Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Local Analgesia10.5.11
Local Analgesia10.5.11
Uploaded by
Rakan KhtoomCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Pharmacology Hesi Exam Study Guide 2015Document96 pagesPharmacology Hesi Exam Study Guide 2015sak genius100% (31)
- Test Bank For Advanced Practice Nursing in The Care of Older Adults 2nd by Kennedy Malone DownloadDocument10 pagesTest Bank For Advanced Practice Nursing in The Care of Older Adults 2nd by Kennedy Malone Downloadericgoodmanfaszgwponk100% (31)
- Hesi Exam Practice Pharmacology PDFDocument55 pagesHesi Exam Practice Pharmacology PDFAna Bienne100% (2)
- Treatment of VKC: 1. Nonpharmacologic Treatment 2. Pharmacologic Treatment 3. Surgery TreatmentDocument18 pagesTreatment of VKC: 1. Nonpharmacologic Treatment 2. Pharmacologic Treatment 3. Surgery TreatmentAllen SallyNo ratings yet
- Drug Allergy BookDocument332 pagesDrug Allergy Bookmegah_asia13No ratings yet
- Duke Anatomy - Lab 20 - Eye & EarDocument19 pagesDuke Anatomy - Lab 20 - Eye & EarabidalibpNo ratings yet
- Common Bacterial and Viral Infection Key Answer FinalDocument10 pagesCommon Bacterial and Viral Infection Key Answer FinalAnu KrupaNo ratings yet
- Local Anaesthesia 07 03 22 CompressedDocument87 pagesLocal Anaesthesia 07 03 22 CompressedkomanaNo ratings yet
- Tinea Versicolor of The Neck As Side Effect of Topical Steroids For Alopecia AreataDocument12 pagesTinea Versicolor of The Neck As Side Effect of Topical Steroids For Alopecia AreataNazihan Safitri AlkatiriNo ratings yet
- Naplex Sample Quiz 3 Review of Attempt 1Document5 pagesNaplex Sample Quiz 3 Review of Attempt 1Ashish PatelNo ratings yet
- TOBRINDocument2 pagesTOBRINmahgadNo ratings yet
- Drugs in Ear DisordersDocument2 pagesDrugs in Ear DisorderstatiNo ratings yet
- Tetanos ClasesDocument6 pagesTetanos Clasesjessica rieraNo ratings yet
- Role of Azole Antifungal Agents in Seborrheic Dermatitis & Dandruff: A ReviewDocument20 pagesRole of Azole Antifungal Agents in Seborrheic Dermatitis & Dandruff: A ReviewHajrah MirandaNo ratings yet
- Administration of Local Anaesthetic in DentistryDocument6 pagesAdministration of Local Anaesthetic in DentistryridaNo ratings yet
- Efficonazole 10% Solution in The Treatment of Toenail OnychomycosisDocument9 pagesEfficonazole 10% Solution in The Treatment of Toenail OnychomycosisNadia Vinka LisdiantiNo ratings yet
- DR Meera Kuppusamy MBBS (IMU), MRCP (UK), Adv Derm Masters (UKM) Consultant Dermatologist Columbia Asia KlangDocument86 pagesDR Meera Kuppusamy MBBS (IMU), MRCP (UK), Adv Derm Masters (UKM) Consultant Dermatologist Columbia Asia KlangdnaielNo ratings yet
- Local AnesthesiaDocument63 pagesLocal AnesthesiaReda IsmaeelNo ratings yet
- Child Measles Eye Eng 300Document52 pagesChild Measles Eye Eng 300DadaNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Eye Medication AdministrationDocument3 pagesInternational Journal of Eye Medication AdministrationMutia Ramadini91No ratings yet
- Gingival Herbal Depigmentation: A Natural Solution??Document9 pagesGingival Herbal Depigmentation: A Natural Solution??IJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Important Topics in OtologyDocument94 pagesImportant Topics in OtologyDr. T. Balasubramanian100% (1)
- Local Anesthesia in Pediatric DentistryDocument51 pagesLocal Anesthesia in Pediatric Dentistryakshi1947100% (3)
- Handbook of Splinting and CastingDocument318 pagesHandbook of Splinting and Castingguillermina paz100% (1)
- KMB III Kel 1 KonjungtivitisDocument19 pagesKMB III Kel 1 Konjungtivitisrkpngnz4xwNo ratings yet
