Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Astigmatism and Astigmatic Imagery
Astigmatism and Astigmatic Imagery
Uploaded by
Claudia SerbanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Astigmatism and Astigmatic Imagery
Astigmatism and Astigmatic Imagery
Uploaded by
Claudia SerbanCopyright:
Available Formats
Astigmatism and astigmatic imagery
Emmetropia Astigmatism
Astigmatism and astigmatic imagery
Astigmatism
Image is out of focus
In the examples I will discuss
today, the astigmatic meridians
are horizontal and vertical like in
the picture. The exact horizontal
is referred to as 180
o
(instead
of 0
o
) while the vertical is 90
o
.
In the clinic you will rarely find the
astigmatic meridians to be exactly
horizontal and vertical.
Blue = represents Vertical meridian
Red = represents Horizontal meridian
Astigmatic Eyes: two principal corneal meridians
a meridian of greatest corneal power
a meridian of least corneal power
Color Code
Emmetropic Eyes: The vertical and horizontal principal
meridians have the same power and focus a distant point
object as a point image on the retinal surface.
The vertical meridian will produce a horizontal line focus of a
distant point object.
In this example, the vertical meridian focuses a distant point object in
front of the retina. This is a myopic refractive error. Lets say the vertical
meridian has a refractive error of -5 D
Imagery in Astigmatic Eyes: Example 1
Looking at the vertical meridian alone!
-5
The horizontal meridian will produce a vertical line focus of a
distant point object.
In this example, the horizontal meridian focuses behind the retina.
This is a hyperopic refractive error. Lets say the horizontal meridian
has a refractive error of +3D
Imagery in Astigmatic Eyes : Example 1
Looking at the horizontal meridian alone!
+3
Imagery in Astigmatic Eyes : Example 1
The vertical and horizontal meridians together
Under normal viewing conditions, the imagery for
a point object has contributions from both
principal meridians:
The horizontal and vertical line foci are both far
away from the retina. What does the retinal image
look like for this example eye?
-5
+3
Imagery in Astigmatic Eyes : Example 1
The image formed by this uncorrected eye looks like a
blur ellipse
Blur
Ellipse
-5
+3
Imagery in Astigmatic Eyes : Example 1
The vertical meridian has greater myopia
(more focusing power) than the horizontal meridian.
This is the most common form of astigmatism
This is known as with-the-rule astigmatism
Next lecture we will talk about correcting astigmatic eyes
-5
+3
Imagery in Astigmatic Eyes : Example 1
-5
+3
The image on the retina for this eye is a blur ellipse.
However, at the dioptric midpoint between the two foci,
the image forms a perfect circle. This is known as the
circle of least confusion (CLC).
For the eye illustrated here, it will
Imagery in Astigmatic Eyes: Example 2
There are practically an infinite number of focal
length combinations for the principal meridians
so we cant discuss every possible astigmatic eye.
What does the image look like for this eye?
-5
plano
Imagery in Astigmatic Eyes: Example 2
The vertical line
focus is on the
retina
-5
plano
Imagery in Astigmatic Eyes: Example 3
plano
+3.0
Imagery in Astigmatic Eyes: Example 3
What the image looks like on the retina
plano
+3.0
Horizontal
Line Focus
Imagery in Astigmatic Eyes: Example 4
-5.0
-2.0
Imagery in Astigmatic Eyes: Example 4
What the image looks like on the retina
-5.0
-2.0
A vertically
elongated
blur ellipse
Imagery in Astigmatic Eyes: Example 5
+1.0
+3.0
Imagery in Astigmatic Eyes: Example 5
What the image looks like on the retina
+1.0
+3.0
A horizontally
elongated
blur ellipse
Imagery in Astigmatic Eyes: Example 6
The Circle of Least Confusion
-5.0
+5.0
At the dioptric midpoint between the two foci,
the image forms a perfect circle. This is known as the
circle of least confusion (CLC).
In this example eye, the CLC is at the retinal plane
Imagery in Astigmatic Eyes: Example 6
The Circle of Least Confusion
-5.0
+5.0
As the name implies, the image is a blur circle
The best visual performance for an uncorrected astigmatism
is said to occur when the CLC is on the retina
Imagery in Astigmatic Eyes: Example 7
Against-the-rule astigmatism
+3.0
-5.0
The horizontal meridian has relatively greater myopia
(more focusing power) than the vertical meridian
This is less common in the general population than
with-the-rule astigmatism
Imagery in Astigmatic Eyes: Example 7
+3.0
-5.0
What does the image look like?
Imagery in Astigmatic Eyes: Example 8
+3.0
plano
Imagery in Astigmatic Eyes: Example 8
What the image looks like on the retina
+3.0
plano
Horizontal
Line Focus
WTR
ATR
It is very important to note that the appearance of the
uncorrected retinal image does NOT provide information
about the type of astigmatism (WTR, ATR). The retinal image
tells you the relative position of the meridians.
