Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
150 viewsRate of Reaction Part 1
Rate of Reaction Part 1
Uploaded by
danielphilip68The document discusses measuring the rate of chemical reactions. It provides examples of fast reactions, such as magnesium reacting with acid, and slow reactions like rusting. The rate of a reaction is defined as the amount of product formed or reactants used up over time. Common ways to measure reaction rate include tracking the decrease in reactants or increase in products over time by measuring volume, mass, or light intensity changes. Graphing experimental data allows calculating reaction rate from the slope. Factors that affect reaction rate and analyzing rate data are also discussed.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- 2019 Caspian-ProfileDocument22 pages2019 Caspian-ProfileCVDian Utama100% (1)
- Experiment 4: Effect of Concentration and Temperature On Rate of Reaction (Dissappearing Cross)Document24 pagesExperiment 4: Effect of Concentration and Temperature On Rate of Reaction (Dissappearing Cross)Malini RajeshNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Titration Practice QuestionsDocument3 pagesIGCSE Titration Practice Questionsdanielphilip68No ratings yet
- Rates and Energetics Mastery BookletDocument20 pagesRates and Energetics Mastery Bookletapi-422428700No ratings yet
- The Rate of Reaction Between Sodium Thiosulphate and Hydrochloric AcidDocument12 pagesThe Rate of Reaction Between Sodium Thiosulphate and Hydrochloric AcidMiriam Barker75% (4)
- Chem Rates of Reaction Lab2Document4 pagesChem Rates of Reaction Lab2JaydaHunte100% (1)
- A-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (10)
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisFrom EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Rate of ReactionDocument20 pagesRate of ReactionQueen BlehNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Rate of ReactionDocument71 pages1.1 Rate of ReactionyiosahhNo ratings yet
- CUP IBChemistry c06 It Rates of ReactionsDocument33 pagesCUP IBChemistry c06 It Rates of ReactionsAdnan ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Measuring The Rate of A Chemical ReactionDocument18 pagesMeasuring The Rate of A Chemical ReactionBexNo ratings yet
- Rate of ReactionDocument5 pagesRate of ReactionlettyNo ratings yet
- Rate of ReactionDocument22 pagesRate of ReactionlettyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Reaction KineticsDocument33 pagesChapter 1 Reaction KineticsryankyleacostaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kine Tics SL: Cicy IrnaDocument24 pagesChemical Kine Tics SL: Cicy Irnalilya roudaniNo ratings yet
- Rate of ReactionDocument27 pagesRate of ReactionShofwa AnnisaaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Chemical ReactionsDocument15 pagesChapter 8 Chemical ReactionsAmmar RizwanNo ratings yet
- Rate of ReactionDocument18 pagesRate of ReactionschlemielzNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction Rate of ReactionDocument12 pagesChemical Reaction Rate of ReactionDon Amaru SarmaNo ratings yet
- Rates of ReactionDocument31 pagesRates of Reactionspamzz063No ratings yet
- Unit 5 Chemical KineticsDocument37 pagesUnit 5 Chemical KineticsSanjay SharmaNo ratings yet
- Rates of ReactionDocument64 pagesRates of Reactionhingleena100% (1)
- Rate of Reaction Controlled AssessmentDocument14 pagesRate of Reaction Controlled AssessmentTheMagicCarpetNo ratings yet
- Rate NotesDocument16 pagesRate NotesMegan GohNo ratings yet
- CHM 207 Kinetics Lecture 1Document14 pagesCHM 207 Kinetics Lecture 1Oluwatosin OsisanyaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry AO3 G10-2 Sungbeen HongDocument14 pagesIGCSE Chemistry AO3 G10-2 Sungbeen HongSungbeen HongNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Rate of Reaction (1.2c)Document75 pages1.3 Rate of Reaction (1.2c)Sha Tasha Natasha0% (1)
- UJIAN PRA 7 TG. 5premierDocument13 pagesUJIAN PRA 7 TG. 5premierNik ZharifNo ratings yet