- Local Anesthesia in Pediatric DentistryDocument70 pagesLocal Anesthesia in Pediatric DentistryNicky Romeo100% (1)
- Apexa No 7Document4 pagesApexa No 7Apexa YadavNo ratings yet
- Guideline On Use of Local Anesthesia For Pediatric Dental PatientsDocument7 pagesGuideline On Use of Local Anesthesia For Pediatric Dental PatientsLisna K. RezkyNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of Efficacy of Oral Terbinafine Alone and Oral Terbinafine With Topical 8% Ciclopirox Olamine in OnychomycosisDocument7 pagesComparative Study of Efficacy of Oral Terbinafine Alone and Oral Terbinafine With Topical 8% Ciclopirox Olamine in OnychomycosisIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- 2018 Neurosensory Pharmacology Ns2Document66 pages2018 Neurosensory Pharmacology Ns2Firsania BungaNo ratings yet
- Suppurative KeratitisDocument30 pagesSuppurative KeratitisTatik Handayani100% (1)
- Ménière Disease (Clinical) - LecturioDocument15 pagesMénière Disease (Clinical) - Lecturioari06roamoranNo ratings yet
- 3.TPD 45 149Document4 pages3.TPD 45 149YuyumNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Exdontia - BDS YR 4Document75 pagesPediatric Exdontia - BDS YR 4Elamaaraeen MadhvanNo ratings yet
- Symposium Toxic Optic Neuropathy: Pradeep Sharma, Reena SharmaDocument5 pagesSymposium Toxic Optic Neuropathy: Pradeep Sharma, Reena SharmaCony NurbayyiniNo ratings yet
- Neural Tube Defects: Group 1Document28 pagesNeural Tube Defects: Group 1imneverwrong2492100% (1)
- 18 Paediatric Regional Block GuidelinesDocument10 pages18 Paediatric Regional Block GuidelinesParvathy R NairNo ratings yet
- SRM College of PhysiotherapyDocument24 pagesSRM College of PhysiotherapyPONMATHI P FACULTY OF PHYSIOTHERAPYNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Eye Disease: DR Aleena ShahDocument33 pagesThyroid Eye Disease: DR Aleena ShahhamsNo ratings yet
- Derma ADDocument49 pagesDerma ADFatima Marwa Teo MaghinayNo ratings yet
- Local Anesthetics and Nerve Blocks HannanDocument57 pagesLocal Anesthetics and Nerve Blocks Hannanpriya_edwinNo ratings yet
- Local Anesthetics and Nerve Blocks HannanDocument57 pagesLocal Anesthetics and Nerve Blocks Hannanpriya_edwinNo ratings yet
- Kasus2Blefarokonjungtivitis BlokSSS Tingkat1Document146 pagesKasus2Blefarokonjungtivitis BlokSSS Tingkat1DhikaNo ratings yet
- Otiflox New Ear DropsDocument9 pagesOtiflox New Ear DropsShreyas ModiNo ratings yet
- Ear, Nose and ThroatDocument14 pagesEar, Nose and ThroatleonNo ratings yet
- 1 - Ocular TraumaDocument31 pages1 - Ocular TraumadeoshiNo ratings yet
- OTITIS EXTERNA Continuing Medical EducationDocument4 pagesOTITIS EXTERNA Continuing Medical EducationhanumzniiNo ratings yet
- Aa 1 MasterRQsDocument93 pagesAa 1 MasterRQsSadhana SabhandasaniNo ratings yet
- Crystal Violet: Material Safety Data SheetDocument10 pagesCrystal Violet: Material Safety Data SheetIolanda VeronicaNo ratings yet
- Dental Management of Patient With Leukemia PedoDocument26 pagesDental Management of Patient With Leukemia PedoFourthMolar.comNo ratings yet
- Dental Management of Patient With Leukemia PedoDocument26 pagesDental Management of Patient With Leukemia PedoFourthMolar.com100% (1)
- Pesticide and Herbicide Poisoning (Editedv2)Document58 pagesPesticide and Herbicide Poisoning (Editedv2)Alex MatthewNo ratings yet
- Principles of Periodontal SurgryDocument106 pagesPrinciples of Periodontal SurgrynusreenNo ratings yet
- كتاب علاج الامراض الجلدية والمعدية topical preparations OTC PDF-1Document150 pagesكتاب علاج الامراض الجلدية والمعدية topical preparations OTC PDF-1ريدان عياشNo ratings yet
