Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Negotiation: GRP IV (U113171-180)
Negotiation: GRP IV (U113171-180)
Uploaded by
CfhunSaatCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- The Gentlemen - S Guide To Effortless Seduction PDFDocument79 pagesThe Gentlemen - S Guide To Effortless Seduction PDFskywalkerf1No ratings yet
- Rabocase 105019Document6 pagesRabocase 105019CfhunSaatNo ratings yet
- Negotations SkillsDocument18 pagesNegotations SkillsAnantha NagNo ratings yet
- Successful Negotiation: Communicating effectively to reach the best solutionsFrom EverandSuccessful Negotiation: Communicating effectively to reach the best solutionsNo ratings yet
- KM Champion Guidelines AsDocument21 pagesKM Champion Guidelines AsCfhunSaatNo ratings yet
- Philosophical Foundation of EducationDocument7 pagesPhilosophical Foundation of EducationIvy Rose Rarela60% (5)
- NEGOTIATION AssignmentDocument54 pagesNEGOTIATION Assignmentdeepak anantNo ratings yet
- Negotiation: Under Supervision: Prof - Dr/Samah Faisal Prepared by Aya Ali Amira EzzatDocument17 pagesNegotiation: Under Supervision: Prof - Dr/Samah Faisal Prepared by Aya Ali Amira EzzatAya HassanNo ratings yet
- Conflict ResolutionDocument57 pagesConflict ResolutionAli Raza100% (1)
- What Is Negotiation (Slide 1 To Slide 90 Summery)Document10 pagesWhat Is Negotiation (Slide 1 To Slide 90 Summery)amrrashed2009No ratings yet
- Negotiation Textbook Summary - 2003Document13 pagesNegotiation Textbook Summary - 2003asli_balciNo ratings yet
- Đàm PhánDocument19 pagesĐàm PhánAnh Thư Nguyễn ThịNo ratings yet
- NEGOTIATIONDocument26 pagesNEGOTIATIONAbdulmajid mtukusyeNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT6 ShabiyaPutri 120404200038Document2 pagesASSIGNMENT6 ShabiyaPutri 120404200038Shabiya Putri ANo ratings yet
- NegotiationDocument42 pagesNegotiationnailesh_limbasiya100% (4)
- NEGOTIATION Final ModuleDocument6 pagesNEGOTIATION Final ModuleShaira RamosNo ratings yet
- Negotiation StyleDocument2 pagesNegotiation StyleMaría José Valdez RussellNo ratings yet
- Negotiation Is A Form of Decision Making in Which Two or More Parties Talk With One AnotherDocument39 pagesNegotiation Is A Form of Decision Making in Which Two or More Parties Talk With One AnotherPranjal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Negotiation Is A Form of Decision Making in Which Two or More Parties Talk With One AnotherDocument39 pagesNegotiation Is A Form of Decision Making in Which Two or More Parties Talk With One AnotherPranjal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Final Negotiation IntroductionDocument31 pagesFinal Negotiation IntroductionShruti GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Mastère (Part 2)Document19 pagesMastère (Part 2)dahwathi najwaNo ratings yet
- IPS NegotiationsDocument19 pagesIPS NegotiationsMairaNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 Study GuideDocument12 pagesExam 1 Study GuideJustineMensik75% (4)
- Nama: Samuel NIM: 20170301173 Business English - 6: AnswerDocument3 pagesNama: Samuel NIM: 20170301173 Business English - 6: Answersamuel pardosiNo ratings yet
- SALES AND RETAIL MANAGEMENT Unit2Document9 pagesSALES AND RETAIL MANAGEMENT Unit2Prgya SinghNo ratings yet
- Meaning of NegotiationDocument16 pagesMeaning of NegotiationThiinlee S DorjeeyNo ratings yet
- Conflict ResolutionDocument18 pagesConflict ResolutionRaj MaanaNo ratings yet
- Negotiation Lect 1Document20 pagesNegotiation Lect 1Arun ShettyNo ratings yet
- U2A4 AcostaB Osvaldo ETNIDocument4 pagesU2A4 AcostaB Osvaldo ETNIaydd PPNo ratings yet
- Negotiation Skills in BusinessDocument8 pagesNegotiation Skills in BusinessGalwng Grace Paul (Grace papa)No ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Conflict ResolutionDocument39 pagesLecture 3 - Conflict Resolutionyennp.hunglanNo ratings yet