- Reaction Kinetics: Continuous Vs Initial Rate DataDocument16 pagesReaction Kinetics: Continuous Vs Initial Rate DatashowhardoNo ratings yet
- Rate Evening 2Document18 pagesRate Evening 2Tom TommmaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry - Rates and EquilibriumDocument22 pagesIGCSE Chemistry - Rates and EquilibriumChemistryKlipz100% (7)
- 6.1 3 Measuring Rates of ReactionDocument18 pages6.1 3 Measuring Rates of ReactionSho baconNo ratings yet
- Chem GauravDocument11 pagesChem GauravKaran YadavNo ratings yet
- Determination of Rate EquationDocument9 pagesDetermination of Rate EquationIsabella ThomasNo ratings yet
- Rate of ReactionDocument12 pagesRate of Reactionj5nfng2zzxNo ratings yet
- Kadar Tindak Balas.K1Document9 pagesKadar Tindak Balas.K1Narah NasNo ratings yet
- Rates of Reaction: by Syed Arham AhsanDocument12 pagesRates of Reaction: by Syed Arham AhsanAryan HossainNo ratings yet
- Rates of ReactionDocument7 pagesRates of Reactionapi-25909541No ratings yet
- Rate of Chemical ReactionsDocument11 pagesRate of Chemical ReactionsWalu BNNo ratings yet
- Rates of ReactionsDocument71 pagesRates of ReactionsMel ManningNo ratings yet
- Module Form 5 .Rate of ReactionDocument8 pagesModule Form 5 .Rate of ReactionChew Gee Lan100% (1)
- RatesDocument22 pagesRatesPeterNo ratings yet
- Modul Kimia SPM A+ 2014Document20 pagesModul Kimia SPM A+ 2014Cikgu Faizal100% (6)
- Mole Ratios and Reaction StoichiometryDocument4 pagesMole Ratios and Reaction StoichiometryAishaNo ratings yet
- IA - Metals and AcidsDocument3 pagesIA - Metals and Acids14nganhc1No ratings yet
- Lajur FixDocument18 pagesLajur FixMoniqsa Purbo SyahraniNo ratings yet
- Kinetics: 6.1 Rates of ReactionDocument20 pagesKinetics: 6.1 Rates of ReactionSeung Hee KimNo ratings yet
- Topik 10 Rate of ReactionDocument33 pagesTopik 10 Rate of ReactionJaaizah JaafarNo ratings yet
- Rate of Reaction Between Calcium Carbonate and Hydrochloric AcidDocument6 pagesRate of Reaction Between Calcium Carbonate and Hydrochloric AcidSimon WayneNo ratings yet
- Ujian Diagnostik Kimia t5Document6 pagesUjian Diagnostik Kimia t5haniimanNo ratings yet
- ChI06 Rates of Reaction TMA B 0817Document21 pagesChI06 Rates of Reaction TMA B 0817Husnul YaqinNo ratings yet
- KineticsDocument91 pagesKineticsbabithakslgNo ratings yet
- 6 Chemical ReactionsDocument19 pages6 Chemical ReactionsAhmed AyazNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics RevisedDocument56 pagesChemical Kinetics RevisedCacey Daiwey CalixtoNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 - Chemical KineticsDocument22 pagesTopic 6 - Chemical KineticsLucia PesentiNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science: Chemistry 7.1 - Rates of ReactionDocument4 pagesIGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science: Chemistry 7.1 - Rates of Reactionda_reaper_dasNo ratings yet
- Chem Form 5Document37 pagesChem Form 5Ashwin Boy Ash100% (1)
- Kinetics Lecture Notes Part 1Document31 pagesKinetics Lecture Notes Part 1NedNo ratings yet
- Sterling Test Prep College Physics Practice Questions: Vol. 1, High Yield College Physics Questions with Detailed ExplanationsFrom EverandSterling Test Prep College Physics Practice Questions: Vol. 1, High Yield College Physics Questions with Detailed ExplanationsNo ratings yet
- GCSE Exam QuestionsDocument155 pagesGCSE Exam Questionsdanielphilip68No ratings yet
- Making Molar Solutions: From LiquidsDocument11 pagesMaking Molar Solutions: From Liquidsdanielphilip68No ratings yet
- Igcse Structure Question 13Document2 pagesIgcse Structure Question 13danielphilip68No ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Igcse Chemistry Carbon CycleDocument35 pagesLesson 2 Igcse Chemistry Carbon Cycledanielphilip68No ratings yet
- Igcse Topic 1 Lesson 1 Water Cycle IgcseDocument25 pagesIgcse Topic 1 Lesson 1 Water Cycle Igcsedanielphilip68100% (1)
- Rates & Energy NotesDocument11 pagesRates & Energy Notesdanielphilip68No ratings yet