- Administration of Local Anaesthetic in DentistryDocument5 pagesAdministration of Local Anaesthetic in DentistryridaNo ratings yet
- Cases in DermatologyDocument110 pagesCases in DermatologyGeorge WoodwardNo ratings yet
- Management of The Draining Ear: ObjectivesDocument6 pagesManagement of The Draining Ear: ObjectivesKazi Zihadul AlamNo ratings yet
- Slide Bells PalsyDocument74 pagesSlide Bells PalsyIrithca Jayanty TengkerNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Facial Palsy, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Facial Palsy, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- JP Journals 10021 1110Document4 pagesJP Journals 10021 1110Rakan KhtoomNo ratings yet
- Osu 1331067181Document67 pagesOsu 1331067181Rakan KhtoomNo ratings yet
- 14985-Article Text-29120-1-10-20210409Document6 pages14985-Article Text-29120-1-10-20210409Rakan KhtoomNo ratings yet
- Applsci 11 06439 v3Document17 pagesApplsci 11 06439 v3Rakan KhtoomNo ratings yet
- Your First VisitDocument2 pagesYour First VisitRakan KhtoomNo ratings yet
- Orthodontic Treatment: Patient Information LeafletDocument2 pagesOrthodontic Treatment: Patient Information LeafletRakan KhtoomNo ratings yet
- How To Keep Your Teeth and Gums HealthyDocument2 pagesHow To Keep Your Teeth and Gums HealthyRakan KhtoomNo ratings yet
- Impacted Canines: Patient Information LeafletDocument2 pagesImpacted Canines: Patient Information LeafletRakan KhtoomNo ratings yet
- Pedo Lab Case PresentationDocument4 pagesPedo Lab Case PresentationRakan KhtoomNo ratings yet
- Enamel GenesisDocument32 pagesEnamel GenesisRakan KhtoomNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of EyeDocument19 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Eyeashwini priyaNo ratings yet
- Complications of Sinus Surgery SariDocument38 pagesComplications of Sinus Surgery SariFebryantiPBundaayabariqNo ratings yet
- Ischemic Optic NeuropathyDocument10 pagesIschemic Optic NeuropathyScerbatiuc CristinaNo ratings yet
- Posterior Ischaemic Optic Neuropathy: Clinical Features, Pathogenesis, and ManagementDocument19 pagesPosterior Ischaemic Optic Neuropathy: Clinical Features, Pathogenesis, and ManagementFriedi Kristian CarlosNo ratings yet
- The OrbitDocument115 pagesThe OrbitPhilip McNelson100% (1)
- Aft Manual 2023 FinalDocument51 pagesAft Manual 2023 FinalMinh Phương Trần100% (1)
- Eyes and Stroke The Visual Aspects of Cerebrovascular DiseaseDocument11 pagesEyes and Stroke The Visual Aspects of Cerebrovascular DiseaseAlessandro ZadraNo ratings yet
- اسئلة تشريحDocument20 pagesاسئلة تشريحابراهيم فلاح حسنNo ratings yet
- Pituitary Gland Anatomy: Embryologic DevelopmentDocument9 pagesPituitary Gland Anatomy: Embryologic DevelopmentRafaelPetitNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka Paper Oftalmia Neonatorum (Sudah Digabung) PDFDocument153 pagesDaftar Pustaka Paper Oftalmia Neonatorum (Sudah Digabung) PDFDewi Sartika100% (1)
- Color Doppler Flow Imaging of Retrobulbar Ocular Blood Flow Changes in Retinal Artery Occlusions Caused by Cosmetic Facial Filler InjectionsDocument5 pagesColor Doppler Flow Imaging of Retrobulbar Ocular Blood Flow Changes in Retinal Artery Occlusions Caused by Cosmetic Facial Filler InjectionsKerlida SantosNo ratings yet
- G5 Nasal CavityDocument41 pagesG5 Nasal CavityGuo YageNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmonics 1st EditionDocument116 pagesOphthalmonics 1st Editiondhavalb2086% (7)
- Anatomi EyelidDocument9 pagesAnatomi EyelidFelyana GunawanNo ratings yet
- Glossary EyeDocument228 pagesGlossary EyeCarolus AugustusNo ratings yet
