Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tetanus: Dr. Rohmania Setiarini
Tetanus: Dr. Rohmania Setiarini
Uploaded by
Annisa Rahmani0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views32 pagesTetanus is a potentially fatal disease caused by a toxin produced by the bacterium Clostridium tetani. It is characterized by painful muscle spasms and rigidity. The bacteria is ubiquitous in soil and enters the body through wounds. The toxin travels to the spinal cord and blocks inhibitory neurotransmitters in the brain, causing sustained muscle contractions. Symptoms range from lockjaw to painful arching of the back. Treatment focuses on wound cleaning, antitoxin administration, controlling spasms, and supportive care. Immunization provides effective prevention against tetanus.
Original Description:
kuliah tetanus dokter nia
Original Title
Tetanus
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentTetanus is a potentially fatal disease caused by a toxin produced by the bacterium Clostridium tetani. It is characterized by painful muscle spasms and rigidity. The bacteria is ubiquitous in soil and enters the body through wounds. The toxin travels to the spinal cord and blocks inhibitory neurotransmitters in the brain, causing sustained muscle contractions. Symptoms range from lockjaw to painful arching of the back. Treatment focuses on wound cleaning, antitoxin administration, controlling spasms, and supportive care. Immunization provides effective prevention against tetanus.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views32 pagesTetanus: Dr. Rohmania Setiarini
Tetanus: Dr. Rohmania Setiarini
Uploaded by
Annisa RahmaniTetanus is a potentially fatal disease caused by a toxin produced by the bacterium Clostridium tetani. It is characterized by painful muscle spasms and rigidity. The bacteria is ubiquitous in soil and enters the body through wounds. The toxin travels to the spinal cord and blocks inhibitory neurotransmitters in the brain, causing sustained muscle contractions. Symptoms range from lockjaw to painful arching of the back. Treatment focuses on wound cleaning, antitoxin administration, controlling spasms, and supportive care. Immunization provides effective prevention against tetanus.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 32
tetanus
dr. Rohmania Setiarini
Tetanus is an acute,often fatal,disease caused by
an exotoxin produced by the bacterium Clostridium
tetani. But prevented by immunization with tetanus
toxoid.
It is characterized by generalized rigidity and
convulsive spasms of skeletal muscles.
epidemiology
Tetanus is an international health problem, as spores are
ubiquitous. The disease occurs almost exclusively in persons
who are unvaccinated or inadequately immunized.
Tetanus occurs worldwide but is more common in hot,
damp climates with soil rich in organic matter.
More common in developing countries.
Clostridium tetani
Cl.tetani is widely
distributed in soil & in
intestine of human
beings & animals.
They cause tetanus in
both man & animal.
Morphology
Gram-positive, 4-
8m0.5m bacillus.
Anaerob
Has straight axis, parallel
sides & rounded ends.
Occurs singly &
occasionally in chains.
sensitive to heat and cannot
survive in the presence of
oxygen
Resistance
Spore resistance to heat show strain variation.
Majority are killed by boiling for 15min.
Some withstand boiling for 3hr & dry heat at
160C for 1hr.
Spores can survive in soil for years & are resistant
to most antiseptics.
Not destroyed by 5% phenol or 0.1% HgCl
2
solution in 2 weeks or more.
Susceptibility
Autoclaving at 121C for 15min kills the spores
readily.
Iodine(1% aqueous soon) and H
2
O
2
kills spores
within few hours.
Toxins
All types produce same toxins which are
pharmacologically & antigenically
identical.
Plasmid mediated.
1.Tetanolysin
2.Tetanospasmin
Tetanolysin
Heat & O
2
labile hemolysin.
Cause red cell lysis.
Pathogenic role not clear.
.
Tetanospasmin
O
2
stable & heat labile neurotoxin.
Good antigen & specifically neutralised by
antitoxin.
Similar to botulinum toxin
Incubation Period
Varies from 1 day to several months.