- BE - Module 6Document20 pagesBE - Module 6Rifna SulistyanisandisastraNo ratings yet
- NegotiationDocument7 pagesNegotiationPriyanshu RanjanNo ratings yet
- Conflict ManagemnetDocument9 pagesConflict Managemnetjugunu0% (1)
- Negotiation Concept Unit1Document34 pagesNegotiation Concept Unit1Manish SinghNo ratings yet
- What Is A Negotiation?: NegotiatingDocument9 pagesWhat Is A Negotiation?: NegotiatingLoredana BandalacNo ratings yet
- NegotiationDocument12 pagesNegotiationPeggytaBruinhartNo ratings yet
- Negotiation Handout 3Document123 pagesNegotiation Handout 3Somnath KejriwalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 02Document5 pagesLecture 02wijerathnadilmiNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Naqash JavedDocument11 pagesPresented By: Naqash JavedNAQASH JAVEDNo ratings yet
- Unit1 Preparing For Negotiations: Negotiation Is A Process Where or Parties With An Issue To Find ADocument100 pagesUnit1 Preparing For Negotiations: Negotiation Is A Process Where or Parties With An Issue To Find ABenjamin Adelwini BugriNo ratings yet
- Negotiation by R22 HENEPENGDocument26 pagesNegotiation by R22 HENEPENGMichael ChinogaraNo ratings yet
- Negotiation SkillsDocument18 pagesNegotiation SkillsArif_Khan_1268No ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document3 pagesAssignment 4Umer MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Business English Session 6Document2 pagesBusiness English Session 6ricky ardiansyah tamaNo ratings yet
- Unit - 4 NEGOTIATIONDocument6 pagesUnit - 4 NEGOTIATIONBangalore Coaching CentreNo ratings yet
- Developing and Practicing Negotiagion SkillsDocument17 pagesDeveloping and Practicing Negotiagion SkillsJenny ANo ratings yet
- NegotiationDocument11 pagesNegotiationRaphael KerimitNo ratings yet
- Negotiation Skills For Effective NegotiationsDocument3 pagesNegotiation Skills For Effective NegotiationssubhendussNo ratings yet
- NegotiationsDocument11 pagesNegotiations063AbhinavGuptaMarketing ANo ratings yet
- Unit 6 The Meeting: Objectives and Strategies For Negotiation MeetingsDocument51 pagesUnit 6 The Meeting: Objectives and Strategies For Negotiation MeetingsBenjamin Adelwini BugriNo ratings yet
- NabDocument31 pagesNabSouvik DeyNo ratings yet
- CH 13 Conflict and NegotiationDocument21 pagesCH 13 Conflict and Negotiationiam arpanNo ratings yet
- Negotiation Skills PPT BBA SEM VDocument19 pagesNegotiation Skills PPT BBA SEM VArshveer SinghNo ratings yet
- NegotiationDocument4 pagesNegotiationbubbelgumgirl001No ratings yet
- NegotiationDocument3 pagesNegotiationArti DasNo ratings yet
- NegotiationDocument37 pagesNegotiationArumka JollyNo ratings yet
- NegotiationsDocument8 pagesNegotiations063AbhinavGuptaMarketing ANo ratings yet
- NegotiationDocument6 pagesNegotiationVaibhav SharmaNo ratings yet
- How To Negotiate: Negotiation tactics that will help you to succeed and achieveFrom EverandHow To Negotiate: Negotiation tactics that will help you to succeed and achieveNo ratings yet
- Outsourcisng PaperDocument60 pagesOutsourcisng PaperCfhunSaatNo ratings yet
- Tandon & Chore CommitteeDocument2 pagesTandon & Chore CommitteeCfhunSaatNo ratings yet
- CD Player State DiagramDocument14 pagesCD Player State DiagramCfhunSaatNo ratings yet
- Zindagi Jahan Shuru Hoti HfaiDocument4 pagesZindagi Jahan Shuru Hoti HfaiCfhunSaatNo ratings yet
- McKinsey Rajat UNDocument3 pagesMcKinsey Rajat UNCfhunSaatNo ratings yet
- Result Problem Applsication FormatDocument1 pageResult Problem Applsication FormatCfhunSaatNo ratings yet
- Modified Portfolio Company Index Company Name Underlying Asset Information Market LotDocument45 pagesModified Portfolio Company Index Company Name Underlying Asset Information Market LotCfhunSaatNo ratings yet
