Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Layout
Layout
Uploaded by
D Nitins SharmaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- BS Assignment Brief - Strategic Planning AssignmentDocument8 pagesBS Assignment Brief - Strategic Planning AssignmentParker Writing ServicesNo ratings yet
- Plant Layout: Submitted By: Lalit MagoDocument18 pagesPlant Layout: Submitted By: Lalit MagoAngelina WattssNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2 - Plant ManagementDocument58 pagesChapter - 2 - Plant ManagementakhilNo ratings yet
- Plant LayoutDocument28 pagesPlant LayoutkirandatarNo ratings yet
- Plant Layout: Lecture Conducted by Apoorva Srivastava, ABS, AMITY, LucknowDocument65 pagesPlant Layout: Lecture Conducted by Apoorva Srivastava, ABS, AMITY, LucknowKavya KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- 02-2 Plant Layout & Piping SystemDocument10 pages02-2 Plant Layout & Piping SystemJhoann CastroNo ratings yet
- 02-2 Plant Layout & Piping SystemDocument10 pages02-2 Plant Layout & Piping SystemLady Abegail AbraoNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 PlantlayoutDocument68 pagesChapter-3 PlantlayoutsrikantushaNo ratings yet
- MP Safety & LayoutDocument11 pagesMP Safety & LayoutM IRFANNo ratings yet
- Types of Layout-PPCDocument14 pagesTypes of Layout-PPCPrajwal RahangdaleNo ratings yet
- Layout DesignDocument5 pagesLayout DesignJessie Radaza Tutor0% (1)
- Product, Process, Fixed and Group LayoutsDocument21 pagesProduct, Process, Fixed and Group LayoutsAjith AntonyNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2021-22 MEE1018 TH VL2021220503069 Reference Material I 01-03-2022 Module 4Document78 pagesWINSEM2021-22 MEE1018 TH VL2021220503069 Reference Material I 01-03-2022 Module 4Harsh VermaNo ratings yet
- Classification and Advantages of Plant LayoutDocument6 pagesClassification and Advantages of Plant LayoutKrishna big fan of maheshbabuNo ratings yet
- Plant-Layout NotesDocument17 pagesPlant-Layout NotesRahul DesaiNo ratings yet
- Plant or Facility LayoutDocument9 pagesPlant or Facility LayoutKelvin mwaiNo ratings yet
- Plant Layout Operation ManagementDocument7 pagesPlant Layout Operation ManagementKAPIL VARSHNEYNo ratings yet
- Product Vs Process LayoutDocument4 pagesProduct Vs Process LayoutvmktptNo ratings yet
- Chapter ThreeDocument60 pagesChapter ThreeEndashaw YohannesNo ratings yet
- Operations Management: Layout and Flow Designs INDocument24 pagesOperations Management: Layout and Flow Designs INIsaac OwusuNo ratings yet
- 05facility LayoutDocument31 pages05facility LayoutDivya ShindeNo ratings yet
- What Is A Plant LayoutDocument5 pagesWhat Is A Plant LayoutVIVEK KUMAR SINGH 13No ratings yet
- Plant Location & Layout DesignDocument26 pagesPlant Location & Layout DesignAli MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Kombolcha Institute of Technology Department of Industrial EngineeringDocument41 pagesKombolcha Institute of Technology Department of Industrial EngineeringFakihat MohammedNo ratings yet
- Plant/Facility LayoutDocument6 pagesPlant/Facility Layoutsourav736eeNo ratings yet
- Operations Management (Bba)Document23 pagesOperations Management (Bba)sssNo ratings yet
- 6-Classification of Layout and Mhs - 160811Document4 pages6-Classification of Layout and Mhs - 160811pammy313No ratings yet
- Om Chapter SixDocument10 pagesOm Chapter Sixsamrawithagos2002No ratings yet
- Plantlayout 111109213112 Phpapp02Document18 pagesPlantlayout 111109213112 Phpapp02Bala KumaranNo ratings yet
- Operation Management RoughDocument9 pagesOperation Management RoughRashi virkudNo ratings yet
