Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sim Presentation
Sim Presentation
Uploaded by
L.a.ZumárragaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sim Presentation
Sim Presentation
Uploaded by
L.a.ZumárragaCopyright:
Available Formats
Covered Page 1
Least Mastered 2
Competency
Guide Card 3
Introduction 4
Introduction 5
Activity Card 1 6
Activity Card 2 7
Activity Card 3 8
Activity Card 4 9
Activity Card 5 10
Enrichment Card 1 16
Enrichment Card 2 17
Enrichment Card 3 18
Enrichment Card 4 19
Enrichment Card 5 20
Assessment Card 1 11
Assessment Card 2 12
Assessment Card 3 13
Assessment Card 4 14
Assessment Card 5 15
Answer Card 16
Reference Card 17
MAIN TASK
State the Second Law of Motion, Law of
Acceleration.
Hello! Im Mr. Accel short for
Acceleration. Welcome to another
fun-filled adventure as we take the
journey to the world of Physics. This
time, we will be talking about the 2
nd
Law of motion, Acceleration. So,
fasten your seatbelt as we go and
learn! Lets go!
Have you watched what happens to a pile of leaves on awindy day? A light breeze might gently scatter the leaves
across the lawn, but a huge gust of wind would send the leaves
whirling into the air. If the wind got stronger, the leaves would soar through the air even fasterand your bike
might even tip over, too! Remember, Newtons First Law tells us that an object will stay at rest or in motion
unless a force changes it. In his second law, he explains how unbalanced forces cause objects to accelerate,
or move faster. Newtons Second Law says that an objects acceleration depends on two things: force and mass.
As the force exerted on an object increases, the acceleration will increase. Thats why when the gentle breeze
turns into a strong gust, the leaves move faster and farther. As the force of the wind increases, the
Acceleration of the moving leaves increases, too. The relationship between acceleration and mass is just the
opposite. The more mass something has, the less it will accelerate. Leaves are light and have very little mass, so
they will accelerate quickly. Your bicycle, on the other hand, has much more
mass than the leaves. The same gust of wind that blew the leaves into your neighbors yard might have scooted
your parked bicycle only a few inches.
Below is a summary of Newtons Second Law. Fill in the missing words to complete the sentences.
Then, complete the riddle below by finding the matching number and writing the letter.
Newtons Second Law
___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ forces cause an object to accelerate.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Acceleration depends on ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ and ___ ___ ___ ___ .
11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19
As the force increases, the ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___
increases, too. 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31
Why did the artist paint on cement blocks instead of paper?
He wanted to create a ___ ___ ___ ______ ___ ___ P ___ ___ ___ ___.
16 4 18 19 28 23 26 29 9 8 25
Newtons Second Law
1. An object with a mass of 11.78 kg experiences a force of 19.80 N. What is the acceleration of the
object?
233.24 m/s/s
3.88 m/s/s
1.68 m/s/s
2. Calculate the acceleration of the car with a mass of 25.69 kg that experiences a force of 29.22 N.
0.88 m/s/s
1.14 m/s/s
750.66
3. An object is suggested with an acceleration of 2.87 m/s/s and a force of 23.33. what is its mass?
8.13 kg
3.12 kg
0.25 kg
Loading & Unloading!
1. An object with a mass of 11.78 kg experiences a force
of 19.80. What is the acceleration of the object?
A. 233.24 m/s2 B. 3.88 m/s2 C. 1.68 m/s2
2. Calculate the acceleration of the car with a mass
of25.69 kg that experiences a force of 29.22 N.
A. 0.88m/s2 B. 1.14 m/s2 C. 750.66 m/s2
3. An object is suggested with an acceleration of 2.87
m/s2 and a force of 23.33. What is its mass?
A. 8.13 m/s2 B. 3.12m/s2 C. 0.25 m/s2
Direction: Solve the following problems and circle the
letter corresponding to its answer.
1. School bus A and School bus B have 35 students each. School bus A runs
45 km/h, while school bus B runs 60 km/h. if they start at the same
position, which school bus do you think will arrive in school first?