- Special Senses 1 - (1) - NDocument128 pagesSpecial Senses 1 - (1) - Naoujahmed123456789010No ratings yet
- 3.trigeminal NerveDocument81 pages3.trigeminal NerverajaniNo ratings yet
- ماكزلو3Document16 pagesماكزلو3haidergamer658No ratings yet
- Optic Nerve Applied Anatomy, Clinical Evaluation and ApproachesDocument80 pagesOptic Nerve Applied Anatomy, Clinical Evaluation and ApproachesKaramsi Gopinath NaikNo ratings yet
- Blood Suppy of BrainDocument54 pagesBlood Suppy of BrainZoya MoraniNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply of The Neck and HeadDocument56 pagesBlood Supply of The Neck and HeadAdrianaNo ratings yet
- Centralretinalarteryocclusion 150821150708 Lva1 App6891 PDFDocument50 pagesCentralretinalarteryocclusion 150821150708 Lva1 App6891 PDFDhivya SekarNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology (Final) PDFDocument15 pagesOphthalmology (Final) PDFadi100% (2)
- Update On Avoiding and Treating Blindness From Fillers - A Recent Review of The World LiteratureDocument36 pagesUpdate On Avoiding and Treating Blindness From Fillers - A Recent Review of The World LiteratureKerlida SantosNo ratings yet
- Trigemina Nerve Sem 2 WordDocument18 pagesTrigemina Nerve Sem 2 WordBharathi GudapatiNo ratings yet
- MCQ Opt Y5 RcafDocument4 pagesMCQ Opt Y5 RcafkoNo ratings yet
- Atlas of Human Anatomy - Including Student Consult Interactive Ancillaries and GuidesDocument11 pagesAtlas of Human Anatomy - Including Student Consult Interactive Ancillaries and GuidesAndrijana StevancevicNo ratings yet
- 6th HEAD & NECK ANATOMICAL LAB D.NASSR ALHUTBANY BLOOD SUPPLY OF HEAD & NECK 2024Document47 pages6th HEAD & NECK ANATOMICAL LAB D.NASSR ALHUTBANY BLOOD SUPPLY OF HEAD & NECK 2024Dr.NASSR AL-HUTBANYNo ratings yet
- Rongga ObitaDocument27 pagesRongga ObitaFadli LatamaNo ratings yet
Local Analgesia10.5.11
Local Analgesia10.5.11
Uploaded by
Rakan KhtoomOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Local Analgesia10.5.11
Local Analgesia10.5.11
Uploaded by
Rakan KhtoomCopyright:
Available Formats
LOCAL
ANALGESIA
Painful procedures are the most important
factor
behind fear and anxiety.
Fear : external threat, anxiety : Internal
threat.
Allergy from Bisulfate (metasulfat)
Two types:
1. Amide LA: Lidocaine, prilocaine, bupivicaine,
levobupivicaine .
- Heat stable, long shelf life, slower onset and long
duration.
- contra indication In malignant hyperpyrexia
2. Ester LA: procaine, cocaine.
benzocaine, tetracaine
- Unstable in solution, fast acting, allergic reaction
- contraindication in choline esterase inadequacy
TOPICAL ANASTHESIA
Types:
1. Lidocaine available as xylocaine in 10% spray
and 5% liquid, its onset 3-5 minutes.
2. Benzocaine available as hurricane gel and
solution 20%, has the lower toxicity than others.
30 sec. The best T.A.
3. Tetracaine not recommended in paediatric
dentistry. Which is 10 times toxic than procaine.
3/14 ML/KG
4.4MG/KG LIDOCAINE
6MG/KG PRILOCAINE
Formulation Max Cartridges
Adult (70) Child (25)
Lidocaine
2% with epinephrine
2%plain
13.9 4.6
8.3 2.8
Mepivacaine
2% with aeocobefrin
3% plain
11.1 3.7
7.4 2.5
Prilocaine
4% with epinephrine
4% plain
8.3 2.8
8.3 2.8
These four mistakes are the most common errors
made by dentists when attempting
to anaesthetize a child:
1. Waving the needle in front of the child.
2. Not getting firm control of the patient head and hands.
3. The use of long needle.
4. The use of inappropriate doses for children.
To avoid systemic reaction (Toxicity):
Slow injection ,aspiration before injection, knowledge of
the
maximum dosage and watchful observation of the patient.