- IEM Unit 1Document21 pagesIEM Unit 1M.suresh SureshNo ratings yet
- Facility LayoutDocument16 pagesFacility LayoutViraj DhuriNo ratings yet
- Plant Layout TelsangDocument10 pagesPlant Layout TelsangKhushi SalgaonkarNo ratings yet
- F INALITYp 3Document23 pagesF INALITYp 3api-3701467100% (1)
- CH 8 Facility Layout - Part1Document29 pagesCH 8 Facility Layout - Part1Muhammad FurqanNo ratings yet
- Class 12 - (Facility Layout)Document11 pagesClass 12 - (Facility Layout)Amna FaisalNo ratings yet
- Plant Layout: Concept, Objectives, Principles and TypesDocument6 pagesPlant Layout: Concept, Objectives, Principles and Typesbernabas100% (1)
- Facilities Layout (Plant Layout)Document8 pagesFacilities Layout (Plant Layout)Kunwar Sa Amit SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Layout Planning Models and DesignDocument14 pagesChapter 6 Layout Planning Models and DesignAngel Micah NepomucenoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Layout Planning Models and DesignDocument14 pagesChapter 6 Layout Planning Models and DesignAngel Micah NepomucenoNo ratings yet
- Facility Layout, PPTDocument22 pagesFacility Layout, PPTsakhawatNo ratings yet
- Facility LayoutDocument34 pagesFacility LayoutTabi AlamNo ratings yet
- Strategic Resource Organization: Facilities Layout: Chapter SixDocument56 pagesStrategic Resource Organization: Facilities Layout: Chapter SixAngela Vidal EstilNo ratings yet
- Mid-Term Assignmen, Group 2WF., Alaa AboualiDocument5 pagesMid-Term Assignmen, Group 2WF., Alaa AboualiAlaa AboaliNo ratings yet
- Facility Layout PRINTABLEDocument8 pagesFacility Layout PRINTABLEMahnoor HayatNo ratings yet
- Week - 5 LAQ - Operations ManagementDocument5 pagesWeek - 5 LAQ - Operations Managementbabitha76260No ratings yet
- Plant LayoutDocument30 pagesPlant LayoutRashi MehraNo ratings yet
- PLant Location - JegadeesanDocument17 pagesPLant Location - JegadeesanShuaib AktharNo ratings yet
- Plant LayoutDocument71 pagesPlant LayoutVikash GuptaNo ratings yet
- 5facility Layout PlanningDocument14 pages5facility Layout PlanningAman SinghNo ratings yet
- PPC-Lec-4-Plant LayoutDocument6 pagesPPC-Lec-4-Plant LayoutRakib100% (1)
- Plant Layout: Concept, Objectives, Principles and TypesDocument9 pagesPlant Layout: Concept, Objectives, Principles and TypesAfad KhanNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Plant LayoutDocument20 pagesPresentation On Plant LayoutSahil NayyarNo ratings yet
- Facility Layout NotesDocument6 pagesFacility Layout NotesOckouri BarnesNo ratings yet
- Plant LayoutDocument51 pagesPlant Layoutعبدالله عمرNo ratings yet
- Facility LayoutDocument36 pagesFacility LayoutRishabh MahajanNo ratings yet
- Process SelectionDocument30 pagesProcess Selectionjaspreet444100% (1)
- Batch Process Presentation)Document17 pagesBatch Process Presentation)Telse Simon100% (1)
- 1613938959om Module 2 Plant Layout Principles of Layout Product and ProcesDocument6 pages1613938959om Module 2 Plant Layout Principles of Layout Product and Procesjuhy vincentNo ratings yet
- Facility LayoutDocument24 pagesFacility LayoutShahenaNo ratings yet
- Fiscal Policy in A Developing Country 2014Document19 pagesFiscal Policy in A Developing Country 2014D Nitins SharmaNo ratings yet
- Total Quality Management & Cost of QualityDocument16 pagesTotal Quality Management & Cost of QualityD Nitins SharmaNo ratings yet
- SEBI Investor Protection GuidelinesDocument1 pageSEBI Investor Protection GuidelinesD Nitins SharmaNo ratings yet
- SIP Guidelines For Students 2014Document11 pagesSIP Guidelines For Students 2014D Nitins SharmaNo ratings yet
- Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer RelationshipsDocument53 pagesMarketing: Managing Profitable Customer RelationshipsD Nitins SharmaNo ratings yet
- 3 - BREAK EVEN ANALYSIS - UploadDocument5 pages3 - BREAK EVEN ANALYSIS - Uploadniaz kilamNo ratings yet
- Lec06c - Bsa 2103 - 011920Document12 pagesLec06c - Bsa 2103 - 011920PeachyNo ratings yet
- Module 2-Asset Allocation-Questions AwniW26jEKDocument21 pagesModule 2-Asset Allocation-Questions AwniW26jEKKp PatelNo ratings yet
- MJC 2 Unit 1,2,3 Business Organisation and ManagementDocument14 pagesMJC 2 Unit 1,2,3 Business Organisation and Managementnk531114No ratings yet
- Shinny Jewel C. Vingno BSA-2 Problem 1-18Document7 pagesShinny Jewel C. Vingno BSA-2 Problem 1-18Shinny Jewel VingnoNo ratings yet
- DIGEST - CIR Vs NLRCDocument2 pagesDIGEST - CIR Vs NLRCMocha Bear100% (2)
- Seminar of Mobile Data MvnoDocument0 pagesSeminar of Mobile Data Mvnofahmi810091No ratings yet
- Petty Cash CycleDocument22 pagesPetty Cash CycleSAlah MOhammed100% (1)
- Construction of Irrigation SchemesDocument46 pagesConstruction of Irrigation SchemesZed Phil Ind100% (1)
- CV Example For ITDocument4 pagesCV Example For ITAleksandar JakimovoskiNo ratings yet
- Presented By-Priya Khandelwal Honey Chordia Sanjhi Neema Mba FT - Iiird Sem DDocument9 pagesPresented By-Priya Khandelwal Honey Chordia Sanjhi Neema Mba FT - Iiird Sem Dpriya khandelwalNo ratings yet
- Yamazumi Process Modeling Tool AdaptiveBMSDocument9 pagesYamazumi Process Modeling Tool AdaptiveBMSBharathNo ratings yet
- Fitero B. Garlitos 2017-E905019: Multiple ChoiceDocument2 pagesFitero B. Garlitos 2017-E905019: Multiple Choicefitz garlitosNo ratings yet
- Ang Tek Lian Vs CADocument2 pagesAng Tek Lian Vs CALee Somar100% (1)
- Toaz - Info Partnership Qs PRDocument8 pagesToaz - Info Partnership Qs PRToni Rose Hernandez LualhatiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Front Office - Chapter1Document61 pagesIntroduction To Front Office - Chapter1Mary Pauline Musca100% (2)
- Applied EconomicsDocument5 pagesApplied EconomicsMaritess Madrid EsperanzaNo ratings yet
- NPD AssignmentDocument3 pagesNPD AssignmentNicky BojeNo ratings yet
- World's Fair Corporation: Executive Committee Meeting Minutes 2Document210 pagesWorld's Fair Corporation: Executive Committee Meeting Minutes 2JohnWilliams86No ratings yet
- SAIC-K-4042 Rev 7Document2 pagesSAIC-K-4042 Rev 7shahzadaNo ratings yet
- HR Critique Paper The Busines of The Business Is HumanDocument2 pagesHR Critique Paper The Busines of The Business Is HumanAnthonyTiuNo ratings yet
- Marketing Strategy of Oriflame India PVT LTD ProjectDocument84 pagesMarketing Strategy of Oriflame India PVT LTD ProjectMona100% (1)
- Link Building ResourcesDocument103 pagesLink Building ResourcesSADGURU AMRITWANI50% (2)
- A Final Board Packet August 7, 2013 - 0.... 5Document199 pagesA Final Board Packet August 7, 2013 - 0.... 5نيرمين احمدNo ratings yet
- Accounting Cycle, Entries and ConceptDocument64 pagesAccounting Cycle, Entries and Conceptdude devil100% (1)
- Construction Manager DutiesDocument5 pagesConstruction Manager Dutiesashsundar100% (1)
- Press Release: For Immediate DistributionDocument3 pagesPress Release: For Immediate DistributionThallusrhamesNo ratings yet
- MisDocument17 pagesMisAyan SnehashisNo ratings yet
- MES Buyers GuideDocument22 pagesMES Buyers GuidetuvaohNo ratings yet
Layout
Layout
Uploaded by
D Nitins SharmaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Layout
Layout
Uploaded by
D Nitins SharmaCopyright:
Available Formats
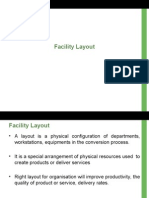
PLANT LAYOUT
Introduction
It includes decisions regarding the physical
allocation of the economic activity centers
in a facility.
