pagesLecture 2 History of ELАліна КопилевичNo ratings yet
- Syllables and Moras in Arabic: 1 CV-, VC-, and C-DialectsDocument31 pagesSyllables and Moras in Arabic: 1 CV-, VC-, and C-Dialectsmimouna bourzegNo ratings yet
- Comparative & Superlative GuideDocument2 pagesComparative & Superlative GuideDannhy GreenNo ratings yet
- MODULE-I Phonology & Morphology IIyrDocument12 pagesMODULE-I Phonology & Morphology IIyrAbhiNo ratings yet
- Table of AdjectivesDocument2 pagesTable of AdjectivesNOOR HUWAIDAH BINTI BALKI KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- How - To.sing.a.song Yvette - GuilbertDocument204 pagesHow - To.sing.a.song Yvette - Guilbertpiu.pianistNo ratings yet
- đề ngữ âm - âm vị học 3Document7 pagesđề ngữ âm - âm vị học 3Khanh VõNo ratings yet
- Un Abecedaire Qui Ne Manque Pas de PiquDocument16 pagesUn Abecedaire Qui Ne Manque Pas de PiquSeka ModlaNo ratings yet
- RPS Bi Tahun 2Document9 pagesRPS Bi Tahun 2Sleapy HeadNo ratings yet
- Virama 1Document1 pageVirama 1SchahebNo ratings yet
- American English Diphthongs and DigraphsDocument6 pagesAmerican English Diphthongs and Digraphsalberto craviotoNo ratings yet
- Bookshelf: Debra GreschnerDocument3 pagesBookshelf: Debra GreschnermarisaNo ratings yet
- Early Reading 14 - A Bug in The Mud PDFDocument6 pagesEarly Reading 14 - A Bug in The Mud PDFKatharina Krawtschenko100% (1)
- Syllabification Algorithm Based On Syllable Rules Matching For Malay LanguageDocument8 pagesSyllabification Algorithm Based On Syllable Rules Matching For Malay LanguageNathanael YehezkielNo ratings yet
- Unit 3, Module - 1Document13 pagesUnit 3, Module - 1Sheethal SarmaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Subject Class Theme Topic Language Focus Main Skill Integrated Skill Teaching Aids Educational Emphases: ConstructivismDocument1 pageLesson Plan Subject Class Theme Topic Language Focus Main Skill Integrated Skill Teaching Aids Educational Emphases: ConstructivismJoanne OngNo ratings yet
- Les Mots ApparentésDocument3 pagesLes Mots ApparentésLancasTchenNo ratings yet
English Phonetics 3
English Phonetics 3
Uploaded by
Mohd Zulkhairi AbdullahOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
English Phonetics 3
English Phonetics 3
Uploaded by
Mohd Zulkhairi AbdullahCopyright:
Available Formats
ENGLISH PHONETICS
AND PHONOLOGY
SEGMENTAL FEATURES
OF SPEECH
INTRODUCTION
The various sounds identified in the
previous sessions do not exist in isolation.
These sounds are stringed together to
form words and words are put together in
connected speech.
The segmental features of speech most
dominant in English
- assimilation
- elision
- linking
ASSIMILATION
It is a regular process in spoken or connected
speech in which a particular sound or phoneme
changes to become more like an adjacent
sound.
There are two types of assimilation:
- progressive assimilation- the sound changes to
match a preceding phoneme or sound that
comes before it.
- regressive assimilation- the sound changes to
match a following phoneme
Place Assimilation- Bilabialisation of Alveolar Sounds
- In PA-phoneme changes to match the place of
articulation of a previous/following sound.
- In spoken English, the alveolar stop [t] changes to [p] in
the following utterances
-`]4 OC wpO
O+
-OE]g]4 OE]E wOOg]O
OC)+
-_]C4 pEEg w_]O
p4g+
-- - The change of [t] to a [p] is an instance of
place assimilation in which the alveolar stop sound
becomes a bilabial stop that follows or a regressive
assimilation
- A similar process of regressive PA- changes of the [d] to
a [b] sound before [m], [b] or [p] in bad pain, bood
bank, good morning-[d] assimilates into [p]
- How about- iron man, question mark, action plan, green
pot, brown bag and fan belt
PA- Velarisation of Alveolar Sounds
- The alveolar stop [t] changing to a velar stop [k]
to match a velar sound such as [k] or [g]
following it.
