Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Group Members Amber Younas E07-009 Muhammad Ramzan E07-042
Group Members Amber Younas E07-009 Muhammad Ramzan E07-042
Uploaded by
Amber YounasCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Management Report On Tesla, Inc.Document7 pagesManagement Report On Tesla, Inc.Naveed IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Telecommunications Networks: Harish MorwaniDocument57 pagesTelecommunications Networks: Harish MorwaniHarish Morwani100% (4)
- Ewsd Training ModuleDocument149 pagesEwsd Training ModuleAnkush Yadav100% (1)
- PSTNDocument24 pagesPSTNAmber YounasNo ratings yet
- PSTNDocument24 pagesPSTNAmber YounasNo ratings yet
- PSTNDocument134 pagesPSTNAbhishek gargNo ratings yet
- Public Switched Telephone NetworkDocument5 pagesPublic Switched Telephone NetworkArturo Yanez S.G.No ratings yet
- Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN)Document4 pagesPublic Switched Telephone Network (PSTN)Akmal KhanNo ratings yet
- Public Switched Telephone NetworkDocument4 pagesPublic Switched Telephone NetworkYemmanAllibNo ratings yet
- Akma Lassig 3RD Roll 36Document4 pagesAkma Lassig 3RD Roll 36Akmal KhanNo ratings yet
- Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN)Document4 pagesPublic Switched Telephone Network (PSTN)Syed Zulfiqar Haider BukhariNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Technology: HistoryDocument4 pagesIntroduction To The Technology: HistoryAlia RhmnNo ratings yet
- A Presentation On An Industrial Training Taken at CTTC-Kolkata (BSNL)Document26 pagesA Presentation On An Industrial Training Taken at CTTC-Kolkata (BSNL)Tajinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Presented By:-: Dhrubajyoti AdakDocument26 pagesPresented By:-: Dhrubajyoti AdakJacob JacobNo ratings yet
- ETE405:: IP Telephony: Instructor: Dr. Mashiur RahmanDocument23 pagesETE405:: IP Telephony: Instructor: Dr. Mashiur RahmanzicobabyNo ratings yet
- PSTN and ISDNDocument29 pagesPSTN and ISDNleangsimNo ratings yet
- Networking EssentialsDocument2 pagesNetworking EssentialsMurugan K CbiNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 The Physical Layer: Btech Extc Trim IX Faculty: Prof. Sonia RelanDocument14 pagesUnit 3 The Physical Layer: Btech Extc Trim IX Faculty: Prof. Sonia RelanManish KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter IVDocument12 pagesChapter IVyohans bisetNo ratings yet
- E1-E2 - Text - Chapter 6. PSTN NETWORK - SERVICESDocument9 pagesE1-E2 - Text - Chapter 6. PSTN NETWORK - SERVICESabhimirachi7077No ratings yet
- Traning Pre (Ashi)Document27 pagesTraning Pre (Ashi)poonamshallyNo ratings yet
- BROAD BAND ACCESS (Wired and Wireless)Document31 pagesBROAD BAND ACCESS (Wired and Wireless)Apeksha KulkarniNo ratings yet
- CSE4255: Telecommunication: Telephone NetworkDocument19 pagesCSE4255: Telecommunication: Telephone NetworkFif PlayerNo ratings yet
- Mux1 Course HandoutDocument92 pagesMux1 Course Handoutalen GacicNo ratings yet
- Gigabit Ethernet Passive Optical NetworksDocument12 pagesGigabit Ethernet Passive Optical NetworksAna Soraya Dueñas OrtizNo ratings yet
- T1 Lines BasicsDocument13 pagesT1 Lines Basicsiimran_ahmdNo ratings yet
- Architectural Choices For Packet Switched Telephone NetworksDocument15 pagesArchitectural Choices For Packet Switched Telephone Networkseugene123No ratings yet
- Cellular Technology PDFDocument16 pagesCellular Technology PDFvengatrajaNo ratings yet
- Digital Transmission Technology An OverviewDocument43 pagesDigital Transmission Technology An OverviewJayesh SinghalNo ratings yet
- InternshipDocument27 pagesInternshipDurgasi HarithaNo ratings yet
- Borscht: Hook Refers To When The Handset Is Idle and Waiting For A Signal Indicating That Someone Wants ToDocument10 pagesBorscht: Hook Refers To When The Handset Is Idle and Waiting For A Signal Indicating That Someone Wants ToNouman Asif100% (1)
- Day 14Document46 pagesDay 14studyxubuntuNo ratings yet
- Telecommunication Systems: Generations of Cellular NetworksDocument5 pagesTelecommunication Systems: Generations of Cellular NetworksFarhan JavaidNo ratings yet
- Unit IiDocument45 pagesUnit IiVENU VNo ratings yet
- Network TopologyDocument2 pagesNetwork Topologyjamek_boyNo ratings yet
- Isdn ReportDocument8 pagesIsdn ReportfyravalNo ratings yet
- CESoP GPON Whitepaper Aug06Document14 pagesCESoP GPON Whitepaper Aug06xheti21No ratings yet
