Professional Documents
Culture Documents
8 (1) Strings
8 (1) Strings
Uploaded by
aparnajanwalkarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
8 (1) Strings
8 (1) Strings
Uploaded by
aparnajanwalkarCopyright:
Available Formats
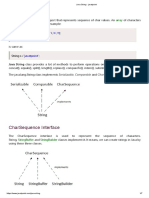
Strings
String Class
It is immutable class Available in java.lang package .
String contain sequences of 16-bit Unicode characters.
The String class contains an immutable string. Once an
instance is created, the string it contains cannot be
changed.
Most common string constructor:
String s1 = new String(immutable); //causes extra
memory allocation for no obvious advantage.
String s1 = immutable; //better
Every string literal is represented internally by an
instance of String. Java classes may have a pool of
such strings.
There are two ways to create String object:
1. By string literal
2. By new keyword
1) String literal is created by double quote.
For Example: String s="Hello";
Each time you create a string literal, the JVM checks the string
constant pool first. If the string already exists in the pool, a
reference to the pooled instance returns. If the string does not
exist in the pool, a new String object instantiates, then is placed
in the pool.
For example
String s1="Welcome";
String s2="Welcome";//no new object will be created
ADV: To make Java more memory efficient (because no new
objects are created if it exists already in string constant pool).
2) By new keyword
String s=new String("Welcome");
//creates two objects and one reference variable
In such case, JVM will create a new String object in normal
(nonpool) Heap memory and the literal "Welcome" will be
placed in the string constant pool. The variable s will refer to
the object in Heap (nonpool).
Why string objects are immutable in java?
Because java uses the concept of string literal. Suppose there
are 5 reference variables, all refers to one object "sachin".If
one reference variable changes the value of the object, it will
be affected to all the reference variables. That is why string
objects are immutable in java.
String Class
Because String is immutable, modifying it is very
expensive, StringBuffer may be the better solution.
String s = 5 + 4 = 20;
2. s = s.trim(); // 5 + 4 = 20
3. s = s.replace(+, x);
String comparison
We can compare two given strings on the basis of content and
reference.
It is used in authentication (by equals() method),sorting (by
compareTo() method), reference matching (by == operator) etc.
There are three ways to compare String objects:
1. By equals() method
2. By = = operator
3. By compareTo() method
equals() method compares the original content of the string. It
compares values of string for equality
The = = operator compares references not values.
compareTo() method compares values and returns an int which
tells if the values compare less than, equal, or greater than
s1 == s2 :0, s1 > s2 :positive value, s1 < s2:negative value
Example:
class Simple{
public static void main(String args[]){
String s1="Sachin";
String s2="Sachin";
String s3=new String("Sachin");
String s4="Saurav";
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));//true
System.out.println(s1.equals(s3));//true
System.out.println(s1.equals(s4));//false
System.out.println(s1==s2);//true (because both refer to same instance)
System.out.println(s1==s3);//false(because s3 refers to instance in nonpool)
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s2));//0
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s4));//non zero
}
}
String Concatenation
Concatenation of strings form a new string i.e. the combination of
multiple strings.
There are two ways to concat string objects:
1. By + (string concatenation) operator
2. By concat() method
Example:
class Simple{
public static void main(String args[]){
String s="Sachin"+" Tendulkar";
System.out.println(s); //Sachin Tendulkar
String s1="Sachin ";
String s2="Tendulkar";
String s3=s1.concat(s2);
System.out.println(s3); //Sachin Tendulkar
}
}
Other String class methods
Method Description
1)public boolean equals(Object
anObject)
Compares this string to the specified
object.
2)public boolean
equalsIgnoreCase(String another)
Compares this String to another
String, ignoring case.
3)public String concat(String str) Concatenates the specified string to
the end of this string.
4)public int compareTo(String str) Compares two strings and returns int
5)public int
compareToIgnoreCase(String str)
Compares two strings, ignoring case
differences.
6)public String substring(int
beginIndex)
Returns a new string that is a
substring of this string.
7)public String substring(int
beginIndex,int endIndex)
Returns a new string that is a
substring of this string.
8)public String toUpperCase() Converts all of the characters in this
String to upper case
9)public String toLowerCase() Converts all of the characters in this String to lower
case.
10)public String trim() Returns a copy of the string, with leading and trailing
whitespace omitted.