Plant layout
Objectives of Facility Layout
Minimizing material handling costs
Efficient utilization of
Space
Labor
Eliminate
Bottlenecks
Waste or redundant movement
Objectives of Facility Layout
Facilitate
Organization structure
Communication and interaction between workers
Manufacturing process
Visual control
Minimize
Manufacturing cycle time or customer flow time
investment
Provide
Convenience, safety and comfort of the employees
Flexibility to adapt to changing conditions
Factors affecting Plant Layout
1. Materials
2. Machinery
3. Labor
4. Material Handling
5. Waiting Time
6. Auxiliary Services
7. The building
8. Future Changes
Basic Types of Layouts
Product Layout
Used in a flow shop for a high volume, standard products
Process Layout
Used in a job shop for a low volume, customized products
Fixed Position Layout
Used in projects for large products e.g., airplanes, ships and
rockets
Cellular layouts
A cell contains a group of machines dedicated for a group of
similar parts
Suitable for producing a wide variety parts in moderate
volume
Product Layout
The pieces of equipment required to make a
Particular product are grouped together
Continuous flow
Repetitive flow (assembly line)
Product Layout for Wine Manufacturer
Advantages
Reduced material
handling activities.
Work in Process almost
eliminated.
Minimum manufacturing
time.
Simplification of the
production planning and
control systems.
Tasks simplification.
Disadvantages:
No flexibility in the
production process.
Low flexibility in the
manufacturing times.
High capital investment.
Every workstation is critical
to the process
The lack of personnel or shut
down of a machine stops the
whole process.
Monotonous work.
Product Layout Advantages and
Disadvantages
Process Layout
Personnel and equipment to perform the same function
are allocated in the same area.
Sequence of operations previously established.
Process Layout for a Machine Shop
Advantages of Process layout
1. Best use of specialization of machines &
employees
2. Flexible variety of products
3. General purpose machines less costly
4. Ability to follow diverse paths
5. Less vulnerable to shutdowns
6. Machine breakdown less of problem
7. Small batch product economy
8. Suitable for incentive pay
Disadvantages of Process layout
1. General purpose machines slower
2. Work routing, scheduling difficult
3. Material handling costs high
4. Material moves slowly
5. Partially finished inventory high large
storage space
6. Communication difficult
7. Some limit to size of parts
Fixed Position Layout
The equipment is brought to the object being
processed, and the object does not move.
Example; House construction.
Cellular Layouts
Every cell contains a group of machines which are
dedicated to the production of a family of parts
Source: J. T. Black, Cellular Manufacturing Systems Reduce Set Up
time, Make Small-Lot Production Economical, Industrial Engineering
Magazine, Nov. 1983. Used with permission from the author.
Cellular Manufacturing Layout
Advantages of Cellular Layouts
Reduced material handling and transit time
Reduced setup time
Reduced work-in-process inventory
Better use of human resources
Better scheduling, easier to control and automate
Disadvantages of Cellular Layouts
Sometimes cells may not be formed
Some cells may be poorly balanced cells.
workers must be multi-skilled and cross-trained.
High capital investment.