It is defined as the time from injury to the
first symptom.
Period of onset
A period of onset of less than 48 hr is
associated with the development of severe
tetanus.
pathogenesis
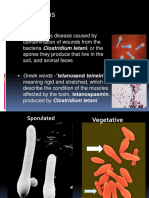
1. C. tetani enters body
from through wound.
3. Germinates under
anaerobic conditions and
begins to multiply and
produce tetnospasmin.
2. Stays in sporulated
form until anaerobic
conditions are presented.
4. Tetnospasmin spreads using
blood and lymphatic system,
and binds to motor neurons.
5. Travels along the axons
to the spinal cord.
6. Binds to sites responsible for
inhibiting skeletal muscle
contraction.
the toxin acts :
Blocks the release of inhibitory
neurotransmitters (glycine and gamma-amino
butyric acid) across the synaptic cleft, which is
required to check the nervous impulse.
If nervous impulses cannot be checked by
normal inhibitory mechanisms, it leads to
unopposed muscular contraction and spasms
that are characteristic of tetanus.
Local tetanus
Persistent spasm of musculature at site of primary
infection (injury site).
Contractions persist for weeks before subsiding.
Its generally milder, 1% cases are fatal but may
precede the generalised tetanus.
Cephalic tetanus
Primary site of infection is head injury or otitis
media.
Associated with disfunction of 1 or more cranial
nerves, most commonly facial nerve.
Poor prognosis.
Generalised tetanus
Most common form(80% of cases).
Presents with a descending pattern.
1
st
sign is trismus(lockjaw) -due to
spasm of masseter muscles.
Followed by stiffness of the neck,
difficulty in swallowing, rigidity of
abdominal muscles.
Tetanus neonatorum
It is the generalised tetanus
that occurs in newborn
infants.
Occurs in infants of non-
immunised mothers.
Tetanus neonatorum
Occurs from infection of
un-healed umbilical stump
particularly when stump is
cut with non-sterile
instrument.
Very poor prognosis
Clinical features
Risus sardonicus: Contraction of the muscles at the angle
of mouth and frontalis
Trismus (Lock Jaw): Spasm of Masseter muscles.
Opisthotonus: Spasm of extensor of the neck, back and
legs to form a backward curvature.
Muscle spasticity
Prolonged muscular action causes sudden, powerful,
and painful contractions of muscle groups. This is
called tetany. These episodes can cause fractures and
muscle tears.
If respiratory muscle is involved apnoea.
Other symptoms include:
Excessive sweating
Fever
Hand or foot spasms
Irritability
Swallowing difficulty
Risus sardonicus
Characteristic sardonic
smile in tetanus
Results from sustained
contraction of facial
muscles.
Opthisthotonus
Back spasm seen in
tetanus
Diagnosis
There are currently no blood tests that can
be used to diagnose tetanus. Diagnosis is
done clinically.