ELECTRONIC DENTAL ANASTHESIA (EDA)
- The electronic signals interfere with the pain message by blocking the
transmission of pain impulse along the neural pathways. (Gate Control
Theory)
- EDA causes some nerve cells to produce local beta endorphins, a
naturally occurring Morphine-like action.
- EDA is known to stimulate the secretion of serotonin which increase the
patient pain threshold.
Advantage :
1. Non invasive, safe, well accepted
2. No risk of allergy, no numbness
Disadvantage:
1. Redness of skin
2. Involuntary twitching of lips, eyelid
Indication:
1. dentally phobic, allergic
2. cavity preparation anterior premolars
3. root scaling and planning
4. myofacial pain
Contraindication:
1. cardiac diseases, pacemakers
2. ocular implants
3. Pregnancy
4. over carotid
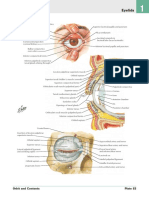
COMPLICATIONS OF AN INTRA-ARTERIAL
INJECTION OF MAXILLARY. AND IDA (ARTERY)
Blood supply to the head and face is via THE EXTERNAL CAROTID
ARTERY
Branches to form INTERNAL MAXILLARY ARTERY, Branches to:
1. Infra orbital artery: infra-orbital area (blanching) and greater palatine
(blanching)
2. Middle meningeal artery and forms branches that anastomose with
A. Ophthalmic artery (ipsilateral eye, eyelid ptosis, medial
strabismus and
amaurosis)
B. Lacrimal artery.
3. Inferior alveolar artery
Occlusal surface of the mandibular permanent first
molar mesiobuccal groove (*) and middle point of the
mesial slope of the distolingual cusp ().
The first wire passing from the mesiobuccal groove and
the middle point of the slope of the distolingual cusp of
the first mandibular molar.
You might also like
- Pharmacology Hesi Exam Study Guide 2015Document96 pagesPharmacology Hesi Exam Study Guide 2015sak genius100% (31)
- Test Bank For Advanced Practice Nursing in The Care of Older Adults 2nd by Kennedy Malone DownloadDocument10 pagesTest Bank For Advanced Practice Nursing in The Care of Older Adults 2nd by Kennedy Malone Downloadericgoodmanfaszgwponk100% (31)
- Hesi Exam Practice Pharmacology PDFDocument55 pagesHesi Exam Practice Pharmacology PDFAna Bienne100% (2)
- Treatment of VKC: 1. Nonpharmacologic Treatment 2. Pharmacologic Treatment 3. Surgery TreatmentDocument18 pagesTreatment of VKC: 1. Nonpharmacologic Treatment 2. Pharmacologic Treatment 3. Surgery TreatmentAllen SallyNo ratings yet
- Drug Allergy BookDocument332 pagesDrug Allergy Bookmegah_asia13No ratings yet
- Duke Anatomy - Lab 20 - Eye & EarDocument19 pagesDuke Anatomy - Lab 20 - Eye & EarabidalibpNo ratings yet
- Common Bacterial and Viral Infection Key Answer FinalDocument10 pagesCommon Bacterial and Viral Infection Key Answer FinalAnu KrupaNo ratings yet
- Local Anaesthesia 07 03 22 CompressedDocument87 pagesLocal Anaesthesia 07 03 22 CompressedkomanaNo ratings yet
- Tinea Versicolor of The Neck As Side Effect of Topical Steroids For Alopecia AreataDocument12 pagesTinea Versicolor of The Neck As Side Effect of Topical Steroids For Alopecia AreataNazihan Safitri AlkatiriNo ratings yet
- Naplex Sample Quiz 3 Review of Attempt 1Document5 pagesNaplex Sample Quiz 3 Review of Attempt 1Ashish PatelNo ratings yet
- TOBRINDocument2 pagesTOBRINmahgadNo ratings yet
- Drugs in Ear DisordersDocument2 pagesDrugs in Ear DisorderstatiNo ratings yet
- Tetanos ClasesDocument6 pagesTetanos Clasesjessica rieraNo ratings yet
- Role of Azole Antifungal Agents in Seborrheic Dermatitis & Dandruff: A ReviewDocument20 pagesRole of Azole Antifungal Agents in Seborrheic Dermatitis & Dandruff: A ReviewHajrah MirandaNo ratings yet
