Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Teknologi Dan Rekayasa: Kompetensi Keahlian Analisis Kimia
Teknologi Dan Rekayasa: Kompetensi Keahlian Analisis Kimia
Uploaded by
Agung SukendarCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Information Technology (Pure Genius-1,2 & 8)Document3 pagesInformation Technology (Pure Genius-1,2 & 8)michael almadenNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Biology FGS0044 Answer All Questions. Diagram of An Animal Cell. Label The PartsDocument3 pagesTutorial Biology FGS0044 Answer All Questions. Diagram of An Animal Cell. Label The PartsPreeti RajasegarNo ratings yet
- Participatory Approach For Safe Shelter Awareness (PASSA) ManualDocument134 pagesParticipatory Approach For Safe Shelter Awareness (PASSA) ManualInternational Federation of Red Cross Red Crescent Societies (IFRC)100% (2)
- Cooling System DeareationDocument27 pagesCooling System DeareationNarendra Joseph Kumar100% (3)
- Menentukan KesadahanDocument16 pagesMenentukan KesadahanDinda VirgianaNo ratings yet
- Chem 3119 Experiment 4 PDFDocument8 pagesChem 3119 Experiment 4 PDFNgoc NguyenNo ratings yet
- PPTDocument13 pagesPPTLakshmi ShivaNo ratings yet
- Chap 5. Coordination ChemistryDocument11 pagesChap 5. Coordination ChemistryweareluluNo ratings yet
- The D & F Block Elements - Class 12 ChemistryDocument39 pagesThe D & F Block Elements - Class 12 ChemistryKanak DagaNo ratings yet
- Water (Unit-Iv) : Joginpally B R Engineering CollegeDocument20 pagesWater (Unit-Iv) : Joginpally B R Engineering CollegeAINo ratings yet
- Book Files I Hate You GiveDocument39 pagesBook Files I Hate You Givesabeethabegam1984No ratings yet
- One Shot-D & F Block (20.11.2020)Document60 pagesOne Shot-D & F Block (20.11.2020)Lobster DarryNo ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry (CHY1701) : Schedule (G1+TG1)Document24 pagesEngineering Chemistry (CHY1701) : Schedule (G1+TG1)Sooraj DevNo ratings yet
- Chem 3119 Experiment 4Document8 pagesChem 3119 Experiment 4Cheyenne MartinsNo ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry Sample EbookDocument10 pagesEngineering Chemistry Sample EbookAman AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Short Notes.Document15 pagesChemistry Short Notes.Mushaa DherreNo ratings yet
- Water QualityDocument52 pagesWater QualityRbc bNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment Water Treatment: Lecture 6: SofteningDocument29 pagesWater Treatment Water Treatment: Lecture 6: SofteningAbo-Khaled MohammedNo ratings yet
- Yodimetria, Yodometria Yodatometria - 2014-IIDocument47 pagesYodimetria, Yodometria Yodatometria - 2014-IIGabby Novillo PillacaNo ratings yet
- D and F Block 20 MinsDocument43 pagesD and F Block 20 MinsStsNo ratings yet
- Came Searmen T Method Color I MetricDocument4 pagesCame Searmen T Method Color I MetricarmanNo ratings yet
- UNIT - 5 Water TechnologyDocument16 pagesUNIT - 5 Water TechnologyR. GAMINGNo ratings yet
- d block new- S KUMARDocument9 pagesd block new- S KUMARshaikhmrezwanNo ratings yet
- Experiment - Detection of Hardness of WaterDocument8 pagesExperiment - Detection of Hardness of WaterRudra ChouhanNo ratings yet
- 05229ce14c4135 Practical Eng Chemistry CH 1Document5 pages05229ce14c4135 Practical Eng Chemistry CH 1Mohit RajaiNo ratings yet
- Softening 2Document5 pagesSoftening 2Xherine Bico CordialNo ratings yet
- Junoon-e-JEE - (JLD 3.0) - D & F Block - 30th JanDocument129 pagesJunoon-e-JEE - (JLD 3.0) - D & F Block - 30th Janabhay singh100% (1)
- Module I and II ChemistryDocument28 pagesModule I and II ChemistryMohd Naif FirozNo ratings yet