- 101 The Pilgrimagde RitualsDocument5 pages101 The Pilgrimagde RitualsCfhunSaatNo ratings yet
- How To Close A SaleDocument21 pagesHow To Close A SaleCfhunSaatNo ratings yet
- 9382 - Best Buy Growth Through Segmentation.Document7 pages9382 - Best Buy Growth Through Segmentation.CfhunSaatNo ratings yet
- ss9 Canadian Federal Government - Unit PlanDocument5 pagesss9 Canadian Federal Government - Unit Planapi-533354288No ratings yet
- Types of Research: DR - Ahmed-Refat AG Refat 1Document54 pagesTypes of Research: DR - Ahmed-Refat AG Refat 1Tabassum KausarNo ratings yet
- Elc590 PersuasiveDocument5 pagesElc590 PersuasiveFatien Zakaria50% (2)
- HL Essay RubricDocument2 pagesHL Essay Rubricapi-520941535No ratings yet
- Eled3221 Lesson ReflectionDocument5 pagesEled3221 Lesson Reflectionapi-337545961No ratings yet
- Pre Service Teachers Perspectives On TheDocument44 pagesPre Service Teachers Perspectives On TheEdison Dela Cruz Jr.No ratings yet
- DLP Formatnew FilipinoDocument4 pagesDLP Formatnew Filipinokristina manlangitNo ratings yet
- Pheromone Guide and Reviews: Alpha-7 Scented: Alpha-7 Scented ReviewedDocument4 pagesPheromone Guide and Reviews: Alpha-7 Scented: Alpha-7 Scented Reviewedngolo1No ratings yet
- Standard 10 PracticumDocument2 pagesStandard 10 Practicumapi-242288743No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Bi 2tDocument4 pagesLesson Plan Bi 2tNadia Sofwan100% (1)
- Trans Math 2-1 and 2-2Document4 pagesTrans Math 2-1 and 2-2api-299624417No ratings yet
- The Act Feelings Reasons For ImpartialityDocument18 pagesThe Act Feelings Reasons For ImpartialityTulungan Para sa Modular at Online ClassesNo ratings yet
- Cold Reading Master ClassDocument7 pagesCold Reading Master ClassSaad Sikandar Hayat100% (1)
- What Is Ericksonian Therapy: The Use of Core Competencies To Operationally Define A Non-Standardized Approach To PsychotherapyDocument16 pagesWhat Is Ericksonian Therapy: The Use of Core Competencies To Operationally Define A Non-Standardized Approach To PsychotherapyرونقالحياةNo ratings yet
- Principles of Speech WritingDocument24 pagesPrinciples of Speech WritingKate Iannel VicenteNo ratings yet
- Assesment of Study Habits of Grade 11 Students of HE ClassDocument2 pagesAssesment of Study Habits of Grade 11 Students of HE ClassGino Dela Vega100% (1)
- Lesson 2 The Self According To PhilosophyDocument8 pagesLesson 2 The Self According To PhilosophyPRINCES ALLEN MATULACNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document19 pagesChapter 4Ruthwik KolanuNo ratings yet
- Description of The 4 Primary TemperamentsDocument1 pageDescription of The 4 Primary TemperamentshalyncaeonNo ratings yet
- H.G International School, Abu Road Unit 3 Physical Fitness, Wellness and LifestyleDocument3 pagesH.G International School, Abu Road Unit 3 Physical Fitness, Wellness and LifestylePractically UselessNo ratings yet
- CMA Franchise BrochureDocument4 pagesCMA Franchise BrochureKyaw Soe HlaingNo ratings yet
- Ebook PDF Child and Adolescent Development in Your Classroom Topical Approach 3rd Edition PDFDocument41 pagesEbook PDF Child and Adolescent Development in Your Classroom Topical Approach 3rd Edition PDFdiana.dobson700100% (43)
- Introduction To Teaching Gifted and Talented ChildrenDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Teaching Gifted and Talented ChildrenSheila G. Dolipas100% (1)
- How Art Can HealDocument16 pagesHow Art Can HealNguyễn Phạm Minh NgọcNo ratings yet
- Artikel Kajian LusianaDocument12 pagesArtikel Kajian LusianaLusiana SNo ratings yet
- Module IiDocument28 pagesModule IiJoselito DepalubosNo ratings yet
- Online PR en Iulian VeghesDocument10 pagesOnline PR en Iulian VeghesIulian MariusNo ratings yet