- Administration of Local Anaesthetic in DentistryDocument6 pagesAdministration of Local Anaesthetic in DentistryridaNo ratings yet
- Efficonazole 10% Solution in The Treatment of Toenail OnychomycosisDocument9 pagesEfficonazole 10% Solution in The Treatment of Toenail OnychomycosisNadia Vinka LisdiantiNo ratings yet
- DR Meera Kuppusamy MBBS (IMU), MRCP (UK), Adv Derm Masters (UKM) Consultant Dermatologist Columbia Asia KlangDocument86 pagesDR Meera Kuppusamy MBBS (IMU), MRCP (UK), Adv Derm Masters (UKM) Consultant Dermatologist Columbia Asia KlangdnaielNo ratings yet
- Local AnesthesiaDocument63 pagesLocal AnesthesiaReda IsmaeelNo ratings yet
- Child Measles Eye Eng 300Document52 pagesChild Measles Eye Eng 300DadaNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Eye Medication AdministrationDocument3 pagesInternational Journal of Eye Medication AdministrationMutia Ramadini91No ratings yet
- Gingival Herbal Depigmentation: A Natural Solution??Document9 pagesGingival Herbal Depigmentation: A Natural Solution??IJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Important Topics in OtologyDocument94 pagesImportant Topics in OtologyDr. T. Balasubramanian100% (1)
- Local Anesthesia in Pediatric DentistryDocument51 pagesLocal Anesthesia in Pediatric Dentistryakshi1947100% (3)
- Handbook of Splinting and CastingDocument318 pagesHandbook of Splinting and Castingguillermina paz100% (1)
- KMB III Kel 1 KonjungtivitisDocument19 pagesKMB III Kel 1 Konjungtivitisrkpngnz4xwNo ratings yet
- Local Anesthesia in Pediatric DentistryDocument70 pagesLocal Anesthesia in Pediatric DentistryNicky Romeo100% (1)
- Apexa No 7Document4 pagesApexa No 7Apexa YadavNo ratings yet
- Guideline On Use of Local Anesthesia For Pediatric Dental PatientsDocument7 pagesGuideline On Use of Local Anesthesia For Pediatric Dental PatientsLisna K. RezkyNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of Efficacy of Oral Terbinafine Alone and Oral Terbinafine With Topical 8% Ciclopirox Olamine in OnychomycosisDocument7 pagesComparative Study of Efficacy of Oral Terbinafine Alone and Oral Terbinafine With Topical 8% Ciclopirox Olamine in OnychomycosisIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- 2018 Neurosensory Pharmacology Ns2Document66 pages2018 Neurosensory Pharmacology Ns2Firsania BungaNo ratings yet
- Suppurative KeratitisDocument30 pagesSuppurative KeratitisTatik Handayani100% (1)
- Ménière Disease (Clinical) - LecturioDocument15 pagesMénière Disease (Clinical) - Lecturioari06roamoranNo ratings yet
- 3.TPD 45 149Document4 pages3.TPD 45 149YuyumNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Exdontia - BDS YR 4Document75 pagesPediatric Exdontia - BDS YR 4Elamaaraeen MadhvanNo ratings yet
- Symposium Toxic Optic Neuropathy: Pradeep Sharma, Reena SharmaDocument5 pagesSymposium Toxic Optic Neuropathy: Pradeep Sharma, Reena SharmaCony NurbayyiniNo ratings yet
- Neural Tube Defects: Group 1Document28 pagesNeural Tube Defects: Group 1imneverwrong2492100% (1)
- 18 Paediatric Regional Block GuidelinesDocument10 pages18 Paediatric Regional Block GuidelinesParvathy R NairNo ratings yet
- SRM College of PhysiotherapyDocument24 pagesSRM College of PhysiotherapyPONMATHI P FACULTY OF PHYSIOTHERAPYNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Eye Disease: DR Aleena ShahDocument33 pagesThyroid Eye Disease: DR Aleena ShahhamsNo ratings yet
- Derma ADDocument49 pagesDerma ADFatima Marwa Teo MaghinayNo ratings yet
