Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reproductive System: Human Life Cycle
Reproductive System: Human Life Cycle
Uploaded by
Ansella KuamanoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Reproductive System: Human Life Cycle
Reproductive System: Human Life Cycle
Uploaded by
Ansella KuamanoCopyright:
Available Formats
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
Human Life Cycle
The reproductive cycle in males and females differs greatly. Sexual maturity in females occurs between the ages of 11-13 and in males from 14-16. DNA is distributed among 46 chromosomes within the nucleus. Mitosis (duplication division) occurs in cells other than reproductive cells. The reproductive system uses mitosis (reduction division). Each reproductive cell contains 23 chromosomes rather than 46 in other cells.
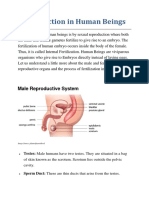
Male Reproductive System
The male reproductive system includes the following: testes, epididymides, vasa deferentia, seminal vesicles, prostate gland, urethra, bulbourethral, and the penis.
The penis is the male organ of sexual intercourse. The penis has a long shaft and an enlarged tip called the glans penis, which at birth is covered by a layer of skin. Circumcision is the surgical removal of the penis foreskin.
Spongy, erectile tissue containing distensible blood spaces extends through the shaft of the penis. During arousal, autonomic nerves release nitric oxide (NO) This leads to the production of cGMP which causes the smooth muscle of incoming arterial walls to relax and the erectile tissue to fill with blood. The veins that take blood away from the penis are compressed and the penis becomes erect.
The testes produce sperm and the male sex hormones. They lie outside the abdominal cavity within the scrotum. The seminiferous tubules are packed with cells undergoing spermatogenesis (production of sperm). Mature sperm has 3 distinct parts: a head, middle piece, and tail. Mitochondria in the middle piece provide energy for the tail movement.
Sex cells reproduce with meiosis as opposed to mitosis. Spermatogenesis occurs as follows:
The hypothalamus has ultimate control of the testes' sexual function because it secretes a hormone called gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH). There are 2 gonadotropic hormones: folliclestimulating (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH), which are present in both males and females. In males, FSH promotes the production of sperm in the seminiferous tubules. LH controls the production of testosterone. Testosterone is the main sex hormone and essential for the normal development and functioning of the male organs.
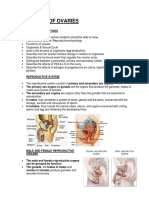
Female Reproductive System
The female reproductive system includes the ovaries, oviducts, uterus, cervix, and vagina.
The ovaries release one egg a month and fertilization occurs in the oviduct. Development occurs in the uterus. The vagina is the birth canal as well as the organ for sexual intercourse and outlet for menstrual flow. Development of the embryo and fetus takes place in the uterus.
The external organs of the female are known collectively as the vulva.
Upon sexual stimulation, the labia minora, the vaginal wall, and the clitoris become engorged with blood. The breasts also swell and the nipples become erect. The labia majora enlarge, redden, and spread away from the vaginal opening. Orgasm occurs the height of sexual response. Unlike males, females have no refractory period and can have multiple orgasms in a single sexual experience.
Female Hormone Levels
Female hormone levels cycle on a monthly basis and the ovarian cycle drives the uterine cycle. An ovary contains many follicles and each one contains an immature egg, called an oocyte. A female is born with as many as 2 million follicles, but is reduced to 300,000-400,000 by puberty. During oogenesis, a single follicle actually goes through all stages in one place within the ovary. As the follicle matures, layers of follicel cells surround a secondary oocyte. Eventually, the mature follicle ruptures, the secondary oocyte is released. The follicle then becomes the corpus luteum which eventually disintegrates.
Oogenesis
The ovarian cycle:
Estrogen and progesterone affect not only the uterus, but other parts of the body as well. Estrogen is largely responsible for secondary sex characteristics in females. Menopause is a period in a woman's life where the ovarian cycle ceases. This occurs around 45-55 years of age.