- Cisco Voice Notes Part 1Document14 pagesCisco Voice Notes Part 1Mohammed Nehal AktherNo ratings yet
- Firebird 6000Document35 pagesFirebird 6000Auguste RenoirNo ratings yet
- Cordless System: Dect, Ct2 and PHPDocument16 pagesCordless System: Dect, Ct2 and PHPAnyingisye MasetaNo ratings yet
- Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) PSTN Services Integrated Service Digital Network (ISDN) Public Land Mobile Networks (PLMN) GSM 3G 4G 5GDocument44 pagesPublic Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) PSTN Services Integrated Service Digital Network (ISDN) Public Land Mobile Networks (PLMN) GSM 3G 4G 5Gyohans bisetNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 IntroductionDocument71 pagesLecture 1 Introductionlim hyNo ratings yet
- MScDCOM-Lec08v2 With AnnotationsDocument7 pagesMScDCOM-Lec08v2 With AnnotationsJai GaizinNo ratings yet
- Industrial Training Seminar On BSNL: Submitted ByDocument36 pagesIndustrial Training Seminar On BSNL: Submitted ByRAVIOOO7No ratings yet
- Telecom Transmission & Switching System: Najam Ul HasanDocument29 pagesTelecom Transmission & Switching System: Najam Ul HasanMuhammad Bilal JunaidNo ratings yet
- Btech Project On GSM Modem Pic16f877a ControllerDocument52 pagesBtech Project On GSM Modem Pic16f877a ControllerTafadzwa Murwira100% (4)
- BSNL TrainingDocument25 pagesBSNL TrainingMission201516No ratings yet
- Unit IIDocument8 pagesUnit IIJayprakash DuveNo ratings yet
- Telecommunication TerminalsDocument13 pagesTelecommunication TerminalsMiki ArsovskiNo ratings yet
- Ofc Assignment 02 ILSADocument12 pagesOfc Assignment 02 ILSAIfra MalikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 SummaryDocument3 pagesChapter 3 SummaryAgodza Wise-one EricNo ratings yet
- Telecom KnowledgeDocument48 pagesTelecom KnowledgeYadi Slamet RiyadiNo ratings yet
- Integrated Services" "Digital Network: Isdn - " "Document6 pagesIntegrated Services" "Digital Network: Isdn - " "soniya_sNo ratings yet
- WMCDocument53 pagesWMCkirtidahiya123No ratings yet
- 10928139Document71 pages10928139NgôĐứcQuânNo ratings yet
- GSM Upto Connection EstablishmentDocument71 pagesGSM Upto Connection Establishment49 SRI RAM KARTHI PNo ratings yet
- BSNL Seminar Project by Abhishek & ShaniDocument27 pagesBSNL Seminar Project by Abhishek & ShaniabhishekNo ratings yet
- Project Name: Calculator (Algorithm Based)Document5 pagesProject Name: Calculator (Algorithm Based)Amber YounasNo ratings yet
- Communication Systems Assignment # 02: QuestionsDocument1 pageCommunication Systems Assignment # 02: QuestionsAmber YounasNo ratings yet
- Communication Systems Assignment # 01 MSC Students: QuestionsDocument1 pageCommunication Systems Assignment # 01 MSC Students: QuestionsAmber YounasNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1Document8 pagesQuiz 1Amber YounasNo ratings yet
- Question No: 1: Command For Finding Currents by Inverse MethodDocument2 pagesQuestion No: 1: Command For Finding Currents by Inverse MethodAmber YounasNo ratings yet
- Lab Assignment # 1 Control Systems: Use of Inverted Pendulum in Controls SystemDocument1 pageLab Assignment # 1 Control Systems: Use of Inverted Pendulum in Controls SystemAmber YounasNo ratings yet
- Project Name: Calculator (Algorithm Based)Document5 pagesProject Name: Calculator (Algorithm Based)Amber YounasNo ratings yet
- Center For Advanced Studies in Engineering: Microcontroller Based Embedded SystemsDocument25 pagesCenter For Advanced Studies in Engineering: Microcontroller Based Embedded SystemsAmber YounasNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document1 pageAssignment 1Amber YounasNo ratings yet
- Assignment#1Document1 pageAssignment#1Amber YounasNo ratings yet
- Lab#1 Ethernet CablingDocument11 pagesLab#1 Ethernet CablingAmber YounasNo ratings yet
- Quiz No 1b Solution - 4Document1 pageQuiz No 1b Solution - 4Amber YounasNo ratings yet
- Quiz No 2b SolutionDocument1 pageQuiz No 2b SolutionAmber YounasNo ratings yet
- Data Communication Networks: Assignment 05Document1 pageData Communication Networks: Assignment 05Amber YounasNo ratings yet
- Data Communication Networks: ImportantDocument1 pageData Communication Networks: ImportantAmber YounasNo ratings yet
- DCN Lab DescriptionDocument2 pagesDCN Lab DescriptionAmber YounasNo ratings yet
- Lab Assignment Fall 2009Document2 pagesLab Assignment Fall 2009Amber YounasNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Zia-ul-Hassan E07-073 Section - A Engineering Project Management Assignment # 05Document5 pagesMuhammad Zia-ul-Hassan E07-073 Section - A Engineering Project Management Assignment # 05Amber YounasNo ratings yet