- Local Anesthetics and Nerve Blocks HannanDocument57 pagesLocal Anesthetics and Nerve Blocks Hannanpriya_edwinNo ratings yet
- Local Anesthetics and Nerve Blocks HannanDocument57 pagesLocal Anesthetics and Nerve Blocks Hannanpriya_edwinNo ratings yet
- Kasus2Blefarokonjungtivitis BlokSSS Tingkat1Document146 pagesKasus2Blefarokonjungtivitis BlokSSS Tingkat1DhikaNo ratings yet
- Otiflox New Ear DropsDocument9 pagesOtiflox New Ear DropsShreyas ModiNo ratings yet
- Ear, Nose and ThroatDocument14 pagesEar, Nose and ThroatleonNo ratings yet
- 1 - Ocular TraumaDocument31 pages1 - Ocular TraumadeoshiNo ratings yet
- OTITIS EXTERNA Continuing Medical EducationDocument4 pagesOTITIS EXTERNA Continuing Medical EducationhanumzniiNo ratings yet
- Aa 1 MasterRQsDocument93 pagesAa 1 MasterRQsSadhana SabhandasaniNo ratings yet
- Crystal Violet: Material Safety Data SheetDocument10 pagesCrystal Violet: Material Safety Data SheetIolanda VeronicaNo ratings yet
- Dental Management of Patient With Leukemia PedoDocument26 pagesDental Management of Patient With Leukemia PedoFourthMolar.comNo ratings yet
- Dental Management of Patient With Leukemia PedoDocument26 pagesDental Management of Patient With Leukemia PedoFourthMolar.com100% (1)
- Pesticide and Herbicide Poisoning (Editedv2)Document58 pagesPesticide and Herbicide Poisoning (Editedv2)Alex MatthewNo ratings yet
- Principles of Periodontal SurgryDocument106 pagesPrinciples of Periodontal SurgrynusreenNo ratings yet
- كتاب علاج الامراض الجلدية والمعدية topical preparations OTC PDF-1Document150 pagesكتاب علاج الامراض الجلدية والمعدية topical preparations OTC PDF-1ريدان عياشNo ratings yet
- Administration of Local Anaesthetic in DentistryDocument5 pagesAdministration of Local Anaesthetic in DentistryridaNo ratings yet
- Cases in DermatologyDocument110 pagesCases in DermatologyGeorge WoodwardNo ratings yet
- Management of The Draining Ear: ObjectivesDocument6 pagesManagement of The Draining Ear: ObjectivesKazi Zihadul AlamNo ratings yet
- Slide Bells PalsyDocument74 pagesSlide Bells PalsyIrithca Jayanty TengkerNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Facial Palsy, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Facial Palsy, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- JP Journals 10021 1110Document4 pagesJP Journals 10021 1110Rakan KhtoomNo ratings yet
- Osu 1331067181Document67 pagesOsu 1331067181Rakan KhtoomNo ratings yet
- 14985-Article Text-29120-1-10-20210409Document6 pages14985-Article Text-29120-1-10-20210409Rakan KhtoomNo ratings yet
- Applsci 11 06439 v3Document17 pagesApplsci 11 06439 v3Rakan KhtoomNo ratings yet
- Your First VisitDocument2 pagesYour First VisitRakan KhtoomNo ratings yet
- Orthodontic Treatment: Patient Information LeafletDocument2 pagesOrthodontic Treatment: Patient Information LeafletRakan KhtoomNo ratings yet
- How To Keep Your Teeth and Gums HealthyDocument2 pagesHow To Keep Your Teeth and Gums HealthyRakan KhtoomNo ratings yet
- Impacted Canines: Patient Information LeafletDocument2 pagesImpacted Canines: Patient Information LeafletRakan KhtoomNo ratings yet
- Pedo Lab Case PresentationDocument4 pagesPedo Lab Case PresentationRakan KhtoomNo ratings yet
- Enamel GenesisDocument32 pagesEnamel GenesisRakan KhtoomNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of EyeDocument19 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Eyeashwini priyaNo ratings yet
- Complications of Sinus Surgery SariDocument38 pagesComplications of Sinus Surgery SariFebryantiPBundaayabariqNo ratings yet