- 5.3 & 5.4 Group 2: What Is The Outcome From Syllabus?Document34 pages5.3 & 5.4 Group 2: What Is The Outcome From Syllabus?ArichandranMuniandyNo ratings yet
- 1-Compleximetric Determination of Water HardnessDocument51 pages1-Compleximetric Determination of Water HardnessBeatrice Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- SofteningDocument8 pagesSofteningKhodarahm FarjoodiNo ratings yet
- 1) Water TechnologyDocument11 pages1) Water TechnologyDevet ValechaNo ratings yet
- Mod 5 Revision Guide 4. Transition MetalsDocument10 pagesMod 5 Revision Guide 4. Transition MetalsrammiejimjamsNo ratings yet
- Monday: - Thermodynamics of Aqueous SolutionsDocument91 pagesMonday: - Thermodynamics of Aqueous SolutionsSri Sakthi SumananNo ratings yet
- 10 Chemical EquationDocument33 pages10 Chemical EquationGlen MangaliNo ratings yet
- CCC预习题Document17 pagesCCC预习题jzdf2d9nnvNo ratings yet
- Unit 4-Water TreatmentDocument11 pagesUnit 4-Water Treatmentgopi nath sahuNo ratings yet
- Water PPT (Fe 22-23)Document46 pagesWater PPT (Fe 22-23)Aaditya MalaniNo ratings yet
- Unit1 ChemDocument35 pagesUnit1 Chemmevxyz123No ratings yet
- 2 Group Two Elements: Beryllium Be Magnesium MG Calcium Ca Strontium SR Barium BaDocument6 pages2 Group Two Elements: Beryllium Be Magnesium MG Calcium Ca Strontium SR Barium BaTheodora HamletNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 Determination of Total Hardness As PPM Calcium CarbonateDocument26 pagesExperiment 4 Determination of Total Hardness As PPM Calcium CarbonateJordanNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Electrocoagulation For Groundwater PurificationDocument5 pagesAssessment of Electrocoagulation For Groundwater Purificationnermeen ahmedNo ratings yet
- D Block Elements NotesDocument12 pagesD Block Elements NotesSMELLY CATNo ratings yet
- Unit-I WaterDocument20 pagesUnit-I Water21EBKCS074PARULNo ratings yet
- Water and Its Treatment MaterialDocument14 pagesWater and Its Treatment MaterialSameer SamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Miscellaneous Treatment Processes: 8.1. SofteningDocument4 pagesChapter 8 Miscellaneous Treatment Processes: 8.1. SofteningShita AlemieNo ratings yet
- Process of Thermal Decomposition of Lithium CarbonateDocument10 pagesProcess of Thermal Decomposition of Lithium CarbonateArdu StuffNo ratings yet
- Redox Lecture Notes (Final - Teacher)Document12 pagesRedox Lecture Notes (Final - Teacher)milopingNo ratings yet
- CH 19Document36 pagesCH 19SylviaNo ratings yet
- D-F-Block IIT JEEDocument26 pagesD-F-Block IIT JEEThe Rock89% (9)
- Titrasi Redoks MatrikulasiDocument23 pagesTitrasi Redoks MatrikulasiDangsony DangNo ratings yet
- CHEM 26.1 Finals ReviewerDocument1 pageCHEM 26.1 Finals ReviewerClara Mirabueno100% (1)
- Lab 5 HardnessDocument3 pagesLab 5 HardnessAnshul MahorNo ratings yet
- Water 12 01374 v2 PDFDocument12 pagesWater 12 01374 v2 PDFArvind KumaresanNo ratings yet
- Hardness RemovalDocument79 pagesHardness RemovalTong SarawutNo ratings yet
- 9-Softning F11Document16 pages9-Softning F11Mohamed JalalaNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-02 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (The D - & F-Block Elements) (Answer)Document2 pagesCbse Test Paper-02 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (The D - & F-Block Elements) (Answer)Shreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- Alkalinity, Hardness, & Lime/Soda Ash Softening BYDocument41 pagesAlkalinity, Hardness, & Lime/Soda Ash Softening BYchichavlajaNo ratings yet
