Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tractus Urinarius: Departemen Anatomi Fk-Usu Medan
Tractus Urinarius: Departemen Anatomi Fk-Usu Medan
Uploaded by
CindyDevinaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tractus Urinarius: Departemen Anatomi Fk-Usu Medan
Tractus Urinarius: Departemen Anatomi Fk-Usu Medan
Uploaded by
CindyDevinaCopyright:
Available Formats
DEPARTEMEN ANATOMI
FK-USU
MEDAN
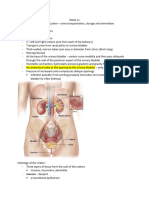
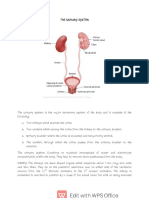
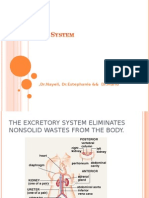
Tractus urinarius
The urinary system of the human body consists of
two kidneys, two ureters, the bladder and a single
urethra.
The kidneys are located on the posterior wall of the
abdomen at waist level. Each kidney is roughly 10
cm long and 5 cm wide, and is encased in a fibrous
outer capsule called the renal capsule.
The main function of the kidneys is to control blood
volume and composition. They do this by filtering
the blood to remove waste products, salts and
water. These are secreted in the form of urine.
The kidneys are located in the posterior part of the
abdomen.
There is one on each side of the spine ,the right kidney
sits just below the liver, the left below the diaphragma
and adjacent to the spleen.
Above each kidney is an adrenal gland (also called the
suprarenal gland). The asymmetry within the abdominal
cavity caused by the liver results in the right kidney
being slightly lower than the left one while the left kidney
is located slightly more medial.
The kidneys are retroperitoneal and
They are approximately at the vertebral level T12 to L3.
The upper parts of the kidneys are partially protected by
the eleventh and twelfth ribs.
Congenital absence of one or both kidneys, known as
unilateral or bilateral renal agenesis, can occur
Ureter
The ureters deliver urine to the bladder from the kidney to
bladder.
The ureters are retroperitoneal, which means that they are
located in the retroperitoneal space .
In adults the ureters are approx 12 inches (30 cm) long and have
a muscular coat that tightens and relaxes to move urine away
from the kidney. This muscular action is controlled by the
autonomic nervous system (ANS) and operates in a similar way
to that of peristalsis in the digestive system.
The ureters pass through the posterior surface of the bladder at
the Ureter Orifices.
Urine drains through the ureters directly into the bladder as there
are no sphincter muscles or valves at the ureter orifices
Bladder
The bladder is located on the floor of the pelvic
cavity. (Other organs, glands and tissues located
in the pelvic cavity include the rectum, gender-
specific reproductive organs, parts of the small
intestine, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and
nerves).
The bladder is located anterior to (i.e. in front of)
the rectum in males.
In females it is also in front of the uterus and
upper vagina so its location is described simply
as "anterior to the uterus and upper vagina".
The urinary bladder is a musculomembranous
sac whose shape is affected by factors including
the person's age and sex - as well as the volume
of urine it contains at the time.
The "superior" or "abdominal" surfaces, and the
"lateral" surfaces of the bladder are covered by
peritoneum.
Bladder in pelvic cavity
Structure of Bladder
The bladder itself ("musculomembranous sac") consists of 4
layers:
Serous
The outer "serous" layer is a partial layer derived from the
peritoneum.
Muscular
The detrusor muscle is the muscle of the urinary bladder
wall.
It consists of three layers of smooth (involuntary) muscle
fibres. The external layer is longitudinal, the middle layer is
circular configuration, and the internal layer is longitudinal .
Sub-mucous
This is a thin layer of areolar tissue .
Mucous
The innermost layer,which contains transitional epithelium
tissue that can stretch. The ability of this tissue to stretch is
important because it contains variable volumes of liquid - as
the bladder is filled and emptied several times per day.
Because it is only loosely attached to the (strong and
substantial) muscular layer, the mucosa falls into many folds
known as rugae when the bladder is empty or is only filled
to a small extent.
Female urethra
At only about 1.5 inches (35 mm) long, the female adult
urethra is shorter than the adult male urethra (approx. or
8 inches, or 200mm).
The female urethra is located immediately behind the
pubic symphysis and is embedded into the front wall of
the vagina.
The urethra itself is a narrow membranous canal that
consists of three layers:
Muscular layer - continuous with the muscular layer of
the bladder, this extends the full length of the urethra.
Thin layer of spongy erectile tissue - including
plexus of veins and bundles of smooth muscle fibres.
Located immediately below the mucous layer.
Mucous layer - internally continuous with the
bladder and lined with laminated epithelium that is
transitional near to the bladder.