You might also like
- BS Assignment Brief - Strategic Planning AssignmentDocument8 pagesBS Assignment Brief - Strategic Planning AssignmentParker Writing ServicesNo ratings yet
- Plant Layout: Submitted By: Lalit MagoDocument18 pagesPlant Layout: Submitted By: Lalit MagoAngelina WattssNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2 - Plant ManagementDocument58 pagesChapter - 2 - Plant ManagementakhilNo ratings yet
- Plant LayoutDocument28 pagesPlant LayoutkirandatarNo ratings yet
- Plant Layout: Lecture Conducted by Apoorva Srivastava, ABS, AMITY, LucknowDocument65 pagesPlant Layout: Lecture Conducted by Apoorva Srivastava, ABS, AMITY, LucknowKavya KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- 02-2 Plant Layout & Piping SystemDocument10 pages02-2 Plant Layout & Piping SystemJhoann CastroNo ratings yet
- 02-2 Plant Layout & Piping SystemDocument10 pages02-2 Plant Layout & Piping SystemLady Abegail AbraoNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 PlantlayoutDocument68 pagesChapter-3 PlantlayoutsrikantushaNo ratings yet
- MP Safety & LayoutDocument11 pagesMP Safety & LayoutM IRFANNo ratings yet
- Types of Layout-PPCDocument14 pagesTypes of Layout-PPCPrajwal RahangdaleNo ratings yet
- Layout DesignDocument5 pagesLayout DesignJessie Radaza Tutor0% (1)
- Product, Process, Fixed and Group LayoutsDocument21 pagesProduct, Process, Fixed and Group LayoutsAjith AntonyNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2021-22 MEE1018 TH VL2021220503069 Reference Material I 01-03-2022 Module 4Document78 pagesWINSEM2021-22 MEE1018 TH VL2021220503069 Reference Material I 01-03-2022 Module 4Harsh VermaNo ratings yet
- Classification and Advantages of Plant LayoutDocument6 pagesClassification and Advantages of Plant LayoutKrishna big fan of maheshbabuNo ratings yet
- Plant-Layout NotesDocument17 pagesPlant-Layout NotesRahul DesaiNo ratings yet
- Plant or Facility LayoutDocument9 pagesPlant or Facility LayoutKelvin mwaiNo ratings yet
- Plant Layout Operation ManagementDocument7 pagesPlant Layout Operation ManagementKAPIL VARSHNEYNo ratings yet
- Product Vs Process LayoutDocument4 pagesProduct Vs Process LayoutvmktptNo ratings yet
- Chapter ThreeDocument60 pagesChapter ThreeEndashaw YohannesNo ratings yet
- Operations Management: Layout and Flow Designs INDocument24 pagesOperations Management: Layout and Flow Designs INIsaac OwusuNo ratings yet
- 05facility LayoutDocument31 pages05facility LayoutDivya ShindeNo ratings yet
- What Is A Plant LayoutDocument5 pagesWhat Is A Plant LayoutVIVEK KUMAR SINGH 13No ratings yet
- Plant Location & Layout DesignDocument26 pagesPlant Location & Layout DesignAli MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Kombolcha Institute of Technology Department of Industrial EngineeringDocument41 pagesKombolcha Institute of Technology Department of Industrial EngineeringFakihat MohammedNo ratings yet
- Plant/Facility LayoutDocument6 pagesPlant/Facility Layoutsourav736eeNo ratings yet
- Operations Management (Bba)Document23 pagesOperations Management (Bba)sssNo ratings yet
- 6-Classification of Layout and Mhs - 160811Document4 pages6-Classification of Layout and Mhs - 160811pammy313No ratings yet
- Om Chapter SixDocument10 pagesOm Chapter Sixsamrawithagos2002No ratings yet
- Plantlayout 111109213112 Phpapp02Document18 pagesPlantlayout 111109213112 Phpapp02Bala KumaranNo ratings yet
- Operation Management RoughDocument9 pagesOperation Management RoughRashi virkudNo ratings yet