11)public boolean startsWith(String prefix) Tests if this string starts with the specified prefix.
12)public boolean endsWith(String suffix) Tests if this string ends with the specified suffix.
13)public char charAt(int index) Returns the char value at the specified index.
14)public int length() Returns the length of this string.
15)public String intern() Returns a canonical representation for the string
object.
16)public byte[] getBytes() Converts string into byte array.
17)public char[] toCharArray() Converts string into char array.
18)public static String valueOf(int i) converts the int into String.
19)public static String valueOf(long i) converts the long into String.
20)public static String valueOf(float i) converts the float into String.
21)public static String valueOf(char[] i) converts the char array into String.
22)public static String valueOf(Object obj) converts the Object into String.
23)public void replaceAll (String firstString,
String secondString)
Changes the firstString with secondString.
String Buffer class
StringBuffer class represents a string that
can be dynamically modified (mutable
string). It contain sequences of 16-bit
Unicode characters.
Constructors:
StringBuffer() - create an empty
buffer
StringBuffer(int length) - create
an empty buffer with a initial capacity
StringBuffer (String str)
Modification operations: append, insert,
reverse, setCharAt and setLength
String Buffer class (cont.)
How StringBuffer is modified?
1. StringBuffer sbuf = new StringBuffer(12345);
2. sbuf.reverse(); // 54321
3. sbuf.insert(3, aaa); // 543aaa21
4. sbuf.append(zzz); // 543aaa21zzz
1
String Buffer class (cont.)
Use toString() to returns the encapsulated string in
StringBuffer object.
The concat() method of the String class and the
append() method of the StringBuffer class glue two
strings together. An easier way to concatenate
strings is to use Javas overloaded + operator.
Example: a + b + c
The Java compiler treats the code above as if it
were the following:
New
StringBuffer().append(a).append(b).append(c).to
String();
String buffer methods
1. public synchronized StringBuffer append(String s): is used to append the
specified string with this string.
2. public synchronized StringBuffer insert(int offset, String s): is used to
insert the specified string with this string at the specified position.
3. public synchronized StringBuffer replace(int startIndex, int endIndex,
String str): is used to replace the string from specified startIndex and
endIndex.
4. public synchronized StringBuffer delete(int startIndex, int endIndex): is
used to delete the string from specified startIndex and endIndex.
5. public synchronized StringBuffer reverse(): is used to reverse the string.
6. public int capacity(): is used to return the current capacity.
7. public void ensureCapacity(int minimumCapacity): is used to ensure the
capacity at least equal to the given minimum.
8. public char charAt(int index): is used to return the character at the
specified position.
9. public String substring(int beginIndex): is used to return the substring
from the specified beginIndex.
10. public String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex): is used to return
the substring from the specified beginIndex and endIndex.
1
StringBuilder
StringBuffer class is synchronized
(thread-safe) i.e. multiple threads
cannot access it simultaneously .So it is
safe and will result in an order.
A mutable sequence of characters. This
class is similar to StringBuffer, but Its
methods are not synchronized.
If Synchronization is not required then
use StringBuilder. It will be faster.
String Tokenizer
The java.util.StringTokenizer class allows you to break a string
into tokens. It is simple way to break string.
It doesn't provide the facility to differentiate numbers, quoted
strings, identifiers etc.
There are 3 constructors defined in the StringTokenizer class.
Constructor Description
StringTokenizer(String str) creates StringTokenizer with
specified string.
StringTokenizer(String str, String
delim)
creates StringTokenizer with
specified string and delimeter.
StringTokenizer(String str, String
delim, boolean returnValue)
creates StringTokenizer with
specified string, delimeter and
returnValue. If return value is true,
delimiter characters are considered
to be tokens. If it is false, delimiter
characters serve to separate tokens.
Methods of string tokenizer class
Public method Description
boolean hasMoreTokens() checks if there is more tokens
available.
String nextToken() returns the next token from the
StringTokenizer object.
String nextToken(String delim) returns the next token based on
the delimeter.
boolean hasMoreElements() same as hasMoreTokens()
method.
Object nextElement() same as nextToken() but its
return type is Object.
int countTokens() returns the total number of
tokens.