Classifications of Astigmatism
Classified on the basis of the
positions of the line foci
formed for a distant point
source with respect to the
retina and the positions of the
principal meridians.
compound
myopic astig.
simple
myopic astig.
mixed astig.
simple
hyperopic astig.
compound
hyperopic astig.
Position of the most powerful meridian
with-the-rule = near vertical (30
deg)
against-the-rule = near horizontal
(30 deg)
oblique = near 45 or 135 (15 deg)
from Obstfeld, 1982
Retinal Image in uncorrected
astigmatic eyes
All the eyes have
against-the-rule
astigmatism.
C = compound
M = myopic
A= astigmatism
S = simple
H = hyperopic
Object is a distant
point source.
You might also like
- 04 Retinal Image SizeDocument32 pages04 Retinal Image SizeMwanja Moses100% (1)
- Guide To Your Prescription-EYEDocument11 pagesGuide To Your Prescription-EYESamuel AntobamNo ratings yet
- 08 Subjective Refraction AstigmatismDocument51 pages08 Subjective Refraction Astigmatismgenalinang100% (1)
- 07 AstigmatismDocument20 pages07 AstigmatismMwanja MosesNo ratings yet
- Astigmatism: Komal Sharma Assistant ProfessorDocument80 pagesAstigmatism: Komal Sharma Assistant ProfessorOphthalmology DiscussionNo ratings yet
- Astigmatisma / SilindrisDocument36 pagesAstigmatisma / SilindrisRimaTresnawatiNo ratings yet
- Astigmatism RXDocument1 pageAstigmatism RXdineshv74@yahoo.comNo ratings yet
- Error of RefractionDocument37 pagesError of RefractionIka KrastanayaNo ratings yet
- COT Flash CardDocument7 pagesCOT Flash CardCarol Chan100% (1)
- Foci MeterDocument41 pagesFoci MeterPomchopUKNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan ObejktifDocument12 pagesPemeriksaan ObejktifMuhammad FadhilNo ratings yet
- MCQ 04 OpticsDocument23 pagesMCQ 04 OpticsAmr AbdulradiNo ratings yet
- Roving Ring ScotomaDocument3 pagesRoving Ring ScotomaDeboprasad DasNo ratings yet
- TimRoot - Chapter 9 - Introduction To OpticsDocument1 pageTimRoot - Chapter 9 - Introduction To OpticsBaeyerNo ratings yet
- Astigmatism - PhysiologyDocument7 pagesAstigmatism - PhysiologyMustafa HaithamNo ratings yet
- Optics Assessment 2019 With AnswersDocument10 pagesOptics Assessment 2019 With AnswersBenjamin NgNo ratings yet
- Optician ManualDocument132 pagesOptician Manualchiamaka anthonyNo ratings yet
- Clinical OpticDocument43 pagesClinical OpticReinhard TuerahNo ratings yet
- AstigmatismDocument47 pagesAstigmatismDiana PhiriNo ratings yet
- 05 Aphakia and PseudophakiaDocument15 pages05 Aphakia and PseudophakiaMwanja Moses100% (1)
- Chapter 9 Introduction To OpticsDocument3 pagesChapter 9 Introduction To OpticsFarah FarahNo ratings yet
- Definition: in Hyperopia, There Is A Discrepancy Between The Refractive Power and Axial Length of The EyeDocument109 pagesDefinition: in Hyperopia, There Is A Discrepancy Between The Refractive Power and Axial Length of The EyeTiodora Wike DsNo ratings yet
- TBL 1 - Refractive Error SlidesDocument66 pagesTBL 1 - Refractive Error SlidesAmirah Azman100% (4)
- Chapter 22Document17 pagesChapter 22Jeferson Alexander Pabon RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Optical SystemDocument23 pagesOptical SystemluckyNo ratings yet
- CH 11Document30 pagesCH 11piyushNo ratings yet
- Refractive ErrorsDocument73 pagesRefractive ErrorsAnggunBW100% (1)
- Full download Experiments in Physiology 11th Edition Woodman Solutions Manual all chapter 2024 pdfDocument29 pagesFull download Experiments in Physiology 11th Edition Woodman Solutions Manual all chapter 2024 pdfbacciuadhimi13100% (7)
- 380 FullDocument2 pages380 FullThilini JayathilakeNo ratings yet
- PHYS 2225 Lab 13 Dispersion and Geometric OpticsDocument6 pagesPHYS 2225 Lab 13 Dispersion and Geometric OpticsT. ArchulettaNo ratings yet
- 5-Eye and Vision-1Document63 pages5-Eye and Vision-1a7ma1212019No ratings yet
- Refractive ErrorsDocument38 pagesRefractive ErrorszahraaNo ratings yet
- Geometrical Optics Lectures (3 of 4)Document14 pagesGeometrical Optics Lectures (3 of 4)OmegaUserNo ratings yet