Estrogen and progesterone have other functions, one affecting the endometrium causing the uterus to undergo a cyclical series of events known as the uterine cycle:
Following unprotected sexual intercourse, many sperm will most likely make their way into the oviduct, where the egg is located following ovulation. Only one sperm fertilizes the egg and it becomes a zygote, which begins development as it travels down the oviduct to the uterus. The endometrium is now prepared to receive the developing embryo.
IUD = INTRA UTERINE DEVICE
You might also like
- Grade 8 Lesson - MitosisDocument3 pagesGrade 8 Lesson - MitosisBerliese Frias93% (28)
- Human Reproduction - Class 10Document7 pagesHuman Reproduction - Class 10faizalNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3 Human Reproduction - WatermarkDocument23 pagesChapter - 3 Human Reproduction - WatermarkDurgesh SainiNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive BiologyDocument8 pagesHuman Reproductive BiologyEda, Haidee Gennie Anne R.No ratings yet
- Maleand Female Reproductive System @muhammad Usama BilalDocument4 pagesMaleand Female Reproductive System @muhammad Usama BilalumerkhanNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemsDocument30 pagesReproductive SystemsMARIAM AVILANo ratings yet
- Reproduction (M, F) : Lecturer: Dr. R. Ahangari University of Central Florida, OrlandoDocument10 pagesReproduction (M, F) : Lecturer: Dr. R. Ahangari University of Central Florida, Orlandokuku411No ratings yet
- MODULE 1-Lesson 2-3Document11 pagesMODULE 1-Lesson 2-3JOHN BRAINARD PEJONo ratings yet
- Gender and Society CompileDocument32 pagesGender and Society Compileクイーンクイーン ロペスNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument6 pagesHuman Reproductionlakshshah5116No ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument28 pagesFemale Reproductive System1-LUMALANG Ashley Anne A.No ratings yet
- Gned 10 - Biomedical Perspective of Gender and SexualityDocument6 pagesGned 10 - Biomedical Perspective of Gender and Sexualityjoanna.filosopoNo ratings yet
- Female Reprodutive System IntoductionDocument6 pagesFemale Reprodutive System IntoductionSai KaushikNo ratings yet
- Ch. 38 Human ReproductionDocument38 pagesCh. 38 Human ReproductionERIC ASAMAMLEH KLEMEHNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document7 pagesChapter 3Abhishek Yadav RNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument3 pagesHuman ReproductionLemon GundersonNo ratings yet
- Bio12 c10 10 7Document8 pagesBio12 c10 10 7Eric McMullenNo ratings yet
- Chapter Ii: Biochemical Perspective in Gender and Sexuality Lesson 1: Anatomy and Physiology of ReproductionDocument10 pagesChapter Ii: Biochemical Perspective in Gender and Sexuality Lesson 1: Anatomy and Physiology of ReproductionDevin Jake Maylas FeoNo ratings yet
- Functions of Ovaries: Learning ObjectivesDocument9 pagesFunctions of Ovaries: Learning ObjectivesUloko ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document16 pagesLecture 3Smasher AustineNo ratings yet
- Coordinated Functions of The Reproductive, Endocrine And2Document27 pagesCoordinated Functions of The Reproductive, Endocrine And2Second BooksNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System and Human Development 2018Document53 pagesReproductive System and Human Development 2018Kâmê KêlâhNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System Powerpoint LectureDocument55 pagesReproductive System Powerpoint LectureJames DaurayNo ratings yet
- Inbound 4525214668487640543Document12 pagesInbound 4525214668487640543Neña Bautista PagalNo ratings yet
- Reproduction & GrowthDocument96 pagesReproduction & Growthbiologi88No ratings yet
- Sexual_Reproduction_in_HumansDocument7 pagesSexual_Reproduction_in_HumansOditor MwaangaNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemDeepak VermaNo ratings yet
- Hormonal Control OVOGENESIS Part2Document12 pagesHormonal Control OVOGENESIS Part2Abd EloihedNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemDeepak VermaNo ratings yet