- Redox ReactionsDocument8 pagesRedox Reactionsdanielphilip68No ratings yet
- 1.3 TestDocument24 pages1.3 Testdanielphilip68No ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibria AS Level ChemistryDocument4 pagesChemical Equilibria AS Level Chemistrydanielphilip68No ratings yet
- Igcse Structure Question 12Document3 pagesIgcse Structure Question 12danielphilip68No ratings yet
- Igcse Structure Question 9Document2 pagesIgcse Structure Question 9danielphilip68No ratings yet
- Igcse Structure Question 10Document2 pagesIgcse Structure Question 10danielphilip68No ratings yet
- Igcse Structure Question 8Document2 pagesIgcse Structure Question 8danielphilip68No ratings yet
- Igcse Structure Question 11Document2 pagesIgcse Structure Question 11danielphilip680% (1)
- Igcse Structure Question 7Document2 pagesIgcse Structure Question 7danielphilip68No ratings yet
- Igcse Structure Question 4: (A) Complete The Following TableDocument2 pagesIgcse Structure Question 4: (A) Complete The Following Tabledanielphilip68No ratings yet
- Igcse Structure Question 5Document2 pagesIgcse Structure Question 5danielphilip68No ratings yet
- Good IGCSE Chemistry CIE Paper 6 Set 1Document15 pagesGood IGCSE Chemistry CIE Paper 6 Set 1danielphilip680% (1)
- Igcse Structure Question 3Document2 pagesIgcse Structure Question 3danielphilip68No ratings yet
- Good Igcse Cie Question 4Document4 pagesGood Igcse Cie Question 4danielphilip68No ratings yet
- Alternative To Practical Questions IGCSEset 1Document15 pagesAlternative To Practical Questions IGCSEset 1danielphilip68100% (1)
- Alternative To Practical Questions IGCSEset 1Document15 pagesAlternative To Practical Questions IGCSEset 1danielphilip68100% (1)
- Aquafina Purification DiagramDocument1 pageAquafina Purification DiagramAyesha ArjamandNo ratings yet
- Respuestas Termoquimica ChangDocument8 pagesRespuestas Termoquimica ChangIsabelNo ratings yet
- Rate Law Worksheet AnswersDocument6 pagesRate Law Worksheet AnswersANGELYN SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Distillation Tutorial in HYSYSDocument7 pagesDistillation Tutorial in HYSYScmlim100% (2)
- Rates of Reaction 2 MSDocument3 pagesRates of Reaction 2 MSNana Barnett QuaicooNo ratings yet
- Exercise Dehydration EngDocument4 pagesExercise Dehydration EngShahram MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Paper Id249 Powergen2012Document21 pagesPaper Id249 Powergen2012arunNo ratings yet
- Basics of Catalysts - Chemistry LibreTextsDocument6 pagesBasics of Catalysts - Chemistry LibreTextsStatus loverNo ratings yet
- Midstream (Petroleum IndustrY)Document2 pagesMidstream (Petroleum IndustrY)Espartaco SmithNo ratings yet
- ANSI-ASME B31 Scope and Exclusions-Chemical Plant and Petroleum Refinery Piping (Documento Word)Document3 pagesANSI-ASME B31 Scope and Exclusions-Chemical Plant and Petroleum Refinery Piping (Documento Word)FRANCISCO RICARDONo ratings yet
- Quadax - Přehled EN NEWDocument16 pagesQuadax - Přehled EN NEWRamazan YaşarNo ratings yet
- 103-Effect of Hydrocarbon Partial Pressure On Propylene Production in The FCCDocument10 pages103-Effect of Hydrocarbon Partial Pressure On Propylene Production in The FCCdonald55555No ratings yet
- Batch 10 TimetableDocument1 pageBatch 10 TimetableMarcoNo ratings yet
- Equipment Included in A CO2 PlantDocument3 pagesEquipment Included in A CO2 Plantgama tokNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice QuestionDocument30 pagesMultiple Choice QuestionJayabrata DasNo ratings yet
- Upgrade of Sulfur Recovery Unit at Ras TanuraDocument8 pagesUpgrade of Sulfur Recovery Unit at Ras Tanurasalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Drizo Gas DehydrationDocument2 pagesDrizo Gas DehydrationAnonymous bHh1L1No ratings yet
- Ucalgary 2020 Du StevenDocument65 pagesUcalgary 2020 Du StevenmnasiroleslamiNo ratings yet
- Disadvantages of HardwaterDocument17 pagesDisadvantages of Hardwaterchemistrymaster96% (24)
- CH 6 Notebook Work Combustion and FlameDocument3 pagesCH 6 Notebook Work Combustion and FlameSamarth SharmaNo ratings yet