- 2 Dioptrique de Loeil Normal 2021.anglaisDocument7 pages2 Dioptrique de Loeil Normal 2021.anglaisHoussemNo ratings yet
- Visual Field TestingDocument16 pagesVisual Field TestingLeigh-Ann AmorosoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology: Refractive ErrorsDocument26 pagesAnatomy & Physiology: Refractive ErrorsAbigael Patricia GutierrezNo ratings yet
- RetinosDocument60 pagesRetinosnickno1100% (1)
- Refractive Errors: Dr. Leow Thye YngDocument55 pagesRefractive Errors: Dr. Leow Thye YngRaissaNo ratings yet
- InTechEtiology and Clinical Presentation of AstigmatismDocument26 pagesInTechEtiology and Clinical Presentation of AstigmatismAnasthasia hutagalungNo ratings yet
- Optics and Refraction For 5 Year Medical Students Mutaz Gharaibeh, MDDocument52 pagesOptics and Refraction For 5 Year Medical Students Mutaz Gharaibeh, MDHidayadNo ratings yet
- Your Answer Was CORRECT: ExplanationDocument8 pagesYour Answer Was CORRECT: ExplanationMuhammed AbdulmajeedNo ratings yet
- 03 Schematic EyesDocument10 pages03 Schematic EyesMwanja Moses100% (1)
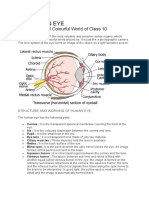
- Human Eye and Colourful World (PW)Document16 pagesHuman Eye and Colourful World (PW)Rahul ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Refraction Training Manual 2006 Mr S May (1)Document44 pagesRefraction Training Manual 2006 Mr S May (1)sadiq90000000No ratings yet
- Refraction Error: Alvina Elsa BidariDocument25 pagesRefraction Error: Alvina Elsa BidariBayu AdityaNo ratings yet
- Refraction Error VinaDocument27 pagesRefraction Error VinaHardiNo ratings yet
- Etiology and Clinical Presentation of Astigmatism: February 2012Document19 pagesEtiology and Clinical Presentation of Astigmatism: February 2012dean evansNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Optic-VioDocument42 pagesPhysiology of Optic-VioViora RiandaNo ratings yet
- Figure 1. Spherical Aberration in A Planoconvex LensDocument20 pagesFigure 1. Spherical Aberration in A Planoconvex LensGabyBenitezNo ratings yet
- 638091067348617757_ch_16light (2)Document4 pages638091067348617757_ch_16light (2)thepixelateanimatorNo ratings yet
- Eye Health / Blindness: Is An Eye Condition With Blurred Vision As Its Main Symptom. The Front Surface of TheDocument10 pagesEye Health / Blindness: Is An Eye Condition With Blurred Vision As Its Main Symptom. The Front Surface of TheJulie BoNo ratings yet
- The Eye Guide Physical ExamDocument85 pagesThe Eye Guide Physical Examtrisna minNo ratings yet
- Aberrations of Optical Systems Including The EyeDocument20 pagesAberrations of Optical Systems Including The EyeCherry OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Astigmatism 1Document14 pagesAstigmatism 1Adewumi AdinoyNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of StereosDocument9 pagesFundamentals of StereosAmit BhuriaNo ratings yet
- Astigmatism 140302140740 Phpapp01Document22 pagesAstigmatism 140302140740 Phpapp01Claudia SerbanNo ratings yet
- Orthoptics - Bc. Hana AdamkovaDocument11 pagesOrthoptics - Bc. Hana AdamkovarutvijkNo ratings yet
- Visual Field Loss in the Real World: A Book of Static Perimetry Test Targets for Eye Health ProfessionalsFrom EverandVisual Field Loss in the Real World: A Book of Static Perimetry Test Targets for Eye Health ProfessionalsNo ratings yet
- Optigal's Q & A for the NOCE: National Opticianry Certification Exam Questions - Basic CertificationFrom EverandOptigal's Q & A for the NOCE: National Opticianry Certification Exam Questions - Basic CertificationNo ratings yet
- Partial Discharge Localization in Transformers Using UHF Detection MethodDocument10 pagesPartial Discharge Localization in Transformers Using UHF Detection Methodmahdi77noroNo ratings yet
- 1-1. Fabrication of Bragg Mirrors by Multilayer Inkjet PrintingDocument8 pages1-1. Fabrication of Bragg Mirrors by Multilayer Inkjet Printingkamru55l.mzrllalNo ratings yet