Example:
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Simple{
public static void main(String args[]){
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer("my,name is, khan);
while (st.hasMoreTokens()) {
System.out.println(st.nextToken());
// System.out.println("Next token is : " + st.nextToken(","));
}
}
}
NOTE: StringTokenizer class is deprecated now. It is recommended to
use split() method of String class or regex (Regular Expression).
1
Thank You
You might also like
- Hcia Ai Dump FileDocument180 pagesHcia Ai Dump FileAdnan AnwarNo ratings yet
- How To Do A Simple RDLC Report Using Visual StudioDocument25 pagesHow To Do A Simple RDLC Report Using Visual StudioInspired Nonsense100% (1)
- String ClassDocument10 pagesString ClassAkshay PatilNo ratings yet
- StringsDocument9 pagesStringsMahi KolliNo ratings yet
- Java String: Charsequence InterfaceDocument13 pagesJava String: Charsequence Interfacenikita_sangalNo ratings yet
- 8 String Class 23 Jul 2020material I 23 Jul 2020 Lecture5 StringsDocument16 pages8 String Class 23 Jul 2020material I 23 Jul 2020 Lecture5 Stringssri harsha namburiNo ratings yet
- Java StringsDocument51 pagesJava StringsPrema,Asst.Prof, CSE Veltech, ChennaiNo ratings yet
- Strings: What You Will Learn in This Lecture?Document10 pagesStrings: What You Will Learn in This Lecture?jameel chowdharyNo ratings yet
- String Interface Package ExceptionDocument154 pagesString Interface Package ExceptionBalaji JadhavNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03 - Arrays & Strings Part-02 StringsDocument25 pagesChapter 03 - Arrays & Strings Part-02 StringsTanveer Ahmed HakroNo ratings yet
- Java StringDocument35 pagesJava StringDaksh MathurNo ratings yet
- String Handling in JavaDocument3 pagesString Handling in JavaYuvateja ChikathiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Java String HandlingDocument56 pagesIntroduction To Java String HandlingRUSHIL SHAHNo ratings yet
- String ClassDocument15 pagesString ClassPrerna GourNo ratings yet
- Java Unit-2Document51 pagesJava Unit-2SRI VIDYA VAHINI DEGREE COLLEGENo ratings yet
- Java StringDocument29 pagesJava Stringarnavytstudio2814No ratings yet
- JAVA LibraryDocument55 pagesJAVA LibrarySourabh JoshiNo ratings yet
- OOP Java - String and ScannerDocument6 pagesOOP Java - String and ScannerTahsin TasnimNo ratings yet
- Java StringDocument29 pagesJava StringGopal SharanNo ratings yet
- Prepared by Zanamwe N at 2014Document33 pagesPrepared by Zanamwe N at 2014Marlon TugweteNo ratings yet
- 12 String - HandlingDocument10 pages12 String - HandlingKuldeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To String HandlingDocument15 pagesIntroduction To String Handlingtarun06No ratings yet
- Unit Iii1Document100 pagesUnit Iii1hasan zahidNo ratings yet
- String NotesDocument202 pagesString NotesCHANDAN SINGHNo ratings yet
- Strings:: Java Programming UNIT-2Document21 pagesStrings:: Java Programming UNIT-2uddagiri sirishaNo ratings yet
- Presesntation On String by Vinod KumarDocument28 pagesPresesntation On String by Vinod KumarvinodNo ratings yet
- Java R20 - UNIT-5Document31 pagesJava R20 - UNIT-5χαλαρός καιԴեւիNo ratings yet
- Unit-6 String and StringbufferDocument5 pagesUnit-6 String and StringbufferParth NakumNo ratings yet
- Characters Strings and StringBuilderDocument21 pagesCharacters Strings and StringBuilderNeil BasabeNo ratings yet
- Experiment5 (Lab5)Document19 pagesExperiment5 (Lab5)sajidNo ratings yet
- String in JavaDocument21 pagesString in JavaSayani ChandraNo ratings yet
- UNIT-5 Java String HandlingDocument72 pagesUNIT-5 Java String HandlingJayanth YNo ratings yet
- Class String: Charsequence Comparable SerializableDocument25 pagesClass String: Charsequence Comparable Serializablegabrielchanchi4529No ratings yet