After passing through the urogenital diaphragm ,the
female urethra ends at the external orifice of
urethra - which is the point at which the urine leaves
the body. This is located between the clitoris and the
vaginal opening.
The passage of urine along the urethra through the
urogenital diaphragm is controlled by the external
urethral sphincter, which is a circular muscle under
voluntary control (that is, it is innervated by the
somatic nervous system, SNS
Male urethra
At about 8-9 inches (200 mm) long, the adult
male urethra is longer than the adult female
urethra (of approx. 1.5 inches 35 mm).
It has three portions (the prostatic urethra, the
membranous urethra, and the spongy urethra )
and extends from the neck of the bladder to the
meatus urinarius at the end of the male
penis/urethra.
The three regions/sections of the male urethra are:
Prostatic Urethra
The prostatic urethra begins at the neck of the bladder
and includes all of the section that passes through the
prostrate gland. It is the widest and most dilatable part
of the male urethral canal.
Membranous Urethra
The membranous urethra is the shortest and narrowest
part of the male urethra. This section measures approx.
0.5 - 0.75 inches (12 - 19 mm) in length and is the
section of the urethra that passes through the male
urogenital diaphragm.
The external urethral sphincter (muscle) is located in
the urogenital diaphragm (as for the female urethra).
The passage of urine along the urethra through the
urogenital diaphragm is controlled by the external
urethral sphincter, which is a circular muscle under
voluntary control (that is, it is innervated by the somatic
nervous system, SNS).
Spongy Urethra
The spongy urethra is the longest of the three
sections.
It is approx. 6 inches (150 mm) in length
It is contained in the corpus spongiosum that
extends from the end of the membranous portion,
passes through the penis, and terminates at the
external orifice of the urethra - which is the point
at which the urine leaves the body.
Thank you
You might also like
- NCA Criminal Law NotesDocument58 pagesNCA Criminal Law Notesukrolandas100% (1)
- The Six-Figure Erotica Author How I Make Six Figures Self-Publishing Erotica NodrmDocument35 pagesThe Six-Figure Erotica Author How I Make Six Figures Self-Publishing Erotica NodrmMarcus McCain100% (2)
- Married Women Are Easier To Seduce PDFDocument31 pagesMarried Women Are Easier To Seduce PDFCarlos Reyes83% (24)
- Ricky's Sex Adventure With Richa BhabhiDocument14 pagesRicky's Sex Adventure With Richa Bhabhigoudtsri33% (3)
- Tractus Urinarius: Departemen Anatomi Fk-Usu MedanDocument21 pagesTractus Urinarius: Departemen Anatomi Fk-Usu MedanRizky Indah SorayaNo ratings yet
- Tractus Urinarius: Departemen Anatomi Fk-Usu MedanDocument23 pagesTractus Urinarius: Departemen Anatomi Fk-Usu MedanSuci SinagaNo ratings yet
- Tractus Urinarius: Departemen Anatomi Fk-Usu MedanDocument29 pagesTractus Urinarius: Departemen Anatomi Fk-Usu Medanjazira rezkikaNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Sistem UrinariaDocument30 pagesAnatomi Sistem UrinariaLili ManaoNo ratings yet
- Anatomi GenitourinariaDocument30 pagesAnatomi Genitourinariamelya susantiNo ratings yet
- The Urinary System Is Made Up of The Kidneys, Ureters, Urethra and BladderDocument4 pagesThe Urinary System Is Made Up of The Kidneys, Ureters, Urethra and BladderdodongcharingNo ratings yet
- Lect4 PelvisDocument26 pagesLect4 PelvisasakingofhNo ratings yet
- Anaphy CKDDocument3 pagesAnaphy CKDSTEFFI GABRIELLE GOLEZNo ratings yet
- 14th Lecture - Urinary System 2Document20 pages14th Lecture - Urinary System 2Zainab Jamal SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Note On MICTURATIO1Document10 pagesNote On MICTURATIO1Lilian EdeniNo ratings yet
- What Is The Urinary System and How Does It Work?: KidneysDocument10 pagesWhat Is The Urinary System and How Does It Work?: KidneysAbdelrhman AboodaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument3 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyThirdie LacorteNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Lower Urinary TractDocument24 pagesAnatomy of The Lower Urinary Tractمحمد حميدانNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Kidney StoneDocument13 pagesTreatment of Kidney StoneFarah AthirahNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument31 pagesUrinary SystemAyro Business CenterNo ratings yet