- Q - Oxidation - ReductionDocument2 pagesQ - Oxidation - ReductionBisad Abu CuriNo ratings yet
- Hardness PDFDocument16 pagesHardness PDFMike magNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Ultra-High Temperature Ceramics: Materials for Extreme Environment ApplicationsFrom EverandUltra-High Temperature Ceramics: Materials for Extreme Environment ApplicationsWilliam G. FahrenholtzNo ratings yet
- Csi 23-0510 - Square Meter Construction LLC Plot No-9132693Document1 pageCsi 23-0510 - Square Meter Construction LLC Plot No-9132693Muhammad AfrasiyabNo ratings yet
- Purchase Order: Barato Supply CompanyDocument4 pagesPurchase Order: Barato Supply CompanyFilna QuiñoNo ratings yet
- Description of HospitalDocument1 pageDescription of HospitalDanica Joy V. JacobaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two: National Income AccountingDocument18 pagesChapter Two: National Income AccountingMenna ElmeslhyNo ratings yet
- Honors 345 Paper 1Document6 pagesHonors 345 Paper 1api-740591437No ratings yet
- CF Dye Selection GuideDocument32 pagesCF Dye Selection GuideRamona AndronesiNo ratings yet
- BW211-212-213D-PD-40-Operating Maintenance InstructionsDocument122 pagesBW211-212-213D-PD-40-Operating Maintenance InstructionsRudi Abu ZahraNo ratings yet
- Công ngh ệ khai thác Petroleum Production Engineering: Chapter 5. Single phase in pipeDocument3 pagesCông ngh ệ khai thác Petroleum Production Engineering: Chapter 5. Single phase in pipeTu Dang TrongNo ratings yet
- AlquimistDocument18 pagesAlquimistWillian RenneNo ratings yet
- HPA200 HPA250 Installation Instructions HPC00100Document27 pagesHPA200 HPA250 Installation Instructions HPC00100jsprtanNo ratings yet
- Public Consulting Group Rev Max Proposal, DCS, Indiana, March 2009Document312 pagesPublic Consulting Group Rev Max Proposal, DCS, Indiana, March 2009Rick ThomaNo ratings yet
- Cellular AdaptationDocument4 pagesCellular AdaptationDenise AngelNo ratings yet
- Protein JournalDocument21 pagesProtein JournalRahmadian Kahfi Zulfa KamilaNo ratings yet
- Subanen HistoryDocument14 pagesSubanen HistoryAllan Mangangot100% (1)
- 2014 Hubsch Z Et Al.Document13 pages2014 Hubsch Z Et Al.vishdubey777No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument26 pagesUntitledCRIS JEFFERSON JUANNo ratings yet
- Network Marketing Opportunity - Vestige Marketing Plan URTSAM - +919711572735Document16 pagesNetwork Marketing Opportunity - Vestige Marketing Plan URTSAM - +919711572735Samir K Mishra100% (1)
- Intro PaperDocument6 pagesIntro PaperbonnmengulloNo ratings yet
- Section: Section:: Student's Information Student's InformationDocument1 pageSection: Section:: Student's Information Student's InformationMello Jane Garcia DedosinNo ratings yet
- Upload Paper For OpapersDocument31 pagesUpload Paper For OpapersMuhamad Eddin SyazriNo ratings yet
- Why Meat Is The Best-Worst ThingDocument2 pagesWhy Meat Is The Best-Worst Thingabbyreader07No ratings yet
- Actuaries CodeDocument4 pagesActuaries CodeShizukaNo ratings yet
- Report137 Pretreatment & Design Considerations - Large Scale Seawater FacilitiesDocument197 pagesReport137 Pretreatment & Design Considerations - Large Scale Seawater FacilitiesLTE002No ratings yet
- Novavax VaccineDocument1 pageNovavax Vaccinealina JCNo ratings yet
- 「青少年瀏覽網上色情資訊的現況及影響研究」調查報告Document120 pages「青少年瀏覽網上色情資訊的現況及影響研究」調查報告Jetco LawNo ratings yet
- World Trade Organization: CriticismDocument44 pagesWorld Trade Organization: Criticismrain06021992No ratings yet
Teknologi Dan Rekayasa: Kompetensi Keahlian Analisis Kimia
