Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mba 8155 Slides 1
Mba 8155 Slides 1
Uploaded by
anon_313759296Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Management Tri Nova CaseDocument4 pagesManagement Tri Nova CaseAie Kah Dupal100% (2)
- The Joker and The Queen - Ed Sheeran Piano-Vocal-GuitarDocument3 pagesThe Joker and The Queen - Ed Sheeran Piano-Vocal-GuitarAngela HallNo ratings yet
- Maintenance and Operational Reliability: 24 Essential Building BlocksFrom EverandMaintenance and Operational Reliability: 24 Essential Building BlocksNo ratings yet
- Operation ManagementDocument79 pagesOperation ManagementSumama IkhlasNo ratings yet
- 935 Robert Bosch Interview Questions in C A Micro Controllers PDFDocument2 pages935 Robert Bosch Interview Questions in C A Micro Controllers PDFdhapra0% (1)
- Mba 8155 Slides 1Document34 pagesMba 8155 Slides 1Archana Ashok AhireNo ratings yet
- Trends and Issues in Operations Management - : Prof. M. RayDocument23 pagesTrends and Issues in Operations Management - : Prof. M. RayAbinash ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-: Operations & Supply Chain StrategyDocument40 pagesChapter 1-: Operations & Supply Chain StrategyDv DickosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-: Operations & Supply Chain StrategyDocument41 pagesChapter 1-: Operations & Supply Chain StrategySannoush376No ratings yet
- Rupesh Patel: Productions and Operations Management ProfDocument51 pagesRupesh Patel: Productions and Operations Management ProfJayendra Patel100% (1)
- Why Study Operations Management?: Systematic Approach To Org. ProcessesDocument33 pagesWhy Study Operations Management?: Systematic Approach To Org. ProcessessenjicsNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document26 pagesLesson 1ravi_nyse100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Operations ManagementDocument26 pagesFundamentals of Operations ManagementCindyorange Ph100% (1)
- Faculty PPT-Competitiveness Through Operation Management - Process Efficiency and Productivity An IntroductionDocument26 pagesFaculty PPT-Competitiveness Through Operation Management - Process Efficiency and Productivity An IntroductionSubhajit BoseNo ratings yet
- Production/Operations ManagementDocument97 pagesProduction/Operations Managementdinesh0014No ratings yet
- Irwin/Mcgraw HillDocument56 pagesIrwin/Mcgraw HillAisha_siddiquiiNo ratings yet
- 1 - Introduction Production ProcessesDocument31 pages1 - Introduction Production ProcessesValeria StratulatNo ratings yet
- Operation ManagementDocument14 pagesOperation ManagementJhomel CastroNo ratings yet
- Strategic Analysis and Choice in Single-Or Dominant-Product Businesses: Building Sustainable Competitive AdvantagesDocument37 pagesStrategic Analysis and Choice in Single-Or Dominant-Product Businesses: Building Sustainable Competitive AdvantagesBasit RazaNo ratings yet
- Om NotesDocument134 pagesOm NotesGovernment PolytechnicNo ratings yet
- Mba III Operations Management (10mba33) NotesDocument99 pagesMba III Operations Management (10mba33) NotesSahil GouthamNo ratings yet
- WK1-BUS5040 - SURVEY OF PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT-topic 1 Introduction-2Document28 pagesWK1-BUS5040 - SURVEY OF PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT-topic 1 Introduction-2Moses SosiNo ratings yet
- Intro Opn MangtDocument76 pagesIntro Opn MangtDeeps KelaniNo ratings yet
- Operation ManagementDocument4 pagesOperation ManagementHananiya GizawNo ratings yet
- BBA 6th Sem POM2 - 3Document34 pagesBBA 6th Sem POM2 - 3ostapNo ratings yet
- 0intro To OMDocument16 pages0intro To OMkunal.nhidclNo ratings yet
- Introduction To OMDocument30 pagesIntroduction To OMtafere99No ratings yet
- Introduction To Operation ManagementDocument49 pagesIntroduction To Operation ManagementHosnain ShahinNo ratings yet
- Chap 002Document15 pagesChap 002Zaharatul Munir SarahNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 Intro To POMDocument21 pagesChap 1 Intro To POMJulius Hans GallegoNo ratings yet
