Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2
2
Uploaded by
Mohmd AbunadaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2
2
Uploaded by
Mohmd AbunadaCopyright:
Available Formats
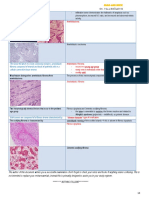
Ameloblastoma
Aameloblastoma
Ameloblastoma
Ameloblastoma
Peripheral Ameloblastoma
ameloblastoma
Ameloblastoma
2. Adenoameloblastoma.
Histological the tumor is characterized by duct like structures
consisting the epithelium compartment of the tumor.
It is encapsulated.
Clinically :
It occurs in young age 2
nd
&3
rd
decade of life.
More common in female.
More common in maxilla.
Usually associated with unerupted tooth
Radio graphically :
Unilocular radiolucent lesion which may resemble.
Treatment :
Since it is encapsulated and not aggressive like ameloplastoma,
conservative surgical excision or enucleation is sufficient.
Adeomatoid
odontogenic
tumor
Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor
Adenomatatoid odontogenic tumor
Adeno-
Ameloblastoma
Adenoameloblastoma
3. Odontoma
a. Compound composite Odon tome .
In which the hard tissues resemble teeth regardless the size and number, and
appear in x-ray as variable numbers of tooth like structure surrounded with
radiolucent line.
b. Complex composite Odon tome.
In which calcified dental structures (enamel, dentin and cement ) may be
scattered without any special pattern.
4. Cementoma .
It is rare solitary slow growing lesion.
It affects the mndibular molar and premolar area.
Radio graphically, it appears as well defined radio-opaque mass surrounded
by radiolucent.
The tumor mass is usually attached to the roots of the teeth.
Per apical cementoma
Complx
odontoma
Complex odontoma
Complex odontoma
Compound
odontoma
Compound odontoma
Compound odontoma
Compound
odontoma
Osteogenic tumors.
1. Osteoma.
a. Enostosis (central osteoma ).
It may be a central area of dense cortical bone.
Radio graphically it is a central circumscribed radio-opaque area.
b. Enostosis (peripherals osteoma ).
Such as torus palatinus, and torus mandibhlaris.
Treatment is by surgical excision.
2. fibro-osteoma or ossifying fibroma.
It is a relatively slow growing tumor that cause early displacement of teeth.
It also cause varying degrees of facial deformity.
Radio graphically, radio-opaque of varying densities
3. Chondroma .
It is a rare tumor of embryonic tissue origin from remnants of immature
cartilage cells.
It is slowly growing and usually appears as a radiolucent area in
radiographs.
It has a great tendency to malignant change.
o s t e o m a
osteoma
Ossifying fiberoma
Peripheral ossifying fibroma
Buccal exostosis
Torus palatinus
Buccal exostosis
Torus mandibularis
4. Myxoma ( fibromyxoma).
It is a tumor of embryonic tissue origin from primitive immature cells, the
one is collapsed by mucoid material.
This tumor is not capsulated.
It is locally invasive, painless slowly growing, producing facial
disfigurement.
It affects the mandible more than the maxilla.
Radio graphically. Honey-comb appearance.
5. Central giant cell lesion ( granuloma or tumor ).
Trauma is suspected to cause the benign lesion.
It affect the symphysis or the angle of the mandible and the maxilla at the
canine fossa.
It produce a painless swelling.
It causes looseness of the teeth and root resorption.
When the cortical plate is perforated by the tumor, bleeding become
frequently from slight trauma to tumor tissues
Radigraphically :
Mulilocular radiolucency with irregular margin.
Treatment :Surgical removal.
Giant cell granuloma
Central giant cell granuloma
Central giant
cell
granuloma
Central giant cell granuloma
Tumor like lesions of the jaws
: Fibrous dysplasia
It shows replacement of normal spongiosa with fibrous tissues, it is slowly
growing.
It tends grow in the 2
nd
decade of life, then stop.
It may produce pronounced facial asymmetry.
It may appear as a radiolucent area in the early stage , then diffuse radio-
opaque mass.
Treatment : conservative surgical contouring.