A.Bus A C. Both B. Bus B
1. Suppose School bus A has 20 students on board and school bus B has 45,
and both buses run at 60 km/h. If start at the same position, which bus will
accelerate and therefore arrive in school the soonest?
A.Bus A
C. Both
B. Bus B
3. What is the mass of an object if a force of 34 N
produces an acceleration of 4 m/s2?
A Bicycle and a rider
together have mass
of 90 kg. if the
bicycle moves at 6.0
N, how much force
is needed to bring it
to a stop in 5.0 s?
SOLUTION
ANSWER
This can help:
a= V1/t
F=ma
A 52-kg water-
skier is being pulled by a
speedboat. The force
causes her to accelerate at
2 m/s2. Calculate the net
force that causes this
acceleration.
What is the force on a
1,000-kg elevator
accelerating at
2m/s2?
What three quantities
are related in
Newtons second Law
of motion?
When the net force
on an object
increases, how does
the objects
acceleration change?
Suppose you doubled
the force acting on an
object. In what way
could you change its
mass to keep its
acceleration
unchanged?
1. According to Newtons Second Law of motion,
force is equal to mass times acceleration.
2. The net force of an object is greater than the
product of its acceleration and its mass.
3. One Newton equals the force required to
accelerate one kilogram of mass at 1 meter per
second square.
4. The acceleration happened in 500
kg and force of 5N is 40 m/s2.
Write T if the statement is
True and F if False.
You might also like
- PhET Collision LabDocument2 pagesPhET Collision Labcaleb fNo ratings yet
- 08 - Newtons Laws Practice WorksheetDocument2 pages08 - Newtons Laws Practice WorksheetShiella Mae Baltazar Bulauitan50% (2)
- History of TrigonometryDocument6 pagesHistory of TrigonometryL.a.Zumárraga100% (1)
- Chapter 9 ProjectsDocument15 pagesChapter 9 ProjectsDeepakKattimaniNo ratings yet
- Sim Presentation Lauri LeighDocument25 pagesSim Presentation Lauri LeighL.a.ZumárragaNo ratings yet
- Week 2.newtons Second Law of Motion ComputationDocument29 pagesWeek 2.newtons Second Law of Motion ComputationKylle AtencioNo ratings yet
- LAS Science9 Q4 MELCDocument7 pagesLAS Science9 Q4 MELCyamatoshiyoasobiNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of Motion Quiz Review: Show All Work For Math ProblemsDocument2 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion Quiz Review: Show All Work For Math ProblemsMohammad Bilal AkramNo ratings yet
- Ms. Aguilar's 9th Grade Physics Day 1: in Class NotesDocument9 pagesMs. Aguilar's 9th Grade Physics Day 1: in Class Notesapi-583788842No ratings yet
- Adv. Physics Revised1st QDocument33 pagesAdv. Physics Revised1st QYlena AllejeNo ratings yet
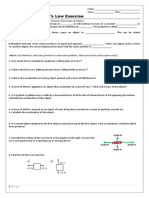
- Newton's Law ExerciseDocument3 pagesNewton's Law ExerciseMaridjan WiwahaNo ratings yet
- Newtons Laws ReviewDocument2 pagesNewtons Laws ReviewHaneen DweikatNo ratings yet
- Newton's Second Law of Motion: Force and AccelerationDocument21 pagesNewton's Second Law of Motion: Force and AccelerationKasey MatthewsNo ratings yet
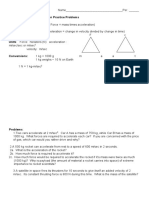
- 05 U3 Ws 4 Newtons 2nd Law PracticeDocument2 pages05 U3 Ws 4 Newtons 2nd Law Practiceapi-197108354No ratings yet
- 17B. Newtons Second Law of MotionDocument17 pages17B. Newtons Second Law of MotionVicky Fortuna OliverosNo ratings yet