- Assignment Report ON: " " (451) Unit - IiiDocument13 pagesAssignment Report ON: " " (451) Unit - IiiRobin GanjooNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Operations and Logistics ManagementDocument76 pagesIntroduction To Operations and Logistics ManagementIndrian MendozaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Operations ManagementDocument77 pagesIntroduction To Operations ManagementPravin SinghNo ratings yet
- POQ MGMTDocument53 pagesPOQ MGMTAruna FeltzNo ratings yet
- Production and Operations Management - Introduction (BSBA)Document48 pagesProduction and Operations Management - Introduction (BSBA)hanna sanchezNo ratings yet
- Operations Management: Operations and Productivity Dr. Vaidy Jayaraman Univ of Miami, FL, USADocument55 pagesOperations Management: Operations and Productivity Dr. Vaidy Jayaraman Univ of Miami, FL, USARahul SachdevaNo ratings yet
- Chapter01and02 (Street08spring)Document67 pagesChapter01and02 (Street08spring)dheeraj_raj_jainNo ratings yet
- Production & Operations ManagementDocument39 pagesProduction & Operations ManagementFarooq IsrarNo ratings yet
- Operation Management Dissertation TopicsDocument7 pagesOperation Management Dissertation TopicsWriteMyPaperReviewsOverlandPark100% (1)
- 02 Operations StrategyDocument13 pages02 Operations StrategyannamationsNo ratings yet
- TQMCH1Document44 pagesTQMCH1Neko MidoriNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Operations and Logistics ManagementDocument76 pagesIntroduction To Operations and Logistics ManagementAbdulhmeed MutalatNo ratings yet
- Operations Management 1Document19 pagesOperations Management 1PrerrakNo ratings yet
- G4-Group AssigmentDocument19 pagesG4-Group AssigmentSamadhi WeeraratneNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument70 pagesUnit ImohssinNo ratings yet
- Production and Operations ManagementDocument9 pagesProduction and Operations Managementaryanboxer786No ratings yet
- Operations Strategy PresentationDocument22 pagesOperations Strategy PresentationbamneakashfunNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document54 pagesUnit 1Benjamin Adelwini BugriNo ratings yet
- 2..operation Strategy in Global EnvironmentDocument32 pages2..operation Strategy in Global EnvironmentGwen WilliamsNo ratings yet
- OPM1Document42 pagesOPM1Ajay emerald hillsNo ratings yet
- Midterm Study Guide Decision Central System MakingDocument37 pagesMidterm Study Guide Decision Central System MakingAndrew PhilipsNo ratings yet
- OperationsManagement Part1Document121 pagesOperationsManagement Part1nethaji_pNo ratings yet
- Tugas 1 (Supply Chain Management)Document9 pagesTugas 1 (Supply Chain Management)mellyNo ratings yet
- EDE Micro Project ReportDocument10 pagesEDE Micro Project ReportViveka NaikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To POMDocument24 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To POMvasanirinkalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction To The Field: Operations Management (OM)Document22 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To The Field: Operations Management (OM)Shahreaz SarkerNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Production and Operations ManagementDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Production and Operations ManagementjayasundaramNo ratings yet
- ch-1 Part IDocument32 pagesch-1 Part IDesu MekonnenNo ratings yet
- MGMT 314 Tutorial 2Document16 pagesMGMT 314 Tutorial 2Lini VargheseNo ratings yet
- Om Final ExamDocument6 pagesOm Final Examaster sebsbeNo ratings yet
- Notes For CA5104 Operations ManagementDocument39 pagesNotes For CA5104 Operations ManagementliliNo ratings yet
- KCEP4313 Operations Man AgementDocument37 pagesKCEP4313 Operations Man Agementkevin chuaNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving: The 5-Why’s: Unlocking the Power of Quality Assurance for Success in BusinessFrom EverandProblem Solving: The 5-Why’s: Unlocking the Power of Quality Assurance for Success in BusinessNo ratings yet
- Use of Headed Reinforcement in Beam - Column JointsDocument24 pagesUse of Headed Reinforcement in Beam - Column JointsHabibi MehediNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CMOS VLSI Design (E158) Final ProjectDocument4 pagesIntroduction To CMOS VLSI Design (E158) Final ProjectbashasvuceNo ratings yet
- Appendix 13a - BACHELOR Internship Final Report Assessment Sheet (202012)Document4 pagesAppendix 13a - BACHELOR Internship Final Report Assessment Sheet (202012)Pang Kok OnnNo ratings yet