(Familial Fibrous Dysplasia): Cherubim
It is familial fibrous dysplasia, that becomes noticeable during the 2
nd
and
3
rd
years of life when fullness of the cheeks.
Gradual improvement or cessation of growth occurs after 10years of age.
Polyostotic Fibrous Dysplasia(Albrights
Syndrome
Affects limb,skull,and jaws during childhood, with cutaneous
pigmentation, endocrine disorders, precocious puberty & premature
skeleton maturation.
Hyperparathyroidism ( Brown tumor )
Increase of serum calcium phosphorus, and
serum alkaline phsphatase which is an
important sign of this lesion.
Radigraphically :Ground glass appearance of
the alveolar bone.
Resolution occur only after parathyroidectomy
Ossifying fibroma
Ossifying fibroma
Fibrous dysplasia
Fibrous dysplasia
cherubism
cherubim
cherubim
cherubism
cherubim
Hyperparathyroidism ( brown tumor)
Hyperpara thyroidism
Premalignant lesions
a. Leukoplakia :
It is white patch or plaque occurring on the surface of the mucous
membrane.
The buccal mucosa, commeasures are most frequently involved,
followed by alveolar mucosa, tongue, lip, hard and soft palates, floor of
the mouth and gingiva.
The surface of the lesion is often rough.
The lesion are white, gray or yellowish white.
b. Leukoedema.
It varies from family opalescence of the mucosa to more definite grayish
white cast with a coarsely wrinkled surface in later stages.
It involves most of the buccal mucosa, and the oral surface of the lips.
c. Intraepithelial carcinoma : ( carcinoma in situ ).
It is a precancerous dyskeratotic process.
Keratininzation is common feature.
The disease in the oral mucosa may appear as an erythromatous, velvet
plaque.
Most common located on gingiva and soft palate.
leukoplakia
leukoplakia
leukoplakia
leukoplakia
You might also like
- Hema 2 - Prelim Topic 1-Intro To HemostasisDocument4 pagesHema 2 - Prelim Topic 1-Intro To HemostasisLowenstein JenzenNo ratings yet
- Grabovoi Numbers For HealingDocument23 pagesGrabovoi Numbers For HealingAna BrunetteNo ratings yet
- AmeloblastomaDocument39 pagesAmeloblastomaarpitpandey961No ratings yet
- Odontogenic Tumor Ameloblastoma: Presented By: Ankita Singh Bds Final Year Roll No 37Document73 pagesOdontogenic Tumor Ameloblastoma: Presented By: Ankita Singh Bds Final Year Roll No 37ankita sethiNo ratings yet
- Odontogenic Tumor: Oral PathologyDocument17 pagesOdontogenic Tumor: Oral PathologyJoker KillerNo ratings yet
- Typical Radiological Features of Tumors and Tumor-Like LesionsDocument19 pagesTypical Radiological Features of Tumors and Tumor-Like LesionsWala GhayadaNo ratings yet
- Oral Pathology: 2-Mesenchymal Origin Tumors A - Odontogenic FibromaDocument4 pagesOral Pathology: 2-Mesenchymal Origin Tumors A - Odontogenic Fibromaعلي صادق جعفرNo ratings yet
- Oral Pathology: Odontogenic TumorsDocument5 pagesOral Pathology: Odontogenic Tumorsعلي صادق جعفرNo ratings yet
- Ameloblastoma: DR - Ansar Uddin Ahmed Asst. Prof and Head Periodontology, Oral Pathology and Oral MedicineDocument33 pagesAmeloblastoma: DR - Ansar Uddin Ahmed Asst. Prof and Head Periodontology, Oral Pathology and Oral MedicineTas DidNo ratings yet
- Benigntumorsofjaw2 130421054527 Phpapp01Document118 pagesBenigntumorsofjaw2 130421054527 Phpapp01orthomedNo ratings yet
- Ameloblastoma 140624025211 Phpapp02Document51 pagesAmeloblastoma 140624025211 Phpapp02agusNo ratings yet