- Quiz No 2a SolutionDocument1 pageQuiz No 2a SolutionAmber YounasNo ratings yet
- Rules & Guidelines LBR - Coca-Cola India PDFDocument20 pagesRules & Guidelines LBR - Coca-Cola India PDFIndianRailRoadsNo ratings yet
- Mercantile Law ReviewerDocument268 pagesMercantile Law ReviewerRon Capala100% (1)
- Role of Idea Development in Effective Essay WritingDocument98 pagesRole of Idea Development in Effective Essay WritingGânőőķ WäřņäNo ratings yet
- Art and CraftsDocument108 pagesArt and CraftsArus TündeNo ratings yet
- Rathmore Parish NewsletterDocument2 pagesRathmore Parish Newsletterapi-199024311No ratings yet
- Comentary On Nostra AetateDocument11 pagesComentary On Nostra AetateJude nnawuiheNo ratings yet
- PMP EVM Questions (20+ Practice Questions Included) EVM Graph QuestionsDocument16 pagesPMP EVM Questions (20+ Practice Questions Included) EVM Graph QuestionsJahidul Islam100% (1)
- CLP Talk 04 - Repentance and Faith PDFDocument5 pagesCLP Talk 04 - Repentance and Faith PDFJason YosoresNo ratings yet
- Special Airline Discount: Dear Murali RamachandranDocument2 pagesSpecial Airline Discount: Dear Murali RamachandranJAJNo ratings yet
- Astrophil and StellaDocument2 pagesAstrophil and StellaChristopher PattonNo ratings yet
- Marine Corps Museum Store Catalog 2011Document25 pagesMarine Corps Museum Store Catalog 2011Chuck Achberger100% (1)
- Cbe White PaperDocument2 pagesCbe White Paperrizwan_habibNo ratings yet
- Vmware Vrealize Automation: Install Configure Manage (V7.6) : View OnlineDocument5 pagesVmware Vrealize Automation: Install Configure Manage (V7.6) : View OnlineSandeep GangadharanNo ratings yet
- Ito 2015Document8 pagesIto 2015laurabarbosamedNo ratings yet
- Gr. Ourhoud - Tender No - Dde 19 - 12 33590 - Supply of Bearing - BeltsDocument2 pagesGr. Ourhoud - Tender No - Dde 19 - 12 33590 - Supply of Bearing - BeltsOussama AmaraNo ratings yet
- V PCDocument14 pagesV PCGiga Networkers100% (1)
- Educational Implications of Classical ConditioningDocument2 pagesEducational Implications of Classical Conditioningmekit bekeleNo ratings yet
- Discussions About Contracts With Customer Other IssuesDocument14 pagesDiscussions About Contracts With Customer Other Issuestrisha0% (1)
- The Effect of Learning Environment On Academic Performance From Students PerspectiveDocument8 pagesThe Effect of Learning Environment On Academic Performance From Students PerspectiveRolly JameroNo ratings yet
- Present Simple Versus Past SimpleDocument2 pagesPresent Simple Versus Past SimpleAnonymous Q21YDaSfNo ratings yet
- Quick Install Yealink Vp530 enDocument2 pagesQuick Install Yealink Vp530 enfastoreldaNo ratings yet
- Muazam MergedDocument25 pagesMuazam MergedAlok SinghNo ratings yet
- Paleolithic: Rehistoric Estern UropeDocument13 pagesPaleolithic: Rehistoric Estern UropeAhmed MohammedNo ratings yet
- Poranek (Peer Gynt)Document21 pagesPoranek (Peer Gynt)Katarzyna ChronowskaNo ratings yet
- Bouvet FactsDocument5 pagesBouvet FactsRich BlackettNo ratings yet
- BPDB RPCL Exam Question Solution 21-01-2019Document5 pagesBPDB RPCL Exam Question Solution 21-01-2019gvgfyfvicykNo ratings yet
- Get Set Go! 5. Workbook (PDFDrive)Document113 pagesGet Set Go! 5. Workbook (PDFDrive)Maureen BravoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - Four Layer Shadow BoxDocument1 pageTutorial - Four Layer Shadow BoxRey LarebilNo ratings yet
- Five Faces of Administrative CultureDocument5 pagesFive Faces of Administrative CultureMarc Russel HerreraNo ratings yet
Group Members Amber Younas E07-009 Muhammad Ramzan E07-042
Group Members Amber Younas E07-009 Muhammad Ramzan E07-042
Uploaded by
Amber YounasOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Group Members Amber Younas E07-009 Muhammad Ramzan E07-042
Group Members Amber Younas E07-009 Muhammad Ramzan E07-042
Uploaded by
Amber YounasCopyright:
Available Formats
PSTN
Group Members
Amber Younas E07-009
Muhammad Ramzan E07-042
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
Introduction
System Architecture
History
Advantages and Disadvantages of PSTN
Comparison Of Circuit Switched And Packet
Switched
Market Volume
Conclusion
2
INTRODUCTION
The public switched telephone network (PSTN) is the
worldwide collection of interconnected public telephone
networks that was designed primarily for voice traffic.