- Sexual ReproductionDocument16 pagesSexual Reproductionprince matamboNo ratings yet
- Dekey Biology ProjectDocument12 pagesDekey Biology ProjecttseringchondenmakhamNo ratings yet
- CP Ovarian Cyst Chap5Document11 pagesCP Ovarian Cyst Chap5Katherine 'Chingboo' Leonico LaudNo ratings yet
- Good Afternoon: Prepared byDocument102 pagesGood Afternoon: Prepared byKrishna PatelNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument3 pagesHuman Reproductive SystemAltheaNo ratings yet
- Unit Ii - Biomedical Perspective in Gender and SexualityDocument14 pagesUnit Ii - Biomedical Perspective in Gender and SexualityhanzellebganNo ratings yet
- Week 16 - Reproductive SystemDocument71 pagesWeek 16 - Reproductive SystemGeevee Naganag VentulaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System: Synopsis Menstrual Cycle Spermatogenesis Oogenesis Process of Reproduction Pregnancy ParturitionDocument57 pagesReproductive System: Synopsis Menstrual Cycle Spermatogenesis Oogenesis Process of Reproduction Pregnancy ParturitionBlack RoseNo ratings yet
- MRGR Reproductive System Ysh17Document13 pagesMRGR Reproductive System Ysh17Yash PandeyNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Reproductive and Sexual HealthDocument34 pagesWeek 3 Reproductive and Sexual Healthraise concern100% (1)
- Male Versus Female Reproductive SystemsDocument6 pagesMale Versus Female Reproductive SystemsAssignmentLab.comNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument89 pagesReproductive SystemIbrahim Mahmoud Ali100% (1)
- Sexual Reproduction in Humans Part 2Document37 pagesSexual Reproduction in Humans Part 2Janae CampbellNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument11 pagesHuman ReproductionScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive Organs - Chapter ReviewDocument3 pagesFemale Reproductive Organs - Chapter Reviewlandegre KNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument23 pagesHuman Reproductive SystemQuennie AceronNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Gender Society 1Document32 pagesModule 2 Gender Society 1John Syvel QuintroNo ratings yet
- Reproductive and Endocrine SystemsDocument38 pagesReproductive and Endocrine SystemsDebbie Ann LaguindabNo ratings yet
- (Reading 6) The Reproductive SystemDocument22 pages(Reading 6) The Reproductive SystemPhú LêNo ratings yet
- Biology Project Class XIIDocument34 pagesBiology Project Class XIIBimal DasNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemDocument7 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemMarl Dindreb JaoNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument30 pagesReproductive SystemmfaizchejamriNo ratings yet
- Text 1Document2 pagesText 1enci1018lanczNo ratings yet
- Types of Animal ReproductionDocument51 pagesTypes of Animal ReproductionBonny Ya SakeusNo ratings yet
- Reproductive HormonesDocument26 pagesReproductive HormonesInji IdupalagiNo ratings yet
- Hormones and ReproductionDocument4 pagesHormones and ReproductionJNo ratings yet
- Chapter 36-1 Reproductive SystemsDocument25 pagesChapter 36-1 Reproductive Systemsnancie8No ratings yet
- Human Reproduction-1Document21 pagesHuman Reproduction-1Coni Espinoza YupanquiNo ratings yet
- Physiology II - PresentationDocument11 pagesPhysiology II - PresentationalshmryalmwydNo ratings yet
- Mammalian Reproductive SystemDocument50 pagesMammalian Reproductive SystemLeena MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Hormones in Human ReproductionDocument93 pagesHormones in Human ReproductionKevin Roi RomeroNo ratings yet
- For K Norie PDFDocument1 pageFor K Norie PDFAnsella KuamanoNo ratings yet
- Made-STR Lama PDFDocument1 pageMade-STR Lama PDFAnsella KuamanoNo ratings yet
- Jadwal Poliklinik September 2022Document2 pagesJadwal Poliklinik September 2022Ansella KuamanoNo ratings yet
- Format Pelaporan Vaksinasi Covid-19 PKM PinelengDocument291 pagesFormat Pelaporan Vaksinasi Covid-19 PKM PinelengAnsella KuamanoNo ratings yet