- The Urinary System PPT EdDocument30 pagesThe Urinary System PPT EdGirmay GebrehiwotNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Urinary System: Lesson 1Document23 pagesChapter 9 Urinary System: Lesson 1Tia AriantiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Lower Urinary TractDocument27 pagesAnatomy of The Lower Urinary Tractمحمد حميدانNo ratings yet
- Anatomy N Physiology of UtiDocument6 pagesAnatomy N Physiology of UtiMarjorie PalaganasNo ratings yet
- Urinary System PDFDocument3 pagesUrinary System PDFMukund NaiduNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Urinary Bladder and UrethraDocument16 pagesAnatomy of Urinary Bladder and UrethraAmalina ZolkefleeNo ratings yet
- grp52 UTI DseDocument9 pagesgrp52 UTI DsekcdgrvnNo ratings yet
- Yuniarti: Anatomy Department Faculty of Medicine UnisbaDocument40 pagesYuniarti: Anatomy Department Faculty of Medicine UnisbaalgutNo ratings yet
- The Pelvic Cavity: Dr:Ahmed Ibrahim Abdi (Nawawi) AnatomistDocument44 pagesThe Pelvic Cavity: Dr:Ahmed Ibrahim Abdi (Nawawi) AnatomistSAKARIYE MAXAMEDNo ratings yet
- 2 Ureter, Urinary Bladder and Urethra XJGDocument51 pages2 Ureter, Urinary Bladder and Urethra XJGwcbkk4vt9fNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology The Female Reproductive SystemDocument11 pagesAnatomy and Physiology The Female Reproductive Systemmelody_kaye272000No ratings yet
- The Urinary SystemDocument8 pagesThe Urinary SystemOlivia MorrisonNo ratings yet
- Online Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreDocument63 pagesOnline Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreabctutorNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY OF THE RENAL SYSTEM - Ayesigwa GeraldDocument13 pagesANATOMY OF THE RENAL SYSTEM - Ayesigwa GeraldAyesigwa Gerald96No ratings yet
- Anatomy ReportDocument7 pagesAnatomy Reportمحمود الموسويNo ratings yet
- مشروع ابو زنيد1Document15 pagesمشروع ابو زنيد1Hareth mohammad mahmod NawajaNo ratings yet
- Male Pelvis2Document63 pagesMale Pelvis2365 DaysNo ratings yet
- Histology of Ureter, Urinary Bladder and Urethra by Dr. RoomiDocument20 pagesHistology of Ureter, Urinary Bladder and Urethra by Dr. RoomiMudassar Roomi100% (4)
- Urinary SystemDocument29 pagesUrinary Systemhabibsaqib773No ratings yet
- Ureters Urinary Bladder UrethraDocument20 pagesUreters Urinary Bladder UrethraFlora PopaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Embryology of Bladder: Dr. Deepesh Kalra Institute of Urology Madras Medical College, ChennaiDocument33 pagesAnatomy and Embryology of Bladder: Dr. Deepesh Kalra Institute of Urology Madras Medical College, ChennaiFatima Zahra Rahim ArchiNo ratings yet
- Bio 210 PPDocument18 pagesBio 210 PPRobin McFaddenNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Urinary Bladder and UrethraDocument57 pagesAnatomy of Urinary Bladder and UrethraHussan AraNo ratings yet
- Bladder InteriorDocument44 pagesBladder InteriorAmjad AmjadNo ratings yet
- Urinary Bladder, Urethra, Adrenals, Blood VesselsDocument47 pagesUrinary Bladder, Urethra, Adrenals, Blood VesselsrajeevshamNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 The Urinary System: Learning OutcomesDocument9 pagesUnit 9 The Urinary System: Learning OutcomesDeolita BadiangNo ratings yet
- FemaleDocument2 pagesFemaleAugust Lorence Bosmion DelvoNo ratings yet
- Renal 1Document37 pagesRenal 1febie pacheco100% (2)
- Lecture 2 - Anatomy of The Ureters, Bladder and UrethraDocument7 pagesLecture 2 - Anatomy of The Ureters, Bladder and UrethraNatalie LiNo ratings yet
- Urinary System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument13 pagesUrinary System Anatomy and PhysiologyKBDNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Urinary SystemDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Urinary SystemIan CruzNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Urinary SystemDocument4 pagesAnatomy of Urinary Systemmarkerrolbartolome520No ratings yet
- Topik 2 2021Document26 pagesTopik 2 2021AnnisNo ratings yet
- Digestive and UrinaryDocument23 pagesDigestive and UrinarySamantha EllaineNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Urinary SystemDocument34 pagesAnatomy of Urinary Systemhana100% (1)