- UK Wooden Pallet 1200 X 1000mmDocument1 pageUK Wooden Pallet 1200 X 1000mmRizwan rizviNo ratings yet
- Security Information and Event Management: Radboud University NijmegenDocument75 pagesSecurity Information and Event Management: Radboud University NijmegenproftechitspecialistNo ratings yet
- Coco Fire Indonesa - Anu 2021Document20 pagesCoco Fire Indonesa - Anu 2021Abizard Niaga UtamaNo ratings yet
- SGX-Listed Hatten Land Diversifies Beyond Melaka Through Proposed Acquisition of Unicity in Seremban, MalaysiaDocument3 pagesSGX-Listed Hatten Land Diversifies Beyond Melaka Through Proposed Acquisition of Unicity in Seremban, MalaysiaWeR1 Consultants Pte LtdNo ratings yet
- CAC Boomerang Flight ManualDocument103 pagesCAC Boomerang Flight ManualAnonymous KeGjwtNo ratings yet
- DIDIDocument3 pagesDIDIRamon GarciaNo ratings yet
- Male Pattern Blondeness: Technique: Natural Level: ColorDocument1 pageMale Pattern Blondeness: Technique: Natural Level: ColorLeo CabelosNo ratings yet
- Price Action ScalperDocument14 pagesPrice Action ScalperMurd DyanNo ratings yet
- Gonzales Vs HechanovaDocument2 pagesGonzales Vs HechanovaJoanne PaulNo ratings yet
- College Athletes Protection and Compensation ActDocument50 pagesCollege Athletes Protection and Compensation ActCody Brunner100% (1)
- BelFone ProChat Trunking System Dispatcher ManualDocument23 pagesBelFone ProChat Trunking System Dispatcher ManualPT.tikicom sinergiutamaNo ratings yet
- Pennsylvania Wing - Aug 2006Document28 pagesPennsylvania Wing - Aug 2006CAP History LibraryNo ratings yet
- Ra Lex Physicians With Advisory2023 Cdo 1Document24 pagesRa Lex Physicians With Advisory2023 Cdo 1mikzhiNo ratings yet
- BTH Thesis ArchiveDocument7 pagesBTH Thesis ArchiveWriteMyPaperForMeFastSingapore100% (1)
- E-Retail Outlet For Ready Made GarmentsDocument11 pagesE-Retail Outlet For Ready Made Garmentsrubi laariNo ratings yet
- One UI Samsung USDocument1 pageOne UI Samsung USRomsamBlaNo ratings yet
- Pig FarmingDocument25 pagesPig Farmingসপ্তক মন্ডল100% (1)
- ACN Micro Project-1Document23 pagesACN Micro Project-1ashutosh dudhaneNo ratings yet
- ProHealth Prime Proposal Form 14sept23Document10 pagesProHealth Prime Proposal Form 14sept23Rahul GoelNo ratings yet
- Hijra Bank Installation Guide For Kaspersky Security CenterDocument54 pagesHijra Bank Installation Guide For Kaspersky Security Centermohammed JundiNo ratings yet
- Mitchell e Villet, 1987 - Reinforcement of Earth Slopes and EmbankmentsDocument330 pagesMitchell e Villet, 1987 - Reinforcement of Earth Slopes and EmbankmentsJordana Furman100% (1)
- Potent Drugs HandlingDocument4 pagesPotent Drugs HandlingOMKAR BHAVLENo ratings yet
- Classical Management TheoryDocument3 pagesClassical Management TheoryQuintine ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Rudolf Elmer's Complaint To The ECHR v. Jersey (Standard Bank)Document13 pagesRudolf Elmer's Complaint To The ECHR v. Jersey (Standard Bank)David LeloupNo ratings yet
Mba 8155 Slides 1
Mba 8155 Slides 1
Uploaded by
anon_313759296Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mba 8155 Slides 1
Mba 8155 Slides 1
Uploaded by
anon_313759296Copyright:
Available Formats
Irwin/McGraw-Hill
Operations Management
Definition
Operations management is defined
as the design, operation, and
improvement of the systems that
create and deliver the firms primary
products and services.
2
Irwin/McGraw-Hill
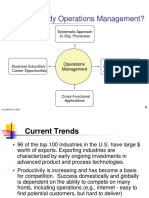
Why Study Operations Management?
Operations
Management
Business Education/
Career Opportunities
Systematic Approach
to Org. Processes
Increase Competitive
Advantage/Survival
Cross-Functional
Applications
3
Irwin/McGraw-Hill
Current Trends
96 of the top 100 industries in the U.S. have large $
worth of exports. Exporting industries are
characterized by early ongoing investments in
advanced product and process technologies.
Productivity is increasing and has become a basis
for competition. Success domestically and globally
is dependent on the ability to compete on many
fronts, including operations (e.g., internet - easy to
find potential customers, but hard to deliver)
Outsourcing of manufacturing and services (e.g.,
India and China) is accelerating.