- ChemEngineering 05 00020Document24 pagesChemEngineering 05 00020chaniefNo ratings yet
- Alkanes: H H C H HDocument6 pagesAlkanes: H H C H HAmirah AmanNo ratings yet
- Customer Name Item NameDocument130 pagesCustomer Name Item Namevelugu john sundar rajuNo ratings yet
- Commissioning SequenceDocument17 pagesCommissioning Sequencebikas_sahaNo ratings yet
- Chemsheets A2 1157 QC KP B ANS NbsyeDocument1 pageChemsheets A2 1157 QC KP B ANS NbsyeMarinaNo ratings yet
- 2.01 Surface Kinetics - Unimolecular Reactions PDFDocument33 pages2.01 Surface Kinetics - Unimolecular Reactions PDFMelchiNo ratings yet
- 7 LischkeDocument81 pages7 LischkeKarthick VelayuthamNo ratings yet
- Design of Lab-Scale Downdraft Gasifier For Biomass GasificationDocument9 pagesDesign of Lab-Scale Downdraft Gasifier For Biomass GasificationMuhammad Shahzad KhurramNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Caustic CorrosionDocument10 pagesPresentation On Caustic CorrosionMuhammad BilalNo ratings yet
Rate of Reaction Part 1
Rate of Reaction Part 1
Uploaded by
danielphilip680 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
150 views19 pagesThe document discusses measuring the rate of chemical reactions. It provides examples of fast reactions, such as magnesium reacting with acid, and slow reactions like rusting. The rate of a reaction is defined as the amount of product formed or reactants used up over time. Common ways to measure reaction rate include tracking the decrease in reactants or increase in products over time by measuring volume, mass, or light intensity changes. Graphing experimental data allows calculating reaction rate from the slope. Factors that affect reaction rate and analyzing rate data are also discussed.
Original Description:
rate of reaction
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses measuring the rate of chemical reactions. It provides examples of fast reactions, such as magnesium reacting with acid, and slow reactions like rusting. The rate of a reaction is defined as the amount of product formed or reactants used up over time. Common ways to measure reaction rate include tracking the decrease in reactants or increase in products over time by measuring volume, mass, or light intensity changes. Graphing experimental data allows calculating reaction rate from the slope. Factors that affect reaction rate and analyzing rate data are also discussed.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
150 views19 pagesRate of Reaction Part 1
Rate of Reaction Part 1
Uploaded by
danielphilip68The document discusses measuring the rate of chemical reactions. It provides examples of fast reactions, such as magnesium reacting with acid, and slow reactions like rusting. The rate of a reaction is defined as the amount of product formed or reactants used up over time. Common ways to measure reaction rate include tracking the decrease in reactants or increase in products over time by measuring volume, mass, or light intensity changes. Graphing experimental data allows calculating reaction rate from the slope. Factors that affect reaction rate and analyzing rate data are also discussed.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 19
Fast or Slow
Put the following into order, fastest to
slowest:
Magnesium reaction with acid
Neutralisation
Firework
Cooking an egg
Sodium reacting with water
Rusting
Rates of Reaction
How can we find out the rate of a reaction?
WAL:
C
B
A
Identify factors that affect the rate of reaction
Describe how the rate of a reaction can be
measured
Analyse data on the rate of a
reaction
Fast or Slow
Put the following into order, fastest to
slowest:
Magnesium reaction with acid
Neutralisation
Firework
Cooking an egg
Sodium reacting with water
Rusting
Fast or Slow
Put the following into order, fastest to
slowest:
Rusting
Cooking an egg
Neutralisation
Firework
Magnesium reaction with acid
Sodium reacting with water
What do we mean by rate?