Principle of Treatment
1. Neutralization of unbound toxin with
Human tetanus immunoglobulin
2. Prevention of further toxin production by
-Wound debridement
-Antibiotics
3. Control of spasm
- Nursing in quiet environment
- avoid unnecessary stimuli
- Protecting the airway
4. Supportive care
- Adequate hydration
- Nutrition
- Treatment of secondary infection
You might also like
- Doctor Who Cures Cancer DescriptionDocument27 pagesDoctor Who Cures Cancer Descriptionhobray3946100% (1)
- TetanusDocument32 pagesTetanusVinotheran MichaelNo ratings yet
- STI GuidelinesDocument39 pagesSTI GuidelinesioanatiuNo ratings yet
- Tetanus SaleemDocument17 pagesTetanus SaleemMueez BalochNo ratings yet
- Tetanu S: By: Reno WaisyahDocument18 pagesTetanu S: By: Reno WaisyahReno WaisyahNo ratings yet
- Management of TetanusDocument7 pagesManagement of TetanusamutiarNo ratings yet
- Group 2 TetanusDocument43 pagesGroup 2 TetanusDaymon, Ma. TeresaNo ratings yet
- Surgery Lecture On: Dr. Ehsanur RezaDocument23 pagesSurgery Lecture On: Dr. Ehsanur Rezaiga sukmaNo ratings yet
- Tetanus DR Moses KazevuDocument13 pagesTetanus DR Moses KazevuMoses Jr KazevuNo ratings yet
- TetanusDocument27 pagesTetanusMohammed FareedNo ratings yet
- Tetanus: W Hat Is Tetanus?Document20 pagesTetanus: W Hat Is Tetanus?Stefanie BlueNo ratings yet
- TetanusDocument3 pagesTetanusRoma Nova Pascual CabarrubiasNo ratings yet
- Tetanus-Dr. A.M IyagbaDocument32 pagesTetanus-Dr. A.M IyagbaDr. Amb. Monday ZaccheausNo ratings yet
- TetanusDocument23 pagesTetanusNadya Noor Mulya Putri100% (1)
- Tetanus: Mrs.G.Manibharathi, MSC (N), Associate ProfessorDocument26 pagesTetanus: Mrs.G.Manibharathi, MSC (N), Associate ProfessormanibharathiNo ratings yet
- Tetanus: Rika Arista Dewi S1-3ADocument14 pagesTetanus: Rika Arista Dewi S1-3ArikaaristadNo ratings yet
- Lovely Professional University: Term Paper of Advanced MicrobiologyDocument11 pagesLovely Professional University: Term Paper of Advanced Microbiology27AlokKumarNo ratings yet
- TetanusDocument79 pagesTetanusSan MohapatraNo ratings yet
- Neonatal TetanusDocument44 pagesNeonatal TetanusJake MillerNo ratings yet
- In The Name of ALLAH The Beneficent and MercifulDocument49 pagesIn The Name of ALLAH The Beneficent and Mercifulcute_honiya100% (1)
- TetanusDocument23 pagesTetanusDhynie Soesila WahyudiNo ratings yet
- Tetanus: Zaidi Abd Hamid Pensyarah Pembantu PerubatanDocument31 pagesTetanus: Zaidi Abd Hamid Pensyarah Pembantu PerubatanSyasya NanaNo ratings yet
- What Is Tetanus?: Clostridium Tetani or The Tetanus Bacillus Is A Slender, Gram-Positive, Anaerobic Rod That MayDocument5 pagesWhat Is Tetanus?: Clostridium Tetani or The Tetanus Bacillus Is A Slender, Gram-Positive, Anaerobic Rod That MayraechcmNo ratings yet
- Tetanus 9 eDocument10 pagesTetanus 9 ea.hooker114No ratings yet
- TetanusDocument12 pagesTetanustinkerbell03No ratings yet
- Tetanus ADocument3 pagesTetanus ASadaqat KhanNo ratings yet
- TetanusDocument7 pagesTetanusArnella HutagalungNo ratings yet
- Tetanus: DR - Richard Arie MonoarfaDocument47 pagesTetanus: DR - Richard Arie MonoarfaarischarompisNo ratings yet
- Status InternusDocument12 pagesStatus InternusPriscaNo ratings yet