WS8
**Wickham Skinner: The Role of the Industrial Managers in the Massive U.S. Negative Trade Balance, April 2000
Factors Affecting a Firm's Ability to Ward off Imports and/or Export
External
transportation costs
logistics resources
labor supply, capabilities
training resources
communications
public infrastructure
Environmental/social
environmental protection
health costs
labor unions
education system
consumer tastes
retailing capabilities
employee
Economic/Political
exchange rates
trade barriers
capital costs
inflation
capital availability
social costs/legal
funds flows
savings rate
interest rates
minimum wage
Suppliers
abilities
coordination
location
competition
cooperation
Technological
R&D
engineering
product development
process development
new products
development process
Corporate
strategy
risk avoidance
role of functions
Fin-Mktg-Mfg-Eng-R&D
balance sheet
financial capacity
marketing policies
export sales competencies
Technological sophistication of mgt
Operations
costs/productivity
quality
delivery cycle
delivery reliability
flexibility for prod change
flexibility for vol. change
New product introduction
inventory mgt.
Prod. Planning Control
Equip. & process tech
#, size, location of facilities
logistics
customer service
information technology
WS6
Irwin/McGraw-Hill
Operations Decision Making
People Plants Parts Processes
Planning and Control
Materials &
Customers
Products &
Services
Input Output
Operations Management
Marketing Strategy Finance Strategy
Marketplace
Corporate Strategy
Operations Strategy
The Transformation Process (value adding)
4
Irwin/McGraw-Hill
Key OM Concepts
Efficiency - Doing something at the lowest
possible cost
Effectiveness - Doing the right things to
create the most value for the organization
Value - Quality divided by price
8
Irwin/McGraw-Hill
Transformations
Physical--manufacturing
Locational--transportation
Exchange--retailing
Storage--warehousing
Physiological--health care
Informational--telecommunications
5
Irwin/McGraw-Hill
Examples of Production Systems
System Inputs Conversion Output
(desired)
Hospital Patients
MDs, Nurses
Medical Supplies
Equipment
Health Care Healthy
Individuals
Restaurant Hungry Customers
Food, Chef
Servers
Atmosphere
Prepare Food
Serve Food
Satisfied
Customers
Automobile
Plant
Sheet Steel
Engine Parts
Tools, Equipment
Workers
Fabrication
and Assembly
of Cars
High Quality
Automobiles
University High School Grads
Teachers, Books
Classroom
Transferring
of Knowledge
and Skills
Educated
Individuals
6
Irwin/McGraw-Hill
Service or Good?
If you drop it on your foot, it wont hurt
you. (Good or service?)
Services never include goods and
goods never include services. (True or
false?)
7
Irwin/McGraw-Hill
What about McDonalds?
Service or Manufacturing?
The company certainly manufactures tangible
products
Why then would we consider McDonalds a
service business?
8
Irwin/McGraw-Hill
Front and Back Office
Front Office
Customer
Service Provider
Back Office
9
Irwin/McGraw-Hill
Core Factory Services
Core Services are basic things that
customers want from products that they
purchase.
Quality
Flexibility
Speed
Price (or production cost)
10
Irwin/McGraw-Hill
Value-Added Services
Value-added services differentiate the
organization from competitors and build
relationships that bind customers to the firm
in a positive way.
Information
Problem Solving and Field Support
Sales Support
11
Irwin/McGraw-Hill
History of Operations
Cottage System
TIME
<1700
1700 - 1800
1850s
1890s
1910s
1930s
1940s
1970s
1980s
1990s
Industrial Revolution
Civil War
Scientific Management
Hawthorne Studies
Mass Customization
Service Revolution
Global Competition
Operations Research
Moving Assembly Line
12
Irwin/McGraw-Hill
Development of OM as a Field The Names
and Emphasis Change, but the Elements
Remain Basically the Same!
Scientific
Management
Moving Assembly
Line
Hawthorne
Studies
Operations
Research
Historical
Underpinnings
Manufacturing
Strategy
TQM &
Six Sigma
JIT/Lean
Manufacturing
Business Process
Reengineering
Manufacturing
Resources Planning
Electronic
Enterprise
Service Quality
and Productivity
Global Supply
Chain Mgt.