Teknologi Dan Rekayasa: Kompetensi Keahlian Analisis Kimia
Uploaded by
Agung SukendarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Teknologi Dan Rekayasa: Kompetensi Keahlian Analisis Kimia
Teknologi Dan Rekayasa: Kompetensi Keahlian Analisis Kimia
Uploaded by
Agung SukendarCopyright:
Available Formats
Teknologi Dan Rekayasa
Kompetensi Keahlian
Analisis Kimia
Analysis of Chemical
Parameters
By : Tedi Hadiana
SMK Negeri 13 Bandung
Hardness
SMK Negeri 13 Bandung
Teknologi dan Rekayasa
Objectives
After this session, the students are
expected to be able :
1. to explain the steps of determination of
hardness
2. to explain the objectives of every step
3. to explain the function of reagents
4. to conduct the determination of hardness
5. to do the calculation in the determination of
hardness
6. to arrange the report of the determination
of hardness
Factors that contribute to Hardness in water
Hardness in water cause by dissolved metal ions
such as Ca
2+
, Mg
2+
, Fe
2+
, Mn
2+
, etc Major
content of Ca
2+
and Mg
2+
dissolved Review of
Hardness contribution to Ca
2+
and Mg
2+
If hardness in high level high content Ca
2+
and
Mg
2+
in water
Usually in area close to mountain with limestone
content of hardness is high
Effect of High level hardness
in water
For industrial :
If hardness and CO
3
2-
/HCO
3
-
are in high level in
water slag formation
Ca
2+
+ CO
3
2-
CaCO
3
(s)
Ca(HCO
3
)
2
(heat) CaCO
3
(s) + H
2
O +CO
2
For sanitation :
Appearance of muddy water
If use for washing wastefully of soap
Types of hardness in water
Total Hardness
Temporary Hardness
Permanent Hardness
Calsium Hardness
Magnesium Hardness
Determination of Hardness
Review cause of hardness are Ca
2+
and Mg
2+
Determination of hardness by titrimetric method Complexometric
Standard solution EDTA (Ethylen Diamin Tetra Acetic
Acid)/Complexon II/TItriplex II
Complexon III/Titriplex III/Na-EDTA
Unit of hardness :
1.
o
D (Germany Degree)
1
o
D = 10 mg CaO/L
2.
o
F (French Degree)
1
o
F = 10 mg CaCO
3
/L
3.
o
E (England Degree)
1
o
E = 1 g/gallon = 14,3 mg CaCO
3
/L
4. America Degree ( mg CaCO
3
/L)
Determination of total hardness
Reactions :
Ca
2+
+ HIn
2-
CaIn
-
+ H
+
Mg
2+
+ HIn
2-
MgIn
-
+ H
+
Ca
2+
+ H
2
Y
2-
CaY
2-
+ 2H
+
Mg
2+
+ H
2
Y
2-
MgY
2-
+ 2H
+
MgIn
-
(reddish-purple)
+ H
2
Y
2-
MgY
2-
+ HIn
2-
(blue)
+ H+
Principle :
Sample of water containing Ca
2+
and Mg
2+
titrated by standard
solution EDTA at pH 10 to EBT as indicator until end point the
colour change from reddish-purple to light blue. At equivalence
point : mol Ca
2+
+ Mg
2+
= mol EDTA
Determination of permanent hardness
Reactions :
Ca(HCO
3
)
2
(heat)
CaCO
3
(s) + H
2
O +CO
2
Mg(HCO
3
)
2
(heat)
Mg(OH)
2
(s) + CO
2
Ca
2+
+ HIn
2-
CaIn
-
+ H
+
//
Mg
2+
+ HIn
2-
MgIn
-
+ H
+
Ca
2+
+ H
2
Y
2-
CaY
2-
+ 2H
+
Mg
2+
+ H
2
Y
2-
MgY
2-
+ 2H
+
MgIn
-
(reddish-purple)
+ H
2
Y
2-
MgY
2-
+ HIn
2-
(blue)
+ H+
Principle :
Temporary hardness in sample lose upon boiling for 15 minutes ,
Ca
2+
and Mg
2+
in centrate titrated by standard solution EDTA at pH 10
to EBT as indicator. At end point the colour change from reddish-
purple to light blue
At equivalence point : mol Ca
2+
+ Mg
2+
= mol EDTA
Determined indirect as following :
Temporary hardness =
total hardness permanent hardness
Determination of temporary hardness
Determination of Calcium Harness
Reaction :
Mg
2+
+ OH
-
Mg(OH)
2
(s)
Ca
2+
+ H
2
In
3-
CaIn
3-
+ 2H
+
Ca
2+
+ H
2
Y
2-
CaY
2-
+ 2H
+
CaIn
3-
(red)
+ H
2
Y
2-
CaY
2-
+ H
2
In
3-
(bluish-purple)
Principle :
Content of Ca
2+
in sample of water titrated by standard EDTA