- Odontogenic MyxomaDocument17 pagesOdontogenic MyxomaMomiji MoritaNo ratings yet
- DevelopmentDocument6 pagesDevelopmentScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Odontogenic TumorsDocument13 pagesOdontogenic Tumorsa.ahmed4922No ratings yet
- Odontomes & Odontogenic Tumors II (Slide 18+19)Document39 pagesOdontomes & Odontogenic Tumors II (Slide 18+19)JustDen09No ratings yet
- HEAD AND NECK 1.robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease ReviewerDocument14 pagesHEAD AND NECK 1.robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease ReviewerSeff Causapin100% (1)
- Odontogenic Tumors4Document69 pagesOdontogenic Tumors4LuthfieHaqNo ratings yet
- Radiographic Interpretation of Tumors of The Jaws: Drg. Shanty Chairani, M.SiDocument82 pagesRadiographic Interpretation of Tumors of The Jaws: Drg. Shanty Chairani, M.SiDini Dwi PuspitaNo ratings yet
- Ameloblastoma: Submitted byDocument9 pagesAmeloblastoma: Submitted byJana AliNo ratings yet
- Odontogenic Tumor PDFDocument93 pagesOdontogenic Tumor PDFEmad Alriashy100% (1)
- Ameloblasto MA: Submitted by Manjari Reshikesh Iv Bds Part Ii Department of Oral and Maxillofacial SurgeryDocument51 pagesAmeloblasto MA: Submitted by Manjari Reshikesh Iv Bds Part Ii Department of Oral and Maxillofacial SurgeryDrRobin SabharwalNo ratings yet
- Benign Non Odontogenic Lesions - 6Document97 pagesBenign Non Odontogenic Lesions - 6Thaer ZabenNo ratings yet
- A Review of AmeloblastomaDocument23 pagesA Review of Ameloblastomagustian_ballack0% (1)
- Mixed Tumors of Odontogenic Origin WordDocument31 pagesMixed Tumors of Odontogenic Origin WordAshimNo ratings yet
- Odontogenic TumorsDocument32 pagesOdontogenic Tumorssatya_mds100% (2)
- Oral Pathology Lec - 1Document11 pagesOral Pathology Lec - 1مصطفى محمدNo ratings yet
- Odontogenic TumorDocument56 pagesOdontogenic TumoramieNo ratings yet
- Odontogenic Tumors IIDocument24 pagesOdontogenic Tumors IIIbn HabibNo ratings yet
- Odontomes & Odontogenic Tumors I: Dr. Tahani AbualteenDocument35 pagesOdontomes & Odontogenic Tumors I: Dr. Tahani AbualteenPrince AhmedNo ratings yet
- Lec. 8 Malignant Bone TumorsDocument17 pagesLec. 8 Malignant Bone Tumorsنور كاضمNo ratings yet
- Benign Bone TumorsDocument63 pagesBenign Bone TumorsAstrid Bernadette Ulina Purba0% (1)
- Session 8 Odontogenic and Non Odontogenic TumorsDocument74 pagesSession 8 Odontogenic and Non Odontogenic TumorsZNo ratings yet
- Case Report Ameloblastic Fibroma: Report of 3 Cases and Literature ReviewDocument5 pagesCase Report Ameloblastic Fibroma: Report of 3 Cases and Literature ReviewcareNo ratings yet
- Odonto Genic TumorsDocument7 pagesOdonto Genic TumorsMcmac YangoNo ratings yet
- New PPT OmrDocument25 pagesNew PPT OmrMinnuNo ratings yet
- Non Odontogenic Tumours of JawDocument22 pagesNon Odontogenic Tumours of JawDrMuskan AroraNo ratings yet
- Submitted by Manjari Reshikesh Iv Bds Part Ii Department of Oral and Maxillofacial SurgeryDocument51 pagesSubmitted by Manjari Reshikesh Iv Bds Part Ii Department of Oral and Maxillofacial SurgerykishoreNo ratings yet
- Oral Pathology - Pathology of JawsDocument35 pagesOral Pathology - Pathology of JawsamaliaNo ratings yet
- Fibrosarcoma Differential DiagnosisDocument10 pagesFibrosarcoma Differential DiagnosisdmdsahNo ratings yet