OMs Emergence
as a Field
13
Irwin/McGraw-Hill
Some Current Issues
Implementing/sustaining Quality Management initiatives
Consolidating operations resulting from mergers
Speeding up the time to get new products to market
Developing flexible production systems to enable mass
customization of products and services
Developing and integrating new technologies
Managing global supplier, production and distribution
networks
Outsourcing
14
Irwin/McGraw-Hill
Purchasing Managers Index
Began 1931
Measures:
New Manufacturing Orders
Production Volume
Deliveries
Inventory Levels
Employment
Index Measures Economic Activity
>50.0% Expanding
<42.7% Contracting
15
Irwin/McGraw-Hill
Purchasing Managers Index
A Leading Indicator since:
- Manufacturing must order materials in
advance of production
- The indicator is based on plans of supply
management (purchasing) executives
Source: Institute for Supply Management
(ISM) ism.org (previously National
Association of Purchasing Management)
15
Irwin/McGraw-Hill
Purchasing Managers Index
Dec-05 55.6 42.7 50
Jan-06 54.8 42.7 50
Feb-06 56.7 42.7 50
Mar-06 55.2 42.7 50
Apr-06 57.3 42.7 50
May-06 54.4 42.7 50
Jun-06 53.8 42.7 50
Jul-06 54.7 42.7 50
Aug-06 54.5 42.7 50
Sep-06 52.9 42.7 50
Oct-06 51.2 42.7 50
Nov-06 49.5 42.7 50
Quality
Management
Statistical
Process Control
Just in Time
Materials Requirement Planning
Inventory Control
Aggregate
Planning
Operations Management - Overview
Project
Management
Supply Chain
Management
Process Analysis
and Design
Process Control
and Improvement
Waiting Line Analysis and
Simulation
Services
Manufacturing
Operations
Strategy
Facility Layout
Consulting and
Reengineering
Process Analysis
Job Design
Capacity Management
Planning for Production
Supply Chain
Strategy
Irwin/McGraw-Hill
Operations Strategy
Customer Needs
Corporate Strategy
Operations Strategy
Decisions on Processes
and Infrastructure
Example
Strategy Process
More Product
Increase Org. Size
Increase Production Capacity
Build New Factory
Irwin/McGraw-Hill
Competitive Dimensions
Cost
Quality and Reliability
Delivery
Flexibility
Speed
Reliability
Coping with Changes in Demand
New Product Introduction
Speed
Flexibility
Irwin/McGraw-Hill
Dealing with Trade-offs
Cost
Quality
Delivery Flexibility
Example II, if we improve
customer service problem
solving by cross-training
personnel to deal with a
wider-range of problems,
they may become less
efficient at dealing with
commonly occurring
problems.
For example, if we reduce costs by reducing product
quality inspections, we might reduce product quality.
Irwin/McGraw-Hill
Order Qualifiers and Winners
Order Qualifiers: Screening criterion
that permits a firms products or
services to be considered as possible
candidates for purchase
Order Winners: Criterion that
differentiates the products or services
of one firm from another
Strategy Begins with Priorities
Consider the personal computer assembler
1. How would we segment the market according to
product group?
2. How would we identify product requirements,
demand patterns, and profit margins for each group?
3. How do we identify order winners and order
qualifiers for each group?
4. How do we convert order winners into specific
performance requirements?
Us
(Core competencies)
Competition
(Them)
Differentiation
Irwin/McGraw-Hill
Manufacturings Role in
Corporate Strategy
Stage I--Internally Neutral - minimize
potential manufacturing negative
Stage II--Externally Neutral - achieve parity
with competitors
Stage III--Internally Supportive - support
business strategy
Stage IV--Externally Supportive -
manufacturing based competitive strategy
Irwin/McGraw-Hill
Four Stages of Service Firm
Competitiveness
Stage I. Available for Service
Stage II. Journeyman
Stage III. Distinctive Competence Achieved
Stage IV. World Class Service Delivery
Irwin/McGraw-Hill
U. S. Competitiveness Drivers
Product Development
speed development & enhance
manufacturability
Waste Reduction (JIT Philosophy)
WIP, space, tool costs, and human effort
Improved Customer-Supplier Relationships
borrowed from Japanese Keiretsu
Improved Leadership
strong, independent boards of directors
Irwin/McGraw-Hill
Execution!!
Unless you translate big thoughts into concrete
steps for action, theyre pointless. (Larry Bossidy)
Strategy is execution. (Louis Gerstner)
In the business world, having a good objective
means nothing if you implement it badly. (Fareed
Zakaria)
You cannot have an execution culture without
robust dialogue - one that brings reality to the
surface through openness, candor, and informality.