The rate of a reaction is the time
taken for a product to form, or
reactants to be used up
Q. What do you understand
by the term rate of reaction?
Rate = amount of product produced (reactants used up) / time taken
REVIEW
Measuring the rate at which
_______ are used up or ______ are
made are two ways of measuring the
______ of a chemical reaction. An
example of a reaction that happens
quickly is a ___________ . A
reaction that happens slowly is
__________ .
REVIEW
+
magnesium
hydrochloric
acid
+
magnesium
chloride
hydrogen
Q. How could you measure the rate of the
reaction? Include the units you would use?
The amount of hydrochloric acid used up
(cm
3
/min).
The amount of magnesium chloride produced
(g/min).
The amount of hydrogen product (cm
3
/min).
Measuring Rate
How could you measure the rate of
these reactions? Use your definition to
help you.
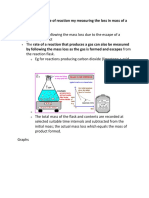
Measuring the decreasing mass of
a reaction
We can measure the
rate at which the
mass of a reaction
mixture changes if
the reaction gives off
a gas.
Measuring the increasing volume of
gas produced
If the reaction
produces a gas we
can measure the
volume of gas and
use that information
to find out the rate of
reaction.
Measuring the decreasing light
passing through a solution
Some reactions
produce an insoluble
precipitate. This
makes the solution
go cloudy and we can
therefore measure
the rate at which the
solid appears.
h
y
d
r
o
g
e
n
p
r
o
d
u
c
e
d
(
c
m
3
)
time (seconds)
10 20 30 40 50
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
0
0
Calculating rate of reaction from
graphs
Total volume is 65cm
3
Total time is 38seconds
What is the total volume produced?
What is the time for the reaction to complete?
Measuring the decreasing light
passing through a solution
Some reactions
produce an insoluble
precipitate. This
makes the solution
go cloudy and we can
therefore measure
the rate at which the
solid appears.
Measuring the decreasing mass of
a reaction
We can measure the
rate at which the
mass of a reaction
mixture changes if
the reaction gives off
a gas.
h
y
d
r
o
g
e
n
p
r
o
d
u
c
e
d
(
c
m
3
)
time (seconds)
10 20 30 40 50
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
0
0
x
y
Calculating rate of reaction from
graphs
rate of reaction =
x
y
rate of reaction =
20 s
45 cm
3
=
2.25 cm
3
/s
The gradient of the graph is equal to the initial
rate of reaction at that time
Graphs tell a story.
Sketch these two graphs and write a sentence to
explain what the graph shows you. ( Hint: 2 marker
styles question)
Question:
Rate = amount of product produce / times takes
= 5 / 25
Rates of Reaction
How can we fond out the rate of a reaction?
WAL:
C
B
A
Identify factors that affect the rate of reaction
Describe how the rate of a reaction can be
measured
Analyse data on the rate of a
reaction
You might also like
- 2019 Caspian-ProfileDocument22 pages2019 Caspian-ProfileCVDian Utama100% (1)
- Experiment 4: Effect of Concentration and Temperature On Rate of Reaction (Dissappearing Cross)Document24 pagesExperiment 4: Effect of Concentration and Temperature On Rate of Reaction (Dissappearing Cross)Malini RajeshNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Titration Practice QuestionsDocument3 pagesIGCSE Titration Practice Questionsdanielphilip68No ratings yet
- Rates and Energetics Mastery BookletDocument20 pagesRates and Energetics Mastery Bookletapi-422428700No ratings yet
- The Rate of Reaction Between Sodium Thiosulphate and Hydrochloric AcidDocument12 pagesThe Rate of Reaction Between Sodium Thiosulphate and Hydrochloric AcidMiriam Barker75% (4)
- Chem Rates of Reaction Lab2Document4 pagesChem Rates of Reaction Lab2JaydaHunte100% (1)
- A-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (10)