- Credit card, smart card, great cook, let go
- The change is an instance of PA in which the
alveolar stop sound becomes a velar stop in
anticipation of a velar sound that follows-
example of regressive assimilation
- Another example is the change of [d] to [g]
sound before [k] and [g]
- Check out these words good cook, ground
control, hard copy, red guitar,
- How about these words human capital,golden
gate, tin can, town clerk.
PA- Palatalisation of Alveolar Sounds
- In connected speech, the sound fricatives [s]
and [z] is palatalised as [e+ C- wL+
before the palatal sounds [e+ C-
w+
-`4 ]4] wpCe
e4C+
--] EO w-e
eOO+
-4) E]C w)L
)]+
- The alveolar fricative [s] precedes palatal
fricative [e] or a palatal approximant [j].
- The change of [s] to a [e+ is an instance of
PA in which the alveolar fricative sound becomes
more like a palatal fricative in anticipation of the
palatal sound that follows- eg of RA
- Check out these words: cheese shop, these
sheep, wise young man
Voicing Assimilation
- A phoneme changes to match the
phonation of a previous or following
sound.
- Can be observed in the pronunciation of a
plural morpheme and the past tense
morpheme- sometimes referred to as
morphophonemic rule.
- You deduce the rule from these examples
Cats, dogs, bees, washed, missed, sipped,
pulled, robbed, lived
Ellision
- In connected speech, it is common for sound
segments to be deleted or omitted.
- It can occur within the word or across word
boundary.
- This segmental feature of speech is commonly
observable in words unstressed syllables which
are omitted in rapid speech.
- Camera [kmrC] medicine [mdsin] memory,
cup of coffee, pen and paper
- In some cased non ellision of a phoneme might
sound odd and is indicative of a non proficient
speaker, eg chocolate, vegetable
Linking
- In rapid speech, sound segments of a
word are seldom discrete or clearly
separated from the sound of other words.
- They become linked or connected.
- In English, the linking [r] is prominent
especially before a vowel.
- Four apes [fO:reips]
- Formula A, media event
- In each instance the [r] sound is inserted
between the juncture of two words.
You might also like
- 99 Pounds - ScoreDocument5 pages99 Pounds - Scoreduane8wagnerNo ratings yet
- Jali-Jali Full ScoreDocument14 pagesJali-Jali Full ScoreGloria Dorothy Rolanda100% (2)
- Kortlandt Beekes ArmeniacaDocument247 pagesKortlandt Beekes ArmeniacaAlexander Nikolaev100% (1)
- Завдання для самостійної роботи з Фонетики 1 курсDocument4 pagesЗавдання для самостійної роботи з Фонетики 1 курсIvanka ShumykNo ratings yet
- Aspects of Connected SpeechDocument32 pagesAspects of Connected SpeechBrendon Jikal100% (2)
- 14 Aspects of Connected SpeechDocument23 pages14 Aspects of Connected Speechammaranas100% (1)
- Phonological Rules: LING101 September 24, 2009Document10 pagesPhonological Rules: LING101 September 24, 2009Francesca GiannottaNo ratings yet
- Task 1Document7 pagesTask 1YUSRI BIN KIPLI MoeNo ratings yet
- English Week 1-4 NotesDocument15 pagesEnglish Week 1-4 Notesfizasm33No ratings yet
- Features of Connected SpeechDocument6 pagesFeatures of Connected Speechdenieb1311No ratings yet
- Modifications of Consonants in Connected SpeechDocument11 pagesModifications of Consonants in Connected Speechelshen mamedovNo ratings yet
- Types of Articulatory ProcessesDocument4 pagesTypes of Articulatory ProcessesDiahNo ratings yet
- A. Assimilatory Processes A. Consonant Assimilates Vowel FeaturesDocument4 pagesA. Assimilatory Processes A. Consonant Assimilates Vowel FeaturesTheywa DeNo ratings yet
- Phonology - PPT With Cover Page v2Document49 pagesPhonology - PPT With Cover Page v2BAH TiarNo ratings yet
- Linguistics NotesDocument5 pagesLinguistics NotesDexter LoughNo ratings yet