The normal phone network, or land line.
3
INTRODUCTION CNTD
Homes are connected to the Central Office (CO) via an analog
PSTN line.
Four wires held in place by a plastic RJ-11 connector.
The inner pair of wires is for line one and the outer pair is for line
two.
Each wire in the pair has a name (tip and ring), and the two
together provide a complete connection to the local CO - giving
rise to the name of this connection: the local loop.
Each pair of wires transmits
voice,
tones
Power
The tones consist of both Dual-Tone Multi-Frequency (DTMF)
tones you send by pressing the buttons on your touch-tone
keypad and information tones from the CO. The power is used to
ring your phone and keep it working when your homes power is
out (otherwise, how could you call and complain?). Even data
from a fax machine or a modem is translated into voice energy -
which sounds like static - before it's sent over the line.
4
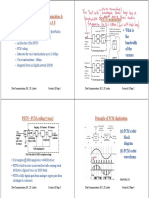
SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE
Digital Trunks
Analog line
Central
Office
(CO)
PSTN is a circuit-switched network.
( a dedicated circuit or channel is established for the
duration of a transmission, such as a telephone call)
Uses digital trunks between Central Office switches
(CO)
Uses analog line from phones to CO
5
HISTORY
The first telephones had no network but were in private
use.
Exchange Principle is used ( each telephone was wired
to a local telephone exchange, and the exchanges were
wired together with trunks)
The PSTN began in 1876 with the formation of American
Bell, which later became AT&T
In the 1970s the telecommunications industry began
implementing packet switched network data services as
in PSTN
Today only the oldest parts of the telephone network use
analog technology
In Recent years digital services have been increasingly
rolled out to end users using services such
as DSL, ISDN, FTTx and cable modem systems.
6
THE PSTN DIGITIZATION
Voice frequency is 100 - 5000 Hz, with the main portion
from 300 3400 Hz
Nyquist Theorem states that sampling must be done at
twice the highest frequency to recreate. 4000 Hz was
chosen as the maximum frequency, thus sampling at
8000 Hz
PCM = 8kHz * 8 bits per sample = 64 kbit/s
7
PUBLIC SWITCHED TELEPHONE NETWORK
Three major components of PSTN:
Local loops
Trunks
Switching Offices
Local CO
408-527-xxxx
22,000 in US
1-10 Km
CAT 3
Tandem
(class 4)
Mostly fiber or
microwave running
ATM or IP
(MCI, Sprint, ATT)
8
CIRCUIT SWITCHING
Time switch
- Makes switching between time slots
- In the figure incoming slot 3 is moved to
outgoing slot 3 for one voice direction
- Each coming timeslot stored in Speech Store
(SS)
- Control store (CS) determines the order the
slot
are read from SS
- The info in CS is determined during setup
phase of the call
Space switch
- makes switching between PCM lines
- works with electronic gates controlled by CS
Cross-point
controlled
by CS
Circuit switching
- dedicated path
- constant delay/bandwidth
- voice/data
- paid by time
- examples: PSTN, VPN
TDMA
9
TIME DIVISION MULTIPLEXING (E1)
The T1 frame is composed of 230 channels
The frame is 193 bits = 1 framing bit + 8 bits * 32 Time Slots (TS)
Framing bit creates an additional channel of 8 kb/s
Frame rate is 8 KHz, each channel is 8K * 7 bits = 56 Kbps
The extra bit is used for CAS (Channel Associated Signaling)
E1 32 channels, 2.048 MHz = 32 ch * 8K * 8 bits/ch, CCS
PCM voice
or data
10
MODERN PSTN HIERARCHY
to international level
Regional transport level
Local transport level
Access transport level
Local exchange
Transit exchange
11
PSTN HIERARCHY CONT.