- Lesson Title: Laws of Motion: Region I Division of Ilocos SurDocument15 pagesLesson Title: Laws of Motion: Region I Division of Ilocos SurJOHN MAYKALE FARRALESNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Day 1Document21 pagesWeek 2 Day 1ROMELLA FAYE BITUINNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in ScienceDocument9 pagesReviewer in ScienceMirasol Mendoza GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Law of AccelerationDocument6 pagesLaw of AccelerationDrech LanadoNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of Motion Quiz Review: ST ND RDDocument3 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion Quiz Review: ST ND RDChristine BaduaNo ratings yet
- Newton WorksheetDocument7 pagesNewton WorksheetjparkteachNo ratings yet
- Worksheet On ForceDocument3 pagesWorksheet On Forcebrenda marie ralutoNo ratings yet
- Law of Acceleration: For SCIENCE Grade 8 Quarter 1/week 1Document14 pagesLaw of Acceleration: For SCIENCE Grade 8 Quarter 1/week 1Je-ann Acu100% (1)
- Newtons Laws F MaDocument12 pagesNewtons Laws F MaMaruli AmbaritaNo ratings yet
- Phyc 2121 1st SemDocument185 pagesPhyc 2121 1st SemGhian Shean MalazarteNo ratings yet
- G9 Q4 Melc 21Document5 pagesG9 Q4 Melc 21Klare MontefalcoNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 ActivitiesDocument5 pagesGrade 8 ActivitiesLhaine F.No ratings yet
- 1 - Newtons Laws AnsDocument7 pages1 - Newtons Laws Anspaniz bNo ratings yet
- Newtons 2nd Law NotesDocument23 pagesNewtons 2nd Law NotesJulio Olivos100% (1)
- Law of Motion Final PDFDocument32 pagesLaw of Motion Final PDFMark RosalesNo ratings yet
- Answer Key To Forces and Energy SGDocument6 pagesAnswer Key To Forces and Energy SGapi-352926987No ratings yet
- Module 4 Grade 12 General PhysicsDocument3 pagesModule 4 Grade 12 General PhysicsLaarni Tolete100% (1)
- Year 10 Physics - T1Document62 pagesYear 10 Physics - T1tejinder gillNo ratings yet
- TQ - MIDTERM - Gen Phys 1Document2 pagesTQ - MIDTERM - Gen Phys 1Ma. Stephanie HerediaNo ratings yet
- Momentum, Impulse and CollusionDocument14 pagesMomentum, Impulse and CollusionZulfanNo ratings yet
- 2nd Law 4Document3 pages2nd Law 4fatpelicanNo ratings yet
- Applications of Newton's 2nd Law: Unit 3, Causes of Motion Worksheet 4Document2 pagesApplications of Newton's 2nd Law: Unit 3, Causes of Motion Worksheet 4Tati AmadorNo ratings yet
- Exam TemplateDocument2 pagesExam Templatejanecil bonzaNo ratings yet
- Physics Chapters 5 HomeworkDocument6 pagesPhysics Chapters 5 HomeworkRuža KukićNo ratings yet
- CSOL Law of AccelerationDocument34 pagesCSOL Law of AccelerationDave SallaoNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of Motion Worksheet.Document2 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion Worksheet.Llama jennerNo ratings yet
- Force Problems With Answers PDFDocument2 pagesForce Problems With Answers PDFSoy Diego AlcantarNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws Worksheet: Name - Date - Teacher - PeriodDocument3 pagesNewton's Laws Worksheet: Name - Date - Teacher - PeriodDavid GiraldoNo ratings yet
- Newton's Second Law Quiz Answer KeyDocument2 pagesNewton's Second Law Quiz Answer KeyRodel VillafuerteNo ratings yet
- Report Newtons LawDocument6 pagesReport Newtons LawMichael LunaNo ratings yet
- Newton's Second LawDocument4 pagesNewton's Second LawMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Newton's: Laws of MotionDocument37 pagesNewton's: Laws of MotionJohn DcNo ratings yet