- English Phonology: 1 Semester 2021 Dr. Eman AlhusaiyanDocument28 pagesEnglish Phonology: 1 Semester 2021 Dr. Eman AlhusaiyanDr.Eman LinguisticsNo ratings yet
- Rhythm &intonationDocument16 pagesRhythm &intonationAnshuman TripathiNo ratings yet
- Connected SpeechDocument66 pagesConnected Speechandrewcook33332No ratings yet
- Week7 Phonological RulesDocument20 pagesWeek7 Phonological Rules6469yhkmtjNo ratings yet
- Phonetics and PhonologyDocument19 pagesPhonetics and PhonologyjayzebraNo ratings yet
- Rules On Subject Verb AgreementDocument20 pagesRules On Subject Verb AgreementMarife BumatayNo ratings yet
- Dr. Riceli C. Mendoza University of Southern Mindanao PhilippinesDocument17 pagesDr. Riceli C. Mendoza University of Southern Mindanao PhilippinesJose Luis Gatillon SotoNo ratings yet
- Phonology: The Sound Patterns of Language: 01:615:201 Introduction To Linguistic Theory Adam SzczegielniakDocument50 pagesPhonology: The Sound Patterns of Language: 01:615:201 Introduction To Linguistic Theory Adam SzczegielniakRahayu Ratu AzizahNo ratings yet
- PhonologyDocument48 pagesPhonologyCaryll BaylonNo ratings yet
- Grammar SchoolDocument21 pagesGrammar SchoolNebojša KrmpotNo ratings yet
- Phonology - PPT RemovedDocument42 pagesPhonology - PPT RemovedTommyNo ratings yet
- Aspects of Connected Speech: TE10003! The Phonology of EnglishDocument15 pagesAspects of Connected Speech: TE10003! The Phonology of EnglishDherick RaleighNo ratings yet
- Cantonese PhonologyDocument9 pagesCantonese PhonologyJorge Guerrero100% (1)
- Phonological Processes Sem1Document23 pagesPhonological Processes Sem1sadiyatariq496No ratings yet
- Connected SpeechDocument6 pagesConnected SpeechValentina CandurinNo ratings yet
- Connected Speech: Communication.... Chat... Talk... Sing..Document16 pagesConnected Speech: Communication.... Chat... Talk... Sing..Dilrabo KoshevaNo ratings yet
- ORAL II - ALLPHONES - CONSONANTS and VOWELSDocument36 pagesORAL II - ALLPHONES - CONSONANTS and VOWELSMaría M MalakNo ratings yet
- Focus in MalagasyDocument22 pagesFocus in Malagasyalexandreq100% (1)
- Assimilation (Change)Document11 pagesAssimilation (Change)Patrícia Argôlo RosaNo ratings yet
- النحو المقارنDocument148 pagesالنحو المقارنAhmedAl-agwedNo ratings yet
- Phonology 3 PDFDocument64 pagesPhonology 3 PDFLingua Academy-club LacNo ratings yet
- Phonics RulesDocument18 pagesPhonics RulesAisy Astarina100% (1)
- The - R - SoundDocument8 pagesThe - R - SoundAgustina AcostaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Classification of Sound UnitsDocument14 pagesLecture 2 - Classification of Sound UnitsDaniel CNo ratings yet
- Assimilation: Is A Process of Alteration of Speech Sounds As A Result of WhichDocument16 pagesAssimilation: Is A Process of Alteration of Speech Sounds As A Result of Whichapi-283816739No ratings yet
- Phonetic Rules VowelsDocument3 pagesPhonetic Rules Vowelsyoussof2008No ratings yet
- PHONOLOGYDocument65 pagesPHONOLOGYcristinesilvaNo ratings yet
- Aspects of Connected SpeechDocument9 pagesAspects of Connected SpeechIosif StalinNo ratings yet
- Connected SpeechDocument7 pagesConnected SpeechMaria Eugenia GlosnickiNo ratings yet
- 9 Place Assimilation & Types of AssimilationDocument16 pages9 Place Assimilation & Types of AssimilationAngelline NyittiNo ratings yet
- Third StageDocument10 pagesThird StageSara N AhmadNo ratings yet
- Features of Connected SpeechDocument30 pagesFeatures of Connected SpeechJoselyn Wrande Sanhueza100% (2)
- Connected Speech BookletDocument32 pagesConnected Speech BookletNELCNo ratings yet
- English and Kazakh Phonemes and Their Allophones: Done by Bagzhan Uais, Aya21-3MDocument20 pagesEnglish and Kazakh Phonemes and Their Allophones: Done by Bagzhan Uais, Aya21-3MBagzhanNo ratings yet
- PHONOLOGY The Sound Patterns of Language 1Document36 pagesPHONOLOGY The Sound Patterns of Language 1Jeannette DeguinonNo ratings yet