Local (example, within a city)
Subscriber connections
Switching within the local exchange
Switching to other exchanges
Transit (county level, say between Tampere and Helsinki)
Switching traffic between different geographical areas within one
country
International
Gateway-type traffic between
different countries
DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing) routes
Rates can follow SONET or SDH standard
SDH
- transport of 1.5/2/6/34/45/140 Mbps within a transmission rate of 155.52 Mbps
- carries for instance ATM and IP within rates that are integer multiples of 155.52 Mbps
12
PSTN SERVICES TO CUSTOMERS
The PSTN has proven effective in providing clear
call quality for consumers over many years.
More Reliable as it provides with the ability to place
calls around the world that remain consistently clear
and reliable.
Dedicated Circuit (No delay and No 1way audio)
Digital services have been increasingly rolled out to
end users, using services such
as DSL, ISDN, FTTx and Cable modem systems.
13
CNTD
. The technology used by the PSTN in the
beginning changed by leaps and bounds and
provides a high quality, automated switching
communications network.
14
ADVANTAGES OF PSTN
No antenna.
Straight forward, well establish technology.
Easy to set up and maintain.
Two-way communications
Event notification through one or more stored telephone
numbers (such as pagers, internet, cell phone, etc.) to
provide a timely warning.
Easy installation, only takes around 5-7 working days,
this will of course be longer if the line needs to be ADSL
preferred.
A PSTN line can be used as either a standard phone
line and/or fax.
If your business is relocating and needs phone lines to
be installed as soon as possible then a PSTN line can
be a temporary solution.
15
DISADVANTAGES OF PSTN
Requires a direct phone line connections
Dedicated line required to complete a call
Limited scalability
Optimum usage of bandwidth not possible
Monthly fees applicable for maintenance
Higher call charges then VoIP (Voice over Internet
Protocol)
16
MARKET VOLUME
Market of PSTN is getting down after their voice call
services were dwarfed by the growing expansion of
mobile phone users in the local telecom market.
The shift from voice call services to data and internet
services came because operators found their existence
under tremendous threat as six mobile phone operators
have long ago eclipsed the land-phone service providers.
PSTN operators could not compete with the mobile
operators in meeting the demand of the ever-growing
customers because of lack of professionalism and
aggressive market policy from their part and adverse
policies on the part of the government which did not allow
them to make a sound take-off.
17
COMPARISON
A comparison of circuit switched and packet-switched
networks.
18
MESSAGE SWITCHING
(a) Circuit switching (b) Message switching (Packet
switching
19
LEADING VENDORS
PSTN ONE is a leading global communications
infrastructure vendor. PSTN ONE enables Internet
telephony service providers (ITSPs) to quickly and
efficiently implement, manage and deliver a wide
range of solutions for their services.
20
THE PATH TOWARDS NGN SOLUTION
PSTN
NGN
Step 1
Why
migrate
Step 2
What
requirements
Step 1
Why
migrate?
Step 3
Which
architecture?
Step 2
What
requirements?
I Page 21 of 23 KEYMILE
FUTURE DIRECTIONS WHY MIGRATE TO NGN?
Telecom service provider
PSTN infrastructure renewal
Network extension: Greenfield and rural
areas
Improve OPEX, reduce CAPEX
Provide new services
Virtual voice service provider
Reduce costs: Bypass other operators
network
Provide new services (IP Centrex)
ISP/broadband provider
Extend business with voice services to
broadband customers
Extend addressable market to narrowband
customers
I Page 22 of 23 KEYMILE
CONCLUSION
Analysts said the PSTN operators are now focusing
on corporate marketing, data services and internet
facilities as they have already realized that they
would not be able to survive in the highly
competitive market by providing services to only
general customers.
"We have so far relied on voice service as our
premium service. Now we are moving to data
services and internet to sustain business."