- Jaw LesionsDocument11 pagesJaw LesionsJose Siritt100% (1)
- Benign Odontogenic Tumors of Jaws (AmeloblastomaDocument70 pagesBenign Odontogenic Tumors of Jaws (Ameloblastomagalina poberezhnikNo ratings yet
- ADAMANTINOMADocument8 pagesADAMANTINOMAfadhlanahmadsNo ratings yet
- Cyst and TumorsDocument40 pagesCyst and TumorsVaibhavi MinotraNo ratings yet
- 10.odontogenic TumorsDocument102 pages10.odontogenic Tumorsabdelrahman amrNo ratings yet
- Bone Tumors: Prepared by DR Pgr.2 Ortho Unit 3 BMCHDocument47 pagesBone Tumors: Prepared by DR Pgr.2 Ortho Unit 3 BMCHMohamed Al-zichrawyNo ratings yet
- Cemento Ossifying Fibroma: A Case ReportDocument4 pagesCemento Ossifying Fibroma: A Case ReportBima Ewando KabanNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis of Pericoronal RadiolucenciesDocument30 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of Pericoronal RadiolucenciesakNo ratings yet
- Unicystic Ameloblastoma in A 23 Year Old Male: A Case: Richa Wadhawan, Bhuvnesh Sharma, Pulkit Sharma and Dharti GajjarDocument6 pagesUnicystic Ameloblastoma in A 23 Year Old Male: A Case: Richa Wadhawan, Bhuvnesh Sharma, Pulkit Sharma and Dharti GajjarTriana Amaliah JayantiNo ratings yet
- Odontogenic Tumours: BY: DR - Madhulaxmi.M Mod: DR - SatishDocument45 pagesOdontogenic Tumours: BY: DR - Madhulaxmi.M Mod: DR - SatishMohammed ZuhaibNo ratings yet
- Dr. Yoseph - The Role of Radiotherapy in The Management of Ameloblastoma and Ameloblastic CarcinomaDocument10 pagesDr. Yoseph - The Role of Radiotherapy in The Management of Ameloblastoma and Ameloblastic CarcinomaOnkologi Radiasi Angkatan 23No ratings yet
- Epulis Fibromatosa MedscapeDocument6 pagesEpulis Fibromatosa MedscapeSofiyahH.AbdulKarimNo ratings yet
- Odontogenic Tumors and Related Jaw Lesions: A) Benign Epithelial TumorsDocument19 pagesOdontogenic Tumors and Related Jaw Lesions: A) Benign Epithelial Tumorsluna zeidNo ratings yet
- Benign Tumors of Epithelial and Mesenchymal Origin inDocument41 pagesBenign Tumors of Epithelial and Mesenchymal Origin inMladen PazinNo ratings yet
- Mixed Radiolucent-Radiopaque LesionsDocument35 pagesMixed Radiolucent-Radiopaque LesionsAmitaNo ratings yet
- Ipe Varghese. V Sudha. S Resmi G. Nair Sherin. NDocument5 pagesIpe Varghese. V Sudha. S Resmi G. Nair Sherin. NeditorompjNo ratings yet
- ODONTOGENIC TUMORS LectureDocument133 pagesODONTOGENIC TUMORS LectureSama N SamirNo ratings yet
- 6 Pediatric Odontogenic Tumors. Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Clinics of North AmericaDocument14 pages6 Pediatric Odontogenic Tumors. Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Clinics of North AmericaalexandreNo ratings yet
- Odontogenic Tumours - (2) L5Document28 pagesOdontogenic Tumours - (2) L5nooraaaNo ratings yet
- Fibrous DysplasiaDocument2 pagesFibrous DysplasiaGus SwanjayaNo ratings yet
- Cholesteatoma, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandCholesteatoma, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Oral Medicine & Pathology from A-ZFrom EverandOral Medicine & Pathology from A-ZRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (9)
- ECR 2024 ProgrammeDocument1,040 pagesECR 2024 ProgrammeLídia AnikNo ratings yet
- EMPHYSEMADocument3 pagesEMPHYSEMATryx N' Krix TrimorNo ratings yet