Robust dialogue starts when people go in with
open minds. You cannot set realistic goals until
youve debated the assumptions behind them.
Irwin/McGraw-Hill
Productivity
Partial measures
output/(single input)
Multi-factor measures
output/(multiple inputs)
Total measure
output/(total inputs)
Inputs
Outputs
= ty Productivi
Irwin/McGraw-Hill
Example
10,000 Units Produced
Sold for $10/unit
500 labor hours
Labor rate: $9/hr
Cost of raw material: $5,000
Cost of purchased material: $25,000
What is the
labor productivity?
Irwin/McGraw-Hill
10,000 units/500hrs = 20 units/hour ...
... or we can arrive at a unitless figure
(10,000 unit*$10/unit)/(500hrs*$9/hr) = 22.22
Example--Labor Productivity
Irwin/McGraw-Hill
Example:
Productivity Measurement
You have just determined that your service
employees have used a total of 2400 hours
of labor this week to process 560 insurance
forms. Last week the same crew used only
2000 hours of labor to process 480 forms.
Is productivity increasing or decreasing?
Irwin/McGraw-Hill
Balanced Scorecard
1. Financial perspective
2. Internal perspective
3. Customer perspective
4. Innovation and learning perspective
You might also like
- Management Tri Nova CaseDocument4 pagesManagement Tri Nova CaseAie Kah Dupal100% (2)
- The Joker and The Queen - Ed Sheeran Piano-Vocal-GuitarDocument3 pagesThe Joker and The Queen - Ed Sheeran Piano-Vocal-GuitarAngela HallNo ratings yet
- Maintenance and Operational Reliability: 24 Essential Building BlocksFrom EverandMaintenance and Operational Reliability: 24 Essential Building BlocksNo ratings yet
- Operation ManagementDocument79 pagesOperation ManagementSumama IkhlasNo ratings yet
- 935 Robert Bosch Interview Questions in C A Micro Controllers PDFDocument2 pages935 Robert Bosch Interview Questions in C A Micro Controllers PDFdhapra0% (1)
- Mba 8155 Slides 1Document34 pagesMba 8155 Slides 1Archana Ashok AhireNo ratings yet
- Trends and Issues in Operations Management - : Prof. M. RayDocument23 pagesTrends and Issues in Operations Management - : Prof. M. RayAbinash ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-: Operations & Supply Chain StrategyDocument40 pagesChapter 1-: Operations & Supply Chain StrategyDv DickosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-: Operations & Supply Chain StrategyDocument41 pagesChapter 1-: Operations & Supply Chain StrategySannoush376No ratings yet
- Rupesh Patel: Productions and Operations Management ProfDocument51 pagesRupesh Patel: Productions and Operations Management ProfJayendra Patel100% (1)
- Why Study Operations Management?: Systematic Approach To Org. ProcessesDocument33 pagesWhy Study Operations Management?: Systematic Approach To Org. ProcessessenjicsNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document26 pagesLesson 1ravi_nyse100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Operations ManagementDocument26 pagesFundamentals of Operations ManagementCindyorange Ph100% (1)
- Faculty PPT-Competitiveness Through Operation Management - Process Efficiency and Productivity An IntroductionDocument26 pagesFaculty PPT-Competitiveness Through Operation Management - Process Efficiency and Productivity An IntroductionSubhajit BoseNo ratings yet
- Production/Operations ManagementDocument97 pagesProduction/Operations Managementdinesh0014No ratings yet
- Irwin/Mcgraw HillDocument56 pagesIrwin/Mcgraw HillAisha_siddiquiiNo ratings yet
- 1 - Introduction Production ProcessesDocument31 pages1 - Introduction Production ProcessesValeria StratulatNo ratings yet
- Operation ManagementDocument14 pagesOperation ManagementJhomel CastroNo ratings yet
- Strategic Analysis and Choice in Single-Or Dominant-Product Businesses: Building Sustainable Competitive AdvantagesDocument37 pagesStrategic Analysis and Choice in Single-Or Dominant-Product Businesses: Building Sustainable Competitive AdvantagesBasit RazaNo ratings yet
- Om NotesDocument134 pagesOm NotesGovernment PolytechnicNo ratings yet
- Mba III Operations Management (10mba33) NotesDocument99 pagesMba III Operations Management (10mba33) NotesSahil GouthamNo ratings yet