solution at pH > 11 to Murexide as indicator. At end point the
colour change from red to bluish-purple
At equivalence point : mol Ca
2+
= mol EDTA
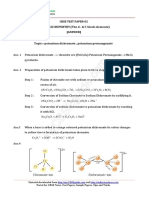
Determination of Magnesium Hardness
Determined indirect as following :
Hardness of Mg
2+
=
Total hardness hardness of Ca
2+
You might also like
- Information Technology (Pure Genius-1,2 & 8)Document3 pagesInformation Technology (Pure Genius-1,2 & 8)michael almadenNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Biology FGS0044 Answer All Questions. Diagram of An Animal Cell. Label The PartsDocument3 pagesTutorial Biology FGS0044 Answer All Questions. Diagram of An Animal Cell. Label The PartsPreeti RajasegarNo ratings yet
- Participatory Approach For Safe Shelter Awareness (PASSA) ManualDocument134 pagesParticipatory Approach For Safe Shelter Awareness (PASSA) ManualInternational Federation of Red Cross Red Crescent Societies (IFRC)100% (2)
- Cooling System DeareationDocument27 pagesCooling System DeareationNarendra Joseph Kumar100% (3)
- Menentukan KesadahanDocument16 pagesMenentukan KesadahanDinda VirgianaNo ratings yet
- Chem 3119 Experiment 4 PDFDocument8 pagesChem 3119 Experiment 4 PDFNgoc NguyenNo ratings yet
- PPTDocument13 pagesPPTLakshmi ShivaNo ratings yet
- Chap 5. Coordination ChemistryDocument11 pagesChap 5. Coordination ChemistryweareluluNo ratings yet
- The D & F Block Elements - Class 12 ChemistryDocument39 pagesThe D & F Block Elements - Class 12 ChemistryKanak DagaNo ratings yet
- Water (Unit-Iv) : Joginpally B R Engineering CollegeDocument20 pagesWater (Unit-Iv) : Joginpally B R Engineering CollegeAINo ratings yet
- Book Files I Hate You GiveDocument39 pagesBook Files I Hate You Givesabeethabegam1984No ratings yet
- One Shot-D & F Block (20.11.2020)Document60 pagesOne Shot-D & F Block (20.11.2020)Lobster DarryNo ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry (CHY1701) : Schedule (G1+TG1)Document24 pagesEngineering Chemistry (CHY1701) : Schedule (G1+TG1)Sooraj DevNo ratings yet
- Chem 3119 Experiment 4Document8 pagesChem 3119 Experiment 4Cheyenne MartinsNo ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry Sample EbookDocument10 pagesEngineering Chemistry Sample EbookAman AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Short Notes.Document15 pagesChemistry Short Notes.Mushaa DherreNo ratings yet
- Water QualityDocument52 pagesWater QualityRbc bNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment Water Treatment: Lecture 6: SofteningDocument29 pagesWater Treatment Water Treatment: Lecture 6: SofteningAbo-Khaled MohammedNo ratings yet
- Yodimetria, Yodometria Yodatometria - 2014-IIDocument47 pagesYodimetria, Yodometria Yodatometria - 2014-IIGabby Novillo PillacaNo ratings yet
- D and F Block 20 MinsDocument43 pagesD and F Block 20 MinsStsNo ratings yet
- Came Searmen T Method Color I MetricDocument4 pagesCame Searmen T Method Color I MetricarmanNo ratings yet
- UNIT - 5 Water TechnologyDocument16 pagesUNIT - 5 Water TechnologyR. GAMINGNo ratings yet
- d block new- S KUMARDocument9 pagesd block new- S KUMARshaikhmrezwanNo ratings yet
- Experiment - Detection of Hardness of WaterDocument8 pagesExperiment - Detection of Hardness of WaterRudra ChouhanNo ratings yet
- 05229ce14c4135 Practical Eng Chemistry CH 1Document5 pages05229ce14c4135 Practical Eng Chemistry CH 1Mohit RajaiNo ratings yet
- Softening 2Document5 pagesSoftening 2Xherine Bico CordialNo ratings yet
- Junoon-e-JEE - (JLD 3.0) - D & F Block - 30th JanDocument129 pagesJunoon-e-JEE - (JLD 3.0) - D & F Block - 30th Janabhay singh100% (1)