- Phonology 17Document104 pagesPhonology 17farhan ramadhanNo ratings yet
- Types of Allophones and Their UsesDocument9 pagesTypes of Allophones and Their UsesDanielGonzálezZambrano83% (6)
- Nouns & AdjDocument4 pagesNouns & AdjНаталія АтласNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 and Chapter 7 - MorphologyDocument14 pagesChapter 6 and Chapter 7 - MorphologyEspe PascualNo ratings yet
- Ngữ âm - âm vị - CONSONANT 1's reviewDocument4 pagesNgữ âm - âm vị - CONSONANT 1's review2357080026No ratings yet
- Lecture 9. Phonological ProcessesDocument4 pagesLecture 9. Phonological Processesbe creativeNo ratings yet
- ÔN TẬP NGỮ ÂM - ÂM VỊ HỌC - LÝ THUYẾTDocument8 pagesÔN TẬP NGỮ ÂM - ÂM VỊ HỌC - LÝ THUYẾTTrà Nguyễn HươngNo ratings yet
- Conjugation: Write, Wrote, Written (Marking byDocument4 pagesConjugation: Write, Wrote, Written (Marking byNylilav Enish Lagdamen NimbraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document13 pagesChapter 7linh nguyenNo ratings yet
- MORPHOLOGY (Morphs, Allomorph, Grammatical and Phonological Conditioning)Document17 pagesMORPHOLOGY (Morphs, Allomorph, Grammatical and Phonological Conditioning)Sergio Felix CuratacaniNo ratings yet
- Seminar (2) ГотовоDocument5 pagesSeminar (2) ГотовоЯна ГержанNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: English VowelsDocument13 pagesUnit 3: English VowelsRachma Gupita100% (2)
- No Nama Tandatangan Kehadiran Catatan: Pendaftaran Peserta Beyblade Alpha One Center (Tamparuli)Document3 pagesNo Nama Tandatangan Kehadiran Catatan: Pendaftaran Peserta Beyblade Alpha One Center (Tamparuli)Mohd Zulkhairi AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Pace Race: Marathon, 1/2 Marathon, 10K & 5K Customizable, Printable Pace BandsDocument3 pagesPace Race: Marathon, 1/2 Marathon, 10K & 5K Customizable, Printable Pace BandsMohd Zulkhairi AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Inovasi PBS Eng Y2 01Document1 pageInovasi PBS Eng Y2 01Mohd Zulkhairi AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Cycle 2Document1 pageCycle 2Mohd Zulkhairi AbdullahNo ratings yet
- New Doc 7Document1 pageNew Doc 7Mohd Zulkhairi AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Lampiran A SK Penimbawan Tuaran Sabah: Tahun 4Document2 pagesLampiran A SK Penimbawan Tuaran Sabah: Tahun 4Mohd Zulkhairi AbdullahNo ratings yet
- New Doc 6Document1 pageNew Doc 6Mohd Zulkhairi AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Bibliografi: Mechanic Module". Research Report - Vol 23, 9.955-967Document2 pagesBibliografi: Mechanic Module". Research Report - Vol 23, 9.955-967Mohd Zulkhairi AbdullahNo ratings yet
- New Doc 36Document1 pageNew Doc 36Mohd Zulkhairi AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Keputusan Analisis Data Dengan Menggunakan Ujian-T Sampel Bersandar Bagi HDocument2 pagesKeputusan Analisis Data Dengan Menggunakan Ujian-T Sampel Bersandar Bagi HMohd Zulkhairi AbdullahNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Introduction of The ResearchDocument43 pages1.0 Introduction of The ResearchMohd Zulkhairi AbdullahNo ratings yet
- TSL3133 AR Proposal RubricDocument10 pagesTSL3133 AR Proposal RubricMohd Zulkhairi AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Lampiran G Keputusan Analisis Diskriptif Soal Selidik Kajian SebenarDocument4 pagesLampiran G Keputusan Analisis Diskriptif Soal Selidik Kajian SebenarMohd Zulkhairi AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Module Edu 3105Document232 pagesModule Edu 3105Mohd Zulkhairi Abdullah50% (2)
- Module TSL 3107Document73 pagesModule TSL 3107Mohd Zulkhairi AbdullahNo ratings yet
- RPH BM RaskanDocument26 pagesRPH BM RaskanMohd Zulkhairi AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Upsr Model Test 1Document17 pagesUpsr Model Test 1Norhaslina Mohd NoorNo ratings yet