- Edup211 Midterm ReviewerDocument9 pagesEdup211 Midterm ReviewerKiana De UngriaNo ratings yet
Negotiation: GRP IV (U113171-180)
Negotiation: GRP IV (U113171-180)
Uploaded by
CfhunSaatOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Negotiation: GRP IV (U113171-180)
Negotiation: GRP IV (U113171-180)
Uploaded by
CfhunSaatCopyright:
Available Formats
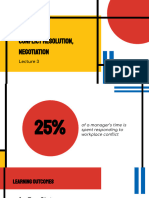
NEGOTIATION
Grp IV ( U113171-180)
Negotiation : Definition
Negotiation is a dialogue between two or more
people or parties, intended to reach an
understanding, resolve point of difference, or gain
advantage in outcome of dialogue, to produce an
agreement upon courses of action, to bargain for
individual or collective advantage, to craft
outcomes to satisfy various interests of two
people/parties involved in negotiation process.
Negotiation is a process where each party
involved in negotiating tries to gain an advantage
for themselves by the end of the process.
Negotiation : Types : 2
Distributive negotiation ( hard-bargaining,
each party at the extreme like a vegetable
vendor and a buyer)
Assertiveness reqd.
One party wins and the other loses
Characteristics to keep in mind :
Bargaining power, the perception of both the
parties w.r.t each other,alternatives (BATNA),
backup point, zone of possible agreement.
BATNA ( Best Alternative to a Negotiated
Agreement) : The alternative that one would
take in case of not reaching an agreement.
BATNA to be determined before negotiation
starts.
Backup point The min or max value that u r
willing to accept.
Integrative
Integrative negotiation ( principled or
interest-based)
Aim : To improve the quality and likelihood of the
negotiated agreement by following a set of
techniques. Win-win situation for both the
parties
Focus on trust and relationship, interests and
values.
4 stages of negotiation
Strategy
Process
Tools
Tactics
Strategy : The relationship and the final
outcome
Process and Tools : Steps that will be followed
and the roles taken in both preparing for and
negotiating i,e the parties, the context, how
negotiation is to be done
Tactics : Detailed statements and actions and
responses to others' statements and action.
Persuasion and influence.
NEGOTIATION STRATEGIES
Accommodating Type
Negotiators will want to arrive at a resolution
quickly and without conflict or the threat of a
severed relationship.
Sensitive to the emotional states, body
language, and verbal signals of the other
parties.
May not get what they wanted.
Avoiding Type
Dont like to negotiate and do so under
compulsion
Tend to defer and dodge the confrontational
aspects of negotiating.
May be perceived as tactful and diplomatic
Collaborating Type
Win-win situation
Enjoy and are good at negotiations. Help in
solving complex issues.
Understand the concerns and interests of the
other parties
Competing Type
Negotiating to win
Strategy oriented
Not concerned about the other party
Compromising Type
Both parties lose and gain
Essential to ensure that your goals are met
and is not an entirely a loss.
This practice followed when time is limited to
close a deal.
Types of Negotiator
3 types : Hard, Soft, Principled
Hard bargainers:
Main aim is to win
Use contentious strategies to influence, are
distrustful of others, use pressure to negotiate.
See others are adversaries
Soft bargainers:
Gentle style of bargaining, offer might not be in
their best interest.
Avoid confrontation, maintain good relations .
Believe in agreement.
Principled bargainers :
Focus on the problem rather than the intentions
and motives of the other party.
Follow an objective approach for negotiation (
like moral standards and fairness, professional
standards )rather than power, presssure, or
any arbitrary procedure.