- WK1-BUS5040 - SURVEY OF PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT-topic 1 Introduction-2Document28 pagesWK1-BUS5040 - SURVEY OF PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT-topic 1 Introduction-2Moses SosiNo ratings yet
- Intro Opn MangtDocument76 pagesIntro Opn MangtDeeps KelaniNo ratings yet
- Operation ManagementDocument4 pagesOperation ManagementHananiya GizawNo ratings yet
- BBA 6th Sem POM2 - 3Document34 pagesBBA 6th Sem POM2 - 3ostapNo ratings yet
- 0intro To OMDocument16 pages0intro To OMkunal.nhidclNo ratings yet
- Introduction To OMDocument30 pagesIntroduction To OMtafere99No ratings yet
- Introduction To Operation ManagementDocument49 pagesIntroduction To Operation ManagementHosnain ShahinNo ratings yet
- Chap 002Document15 pagesChap 002Zaharatul Munir SarahNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 Intro To POMDocument21 pagesChap 1 Intro To POMJulius Hans GallegoNo ratings yet
- Assignment Report ON: " " (451) Unit - IiiDocument13 pagesAssignment Report ON: " " (451) Unit - IiiRobin GanjooNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Operations and Logistics ManagementDocument76 pagesIntroduction To Operations and Logistics ManagementIndrian MendozaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Operations ManagementDocument77 pagesIntroduction To Operations ManagementPravin SinghNo ratings yet
- POQ MGMTDocument53 pagesPOQ MGMTAruna FeltzNo ratings yet
- Production and Operations Management - Introduction (BSBA)Document48 pagesProduction and Operations Management - Introduction (BSBA)hanna sanchezNo ratings yet
- Operations Management: Operations and Productivity Dr. Vaidy Jayaraman Univ of Miami, FL, USADocument55 pagesOperations Management: Operations and Productivity Dr. Vaidy Jayaraman Univ of Miami, FL, USARahul SachdevaNo ratings yet
- Chapter01and02 (Street08spring)Document67 pagesChapter01and02 (Street08spring)dheeraj_raj_jainNo ratings yet
- Production & Operations ManagementDocument39 pagesProduction & Operations ManagementFarooq IsrarNo ratings yet
- Operation Management Dissertation TopicsDocument7 pagesOperation Management Dissertation TopicsWriteMyPaperReviewsOverlandPark100% (1)
- 02 Operations StrategyDocument13 pages02 Operations StrategyannamationsNo ratings yet
- TQMCH1Document44 pagesTQMCH1Neko MidoriNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Operations and Logistics ManagementDocument76 pagesIntroduction To Operations and Logistics ManagementAbdulhmeed MutalatNo ratings yet
- Operations Management 1Document19 pagesOperations Management 1PrerrakNo ratings yet
- G4-Group AssigmentDocument19 pagesG4-Group AssigmentSamadhi WeeraratneNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument70 pagesUnit ImohssinNo ratings yet
- Production and Operations ManagementDocument9 pagesProduction and Operations Managementaryanboxer786No ratings yet
- Operations Strategy PresentationDocument22 pagesOperations Strategy PresentationbamneakashfunNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document54 pagesUnit 1Benjamin Adelwini BugriNo ratings yet
- 2..operation Strategy in Global EnvironmentDocument32 pages2..operation Strategy in Global EnvironmentGwen WilliamsNo ratings yet
- OPM1Document42 pagesOPM1Ajay emerald hillsNo ratings yet
- Midterm Study Guide Decision Central System MakingDocument37 pagesMidterm Study Guide Decision Central System MakingAndrew PhilipsNo ratings yet
- OperationsManagement Part1Document121 pagesOperationsManagement Part1nethaji_pNo ratings yet
- Tugas 1 (Supply Chain Management)Document9 pagesTugas 1 (Supply Chain Management)mellyNo ratings yet
- EDE Micro Project ReportDocument10 pagesEDE Micro Project ReportViveka NaikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To POMDocument24 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To POMvasanirinkalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction To The Field: Operations Management (OM)Document22 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To The Field: Operations Management (OM)Shahreaz SarkerNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Production and Operations ManagementDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Production and Operations ManagementjayasundaramNo ratings yet