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisFrom EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Rate of ReactionDocument20 pagesRate of ReactionQueen BlehNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Rate of ReactionDocument71 pages1.1 Rate of ReactionyiosahhNo ratings yet
- CUP IBChemistry c06 It Rates of ReactionsDocument33 pagesCUP IBChemistry c06 It Rates of ReactionsAdnan ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Measuring The Rate of A Chemical ReactionDocument18 pagesMeasuring The Rate of A Chemical ReactionBexNo ratings yet
- Rate of ReactionDocument5 pagesRate of ReactionlettyNo ratings yet
- Rate of ReactionDocument22 pagesRate of ReactionlettyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Reaction KineticsDocument33 pagesChapter 1 Reaction KineticsryankyleacostaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kine Tics SL: Cicy IrnaDocument24 pagesChemical Kine Tics SL: Cicy Irnalilya roudaniNo ratings yet
- Rate of ReactionDocument27 pagesRate of ReactionShofwa AnnisaaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Chemical ReactionsDocument15 pagesChapter 8 Chemical ReactionsAmmar RizwanNo ratings yet
- Rate of ReactionDocument18 pagesRate of ReactionschlemielzNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction Rate of ReactionDocument12 pagesChemical Reaction Rate of ReactionDon Amaru SarmaNo ratings yet
- Rates of ReactionDocument31 pagesRates of Reactionspamzz063No ratings yet
- Unit 5 Chemical KineticsDocument37 pagesUnit 5 Chemical KineticsSanjay SharmaNo ratings yet
- Rates of ReactionDocument64 pagesRates of Reactionhingleena100% (1)
- Rate of Reaction Controlled AssessmentDocument14 pagesRate of Reaction Controlled AssessmentTheMagicCarpetNo ratings yet
- Rate NotesDocument16 pagesRate NotesMegan GohNo ratings yet
- CHM 207 Kinetics Lecture 1Document14 pagesCHM 207 Kinetics Lecture 1Oluwatosin OsisanyaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry AO3 G10-2 Sungbeen HongDocument14 pagesIGCSE Chemistry AO3 G10-2 Sungbeen HongSungbeen HongNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Rate of Reaction (1.2c)Document75 pages1.3 Rate of Reaction (1.2c)Sha Tasha Natasha0% (1)
- UJIAN PRA 7 TG. 5premierDocument13 pagesUJIAN PRA 7 TG. 5premierNik ZharifNo ratings yet
- Reaction Kinetics: Continuous Vs Initial Rate DataDocument16 pagesReaction Kinetics: Continuous Vs Initial Rate DatashowhardoNo ratings yet
- Rate Evening 2Document18 pagesRate Evening 2Tom TommmaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry - Rates and EquilibriumDocument22 pagesIGCSE Chemistry - Rates and EquilibriumChemistryKlipz100% (7)
- 6.1 3 Measuring Rates of ReactionDocument18 pages6.1 3 Measuring Rates of ReactionSho baconNo ratings yet
- Chem GauravDocument11 pagesChem GauravKaran YadavNo ratings yet
- Determination of Rate EquationDocument9 pagesDetermination of Rate EquationIsabella ThomasNo ratings yet
- Rate of ReactionDocument12 pagesRate of Reactionj5nfng2zzxNo ratings yet
- Kadar Tindak Balas.K1Document9 pagesKadar Tindak Balas.K1Narah NasNo ratings yet
- Rates of Reaction: by Syed Arham AhsanDocument12 pagesRates of Reaction: by Syed Arham AhsanAryan HossainNo ratings yet
- Rates of ReactionDocument7 pagesRates of Reactionapi-25909541No ratings yet
- Rate of Chemical ReactionsDocument11 pagesRate of Chemical ReactionsWalu BNNo ratings yet
- Rates of ReactionsDocument71 pagesRates of ReactionsMel ManningNo ratings yet
- Module Form 5 .Rate of ReactionDocument8 pagesModule Form 5 .Rate of ReactionChew Gee Lan100% (1)
- RatesDocument22 pagesRatesPeterNo ratings yet
- Modul Kimia SPM A+ 2014Document20 pagesModul Kimia SPM A+ 2014Cikgu Faizal100% (6)
- Mole Ratios and Reaction StoichiometryDocument4 pagesMole Ratios and Reaction StoichiometryAishaNo ratings yet