- IEM Unit 1Document21 pagesIEM Unit 1M.suresh SureshNo ratings yet
- Facility LayoutDocument16 pagesFacility LayoutViraj DhuriNo ratings yet
- Plant Layout TelsangDocument10 pagesPlant Layout TelsangKhushi SalgaonkarNo ratings yet
- F INALITYp 3Document23 pagesF INALITYp 3api-3701467100% (1)
- CH 8 Facility Layout - Part1Document29 pagesCH 8 Facility Layout - Part1Muhammad FurqanNo ratings yet
- Class 12 - (Facility Layout)Document11 pagesClass 12 - (Facility Layout)Amna FaisalNo ratings yet
- Plant Layout: Concept, Objectives, Principles and TypesDocument6 pagesPlant Layout: Concept, Objectives, Principles and Typesbernabas100% (1)
- Facilities Layout (Plant Layout)Document8 pagesFacilities Layout (Plant Layout)Kunwar Sa Amit SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Layout Planning Models and DesignDocument14 pagesChapter 6 Layout Planning Models and DesignAngel Micah NepomucenoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Layout Planning Models and DesignDocument14 pagesChapter 6 Layout Planning Models and DesignAngel Micah NepomucenoNo ratings yet
- Facility Layout, PPTDocument22 pagesFacility Layout, PPTsakhawatNo ratings yet
- Facility LayoutDocument34 pagesFacility LayoutTabi AlamNo ratings yet
- Strategic Resource Organization: Facilities Layout: Chapter SixDocument56 pagesStrategic Resource Organization: Facilities Layout: Chapter SixAngela Vidal EstilNo ratings yet
- Mid-Term Assignmen, Group 2WF., Alaa AboualiDocument5 pagesMid-Term Assignmen, Group 2WF., Alaa AboualiAlaa AboaliNo ratings yet
- Facility Layout PRINTABLEDocument8 pagesFacility Layout PRINTABLEMahnoor HayatNo ratings yet
- Week - 5 LAQ - Operations ManagementDocument5 pagesWeek - 5 LAQ - Operations Managementbabitha76260No ratings yet
- Plant LayoutDocument30 pagesPlant LayoutRashi MehraNo ratings yet
- PLant Location - JegadeesanDocument17 pagesPLant Location - JegadeesanShuaib AktharNo ratings yet
- Plant LayoutDocument71 pagesPlant LayoutVikash GuptaNo ratings yet
- 5facility Layout PlanningDocument14 pages5facility Layout PlanningAman SinghNo ratings yet
- PPC-Lec-4-Plant LayoutDocument6 pagesPPC-Lec-4-Plant LayoutRakib100% (1)
- Plant Layout: Concept, Objectives, Principles and TypesDocument9 pagesPlant Layout: Concept, Objectives, Principles and TypesAfad KhanNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Plant LayoutDocument20 pagesPresentation On Plant LayoutSahil NayyarNo ratings yet
- Facility Layout NotesDocument6 pagesFacility Layout NotesOckouri BarnesNo ratings yet
- Plant LayoutDocument51 pagesPlant Layoutعبدالله عمرNo ratings yet
- Facility LayoutDocument36 pagesFacility LayoutRishabh MahajanNo ratings yet
- Process SelectionDocument30 pagesProcess Selectionjaspreet444100% (1)
- Batch Process Presentation)Document17 pagesBatch Process Presentation)Telse Simon100% (1)
- 1613938959om Module 2 Plant Layout Principles of Layout Product and ProcesDocument6 pages1613938959om Module 2 Plant Layout Principles of Layout Product and Procesjuhy vincentNo ratings yet
- Facility LayoutDocument24 pagesFacility LayoutShahenaNo ratings yet
- Fiscal Policy in A Developing Country 2014Document19 pagesFiscal Policy in A Developing Country 2014D Nitins SharmaNo ratings yet
- Total Quality Management & Cost of QualityDocument16 pagesTotal Quality Management & Cost of QualityD Nitins SharmaNo ratings yet
- SEBI Investor Protection GuidelinesDocument1 pageSEBI Investor Protection GuidelinesD Nitins SharmaNo ratings yet