23
REFERENCES
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Public_switched_telepho
ne_network
http://www.ehow.com/list_7311472_advantages-
pstn.html
http://www.in4ma.co.uk/faq/pstn.html
http://www.thefinancialexpress-
bd.com/more.php?news_id=95522
24
You might also like
- Management Report On Tesla, Inc.Document7 pagesManagement Report On Tesla, Inc.Naveed IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Telecommunications Networks: Harish MorwaniDocument57 pagesTelecommunications Networks: Harish MorwaniHarish Morwani100% (4)
- Ewsd Training ModuleDocument149 pagesEwsd Training ModuleAnkush Yadav100% (1)
- PSTNDocument24 pagesPSTNAmber YounasNo ratings yet
- PSTNDocument24 pagesPSTNAmber YounasNo ratings yet
- PSTNDocument134 pagesPSTNAbhishek gargNo ratings yet
- Public Switched Telephone NetworkDocument5 pagesPublic Switched Telephone NetworkArturo Yanez S.G.No ratings yet
- Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN)Document4 pagesPublic Switched Telephone Network (PSTN)Akmal KhanNo ratings yet
- Public Switched Telephone NetworkDocument4 pagesPublic Switched Telephone NetworkYemmanAllibNo ratings yet
- Akma Lassig 3RD Roll 36Document4 pagesAkma Lassig 3RD Roll 36Akmal KhanNo ratings yet
- Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN)Document4 pagesPublic Switched Telephone Network (PSTN)Syed Zulfiqar Haider BukhariNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Technology: HistoryDocument4 pagesIntroduction To The Technology: HistoryAlia RhmnNo ratings yet
- A Presentation On An Industrial Training Taken at CTTC-Kolkata (BSNL)Document26 pagesA Presentation On An Industrial Training Taken at CTTC-Kolkata (BSNL)Tajinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Presented By:-: Dhrubajyoti AdakDocument26 pagesPresented By:-: Dhrubajyoti AdakJacob JacobNo ratings yet
- ETE405:: IP Telephony: Instructor: Dr. Mashiur RahmanDocument23 pagesETE405:: IP Telephony: Instructor: Dr. Mashiur RahmanzicobabyNo ratings yet
- PSTN and ISDNDocument29 pagesPSTN and ISDNleangsimNo ratings yet
- Networking EssentialsDocument2 pagesNetworking EssentialsMurugan K CbiNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 The Physical Layer: Btech Extc Trim IX Faculty: Prof. Sonia RelanDocument14 pagesUnit 3 The Physical Layer: Btech Extc Trim IX Faculty: Prof. Sonia RelanManish KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter IVDocument12 pagesChapter IVyohans bisetNo ratings yet
- E1-E2 - Text - Chapter 6. PSTN NETWORK - SERVICESDocument9 pagesE1-E2 - Text - Chapter 6. PSTN NETWORK - SERVICESabhimirachi7077No ratings yet
- Traning Pre (Ashi)Document27 pagesTraning Pre (Ashi)poonamshallyNo ratings yet
- BROAD BAND ACCESS (Wired and Wireless)Document31 pagesBROAD BAND ACCESS (Wired and Wireless)Apeksha KulkarniNo ratings yet
- CSE4255: Telecommunication: Telephone NetworkDocument19 pagesCSE4255: Telecommunication: Telephone NetworkFif PlayerNo ratings yet
- Mux1 Course HandoutDocument92 pagesMux1 Course Handoutalen GacicNo ratings yet
- Gigabit Ethernet Passive Optical NetworksDocument12 pagesGigabit Ethernet Passive Optical NetworksAna Soraya Dueñas OrtizNo ratings yet
- T1 Lines BasicsDocument13 pagesT1 Lines Basicsiimran_ahmdNo ratings yet
- Architectural Choices For Packet Switched Telephone NetworksDocument15 pagesArchitectural Choices For Packet Switched Telephone Networkseugene123No ratings yet
- Cellular Technology PDFDocument16 pagesCellular Technology PDFvengatrajaNo ratings yet
- Digital Transmission Technology An OverviewDocument43 pagesDigital Transmission Technology An OverviewJayesh SinghalNo ratings yet
- InternshipDocument27 pagesInternshipDurgasi HarithaNo ratings yet
- Borscht: Hook Refers To When The Handset Is Idle and Waiting For A Signal Indicating That Someone Wants ToDocument10 pagesBorscht: Hook Refers To When The Handset Is Idle and Waiting For A Signal Indicating That Someone Wants ToNouman Asif100% (1)
- Day 14Document46 pagesDay 14studyxubuntuNo ratings yet
- Telecommunication Systems: Generations of Cellular NetworksDocument5 pagesTelecommunication Systems: Generations of Cellular NetworksFarhan JavaidNo ratings yet
- Unit IiDocument45 pagesUnit IiVENU VNo ratings yet