- Science 9 - Module 3Document5 pagesScience 9 - Module 3adriantanjay13No ratings yet
- Test+Review+TMD 2Document4 pagesTest+Review+TMD 2Deborah OlofinkuadeNo ratings yet
- Calculating Force WorksheetDocument2 pagesCalculating Force WorksheetCel GrandeNo ratings yet
- A P Newton S Laws NotesDocument11 pagesA P Newton S Laws NotesCiv NortubNo ratings yet
- Quiz-Newtons Laws of Motion: Name - Date - ClassDocument5 pagesQuiz-Newtons Laws of Motion: Name - Date - ClassAlexandrea- Shelly Crutcher-HorsleyNo ratings yet
- G8 Summative TestDocument2 pagesG8 Summative TestMichaelAbdonDomingoFavoNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws ExamplesDocument5 pagesNewton's Laws Exampleshola0987No ratings yet
- Law of Acceleration: Sir Isaac NewtonDocument3 pagesLaw of Acceleration: Sir Isaac NewtonEricka HuseñaNo ratings yet
- L3 Impulse and MomentumDocument82 pagesL3 Impulse and MomentumappleNo ratings yet
- Forces & Motion Classwork & Homework-2013!07!30Document10 pagesForces & Motion Classwork & Homework-2013!07!30Boldie LutwigNo ratings yet
- L9 - Newtons Laws of MotionDocument17 pagesL9 - Newtons Laws of MotionMeeta DeviNo ratings yet
- Type of Event FinaleDocument11 pagesType of Event FinaleL.a.ZumárragaNo ratings yet
- Manual Book Report Format1Document2 pagesManual Book Report Format1L.a.ZumárragaNo ratings yet
- Music TheoryDocument191 pagesMusic TheoryMarc Charlotte100% (41)
- Ojt Narrative FormatDocument12 pagesOjt Narrative FormatL.a.ZumárragaNo ratings yet
- HandyMeal Sept.2018 Financial45Document50 pagesHandyMeal Sept.2018 Financial45L.a.ZumárragaNo ratings yet
- LetterDocument3 pagesLetterL.a.ZumárragaNo ratings yet
- Business Address: Bldg. 3 Tanauan Public Market Tanauan City, BatangasDocument2 pagesBusiness Address: Bldg. 3 Tanauan Public Market Tanauan City, BatangasL.a.ZumárragaNo ratings yet
- Comm ArtsDocument13 pagesComm ArtsL.a.ZumárragaNo ratings yet
- Quantity Item Description Price: Jersey Top Only Spandex Fabric With Rubberized Print 340.00Document1 pageQuantity Item Description Price: Jersey Top Only Spandex Fabric With Rubberized Print 340.00L.a.ZumárragaNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document1 pagePresentation 1L.a.ZumárragaNo ratings yet
- Header LpuDocument3 pagesHeader LpuL.a.ZumárragaNo ratings yet
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection / Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (HIV/AIDS) IsDocument4 pagesHuman Immunodeficiency Virus Infection / Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (HIV/AIDS) IsL.a.ZumárragaNo ratings yet
- Bida Ka, LogoDocument3 pagesBida Ka, LogoL.a.ZumárragaNo ratings yet
- Unang YugtoDocument3 pagesUnang YugtoL.a.ZumárragaNo ratings yet
- Novena of St. GerardDocument5 pagesNovena of St. GerardL.a.ZumárragaNo ratings yet
- ThesisDocument115 pagesThesisL.a.Zumárraga50% (2)
- Basic Words and Phrases in ArabicDocument6 pagesBasic Words and Phrases in ArabicL.a.ZumárragaNo ratings yet
- Seasons of Love LyricsDocument1 pageSeasons of Love LyricsL.a.ZumárragaNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire - FinalDocument20 pagesQuestionnaire - FinalL.a.ZumárragaNo ratings yet
- Sim Presentation Lauri LeighDocument25 pagesSim Presentation Lauri LeighL.a.ZumárragaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Laws of Motion Notes Manoj SirDocument15 pagesChapter 5 Laws of Motion Notes Manoj SirSTUDY WITH MADHAVNo ratings yet