- TetanusDocument12 pagesTetanusYulisa FitrianiNo ratings yet
- TETANUSDocument38 pagesTETANUSGumilar Galih PratamaNo ratings yet
- Clostridium Tetani: Tejpratap S.P. Tiwari, MD Pedro L. Moro, MD, MPH and Anna M. Acosta, MDDocument14 pagesClostridium Tetani: Tejpratap S.P. Tiwari, MD Pedro L. Moro, MD, MPH and Anna M. Acosta, MDClaudia FreyonaNo ratings yet
- Common Communicable Infectious Disease:: TetanusDocument19 pagesCommon Communicable Infectious Disease:: TetanusJayvee Novenario CasaljayNo ratings yet
- TetanusDocument7 pagesTetanusKimchi LynnNo ratings yet
- Tetanus PDFDocument10 pagesTetanus PDFVina MuspitaNo ratings yet
- Tetanus: Surgery Lecture OnDocument23 pagesTetanus: Surgery Lecture OnJasonWalkerNo ratings yet
- TetanusDocument12 pagesTetanusKidistNo ratings yet
- Brucellosis: The Short Textbook of PediatricsDocument3 pagesBrucellosis: The Short Textbook of PediatricsHosny M IsseNo ratings yet
- C. Tetani FinalDocument3 pagesC. Tetani FinalSajjad Hossain ShuvoNo ratings yet
- TetanusDocument37 pagesTetanusMuwanga faizoNo ratings yet
- A Seminar On The Topic TetanusDocument16 pagesA Seminar On The Topic TetanusRajat PadhanNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho GenesisDocument11 pagesPa Tho GenesisBeth AvelinoNo ratings yet
- 388tetanus For WebsiteDocument51 pages388tetanus For Websitehafiz ikhsanNo ratings yet
- Ni Komang Saraswita Laksmi: Puskesmas Mendoyo I, Bali, IndonesiaDocument6 pagesNi Komang Saraswita Laksmi: Puskesmas Mendoyo I, Bali, IndonesiaRirhy SaragihNo ratings yet
- Kepaniteraan Klinik RSD Mardi Waluyo Blitar - FK Unisma: Pembimbing: Dr. Utchu Tedja Mulya SP.BDocument35 pagesKepaniteraan Klinik RSD Mardi Waluyo Blitar - FK Unisma: Pembimbing: Dr. Utchu Tedja Mulya SP.BDada DoniNo ratings yet
- TetanusDocument102 pagesTetanusMo Oo MooNo ratings yet
- Tetanus 160530145856Document25 pagesTetanus 160530145856Gargi ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Tetanu S: Dr. MaslianiDocument74 pagesTetanu S: Dr. MaslianiHengky HanggaraNo ratings yet
- TetanusDocument47 pagesTetanusSyamsul Arifin100% (3)
- The Pa Tho Physiology of TetanusDocument3 pagesThe Pa Tho Physiology of Tetanusmai_serpicNo ratings yet
- Tetanus: Ma. Theresa Dj. YumangDocument28 pagesTetanus: Ma. Theresa Dj. YumangJean SarocamNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic BacteriaDocument65 pagesAnaerobic BacteriaJames TorresNo ratings yet
- TETANUSDocument3 pagesTETANUSfxbukenyaNo ratings yet
- Tetanus: Eu MBCHB 3 DR D M KillingoDocument44 pagesTetanus: Eu MBCHB 3 DR D M KillingoArjay VisitacionNo ratings yet
- TetanusDocument31 pagesTetanusreresNo ratings yet
- K6 - Tetanus PEDIATRICDocument23 pagesK6 - Tetanus PEDIATRICbanuperiahNo ratings yet
- TetanusDocument5 pagesTetanusasmaeserNo ratings yet
- !tetanus MDocument22 pages!tetanus MWendo yayahNo ratings yet
- Tetanus: Dr.I.SelvarajDocument47 pagesTetanus: Dr.I.SelvarajimyoongsNo ratings yet
- Abdelfattah Monged Selim - Tetanus 2Document25 pagesAbdelfattah Monged Selim - Tetanus 2Saja MaraqaNo ratings yet
- TetanusDocument35 pagesTetanusWaNda GrNo ratings yet
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandCarpal Tunnel Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Disease Cheat SheetDocument393 pagesDisease Cheat Sheetsurviving nursing school50% (2)