You might also like
- The Gentlemen - S Guide To Effortless Seduction PDFDocument79 pagesThe Gentlemen - S Guide To Effortless Seduction PDFskywalkerf1No ratings yet
- Rabocase 105019Document6 pagesRabocase 105019CfhunSaatNo ratings yet
- Negotations SkillsDocument18 pagesNegotations SkillsAnantha NagNo ratings yet
- Successful Negotiation: Communicating effectively to reach the best solutionsFrom EverandSuccessful Negotiation: Communicating effectively to reach the best solutionsNo ratings yet
- KM Champion Guidelines AsDocument21 pagesKM Champion Guidelines AsCfhunSaatNo ratings yet
- Philosophical Foundation of EducationDocument7 pagesPhilosophical Foundation of EducationIvy Rose Rarela60% (5)
- NEGOTIATION AssignmentDocument54 pagesNEGOTIATION Assignmentdeepak anantNo ratings yet
- Negotiation: Under Supervision: Prof - Dr/Samah Faisal Prepared by Aya Ali Amira EzzatDocument17 pagesNegotiation: Under Supervision: Prof - Dr/Samah Faisal Prepared by Aya Ali Amira EzzatAya HassanNo ratings yet
- Conflict ResolutionDocument57 pagesConflict ResolutionAli Raza100% (1)
- What Is Negotiation (Slide 1 To Slide 90 Summery)Document10 pagesWhat Is Negotiation (Slide 1 To Slide 90 Summery)amrrashed2009No ratings yet
- Negotiation Textbook Summary - 2003Document13 pagesNegotiation Textbook Summary - 2003asli_balciNo ratings yet
- Đàm PhánDocument19 pagesĐàm PhánAnh Thư Nguyễn ThịNo ratings yet
- NEGOTIATIONDocument26 pagesNEGOTIATIONAbdulmajid mtukusyeNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT6 ShabiyaPutri 120404200038Document2 pagesASSIGNMENT6 ShabiyaPutri 120404200038Shabiya Putri ANo ratings yet
- NegotiationDocument42 pagesNegotiationnailesh_limbasiya100% (4)
- NEGOTIATION Final ModuleDocument6 pagesNEGOTIATION Final ModuleShaira RamosNo ratings yet
- Negotiation StyleDocument2 pagesNegotiation StyleMaría José Valdez RussellNo ratings yet
- Negotiation Is A Form of Decision Making in Which Two or More Parties Talk With One AnotherDocument39 pagesNegotiation Is A Form of Decision Making in Which Two or More Parties Talk With One AnotherPranjal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Negotiation Is A Form of Decision Making in Which Two or More Parties Talk With One AnotherDocument39 pagesNegotiation Is A Form of Decision Making in Which Two or More Parties Talk With One AnotherPranjal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Final Negotiation IntroductionDocument31 pagesFinal Negotiation IntroductionShruti GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Mastère (Part 2)Document19 pagesMastère (Part 2)dahwathi najwaNo ratings yet
- IPS NegotiationsDocument19 pagesIPS NegotiationsMairaNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 Study GuideDocument12 pagesExam 1 Study GuideJustineMensik75% (4)
- Nama: Samuel NIM: 20170301173 Business English - 6: AnswerDocument3 pagesNama: Samuel NIM: 20170301173 Business English - 6: Answersamuel pardosiNo ratings yet
- SALES AND RETAIL MANAGEMENT Unit2Document9 pagesSALES AND RETAIL MANAGEMENT Unit2Prgya SinghNo ratings yet
- Meaning of NegotiationDocument16 pagesMeaning of NegotiationThiinlee S DorjeeyNo ratings yet
- Conflict ResolutionDocument18 pagesConflict ResolutionRaj MaanaNo ratings yet
- Negotiation Lect 1Document20 pagesNegotiation Lect 1Arun ShettyNo ratings yet
- U2A4 AcostaB Osvaldo ETNIDocument4 pagesU2A4 AcostaB Osvaldo ETNIaydd PPNo ratings yet
- Negotiation Skills in BusinessDocument8 pagesNegotiation Skills in BusinessGalwng Grace Paul (Grace papa)No ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Conflict ResolutionDocument39 pagesLecture 3 - Conflict Resolutionyennp.hunglanNo ratings yet
- BE - Module 6Document20 pagesBE - Module 6Rifna SulistyanisandisastraNo ratings yet