- PHY1004L. - Lab 8 - Energy of A Tossed BallDocument9 pagesPHY1004L. - Lab 8 - Energy of A Tossed Balldiegocely700615No ratings yet
- Circular Motion Practice Problems AP Physics 1-14-15Document3 pagesCircular Motion Practice Problems AP Physics 1-14-15Melanie HarperNo ratings yet
- Science 8 TQDocument6 pagesScience 8 TQAnnie Bagalacsa Cepe-TeodoroNo ratings yet
- 3 4 1 4-Projectile-MotionDocument78 pages3 4 1 4-Projectile-MotionZil HummaNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges, Forces, and Fields: Fall 2008 Lecture 1-1 Physics 231Document40 pagesElectric Charges, Forces, and Fields: Fall 2008 Lecture 1-1 Physics 231IntikhabNo ratings yet
- Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia: Mechanical Engineering Dynamics DDE2063 BY En. Khairulnizam Bin OthmanDocument22 pagesUniversiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia: Mechanical Engineering Dynamics DDE2063 BY En. Khairulnizam Bin OthmanKhairul HafizNo ratings yet
- Ch. 5 KinematicsDocument11 pagesCh. 5 KinematicsJoanne Aga EslavaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - KinematicsDocument12 pagesChapter 1 - KinematicsGerman MartinNo ratings yet
- 19910009728Document118 pages19910009728ramsiNo ratings yet
- Motion ProblemsDocument29 pagesMotion ProblemsBretana joanNo ratings yet
- Rigid Body Dynamics Theory - EDocument45 pagesRigid Body Dynamics Theory - Ethinkiit100% (3)
- My 8.01x NotesDocument417 pagesMy 8.01x Notesserenity3290100% (5)
- Dinamik & Mechanism BMCG1253 Kinematic of Particles: Rectangular Components of Curvilinear MotionDocument3 pagesDinamik & Mechanism BMCG1253 Kinematic of Particles: Rectangular Components of Curvilinear MotionHui ShanNo ratings yet
- Wk1-2 Module 1Document61 pagesWk1-2 Module 1JonathanNo ratings yet
- M.tech Kinematics Dynamics Lab RecDocument20 pagesM.tech Kinematics Dynamics Lab Recmevitsn6No ratings yet
- UNIT 1-Introduction To DanceDocument3 pagesUNIT 1-Introduction To Dancerom keroNo ratings yet
- Kinematics LectureDocument60 pagesKinematics LectureHart GensoliNo ratings yet
- Angular Kinetics Moment-AnswerDocument5 pagesAngular Kinetics Moment-AnswerpatenggNo ratings yet
- AP Sem 1 Final ReviewDocument42 pagesAP Sem 1 Final ReviewSakib AlamNo ratings yet
- DigiTrainer Manual 2.00 ENGDocument21 pagesDigiTrainer Manual 2.00 ENGgeorgel22000No ratings yet
- Formula FizikDocument9 pagesFormula Fizikqaslun basheer100% (2)
- EM Vibration RangesDocument1 pageEM Vibration RangespmkarNo ratings yet
- 846 Physics Definitions by Sajid Ali TalpurDocument15 pages846 Physics Definitions by Sajid Ali TalpurMuneer KaleriNo ratings yet
- WAEC PHYSICS SyllabusDocument59 pagesWAEC PHYSICS SyllabusSani MubarakNo ratings yet
- CUCET 2020 B Tech Syllabus Part B PDFDocument7 pagesCUCET 2020 B Tech Syllabus Part B PDFsonu peterNo ratings yet
- International GCSE Single Science Award Student Book SampleDocument21 pagesInternational GCSE Single Science Award Student Book SampleAnastasia NurhalimNo ratings yet
- Exam #1: PHY 211: General Physics (Calculus) NameDocument9 pagesExam #1: PHY 211: General Physics (Calculus) NameirfanNo ratings yet
- Physics 2 - Speed, Velocity and AccelerationDocument74 pagesPhysics 2 - Speed, Velocity and AccelerationHakim Abbas Ali Phalasiya100% (1)