- ch-1 Part IDocument32 pagesch-1 Part IDesu MekonnenNo ratings yet
- MGMT 314 Tutorial 2Document16 pagesMGMT 314 Tutorial 2Lini VargheseNo ratings yet
- Om Final ExamDocument6 pagesOm Final Examaster sebsbeNo ratings yet
- Notes For CA5104 Operations ManagementDocument39 pagesNotes For CA5104 Operations ManagementliliNo ratings yet
- KCEP4313 Operations Man AgementDocument37 pagesKCEP4313 Operations Man Agementkevin chuaNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving: The 5-Why’s: Unlocking the Power of Quality Assurance for Success in BusinessFrom EverandProblem Solving: The 5-Why’s: Unlocking the Power of Quality Assurance for Success in BusinessNo ratings yet
- Use of Headed Reinforcement in Beam - Column JointsDocument24 pagesUse of Headed Reinforcement in Beam - Column JointsHabibi MehediNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CMOS VLSI Design (E158) Final ProjectDocument4 pagesIntroduction To CMOS VLSI Design (E158) Final ProjectbashasvuceNo ratings yet
- Appendix 13a - BACHELOR Internship Final Report Assessment Sheet (202012)Document4 pagesAppendix 13a - BACHELOR Internship Final Report Assessment Sheet (202012)Pang Kok OnnNo ratings yet
- UK Wooden Pallet 1200 X 1000mmDocument1 pageUK Wooden Pallet 1200 X 1000mmRizwan rizviNo ratings yet
- Security Information and Event Management: Radboud University NijmegenDocument75 pagesSecurity Information and Event Management: Radboud University NijmegenproftechitspecialistNo ratings yet
- Coco Fire Indonesa - Anu 2021Document20 pagesCoco Fire Indonesa - Anu 2021Abizard Niaga UtamaNo ratings yet
- SGX-Listed Hatten Land Diversifies Beyond Melaka Through Proposed Acquisition of Unicity in Seremban, MalaysiaDocument3 pagesSGX-Listed Hatten Land Diversifies Beyond Melaka Through Proposed Acquisition of Unicity in Seremban, MalaysiaWeR1 Consultants Pte LtdNo ratings yet
- CAC Boomerang Flight ManualDocument103 pagesCAC Boomerang Flight ManualAnonymous KeGjwtNo ratings yet
- DIDIDocument3 pagesDIDIRamon GarciaNo ratings yet
- Male Pattern Blondeness: Technique: Natural Level: ColorDocument1 pageMale Pattern Blondeness: Technique: Natural Level: ColorLeo CabelosNo ratings yet
- Price Action ScalperDocument14 pagesPrice Action ScalperMurd DyanNo ratings yet
- Gonzales Vs HechanovaDocument2 pagesGonzales Vs HechanovaJoanne PaulNo ratings yet
- College Athletes Protection and Compensation ActDocument50 pagesCollege Athletes Protection and Compensation ActCody Brunner100% (1)
- BelFone ProChat Trunking System Dispatcher ManualDocument23 pagesBelFone ProChat Trunking System Dispatcher ManualPT.tikicom sinergiutamaNo ratings yet
- Pennsylvania Wing - Aug 2006Document28 pagesPennsylvania Wing - Aug 2006CAP History LibraryNo ratings yet
- Ra Lex Physicians With Advisory2023 Cdo 1Document24 pagesRa Lex Physicians With Advisory2023 Cdo 1mikzhiNo ratings yet
- BTH Thesis ArchiveDocument7 pagesBTH Thesis ArchiveWriteMyPaperForMeFastSingapore100% (1)
- E-Retail Outlet For Ready Made GarmentsDocument11 pagesE-Retail Outlet For Ready Made Garmentsrubi laariNo ratings yet
- One UI Samsung USDocument1 pageOne UI Samsung USRomsamBlaNo ratings yet
- Pig FarmingDocument25 pagesPig Farmingসপ্তক মন্ডল100% (1)
- ACN Micro Project-1Document23 pagesACN Micro Project-1ashutosh dudhaneNo ratings yet
- ProHealth Prime Proposal Form 14sept23Document10 pagesProHealth Prime Proposal Form 14sept23Rahul GoelNo ratings yet
- Hijra Bank Installation Guide For Kaspersky Security CenterDocument54 pagesHijra Bank Installation Guide For Kaspersky Security Centermohammed JundiNo ratings yet
- Mitchell e Villet, 1987 - Reinforcement of Earth Slopes and EmbankmentsDocument330 pagesMitchell e Villet, 1987 - Reinforcement of Earth Slopes and EmbankmentsJordana Furman100% (1)
- Potent Drugs HandlingDocument4 pagesPotent Drugs HandlingOMKAR BHAVLENo ratings yet
- Classical Management TheoryDocument3 pagesClassical Management TheoryQuintine ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Rudolf Elmer's Complaint To The ECHR v. Jersey (Standard Bank)Document13 pagesRudolf Elmer's Complaint To The ECHR v. Jersey (Standard Bank)David LeloupNo ratings yet