- Depth-Fused 3-D (DFD) Display With Multiple Viewing ZonesDocument8 pagesDepth-Fused 3-D (DFD) Display With Multiple Viewing ZonesLong HoàngNo ratings yet
- Bansal Classes Chemistry Study Material For IIT JEEDocument824 pagesBansal Classes Chemistry Study Material For IIT JEEHarshitShukla0% (1)
- 12.6 Perform An Activity - Measuring The Critical Angle For Various MediaDocument2 pages12.6 Perform An Activity - Measuring The Critical Angle For Various MediaRajeshri SoniNo ratings yet
- Consumer Lighting: List PriceDocument56 pagesConsumer Lighting: List Pricesuji91No ratings yet
- Extra Credit Optical Color MixingDocument3 pagesExtra Credit Optical Color Mixingmtim360No ratings yet
- Introduction To LightDocument9 pagesIntroduction To LightJohn JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Allen Mann-Infrared Optics and Zoom Lenses, Second Edition (SPIE Tutorial Text Vol. TT83) (Tutorial Texts in Optical Engineering) - SPIE Publications (2009)Document173 pagesAllen Mann-Infrared Optics and Zoom Lenses, Second Edition (SPIE Tutorial Text Vol. TT83) (Tutorial Texts in Optical Engineering) - SPIE Publications (2009)malaerbaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To EMFTDocument19 pagesIntroduction To EMFTVikas KaushikNo ratings yet
- Midstage Line Amplifier 2 (MLA2 C-Band) Circuit Packs (NTK552FAE5 and NTK552FB)Document18 pagesMidstage Line Amplifier 2 (MLA2 C-Band) Circuit Packs (NTK552FAE5 and NTK552FB)Đặng LựcNo ratings yet
- Lomo LC-A Manual (English)Document30 pagesLomo LC-A Manual (English)sonic youtherNo ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanics Lectures NoteDocument69 pagesQuantum Mechanics Lectures NoteNirmalya NandiNo ratings yet
- User Guide Cough AssistDocument26 pagesUser Guide Cough AssistJesus Alonso Hernandez ANo ratings yet
- Radiative Heat Transfer: John Richard ThomeDocument55 pagesRadiative Heat Transfer: John Richard ThomeJames MathseonNo ratings yet
- Optical Recording and CommunicationsDocument18 pagesOptical Recording and CommunicationsAchuNo ratings yet
- Compound Microscope Parts: Structural ComponentsDocument3 pagesCompound Microscope Parts: Structural ComponentsJanuary Pentinio AbarentosNo ratings yet
- PT - English 6 - Q2Document6 pagesPT - English 6 - Q2YselYap0% (1)
- (H,) I 111j) D F Spherical Aberration. Spherical AberrationDocument3 pages(H,) I 111j) D F Spherical Aberration. Spherical AberrationGamer HelperNo ratings yet
- Xglo & Lightsystem Indoor/Outdoor Loosetube, Dca - Emea: Ordering InformationDocument2 pagesXglo & Lightsystem Indoor/Outdoor Loosetube, Dca - Emea: Ordering InformationDemetri M. ScytheNo ratings yet
- Final Lesson Exemplar in Science 10Document9 pagesFinal Lesson Exemplar in Science 10Jundell C. Diaz100% (1)
- Gami 16mmDocument30 pagesGami 16mmwang leiNo ratings yet
- New Minimum Requirement Questions For Biophysics PDFDocument14 pagesNew Minimum Requirement Questions For Biophysics PDFLydia AitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 34 and 35 Ray Optics Summary of LecturesDocument50 pagesChapter 34 and 35 Ray Optics Summary of Lecturessouad El FerjaniNo ratings yet
- 12V WallchartDocument2 pages12V WallchartkjsjnjdujshskkhdhNo ratings yet
- 1905 Miraculous YearDocument12 pages1905 Miraculous YeardrnnmurtyNo ratings yet
- Atomic Line Spectra of Noble Gases and Metallic Vapors: Experiment No. 1Document6 pagesAtomic Line Spectra of Noble Gases and Metallic Vapors: Experiment No. 1ayushNo ratings yet
- Determination of Solar Reflectance Near Ambient Temperature Using A Portable Solar ReflectometerDocument5 pagesDetermination of Solar Reflectance Near Ambient Temperature Using A Portable Solar ReflectometerAhmed AlzubaidiNo ratings yet
- Saxon 705 Refractor TelescopeDocument3 pagesSaxon 705 Refractor TelescopeHarukaNiLauNo ratings yet
- Daniel Fry ATOMS GALAXIES AND UNDERSTANDINGDocument44 pagesDaniel Fry ATOMS GALAXIES AND UNDERSTANDINGNyTamasNo ratings yet