- NegotiationDocument7 pagesNegotiationPriyanshu RanjanNo ratings yet
- Conflict ManagemnetDocument9 pagesConflict Managemnetjugunu0% (1)
- Negotiation Concept Unit1Document34 pagesNegotiation Concept Unit1Manish SinghNo ratings yet
- What Is A Negotiation?: NegotiatingDocument9 pagesWhat Is A Negotiation?: NegotiatingLoredana BandalacNo ratings yet
- NegotiationDocument12 pagesNegotiationPeggytaBruinhartNo ratings yet
- Negotiation Handout 3Document123 pagesNegotiation Handout 3Somnath KejriwalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 02Document5 pagesLecture 02wijerathnadilmiNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Naqash JavedDocument11 pagesPresented By: Naqash JavedNAQASH JAVEDNo ratings yet
- Unit1 Preparing For Negotiations: Negotiation Is A Process Where or Parties With An Issue To Find ADocument100 pagesUnit1 Preparing For Negotiations: Negotiation Is A Process Where or Parties With An Issue To Find ABenjamin Adelwini BugriNo ratings yet
- Negotiation by R22 HENEPENGDocument26 pagesNegotiation by R22 HENEPENGMichael ChinogaraNo ratings yet
- Negotiation SkillsDocument18 pagesNegotiation SkillsArif_Khan_1268No ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document3 pagesAssignment 4Umer MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Business English Session 6Document2 pagesBusiness English Session 6ricky ardiansyah tamaNo ratings yet
- Unit - 4 NEGOTIATIONDocument6 pagesUnit - 4 NEGOTIATIONBangalore Coaching CentreNo ratings yet
- Developing and Practicing Negotiagion SkillsDocument17 pagesDeveloping and Practicing Negotiagion SkillsJenny ANo ratings yet
- NegotiationDocument11 pagesNegotiationRaphael KerimitNo ratings yet
- Negotiation Skills For Effective NegotiationsDocument3 pagesNegotiation Skills For Effective NegotiationssubhendussNo ratings yet
- NegotiationsDocument11 pagesNegotiations063AbhinavGuptaMarketing ANo ratings yet
- Unit 6 The Meeting: Objectives and Strategies For Negotiation MeetingsDocument51 pagesUnit 6 The Meeting: Objectives and Strategies For Negotiation MeetingsBenjamin Adelwini BugriNo ratings yet
- NabDocument31 pagesNabSouvik DeyNo ratings yet
- CH 13 Conflict and NegotiationDocument21 pagesCH 13 Conflict and Negotiationiam arpanNo ratings yet
- Negotiation Skills PPT BBA SEM VDocument19 pagesNegotiation Skills PPT BBA SEM VArshveer SinghNo ratings yet
- NegotiationDocument4 pagesNegotiationbubbelgumgirl001No ratings yet
- NegotiationDocument3 pagesNegotiationArti DasNo ratings yet
- NegotiationDocument37 pagesNegotiationArumka JollyNo ratings yet
- NegotiationsDocument8 pagesNegotiations063AbhinavGuptaMarketing ANo ratings yet
- NegotiationDocument6 pagesNegotiationVaibhav SharmaNo ratings yet
- How To Negotiate: Negotiation tactics that will help you to succeed and achieveFrom EverandHow To Negotiate: Negotiation tactics that will help you to succeed and achieveNo ratings yet
- Outsourcisng PaperDocument60 pagesOutsourcisng PaperCfhunSaatNo ratings yet
- Tandon & Chore CommitteeDocument2 pagesTandon & Chore CommitteeCfhunSaatNo ratings yet
- CD Player State DiagramDocument14 pagesCD Player State DiagramCfhunSaatNo ratings yet
- Zindagi Jahan Shuru Hoti HfaiDocument4 pagesZindagi Jahan Shuru Hoti HfaiCfhunSaatNo ratings yet
- McKinsey Rajat UNDocument3 pagesMcKinsey Rajat UNCfhunSaatNo ratings yet
- Result Problem Applsication FormatDocument1 pageResult Problem Applsication FormatCfhunSaatNo ratings yet
- Modified Portfolio Company Index Company Name Underlying Asset Information Market LotDocument45 pagesModified Portfolio Company Index Company Name Underlying Asset Information Market LotCfhunSaatNo ratings yet
- 101 The Pilgrimagde RitualsDocument5 pages101 The Pilgrimagde RitualsCfhunSaatNo ratings yet