- Module Lga 3102Document123 pagesModule Lga 3102Mohd Zulkhairi AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Module TSL 3108Document96 pagesModule TSL 3108Mohd Zulkhairi Abdullah100% (2)
- English Phonetics and Phonology 6Document20 pagesEnglish Phonetics and Phonology 6Mohd Zulkhairi AbdullahNo ratings yet
- English Phonetics and Phonology 5Document18 pagesEnglish Phonetics and Phonology 5Mohd Zulkhairi AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Task 4 - Luisa Fernanda Godoy TorresDocument6 pagesTask 4 - Luisa Fernanda Godoy TorresLuisa Fernanda GodoyNo ratings yet
- Task 6-Oral-Production-ActivityDocument12 pagesTask 6-Oral-Production-ActivityIVONNE GARCIANo ratings yet
- 2nd Year PhoneticsDocument4 pages2nd Year Phoneticskhadidja bnh0% (1)
- Phonetic and Pronunciation ExerciseDocument3 pagesPhonetic and Pronunciation ExerciseThư ĐỗNo ratings yet
- Phonological Processes in Connected SpeechDocument7 pagesPhonological Processes in Connected Speechsara ciullaNo ratings yet
- Studies in Lycian and Carian Phonology ADocument30 pagesStudies in Lycian and Carian Phonology AMar AlexNo ratings yet
- Kakyo - Zeami's Fundamental Principles of Acting. Part ThreeDocument23 pagesKakyo - Zeami's Fundamental Principles of Acting. Part ThreeBru PereiraNo ratings yet
- Add On - CERTIFICATE COURSE IN SPOKEN ENGLISH FOR COMMUNICATION SKILLDocument5 pagesAdd On - CERTIFICATE COURSE IN SPOKEN ENGLISH FOR COMMUNICATION SKILLSimran KaurNo ratings yet
- Slovenačka FonologijaDocument4 pagesSlovenačka FonologijaHaris HadžibaščauševićNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 History of ELDocument7 pagesLecture 2 History of ELАліна КопилевичNo ratings yet
- Syllables and Moras in Arabic: 1 CV-, VC-, and C-DialectsDocument31 pagesSyllables and Moras in Arabic: 1 CV-, VC-, and C-Dialectsmimouna bourzegNo ratings yet
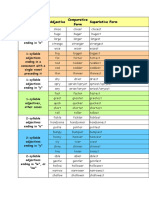
- Comparative & Superlative GuideDocument2 pagesComparative & Superlative GuideDannhy GreenNo ratings yet
- MODULE-I Phonology & Morphology IIyrDocument12 pagesMODULE-I Phonology & Morphology IIyrAbhiNo ratings yet
- Table of AdjectivesDocument2 pagesTable of AdjectivesNOOR HUWAIDAH BINTI BALKI KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- How - To.sing.a.song Yvette - GuilbertDocument204 pagesHow - To.sing.a.song Yvette - Guilbertpiu.pianistNo ratings yet
- đề ngữ âm - âm vị học 3Document7 pagesđề ngữ âm - âm vị học 3Khanh VõNo ratings yet
- Un Abecedaire Qui Ne Manque Pas de PiquDocument16 pagesUn Abecedaire Qui Ne Manque Pas de PiquSeka ModlaNo ratings yet
- RPS Bi Tahun 2Document9 pagesRPS Bi Tahun 2Sleapy HeadNo ratings yet
- Virama 1Document1 pageVirama 1SchahebNo ratings yet
- American English Diphthongs and DigraphsDocument6 pagesAmerican English Diphthongs and Digraphsalberto craviotoNo ratings yet
- Bookshelf: Debra GreschnerDocument3 pagesBookshelf: Debra GreschnermarisaNo ratings yet
- Early Reading 14 - A Bug in The Mud PDFDocument6 pagesEarly Reading 14 - A Bug in The Mud PDFKatharina Krawtschenko100% (1)
- Syllabification Algorithm Based On Syllable Rules Matching For Malay LanguageDocument8 pagesSyllabification Algorithm Based On Syllable Rules Matching For Malay LanguageNathanael YehezkielNo ratings yet
- Unit 3, Module - 1Document13 pagesUnit 3, Module - 1Sheethal SarmaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Subject Class Theme Topic Language Focus Main Skill Integrated Skill Teaching Aids Educational Emphases: ConstructivismDocument1 pageLesson Plan Subject Class Theme Topic Language Focus Main Skill Integrated Skill Teaching Aids Educational Emphases: ConstructivismJoanne OngNo ratings yet
- Les Mots ApparentésDocument3 pagesLes Mots ApparentésLancasTchenNo ratings yet