- IA - Metals and AcidsDocument3 pagesIA - Metals and Acids14nganhc1No ratings yet
- Lajur FixDocument18 pagesLajur FixMoniqsa Purbo SyahraniNo ratings yet
- Kinetics: 6.1 Rates of ReactionDocument20 pagesKinetics: 6.1 Rates of ReactionSeung Hee KimNo ratings yet
- Topik 10 Rate of ReactionDocument33 pagesTopik 10 Rate of ReactionJaaizah JaafarNo ratings yet
- Rate of Reaction Between Calcium Carbonate and Hydrochloric AcidDocument6 pagesRate of Reaction Between Calcium Carbonate and Hydrochloric AcidSimon WayneNo ratings yet
- Ujian Diagnostik Kimia t5Document6 pagesUjian Diagnostik Kimia t5haniimanNo ratings yet
- ChI06 Rates of Reaction TMA B 0817Document21 pagesChI06 Rates of Reaction TMA B 0817Husnul YaqinNo ratings yet
- KineticsDocument91 pagesKineticsbabithakslgNo ratings yet
- 6 Chemical ReactionsDocument19 pages6 Chemical ReactionsAhmed AyazNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics RevisedDocument56 pagesChemical Kinetics RevisedCacey Daiwey CalixtoNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 - Chemical KineticsDocument22 pagesTopic 6 - Chemical KineticsLucia PesentiNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science: Chemistry 7.1 - Rates of ReactionDocument4 pagesIGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science: Chemistry 7.1 - Rates of Reactionda_reaper_dasNo ratings yet
- Chem Form 5Document37 pagesChem Form 5Ashwin Boy Ash100% (1)
- Kinetics Lecture Notes Part 1Document31 pagesKinetics Lecture Notes Part 1NedNo ratings yet
- Sterling Test Prep College Physics Practice Questions: Vol. 1, High Yield College Physics Questions with Detailed ExplanationsFrom EverandSterling Test Prep College Physics Practice Questions: Vol. 1, High Yield College Physics Questions with Detailed ExplanationsNo ratings yet
- GCSE Exam QuestionsDocument155 pagesGCSE Exam Questionsdanielphilip68No ratings yet
- Making Molar Solutions: From LiquidsDocument11 pagesMaking Molar Solutions: From Liquidsdanielphilip68No ratings yet
- Igcse Structure Question 13Document2 pagesIgcse Structure Question 13danielphilip68No ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Igcse Chemistry Carbon CycleDocument35 pagesLesson 2 Igcse Chemistry Carbon Cycledanielphilip68No ratings yet
- Igcse Topic 1 Lesson 1 Water Cycle IgcseDocument25 pagesIgcse Topic 1 Lesson 1 Water Cycle Igcsedanielphilip68100% (1)
- Rates & Energy NotesDocument11 pagesRates & Energy Notesdanielphilip68No ratings yet
- Redox ReactionsDocument8 pagesRedox Reactionsdanielphilip68No ratings yet
- 1.3 TestDocument24 pages1.3 Testdanielphilip68No ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibria AS Level ChemistryDocument4 pagesChemical Equilibria AS Level Chemistrydanielphilip68No ratings yet
- Igcse Structure Question 12Document3 pagesIgcse Structure Question 12danielphilip68No ratings yet
- Igcse Structure Question 9Document2 pagesIgcse Structure Question 9danielphilip68No ratings yet
- Igcse Structure Question 10Document2 pagesIgcse Structure Question 10danielphilip68No ratings yet
- Igcse Structure Question 8Document2 pagesIgcse Structure Question 8danielphilip68No ratings yet
- Igcse Structure Question 11Document2 pagesIgcse Structure Question 11danielphilip680% (1)
- Igcse Structure Question 7Document2 pagesIgcse Structure Question 7danielphilip68No ratings yet
- Igcse Structure Question 4: (A) Complete The Following TableDocument2 pagesIgcse Structure Question 4: (A) Complete The Following Tabledanielphilip68No ratings yet
- Igcse Structure Question 5Document2 pagesIgcse Structure Question 5danielphilip68No ratings yet
- Good IGCSE Chemistry CIE Paper 6 Set 1Document15 pagesGood IGCSE Chemistry CIE Paper 6 Set 1danielphilip680% (1)