- The Kidneys (Nephros) : FunctionsDocument6 pagesThe Kidneys (Nephros) : FunctionsOjambo FlaviaNo ratings yet
- The Urinary SystemDocument11 pagesThe Urinary SystemInvisible eyeNo ratings yet
- Blue Aesthetic Graphic Designer Portfolio PresentationDocument35 pagesBlue Aesthetic Graphic Designer Portfolio PresentationIrfan NasrullahNo ratings yet
- ,DR - Nayeli, DR - Estephanie && DR - MarioDocument7 pages,DR - Nayeli, DR - Estephanie && DR - Mariomsacosta7No ratings yet
- Excretory System ReportDocument15 pagesExcretory System ReportScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Urinary System: Prepared By:louela QuiaoDocument66 pagesUrinary System: Prepared By:louela QuiaoLouela QuiaoNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System 1Document9 pagesReproductive System 1Marvel NnaemekaNo ratings yet
- Bowel and BladderDocument21 pagesBowel and BladderPriya YadavNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Kidney and ExcretionDocument57 pagesPhysiology of Kidney and ExcretionWenny KalamiNo ratings yet
- Y Chromosome Fact SheetDocument1 pageY Chromosome Fact SheetTzuyu TchaikovskyNo ratings yet
- Prof. Vibhuti Patel On Violence Against Women in South AsiaDocument19 pagesProf. Vibhuti Patel On Violence Against Women in South AsiaVibhuti PatelNo ratings yet
- Photo Pro1-3Document24 pagesPhoto Pro1-3saifullahNo ratings yet
- The Queer and Transgender Resilience Workbook 1Document226 pagesThe Queer and Transgender Resilience Workbook 1nikola 89100% (1)
- Boy637@mail - Ru: Contact:, ICQ 4-723-158, Skype - Live:rurulDocument60 pagesBoy637@mail - Ru: Contact:, ICQ 4-723-158, Skype - Live:rurulmetalgrobick1791No ratings yet
- The Impact of Internet Pornography On Marriage And..Document36 pagesThe Impact of Internet Pornography On Marriage And..azxsdc1234100% (1)
- Lusungu Children's Home - ZambiaDocument5 pagesLusungu Children's Home - ZambiaClare Nkwanga-JollyNo ratings yet
- TELLIS, Ashley BALA, Sruti - (Eds) - (2015) - The Global Trajectories of Queerness - Re-Thinking Same-Sex Politics in The Global South.Document270 pagesTELLIS, Ashley BALA, Sruti - (Eds) - (2015) - The Global Trajectories of Queerness - Re-Thinking Same-Sex Politics in The Global South.Junior LopesNo ratings yet
- 49 Best Sex Positions For Better Stimulation and Stronger OrgasmsDocument1 page49 Best Sex Positions For Better Stimulation and Stronger OrgasmsellaNo ratings yet
- EmbryologyDocument15 pagesEmbryologyKoushal Sharma, JammuNo ratings yet
- Crime and The MediaDocument27 pagesCrime and The Mediaapi-291832916No ratings yet
- On Female Identity WritingDocument16 pagesOn Female Identity Writingbetti06No ratings yet
- The LGBT Movement Health Issues - The Dangers of Anal SexDocument51 pagesThe LGBT Movement Health Issues - The Dangers of Anal SexAntonio Bernard100% (1)
- Fonseka DragonfliesDocument320 pagesFonseka DragonfliesKithmini Ouchithya WickramarachchiNo ratings yet
- Dreams Part 1Document10 pagesDreams Part 1nataliekuchikiNo ratings yet
- Sexing Differances: Anne-Emmanuelle BergerDocument17 pagesSexing Differances: Anne-Emmanuelle BergerM. Pilar Palacios AlamosNo ratings yet
- People vs. GarciaDocument15 pagesPeople vs. GarcialeeashleeNo ratings yet
- Rosario 3B Letter To The Agency FINALDocument7 pagesRosario 3B Letter To The Agency FINALSheenly CordovaNo ratings yet
- GEN003 Science Technology Society P1 Q1Document2 pagesGEN003 Science Technology Society P1 Q1jamsnssNo ratings yet
- WalkthroughDocument50 pagesWalkthroughnevermore11No ratings yet
- It's Not About Sex, It's About Soul 80kDocument226 pagesIt's Not About Sex, It's About Soul 80kNikolás RojasNo ratings yet
- Critical Reading On The Calling's 'Stigmatized'Document15 pagesCritical Reading On The Calling's 'Stigmatized'colenearcainaNo ratings yet
- Body Language and GesturesDocument32 pagesBody Language and Gesturesbenitadua4104100% (1)
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection / Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (HIV/AIDS) IsDocument4 pagesHuman Immunodeficiency Virus Infection / Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (HIV/AIDS) IsL.a.ZumárragaNo ratings yet
- Body Coordination FORM 4 SCIENCEDocument15 pagesBody Coordination FORM 4 SCIENCESiti NorhayatiNo ratings yet
- Sex RolesDocument2 pagesSex RolesbabyNo ratings yet