- Strings NotesDocument15 pagesStrings NotessanjaysgryffindorNo ratings yet
- JAVA UNIT-2 NotesDocument21 pagesJAVA UNIT-2 NotesAkankshaNo ratings yet
- Using Library Classes and PackagesDocument20 pagesUsing Library Classes and PackagesRISHABH YADAVNo ratings yet
- Java StringDocument9 pagesJava StringJanhvi AherNo ratings yet
- Char&String in JavaDocument7 pagesChar&String in JavasunilkarapiitNo ratings yet
- Theory PDFDocument24 pagesTheory PDFNibedan PalNo ratings yet
- Testing ObjectsDocument10 pagesTesting ObjectsNani NagNo ratings yet
- 1 - Java StringDocument7 pages1 - Java StringAshray GuptaNo ratings yet
- String in Java: Prepared byDocument41 pagesString in Java: Prepared byRohit BrlaNo ratings yet
- Java Unit2Document23 pagesJava Unit2mynavathirNo ratings yet
- CH 08Document26 pagesCH 08manojabholeNo ratings yet
- Understanding String Handling: ImmutableDocument8 pagesUnderstanding String Handling: ImmutableGurudas SwainNo ratings yet
- Java EnumDocument30 pagesJava EnumRaga PriyaNo ratings yet
- Strings: Mutable Object - You Can Change The States and Fields After The Object IsDocument10 pagesStrings: Mutable Object - You Can Change The States and Fields After The Object IsShaik KousarNo ratings yet
- Java 4th UnitDocument46 pagesJava 4th UnitgcerameshNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Java String HandlingDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Java String HandlingArchana R gopinathNo ratings yet
- StringsDocument11 pagesStringsReshma ChowdaryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document24 pagesChapter 4Abrham TegegneNo ratings yet
- Java StringsDocument7 pagesJava Stringspaluru sandeepNo ratings yet
- 4.using Java ObjectsDocument35 pages4.using Java ObjectsSatya Prakash MohapatraNo ratings yet
- String Class.Document6 pagesString Class.رەڭدار ھاياتNo ratings yet
- Class String: Charsequence Comparable SerializableDocument34 pagesClass String: Charsequence Comparable SerializableemsatauaNo ratings yet
- 07 SlideDocument32 pages07 SlideJorel CruzNo ratings yet
- Java StringBuffer ClassDocument18 pagesJava StringBuffer ClassVds KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - StringDocument34 pagesModule 2 - StringDhriti NayyarNo ratings yet
- StringsDocument22 pagesStringsisayashpbende26No ratings yet
- String NotesDocument5 pagesString Notesmkiran888No ratings yet
- Manipulating Strings: StringDocument12 pagesManipulating Strings: StringSachin NagNo ratings yet
- ITI APP TrackerDocument1 pageITI APP TrackeraparnajanwalkarNo ratings yet
- DocumentationDocument35 pagesDocumentationaparnajanwalkarNo ratings yet
- Divide and Conquer: For ExampleDocument2 pagesDivide and Conquer: For ExampleaparnajanwalkarNo ratings yet
- Sanet - CD - Excel Homework Exercises ANSWERSDocument45 pagesSanet - CD - Excel Homework Exercises ANSWERSaparnajanwalkarNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Mobile TechnologiesDocument4 pagesSyllabus Mobile TechnologiesaparnajanwalkarNo ratings yet
- Seminar TopicDocument1 pageSeminar TopicaparnajanwalkarNo ratings yet
- Projects ListDocument4 pagesProjects ListaparnajanwalkarNo ratings yet
- CWC A Distributed Computing Infrastructure Using SmartphonesDocument4 pagesCWC A Distributed Computing Infrastructure Using SmartphonesaparnajanwalkarNo ratings yet
- Project ProposalDocument1 pageProject ProposalaparnajanwalkarNo ratings yet
- "College Stationary Management System.": Bachelor in Business Administration Computer Application (Semester V)Document21 pages"College Stationary Management System.": Bachelor in Business Administration Computer Application (Semester V)aparnajanwalkarNo ratings yet