- Module I and II ChemistryDocument28 pagesModule I and II ChemistryMohd Naif FirozNo ratings yet
- 5.3 & 5.4 Group 2: What Is The Outcome From Syllabus?Document34 pages5.3 & 5.4 Group 2: What Is The Outcome From Syllabus?ArichandranMuniandyNo ratings yet
- 1-Compleximetric Determination of Water HardnessDocument51 pages1-Compleximetric Determination of Water HardnessBeatrice Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- SofteningDocument8 pagesSofteningKhodarahm FarjoodiNo ratings yet
- 1) Water TechnologyDocument11 pages1) Water TechnologyDevet ValechaNo ratings yet
- Mod 5 Revision Guide 4. Transition MetalsDocument10 pagesMod 5 Revision Guide 4. Transition MetalsrammiejimjamsNo ratings yet
- Monday: - Thermodynamics of Aqueous SolutionsDocument91 pagesMonday: - Thermodynamics of Aqueous SolutionsSri Sakthi SumananNo ratings yet
- 10 Chemical EquationDocument33 pages10 Chemical EquationGlen MangaliNo ratings yet
- CCC预习题Document17 pagesCCC预习题jzdf2d9nnvNo ratings yet
- Unit 4-Water TreatmentDocument11 pagesUnit 4-Water Treatmentgopi nath sahuNo ratings yet
- Water PPT (Fe 22-23)Document46 pagesWater PPT (Fe 22-23)Aaditya MalaniNo ratings yet
- Unit1 ChemDocument35 pagesUnit1 Chemmevxyz123No ratings yet
- 2 Group Two Elements: Beryllium Be Magnesium MG Calcium Ca Strontium SR Barium BaDocument6 pages2 Group Two Elements: Beryllium Be Magnesium MG Calcium Ca Strontium SR Barium BaTheodora HamletNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 Determination of Total Hardness As PPM Calcium CarbonateDocument26 pagesExperiment 4 Determination of Total Hardness As PPM Calcium CarbonateJordanNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Electrocoagulation For Groundwater PurificationDocument5 pagesAssessment of Electrocoagulation For Groundwater Purificationnermeen ahmedNo ratings yet
- D Block Elements NotesDocument12 pagesD Block Elements NotesSMELLY CATNo ratings yet
- Unit-I WaterDocument20 pagesUnit-I Water21EBKCS074PARULNo ratings yet
- Water and Its Treatment MaterialDocument14 pagesWater and Its Treatment MaterialSameer SamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Miscellaneous Treatment Processes: 8.1. SofteningDocument4 pagesChapter 8 Miscellaneous Treatment Processes: 8.1. SofteningShita AlemieNo ratings yet
- Process of Thermal Decomposition of Lithium CarbonateDocument10 pagesProcess of Thermal Decomposition of Lithium CarbonateArdu StuffNo ratings yet
- Redox Lecture Notes (Final - Teacher)Document12 pagesRedox Lecture Notes (Final - Teacher)milopingNo ratings yet
- CH 19Document36 pagesCH 19SylviaNo ratings yet
- D-F-Block IIT JEEDocument26 pagesD-F-Block IIT JEEThe Rock89% (9)
- Titrasi Redoks MatrikulasiDocument23 pagesTitrasi Redoks MatrikulasiDangsony DangNo ratings yet
- CHEM 26.1 Finals ReviewerDocument1 pageCHEM 26.1 Finals ReviewerClara Mirabueno100% (1)
- Lab 5 HardnessDocument3 pagesLab 5 HardnessAnshul MahorNo ratings yet
- Water 12 01374 v2 PDFDocument12 pagesWater 12 01374 v2 PDFArvind KumaresanNo ratings yet
- Hardness RemovalDocument79 pagesHardness RemovalTong SarawutNo ratings yet
- 9-Softning F11Document16 pages9-Softning F11Mohamed JalalaNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-02 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (The D - & F-Block Elements) (Answer)Document2 pagesCbse Test Paper-02 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (The D - & F-Block Elements) (Answer)Shreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- Alkalinity, Hardness, & Lime/Soda Ash Softening BYDocument41 pagesAlkalinity, Hardness, & Lime/Soda Ash Softening BYchichavlajaNo ratings yet