- SIP Guidelines For Students 2014Document11 pagesSIP Guidelines For Students 2014D Nitins SharmaNo ratings yet
- Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer RelationshipsDocument53 pagesMarketing: Managing Profitable Customer RelationshipsD Nitins SharmaNo ratings yet
- 3 - BREAK EVEN ANALYSIS - UploadDocument5 pages3 - BREAK EVEN ANALYSIS - Uploadniaz kilamNo ratings yet
- Lec06c - Bsa 2103 - 011920Document12 pagesLec06c - Bsa 2103 - 011920PeachyNo ratings yet
- Module 2-Asset Allocation-Questions AwniW26jEKDocument21 pagesModule 2-Asset Allocation-Questions AwniW26jEKKp PatelNo ratings yet
- MJC 2 Unit 1,2,3 Business Organisation and ManagementDocument14 pagesMJC 2 Unit 1,2,3 Business Organisation and Managementnk531114No ratings yet
- Shinny Jewel C. Vingno BSA-2 Problem 1-18Document7 pagesShinny Jewel C. Vingno BSA-2 Problem 1-18Shinny Jewel VingnoNo ratings yet
- DIGEST - CIR Vs NLRCDocument2 pagesDIGEST - CIR Vs NLRCMocha Bear100% (2)
- Seminar of Mobile Data MvnoDocument0 pagesSeminar of Mobile Data Mvnofahmi810091No ratings yet
- Petty Cash CycleDocument22 pagesPetty Cash CycleSAlah MOhammed100% (1)
- Construction of Irrigation SchemesDocument46 pagesConstruction of Irrigation SchemesZed Phil Ind100% (1)
- CV Example For ITDocument4 pagesCV Example For ITAleksandar JakimovoskiNo ratings yet
- Presented By-Priya Khandelwal Honey Chordia Sanjhi Neema Mba FT - Iiird Sem DDocument9 pagesPresented By-Priya Khandelwal Honey Chordia Sanjhi Neema Mba FT - Iiird Sem Dpriya khandelwalNo ratings yet
- Yamazumi Process Modeling Tool AdaptiveBMSDocument9 pagesYamazumi Process Modeling Tool AdaptiveBMSBharathNo ratings yet
- Fitero B. Garlitos 2017-E905019: Multiple ChoiceDocument2 pagesFitero B. Garlitos 2017-E905019: Multiple Choicefitz garlitosNo ratings yet
- Ang Tek Lian Vs CADocument2 pagesAng Tek Lian Vs CALee Somar100% (1)
- Toaz - Info Partnership Qs PRDocument8 pagesToaz - Info Partnership Qs PRToni Rose Hernandez LualhatiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Front Office - Chapter1Document61 pagesIntroduction To Front Office - Chapter1Mary Pauline Musca100% (2)
- Applied EconomicsDocument5 pagesApplied EconomicsMaritess Madrid EsperanzaNo ratings yet
- NPD AssignmentDocument3 pagesNPD AssignmentNicky BojeNo ratings yet
- World's Fair Corporation: Executive Committee Meeting Minutes 2Document210 pagesWorld's Fair Corporation: Executive Committee Meeting Minutes 2JohnWilliams86No ratings yet
- SAIC-K-4042 Rev 7Document2 pagesSAIC-K-4042 Rev 7shahzadaNo ratings yet
- HR Critique Paper The Busines of The Business Is HumanDocument2 pagesHR Critique Paper The Busines of The Business Is HumanAnthonyTiuNo ratings yet
- Marketing Strategy of Oriflame India PVT LTD ProjectDocument84 pagesMarketing Strategy of Oriflame India PVT LTD ProjectMona100% (1)
- Link Building ResourcesDocument103 pagesLink Building ResourcesSADGURU AMRITWANI50% (2)
- A Final Board Packet August 7, 2013 - 0.... 5Document199 pagesA Final Board Packet August 7, 2013 - 0.... 5نيرمين احمدNo ratings yet
- Accounting Cycle, Entries and ConceptDocument64 pagesAccounting Cycle, Entries and Conceptdude devil100% (1)
- Construction Manager DutiesDocument5 pagesConstruction Manager Dutiesashsundar100% (1)
- Press Release: For Immediate DistributionDocument3 pagesPress Release: For Immediate DistributionThallusrhamesNo ratings yet
- MisDocument17 pagesMisAyan SnehashisNo ratings yet
- MES Buyers GuideDocument22 pagesMES Buyers GuidetuvaohNo ratings yet