- Course:Windows Development - C# Module:Programming Invisualc#Document9 pagesCourse:Windows Development - C# Module:Programming Invisualc#aparnajanwalkarNo ratings yet
- Flow of Easy LeaveDocument15 pagesFlow of Easy LeaveaparnajanwalkarNo ratings yet
- Sample QuestionsDocument4 pagesSample QuestionsaparnajanwalkarNo ratings yet
- Assignment No 2Document2 pagesAssignment No 2aparnajanwalkarNo ratings yet
- ThinkPad P72 DatasheetDocument2 pagesThinkPad P72 DatasheetyovocNo ratings yet
- DICD Multiple Choice Questions UNIT-1Document5 pagesDICD Multiple Choice Questions UNIT-1TARUN PRASADNo ratings yet
- Reset The Password of The Admin User On A Cisco Firepower SystemDocument7 pagesReset The Password of The Admin User On A Cisco Firepower SystemWafikNo ratings yet
- PH Control Kel. 5 4a S1Document21 pagesPH Control Kel. 5 4a S1zahrah nadhirah kaniaNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Data Structures and Algorithm Analysis in Java 3rd Edition Weiss Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Data Structures and Algorithm Analysis in Java 3rd Edition Weiss Solutions Manual PDFhudsons6opk100% (21)
- Global 5G - Implications of A Transformational Technology - Reference PresentationDocument132 pagesGlobal 5G - Implications of A Transformational Technology - Reference Presentationlotfi jemli100% (1)
- Radhika Mirge Finl22Document18 pagesRadhika Mirge Finl22Ashutosh KurhadeNo ratings yet
- Repeater: Installation and Operation ManualDocument7 pagesRepeater: Installation and Operation ManualBratu IonNo ratings yet
- OS GTU Study Material Presentations Unit-3!4!06052021064149AMDocument82 pagesOS GTU Study Material Presentations Unit-3!4!06052021064149AMHARSHIT KEVADIYANo ratings yet
- Infineon AURIX - TC3xx - Part1 UserManual v02 - 00 EN PDFDocument2,080 pagesInfineon AURIX - TC3xx - Part1 UserManual v02 - 00 EN PDFSanjay BhatNo ratings yet
- OUA Quick Install Guide 2.7.0.2Document21 pagesOUA Quick Install Guide 2.7.0.2Aditya DasNo ratings yet
- 2018 - Karnouskos Et Al. - The Applicability of ISOIEC 25023 Measures To The Integration of Agents and Automation SystemsDocument8 pages2018 - Karnouskos Et Al. - The Applicability of ISOIEC 25023 Measures To The Integration of Agents and Automation Systemsike rhimaNo ratings yet
- Computer Science: CATALOG 2019/2020Document9 pagesComputer Science: CATALOG 2019/2020StarNo ratings yet
- 07 Chapter1Document16 pages07 Chapter1Ratnesh ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- EN Handicare PhotoSurvey3D FAQDocument5 pagesEN Handicare PhotoSurvey3D FAQFrank PostNo ratings yet
- SchneiderDocument331 pagesSchneiderAngelo AmayNo ratings yet
- 0025192-Брошюра (eng)Document2 pages0025192-Брошюра (eng)Sidorov IvanNo ratings yet
- C++ Knowledge BaseDocument5 pagesC++ Knowledge BaseSidharth ShekharNo ratings yet
- Intern Backend Developer CVDocument1 pageIntern Backend Developer CVSeen AniNo ratings yet
- Truminds 5G ExpertiseDocument30 pagesTruminds 5G ExpertiseA.H TelecomNo ratings yet
- 6GK50050BA001AB2 Datasheet enDocument2 pages6GK50050BA001AB2 Datasheet enLuis BritoNo ratings yet
- Altai MIS120P Catalog Eng 201201Document2 pagesAltai MIS120P Catalog Eng 201201adesedas2009No ratings yet
- # Installation GuideDocument2 pages# Installation GuideKarolina LewandowskaNo ratings yet
- Drop Mikrotik Brute ForcersDocument2 pagesDrop Mikrotik Brute ForcersAlbert KamuniNo ratings yet
- Grid and Cloud ComputingDocument46 pagesGrid and Cloud ComputingUsama Abdur RahmanNo ratings yet
- VFD Power Stack Parts Saudi Arabia 31.12.2018Document1 pageVFD Power Stack Parts Saudi Arabia 31.12.2018hanzal7No ratings yet
- Module 3 - CryptographyDocument25 pagesModule 3 - CryptographyDon JinoNo ratings yet
- Validation and SubstitutionDocument3 pagesValidation and SubstitutionSarf FaizalNo ratings yet