- Q - Oxidation - ReductionDocument2 pagesQ - Oxidation - ReductionBisad Abu CuriNo ratings yet
- Hardness PDFDocument16 pagesHardness PDFMike magNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Ultra-High Temperature Ceramics: Materials for Extreme Environment ApplicationsFrom EverandUltra-High Temperature Ceramics: Materials for Extreme Environment ApplicationsWilliam G. FahrenholtzNo ratings yet
- Csi 23-0510 - Square Meter Construction LLC Plot No-9132693Document1 pageCsi 23-0510 - Square Meter Construction LLC Plot No-9132693Muhammad AfrasiyabNo ratings yet
- Purchase Order: Barato Supply CompanyDocument4 pagesPurchase Order: Barato Supply CompanyFilna QuiñoNo ratings yet
- Description of HospitalDocument1 pageDescription of HospitalDanica Joy V. JacobaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two: National Income AccountingDocument18 pagesChapter Two: National Income AccountingMenna ElmeslhyNo ratings yet
- Honors 345 Paper 1Document6 pagesHonors 345 Paper 1api-740591437No ratings yet
- CF Dye Selection GuideDocument32 pagesCF Dye Selection GuideRamona AndronesiNo ratings yet
- BW211-212-213D-PD-40-Operating Maintenance InstructionsDocument122 pagesBW211-212-213D-PD-40-Operating Maintenance InstructionsRudi Abu ZahraNo ratings yet
- Công ngh ệ khai thác Petroleum Production Engineering: Chapter 5. Single phase in pipeDocument3 pagesCông ngh ệ khai thác Petroleum Production Engineering: Chapter 5. Single phase in pipeTu Dang TrongNo ratings yet
- AlquimistDocument18 pagesAlquimistWillian RenneNo ratings yet
- HPA200 HPA250 Installation Instructions HPC00100Document27 pagesHPA200 HPA250 Installation Instructions HPC00100jsprtanNo ratings yet
- Public Consulting Group Rev Max Proposal, DCS, Indiana, March 2009Document312 pagesPublic Consulting Group Rev Max Proposal, DCS, Indiana, March 2009Rick ThomaNo ratings yet
- Cellular AdaptationDocument4 pagesCellular AdaptationDenise AngelNo ratings yet
- Protein JournalDocument21 pagesProtein JournalRahmadian Kahfi Zulfa KamilaNo ratings yet
- Subanen HistoryDocument14 pagesSubanen HistoryAllan Mangangot100% (1)
- 2014 Hubsch Z Et Al.Document13 pages2014 Hubsch Z Et Al.vishdubey777No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument26 pagesUntitledCRIS JEFFERSON JUANNo ratings yet
- Network Marketing Opportunity - Vestige Marketing Plan URTSAM - +919711572735Document16 pagesNetwork Marketing Opportunity - Vestige Marketing Plan URTSAM - +919711572735Samir K Mishra100% (1)
- Intro PaperDocument6 pagesIntro PaperbonnmengulloNo ratings yet
- Section: Section:: Student's Information Student's InformationDocument1 pageSection: Section:: Student's Information Student's InformationMello Jane Garcia DedosinNo ratings yet
- Upload Paper For OpapersDocument31 pagesUpload Paper For OpapersMuhamad Eddin SyazriNo ratings yet
- Why Meat Is The Best-Worst ThingDocument2 pagesWhy Meat Is The Best-Worst Thingabbyreader07No ratings yet
- Actuaries CodeDocument4 pagesActuaries CodeShizukaNo ratings yet
- Report137 Pretreatment & Design Considerations - Large Scale Seawater FacilitiesDocument197 pagesReport137 Pretreatment & Design Considerations - Large Scale Seawater FacilitiesLTE002No ratings yet
- Novavax VaccineDocument1 pageNovavax Vaccinealina JCNo ratings yet
- 「青少年瀏覽網上色情資訊的現況及影響研究」調查報告Document120 pages「青少年瀏覽網上色情資訊的現況及影響研究」調查報告Jetco LawNo ratings yet
- World Trade Organization: CriticismDocument44 pagesWorld Trade Organization: Criticismrain06021992No ratings yet