- Blunt Trauma AbdomenDocument41 pagesBlunt Trauma AbdomenSanthanu SukumaranNo ratings yet
- Rwanda Medicaments EssentielsDocument85 pagesRwanda Medicaments EssentielsportosinNo ratings yet
- Couching in Ancient India: SushrutaDocument3 pagesCouching in Ancient India: SushrutaDeepak RamNo ratings yet
- Topnotch Pharma Supertable JAN 2016Document166 pagesTopnotch Pharma Supertable JAN 2016Dar AD50% (2)
- .Spina Bifida UPDATED2Document33 pages.Spina Bifida UPDATED2Ess IsnotyouNo ratings yet
- Ebus PDFDocument5 pagesEbus PDFNikolay ToméNo ratings yet
- Note by Izza - Acute Decompensated Heart FailureDocument3 pagesNote by Izza - Acute Decompensated Heart FailureIzzati N. SariNo ratings yet
- 2003 ADA Preconception Care DiabetesDocument3 pages2003 ADA Preconception Care Diabetesannisafaujiah033No ratings yet
- Jeffreybtruongresume Medical SchoolDocument3 pagesJeffreybtruongresume Medical Schoolapi-531418816No ratings yet
- Fever in IcuDocument17 pagesFever in Iculakshminivas PingaliNo ratings yet
- Dermatology Supplement v2018 PDFDocument39 pagesDermatology Supplement v2018 PDFVenice Jamaila DagcutanNo ratings yet
- Implementing Improvement Strategies To Prevent Unplanned Extubation in Neonatal Intensive Care Units - SLIDE DECKDocument19 pagesImplementing Improvement Strategies To Prevent Unplanned Extubation in Neonatal Intensive Care Units - SLIDE DECKeman hamzaNo ratings yet
- Lower Section Caeserian SectionDocument7 pagesLower Section Caeserian SectionSampat Kumawat100% (4)
- In The Know Understanding The Cancer ExperienceDocument24 pagesIn The Know Understanding The Cancer ExperienceTedEscobedoNo ratings yet
- Hypertonic Saline (3% and 5% Sodium Chloride Injection) Drug Information - Description, User Reviews, Drug Side Effects, Interactions - Prescribing Information at RxListDocument2 pagesHypertonic Saline (3% and 5% Sodium Chloride Injection) Drug Information - Description, User Reviews, Drug Side Effects, Interactions - Prescribing Information at RxListMuhammad AsadNo ratings yet
- What Is A Migraine?Document7 pagesWhat Is A Migraine?AngelaNo ratings yet
- Bangsal GIN MG 1Document10 pagesBangsal GIN MG 1Iman Ru-ancaNo ratings yet
- Final Announcement KOPAPDI XVIII Semarang 2022Document25 pagesFinal Announcement KOPAPDI XVIII Semarang 2022Ayu Ika PuspitaNo ratings yet
- Laryngeal Cancer Concept MapDocument1 pageLaryngeal Cancer Concept MapTessa Claire JaranowskiNo ratings yet
- National Guidelines On Management of Dengue Fever & Dengue Haemorrhagic Fever in Children and Adolescents - Sri LankaDocument53 pagesNational Guidelines On Management of Dengue Fever & Dengue Haemorrhagic Fever in Children and Adolescents - Sri LankaNational Dengue Control Unit,Sri Lanka100% (1)
- Low Back Pain and Associated Risk Factors Among.8Document6 pagesLow Back Pain and Associated Risk Factors Among.8Teti HLCNo ratings yet
- Perinat FinalDocument44 pagesPerinat FinalMaanNo ratings yet
- DR - Elamaran.E Senior Resident Dept. of CTVS, JIPMERDocument43 pagesDR - Elamaran.E Senior Resident Dept. of CTVS, JIPMEREla MaranNo ratings yet
- Photodynamic TherapyDocument5 pagesPhotodynamic TherapyPranav UpadhyayaNo ratings yet
- Do Not Resuscitate Order FORDocument3 pagesDo Not Resuscitate Order FORQiew IkiNo ratings yet
- Case Report: Penile ParaffinomaDocument2 pagesCase Report: Penile ParaffinomaNunuh SulaemanNo ratings yet