- Ncs University System Department of Health Sciences: Discipline (MLT-04) (VIROLOGY &MYCOLOGY)Document5 pagesNcs University System Department of Health Sciences: Discipline (MLT-04) (VIROLOGY &MYCOLOGY)Habib UllahNo ratings yet
- AmVetPub August2016Document20 pagesAmVetPub August2016NoSpamNo ratings yet
- Babesiosis in AnimalsDocument15 pagesBabesiosis in AnimalshasbshahNo ratings yet
- Biology Terms Grade 9 ReviewerDocument3 pagesBiology Terms Grade 9 ReviewerGreta Uy Sevilla100% (1)
- Essay On Youth Health - Mental IllnessDocument1 pageEssay On Youth Health - Mental IllnessGulara AzimzadehNo ratings yet
- CytomegalovirusDocument33 pagesCytomegalovirusAnggi Tridinanti PutriNo ratings yet
- CSSDDocument32 pagesCSSDRAHUL100% (1)
- Department of Genetics: Covid-19 RT PCRDocument1 pageDepartment of Genetics: Covid-19 RT PCRAshwin ShajiNo ratings yet
- Croup: Straight To The Point of CareDocument36 pagesCroup: Straight To The Point of CareNana OkujavaNo ratings yet
- Linfatic System HeelDocument4 pagesLinfatic System HeelPablo Matas Soria100% (1)
- Spotting Experiments Class 12Document21 pagesSpotting Experiments Class 12Ridyangam Dubey100% (3)
- Gene SileningDocument30 pagesGene SileningSajjad AhmadNo ratings yet
- The Antibacterial Activity of Dayak Onion (Eleutherine Palmifolia (L.) Merr) Towards Pathogenic BacteriaDocument14 pagesThe Antibacterial Activity of Dayak Onion (Eleutherine Palmifolia (L.) Merr) Towards Pathogenic BacteriatiabellaraNo ratings yet
- Common ColdDocument6 pagesCommon ColdRAM SOFTWARENo ratings yet
- Gpat Reference NotesDocument9 pagesGpat Reference NotesPreethi KiranNo ratings yet
- Ot ProtocolDocument38 pagesOt ProtocolSelva KumarNo ratings yet
- Ciclo de AEROLIN: DIA Aerolin Divisão 7:30 12:30 18:30Document2 pagesCiclo de AEROLIN: DIA Aerolin Divisão 7:30 12:30 18:30Diego NavarroNo ratings yet
- Provides Protective Immunity To Rainbow Trout. A Conserved Aeromonas Salmonicida PorinDocument7 pagesProvides Protective Immunity To Rainbow Trout. A Conserved Aeromonas Salmonicida PorinKasagalaNo ratings yet
- Expanded Program On Immunization (Philippines)Document10 pagesExpanded Program On Immunization (Philippines)Karen Bianca Espinola, MD. DPBA.No ratings yet
- v16 n3Document219 pagesv16 n3Mark ReinhardtNo ratings yet
- Who Midwife ManualDocument282 pagesWho Midwife ManualSri Rama Suryatez Kattula100% (2)
- Vax Pseudo FlipDocument9 pagesVax Pseudo FlipMichael McIntoshNo ratings yet
- Risk Groups: Viruses: Rev.: 1.0 (C) 1988, American Biological Safety AssociationDocument10 pagesRisk Groups: Viruses: Rev.: 1.0 (C) 1988, American Biological Safety Associationcarlo melgarNo ratings yet
- Fevers: Usually A Positive Sign That The Body Is Fighting Infection."Document3 pagesFevers: Usually A Positive Sign That The Body Is Fighting Infection."Theresa OsmerNo ratings yet
- DR Navin DangDocument2 pagesDR Navin DangdrdangsofficeNo ratings yet
- Mastoiditis NCP Sensory PerceptionDocument15 pagesMastoiditis NCP Sensory Perception081907475889100% (1)
- Immunology Chapters 1-2 Question Study GuideDocument2 pagesImmunology Chapters 1-2 Question Study GuideEduardo CarderoNo ratings yet