- Network TopologyDocument2 pagesNetwork Topologyjamek_boyNo ratings yet
- Isdn ReportDocument8 pagesIsdn ReportfyravalNo ratings yet
- CESoP GPON Whitepaper Aug06Document14 pagesCESoP GPON Whitepaper Aug06xheti21No ratings yet
- Cisco Voice Notes Part 1Document14 pagesCisco Voice Notes Part 1Mohammed Nehal AktherNo ratings yet
- Firebird 6000Document35 pagesFirebird 6000Auguste RenoirNo ratings yet
- Cordless System: Dect, Ct2 and PHPDocument16 pagesCordless System: Dect, Ct2 and PHPAnyingisye MasetaNo ratings yet
- Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) PSTN Services Integrated Service Digital Network (ISDN) Public Land Mobile Networks (PLMN) GSM 3G 4G 5GDocument44 pagesPublic Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) PSTN Services Integrated Service Digital Network (ISDN) Public Land Mobile Networks (PLMN) GSM 3G 4G 5Gyohans bisetNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 IntroductionDocument71 pagesLecture 1 Introductionlim hyNo ratings yet
- MScDCOM-Lec08v2 With AnnotationsDocument7 pagesMScDCOM-Lec08v2 With AnnotationsJai GaizinNo ratings yet
- Industrial Training Seminar On BSNL: Submitted ByDocument36 pagesIndustrial Training Seminar On BSNL: Submitted ByRAVIOOO7No ratings yet
- Telecom Transmission & Switching System: Najam Ul HasanDocument29 pagesTelecom Transmission & Switching System: Najam Ul HasanMuhammad Bilal JunaidNo ratings yet
- Btech Project On GSM Modem Pic16f877a ControllerDocument52 pagesBtech Project On GSM Modem Pic16f877a ControllerTafadzwa Murwira100% (4)
- BSNL TrainingDocument25 pagesBSNL TrainingMission201516No ratings yet
- Unit IIDocument8 pagesUnit IIJayprakash DuveNo ratings yet
- Telecommunication TerminalsDocument13 pagesTelecommunication TerminalsMiki ArsovskiNo ratings yet
- Ofc Assignment 02 ILSADocument12 pagesOfc Assignment 02 ILSAIfra MalikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 SummaryDocument3 pagesChapter 3 SummaryAgodza Wise-one EricNo ratings yet
- Telecom KnowledgeDocument48 pagesTelecom KnowledgeYadi Slamet RiyadiNo ratings yet
- Integrated Services" "Digital Network: Isdn - " "Document6 pagesIntegrated Services" "Digital Network: Isdn - " "soniya_sNo ratings yet
- WMCDocument53 pagesWMCkirtidahiya123No ratings yet
- 10928139Document71 pages10928139NgôĐứcQuânNo ratings yet
- GSM Upto Connection EstablishmentDocument71 pagesGSM Upto Connection Establishment49 SRI RAM KARTHI PNo ratings yet
- BSNL Seminar Project by Abhishek & ShaniDocument27 pagesBSNL Seminar Project by Abhishek & ShaniabhishekNo ratings yet
- Project Name: Calculator (Algorithm Based)Document5 pagesProject Name: Calculator (Algorithm Based)Amber YounasNo ratings yet
- Communication Systems Assignment # 02: QuestionsDocument1 pageCommunication Systems Assignment # 02: QuestionsAmber YounasNo ratings yet
- Communication Systems Assignment # 01 MSC Students: QuestionsDocument1 pageCommunication Systems Assignment # 01 MSC Students: QuestionsAmber YounasNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1Document8 pagesQuiz 1Amber YounasNo ratings yet
- Question No: 1: Command For Finding Currents by Inverse MethodDocument2 pagesQuestion No: 1: Command For Finding Currents by Inverse MethodAmber YounasNo ratings yet
- Lab Assignment # 1 Control Systems: Use of Inverted Pendulum in Controls SystemDocument1 pageLab Assignment # 1 Control Systems: Use of Inverted Pendulum in Controls SystemAmber YounasNo ratings yet
- Project Name: Calculator (Algorithm Based)Document5 pagesProject Name: Calculator (Algorithm Based)Amber YounasNo ratings yet
- Center For Advanced Studies in Engineering: Microcontroller Based Embedded SystemsDocument25 pagesCenter For Advanced Studies in Engineering: Microcontroller Based Embedded SystemsAmber YounasNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document1 pageAssignment 1Amber YounasNo ratings yet
- Assignment#1Document1 pageAssignment#1Amber YounasNo ratings yet
- Lab#1 Ethernet CablingDocument11 pagesLab#1 Ethernet CablingAmber YounasNo ratings yet
- Quiz No 1b Solution - 4Document1 pageQuiz No 1b Solution - 4Amber YounasNo ratings yet
- Quiz No 2b SolutionDocument1 pageQuiz No 2b SolutionAmber YounasNo ratings yet