- Ischemic Optic NeuropathyDocument10 pagesIschemic Optic NeuropathyScerbatiuc CristinaNo ratings yet
- Posterior Ischaemic Optic Neuropathy: Clinical Features, Pathogenesis, and ManagementDocument19 pagesPosterior Ischaemic Optic Neuropathy: Clinical Features, Pathogenesis, and ManagementFriedi Kristian CarlosNo ratings yet
- The OrbitDocument115 pagesThe OrbitPhilip McNelson100% (1)
- Aft Manual 2023 FinalDocument51 pagesAft Manual 2023 FinalMinh Phương Trần100% (1)
- Eyes and Stroke The Visual Aspects of Cerebrovascular DiseaseDocument11 pagesEyes and Stroke The Visual Aspects of Cerebrovascular DiseaseAlessandro ZadraNo ratings yet
- اسئلة تشريحDocument20 pagesاسئلة تشريحابراهيم فلاح حسنNo ratings yet
- Pituitary Gland Anatomy: Embryologic DevelopmentDocument9 pagesPituitary Gland Anatomy: Embryologic DevelopmentRafaelPetitNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka Paper Oftalmia Neonatorum (Sudah Digabung) PDFDocument153 pagesDaftar Pustaka Paper Oftalmia Neonatorum (Sudah Digabung) PDFDewi Sartika100% (1)
- Color Doppler Flow Imaging of Retrobulbar Ocular Blood Flow Changes in Retinal Artery Occlusions Caused by Cosmetic Facial Filler InjectionsDocument5 pagesColor Doppler Flow Imaging of Retrobulbar Ocular Blood Flow Changes in Retinal Artery Occlusions Caused by Cosmetic Facial Filler InjectionsKerlida SantosNo ratings yet
- G5 Nasal CavityDocument41 pagesG5 Nasal CavityGuo YageNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmonics 1st EditionDocument116 pagesOphthalmonics 1st Editiondhavalb2086% (7)
- Anatomi EyelidDocument9 pagesAnatomi EyelidFelyana GunawanNo ratings yet
- Glossary EyeDocument228 pagesGlossary EyeCarolus AugustusNo ratings yet
- Special Senses 1 - (1) - NDocument128 pagesSpecial Senses 1 - (1) - Naoujahmed123456789010No ratings yet
- 3.trigeminal NerveDocument81 pages3.trigeminal NerverajaniNo ratings yet
- ماكزلو3Document16 pagesماكزلو3haidergamer658No ratings yet
- Optic Nerve Applied Anatomy, Clinical Evaluation and ApproachesDocument80 pagesOptic Nerve Applied Anatomy, Clinical Evaluation and ApproachesKaramsi Gopinath NaikNo ratings yet
- Blood Suppy of BrainDocument54 pagesBlood Suppy of BrainZoya MoraniNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply of The Neck and HeadDocument56 pagesBlood Supply of The Neck and HeadAdrianaNo ratings yet
- Centralretinalarteryocclusion 150821150708 Lva1 App6891 PDFDocument50 pagesCentralretinalarteryocclusion 150821150708 Lva1 App6891 PDFDhivya SekarNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology (Final) PDFDocument15 pagesOphthalmology (Final) PDFadi100% (2)
- Update On Avoiding and Treating Blindness From Fillers - A Recent Review of The World LiteratureDocument36 pagesUpdate On Avoiding and Treating Blindness From Fillers - A Recent Review of The World LiteratureKerlida SantosNo ratings yet
- Trigemina Nerve Sem 2 WordDocument18 pagesTrigemina Nerve Sem 2 WordBharathi GudapatiNo ratings yet
- MCQ Opt Y5 RcafDocument4 pagesMCQ Opt Y5 RcafkoNo ratings yet
- Atlas of Human Anatomy - Including Student Consult Interactive Ancillaries and GuidesDocument11 pagesAtlas of Human Anatomy - Including Student Consult Interactive Ancillaries and GuidesAndrijana StevancevicNo ratings yet
- 6th HEAD & NECK ANATOMICAL LAB D.NASSR ALHUTBANY BLOOD SUPPLY OF HEAD & NECK 2024Document47 pages6th HEAD & NECK ANATOMICAL LAB D.NASSR ALHUTBANY BLOOD SUPPLY OF HEAD & NECK 2024Dr.NASSR AL-HUTBANYNo ratings yet
- Rongga ObitaDocument27 pagesRongga ObitaFadli LatamaNo ratings yet