- Family PlanningDocument12 pagesFamily Planningeriska yunita sariNo ratings yet
- Proliferative EndometriumDocument4 pagesProliferative EndometriumKristine Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology: Male Reproductive SystemDocument7 pagesAnatomy & Physiology: Male Reproductive Systemkristel ludangcoNo ratings yet
- 12 Biology Notes Ch02 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument7 pages12 Biology Notes Ch02 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsJatin kumar100% (1)
- Unit Test 2with AnswersDocument22 pagesUnit Test 2with AnswersPhysicshekNo ratings yet
- Plants WorksheetDocument5 pagesPlants WorksheetRachel LeeNo ratings yet
- CH 16 ReproductionDocument72 pagesCH 16 Reproductionqonita.hanifa7No ratings yet
- Santrock Powerpoint Chapter 2Document32 pagesSantrock Powerpoint Chapter 2shaigest100% (1)
- Influence of Incubation Temperature On I. Gross Embryology, Temperature Tolerance and Rates of Embryonic DevelopmentDocument17 pagesInfluence of Incubation Temperature On I. Gross Embryology, Temperature Tolerance and Rates of Embryonic DevelopmentJuan Camilo SantillanNo ratings yet
- Biology (044) - Practical Lab Manual (Term - 1)Document24 pagesBiology (044) - Practical Lab Manual (Term - 1)Tejeswar MajhiNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1Document2 pagesExercise 1Elishae SamonteNo ratings yet
- Carlos Simon, Antonio Pellicer-Stem Cells in Human Reproduction_ Basic Science and Therapeutic Potential, 2nd Edition (Reproductive Medicine & Assisted Reproductive Techniques)-Informa Healthcare (200Document273 pagesCarlos Simon, Antonio Pellicer-Stem Cells in Human Reproduction_ Basic Science and Therapeutic Potential, 2nd Edition (Reproductive Medicine & Assisted Reproductive Techniques)-Informa Healthcare (200yasirhistoNo ratings yet
- Classification of PlantsDocument5 pagesClassification of PlantsodylorNo ratings yet
- The Most Underappreciated Fact About Men by Roy BaumeisterDocument19 pagesThe Most Underappreciated Fact About Men by Roy BaumeisterMark PlusNo ratings yet
- Specialized Crime Investigation: Lesson 15Document7 pagesSpecialized Crime Investigation: Lesson 15Apple AsneNo ratings yet
- Conducta Reproductiva en Pequeños AnimalesDocument13 pagesConducta Reproductiva en Pequeños AnimalesmateosanchezNo ratings yet
- Class 9 ICSE Chapter 4 - The FlowersDocument7 pagesClass 9 ICSE Chapter 4 - The FlowersArpan KaurNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Lesson Perpetuation of LifeDocument2 pages2.3 Lesson Perpetuation of LifeHazel Aloha100% (1)
- NAME: Sonwalkar Pratik Rohidas Class: 12 R1 Subject: Biology TOPIC: Detailed Study On Infertility Its Causes and TreatmentDocument27 pagesNAME: Sonwalkar Pratik Rohidas Class: 12 R1 Subject: Biology TOPIC: Detailed Study On Infertility Its Causes and TreatmentPratik Sonwalkar0% (1)
- Sex Exploring The Complexities of Human IntimacyDocument2 pagesSex Exploring The Complexities of Human IntimacyGeorge EnacheNo ratings yet
- 16.3 Darwin Presents His CaseDocument25 pages16.3 Darwin Presents His CaseAlex BeilmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. Cell Division: Inter PhaseDocument8 pagesChapter 1. Cell Division: Inter PhaseankurbiologyNo ratings yet
- Genetics Study Guide Answers 1Document2 pagesGenetics Study Guide Answers 1KellyNo ratings yet
- Egg Freezing ProcessDocument3 pagesEgg Freezing Processavisaivf26No ratings yet
- Ploidy BreedingDocument32 pagesPloidy BreedingKavita Mohite80% (5)
- Revision Assignment Class X Ch-How Do Organisms Reproduce?Document2 pagesRevision Assignment Class X Ch-How Do Organisms Reproduce?Gayathri . MNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument19 pagesMeiosisMimie Roslee100% (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 5Document3 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science 5Rosiel Domingo-talosig86% (7)
- Biology Investigatory ProjectDocument21 pagesBiology Investigatory ProjectSubhiksha100% (1)