- Data Communication Networks: Assignment 05Document1 pageData Communication Networks: Assignment 05Amber YounasNo ratings yet
- Data Communication Networks: ImportantDocument1 pageData Communication Networks: ImportantAmber YounasNo ratings yet
- DCN Lab DescriptionDocument2 pagesDCN Lab DescriptionAmber YounasNo ratings yet
- Lab Assignment Fall 2009Document2 pagesLab Assignment Fall 2009Amber YounasNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Zia-ul-Hassan E07-073 Section - A Engineering Project Management Assignment # 05Document5 pagesMuhammad Zia-ul-Hassan E07-073 Section - A Engineering Project Management Assignment # 05Amber YounasNo ratings yet
- Quiz No 2a SolutionDocument1 pageQuiz No 2a SolutionAmber YounasNo ratings yet
- Rules & Guidelines LBR - Coca-Cola India PDFDocument20 pagesRules & Guidelines LBR - Coca-Cola India PDFIndianRailRoadsNo ratings yet
- Mercantile Law ReviewerDocument268 pagesMercantile Law ReviewerRon Capala100% (1)
- Role of Idea Development in Effective Essay WritingDocument98 pagesRole of Idea Development in Effective Essay WritingGânőőķ WäřņäNo ratings yet
- Art and CraftsDocument108 pagesArt and CraftsArus TündeNo ratings yet
- Rathmore Parish NewsletterDocument2 pagesRathmore Parish Newsletterapi-199024311No ratings yet
- Comentary On Nostra AetateDocument11 pagesComentary On Nostra AetateJude nnawuiheNo ratings yet
- PMP EVM Questions (20+ Practice Questions Included) EVM Graph QuestionsDocument16 pagesPMP EVM Questions (20+ Practice Questions Included) EVM Graph QuestionsJahidul Islam100% (1)
- CLP Talk 04 - Repentance and Faith PDFDocument5 pagesCLP Talk 04 - Repentance and Faith PDFJason YosoresNo ratings yet
- Special Airline Discount: Dear Murali RamachandranDocument2 pagesSpecial Airline Discount: Dear Murali RamachandranJAJNo ratings yet
- Astrophil and StellaDocument2 pagesAstrophil and StellaChristopher PattonNo ratings yet
- Marine Corps Museum Store Catalog 2011Document25 pagesMarine Corps Museum Store Catalog 2011Chuck Achberger100% (1)
- Cbe White PaperDocument2 pagesCbe White Paperrizwan_habibNo ratings yet
- Vmware Vrealize Automation: Install Configure Manage (V7.6) : View OnlineDocument5 pagesVmware Vrealize Automation: Install Configure Manage (V7.6) : View OnlineSandeep GangadharanNo ratings yet
- Ito 2015Document8 pagesIto 2015laurabarbosamedNo ratings yet
- Gr. Ourhoud - Tender No - Dde 19 - 12 33590 - Supply of Bearing - BeltsDocument2 pagesGr. Ourhoud - Tender No - Dde 19 - 12 33590 - Supply of Bearing - BeltsOussama AmaraNo ratings yet
- V PCDocument14 pagesV PCGiga Networkers100% (1)
- Educational Implications of Classical ConditioningDocument2 pagesEducational Implications of Classical Conditioningmekit bekeleNo ratings yet
- Discussions About Contracts With Customer Other IssuesDocument14 pagesDiscussions About Contracts With Customer Other Issuestrisha0% (1)
- The Effect of Learning Environment On Academic Performance From Students PerspectiveDocument8 pagesThe Effect of Learning Environment On Academic Performance From Students PerspectiveRolly JameroNo ratings yet
- Present Simple Versus Past SimpleDocument2 pagesPresent Simple Versus Past SimpleAnonymous Q21YDaSfNo ratings yet
- Quick Install Yealink Vp530 enDocument2 pagesQuick Install Yealink Vp530 enfastoreldaNo ratings yet
- Muazam MergedDocument25 pagesMuazam MergedAlok SinghNo ratings yet
- Paleolithic: Rehistoric Estern UropeDocument13 pagesPaleolithic: Rehistoric Estern UropeAhmed MohammedNo ratings yet
- Poranek (Peer Gynt)Document21 pagesPoranek (Peer Gynt)Katarzyna ChronowskaNo ratings yet
- Bouvet FactsDocument5 pagesBouvet FactsRich BlackettNo ratings yet
- BPDB RPCL Exam Question Solution 21-01-2019Document5 pagesBPDB RPCL Exam Question Solution 21-01-2019gvgfyfvicykNo ratings yet
- Get Set Go! 5. Workbook (PDFDrive)Document113 pagesGet Set Go! 5. Workbook (PDFDrive)Maureen BravoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - Four Layer Shadow BoxDocument1 pageTutorial - Four Layer Shadow BoxRey LarebilNo ratings yet
- Five Faces of Administrative CultureDocument5 pagesFive Faces of Administrative CultureMarc Russel HerreraNo ratings yet