- How To Close A SaleDocument21 pagesHow To Close A SaleCfhunSaatNo ratings yet
- 9382 - Best Buy Growth Through Segmentation.Document7 pages9382 - Best Buy Growth Through Segmentation.CfhunSaatNo ratings yet
- ss9 Canadian Federal Government - Unit PlanDocument5 pagesss9 Canadian Federal Government - Unit Planapi-533354288No ratings yet
- Types of Research: DR - Ahmed-Refat AG Refat 1Document54 pagesTypes of Research: DR - Ahmed-Refat AG Refat 1Tabassum KausarNo ratings yet
- Elc590 PersuasiveDocument5 pagesElc590 PersuasiveFatien Zakaria50% (2)
- HL Essay RubricDocument2 pagesHL Essay Rubricapi-520941535No ratings yet
- Eled3221 Lesson ReflectionDocument5 pagesEled3221 Lesson Reflectionapi-337545961No ratings yet
- Pre Service Teachers Perspectives On TheDocument44 pagesPre Service Teachers Perspectives On TheEdison Dela Cruz Jr.No ratings yet
- DLP Formatnew FilipinoDocument4 pagesDLP Formatnew Filipinokristina manlangitNo ratings yet
- Pheromone Guide and Reviews: Alpha-7 Scented: Alpha-7 Scented ReviewedDocument4 pagesPheromone Guide and Reviews: Alpha-7 Scented: Alpha-7 Scented Reviewedngolo1No ratings yet
- Standard 10 PracticumDocument2 pagesStandard 10 Practicumapi-242288743No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Bi 2tDocument4 pagesLesson Plan Bi 2tNadia Sofwan100% (1)
- Trans Math 2-1 and 2-2Document4 pagesTrans Math 2-1 and 2-2api-299624417No ratings yet
- The Act Feelings Reasons For ImpartialityDocument18 pagesThe Act Feelings Reasons For ImpartialityTulungan Para sa Modular at Online ClassesNo ratings yet
- Cold Reading Master ClassDocument7 pagesCold Reading Master ClassSaad Sikandar Hayat100% (1)
- What Is Ericksonian Therapy: The Use of Core Competencies To Operationally Define A Non-Standardized Approach To PsychotherapyDocument16 pagesWhat Is Ericksonian Therapy: The Use of Core Competencies To Operationally Define A Non-Standardized Approach To PsychotherapyرونقالحياةNo ratings yet
- Principles of Speech WritingDocument24 pagesPrinciples of Speech WritingKate Iannel VicenteNo ratings yet
- Assesment of Study Habits of Grade 11 Students of HE ClassDocument2 pagesAssesment of Study Habits of Grade 11 Students of HE ClassGino Dela Vega100% (1)
- Lesson 2 The Self According To PhilosophyDocument8 pagesLesson 2 The Self According To PhilosophyPRINCES ALLEN MATULACNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document19 pagesChapter 4Ruthwik KolanuNo ratings yet
- Description of The 4 Primary TemperamentsDocument1 pageDescription of The 4 Primary TemperamentshalyncaeonNo ratings yet
- H.G International School, Abu Road Unit 3 Physical Fitness, Wellness and LifestyleDocument3 pagesH.G International School, Abu Road Unit 3 Physical Fitness, Wellness and LifestylePractically UselessNo ratings yet
- CMA Franchise BrochureDocument4 pagesCMA Franchise BrochureKyaw Soe HlaingNo ratings yet
- Ebook PDF Child and Adolescent Development in Your Classroom Topical Approach 3rd Edition PDFDocument41 pagesEbook PDF Child and Adolescent Development in Your Classroom Topical Approach 3rd Edition PDFdiana.dobson700100% (43)
- Introduction To Teaching Gifted and Talented ChildrenDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Teaching Gifted and Talented ChildrenSheila G. Dolipas100% (1)
- How Art Can HealDocument16 pagesHow Art Can HealNguyễn Phạm Minh NgọcNo ratings yet
- Artikel Kajian LusianaDocument12 pagesArtikel Kajian LusianaLusiana SNo ratings yet
- Module IiDocument28 pagesModule IiJoselito DepalubosNo ratings yet
- Online PR en Iulian VeghesDocument10 pagesOnline PR en Iulian VeghesIulian MariusNo ratings yet
- Edup211 Midterm ReviewerDocument9 pagesEdup211 Midterm ReviewerKiana De UngriaNo ratings yet