- Igcse Structure Question 3Document2 pagesIgcse Structure Question 3danielphilip68No ratings yet
- Good Igcse Cie Question 4Document4 pagesGood Igcse Cie Question 4danielphilip68No ratings yet
- Alternative To Practical Questions IGCSEset 1Document15 pagesAlternative To Practical Questions IGCSEset 1danielphilip68100% (1)
- Alternative To Practical Questions IGCSEset 1Document15 pagesAlternative To Practical Questions IGCSEset 1danielphilip68100% (1)
- Aquafina Purification DiagramDocument1 pageAquafina Purification DiagramAyesha ArjamandNo ratings yet
- Respuestas Termoquimica ChangDocument8 pagesRespuestas Termoquimica ChangIsabelNo ratings yet
- Rate Law Worksheet AnswersDocument6 pagesRate Law Worksheet AnswersANGELYN SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Distillation Tutorial in HYSYSDocument7 pagesDistillation Tutorial in HYSYScmlim100% (2)
- Rates of Reaction 2 MSDocument3 pagesRates of Reaction 2 MSNana Barnett QuaicooNo ratings yet
- Exercise Dehydration EngDocument4 pagesExercise Dehydration EngShahram MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Paper Id249 Powergen2012Document21 pagesPaper Id249 Powergen2012arunNo ratings yet
- Basics of Catalysts - Chemistry LibreTextsDocument6 pagesBasics of Catalysts - Chemistry LibreTextsStatus loverNo ratings yet
- Midstream (Petroleum IndustrY)Document2 pagesMidstream (Petroleum IndustrY)Espartaco SmithNo ratings yet
- ANSI-ASME B31 Scope and Exclusions-Chemical Plant and Petroleum Refinery Piping (Documento Word)Document3 pagesANSI-ASME B31 Scope and Exclusions-Chemical Plant and Petroleum Refinery Piping (Documento Word)FRANCISCO RICARDONo ratings yet
- Quadax - Přehled EN NEWDocument16 pagesQuadax - Přehled EN NEWRamazan YaşarNo ratings yet
- 103-Effect of Hydrocarbon Partial Pressure On Propylene Production in The FCCDocument10 pages103-Effect of Hydrocarbon Partial Pressure On Propylene Production in The FCCdonald55555No ratings yet
- Batch 10 TimetableDocument1 pageBatch 10 TimetableMarcoNo ratings yet
- Equipment Included in A CO2 PlantDocument3 pagesEquipment Included in A CO2 Plantgama tokNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice QuestionDocument30 pagesMultiple Choice QuestionJayabrata DasNo ratings yet
- Upgrade of Sulfur Recovery Unit at Ras TanuraDocument8 pagesUpgrade of Sulfur Recovery Unit at Ras Tanurasalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Drizo Gas DehydrationDocument2 pagesDrizo Gas DehydrationAnonymous bHh1L1No ratings yet
- Ucalgary 2020 Du StevenDocument65 pagesUcalgary 2020 Du StevenmnasiroleslamiNo ratings yet
- Disadvantages of HardwaterDocument17 pagesDisadvantages of Hardwaterchemistrymaster96% (24)
- CH 6 Notebook Work Combustion and FlameDocument3 pagesCH 6 Notebook Work Combustion and FlameSamarth SharmaNo ratings yet
- ChemEngineering 05 00020Document24 pagesChemEngineering 05 00020chaniefNo ratings yet
- Alkanes: H H C H HDocument6 pagesAlkanes: H H C H HAmirah AmanNo ratings yet
- Customer Name Item NameDocument130 pagesCustomer Name Item Namevelugu john sundar rajuNo ratings yet
- Commissioning SequenceDocument17 pagesCommissioning Sequencebikas_sahaNo ratings yet
- Chemsheets A2 1157 QC KP B ANS NbsyeDocument1 pageChemsheets A2 1157 QC KP B ANS NbsyeMarinaNo ratings yet
- 2.01 Surface Kinetics - Unimolecular Reactions PDFDocument33 pages2.01 Surface Kinetics - Unimolecular Reactions PDFMelchiNo ratings yet
- 7 LischkeDocument81 pages7 LischkeKarthick VelayuthamNo ratings yet
- Design of Lab-Scale Downdraft Gasifier For Biomass GasificationDocument9 pagesDesign of Lab-Scale Downdraft Gasifier For Biomass GasificationMuhammad Shahzad KhurramNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Caustic CorrosionDocument10 pagesPresentation On Caustic CorrosionMuhammad BilalNo ratings yet