Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Networking: What Is A Network ?
Networking: What Is A Network ?
Uploaded by
Pavan KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Introduction To Computer NetworkDocument37 pagesIntroduction To Computer NetworkUtpal KantNo ratings yet
- Software-Defined Networks: A Systems ApproachFrom EverandSoftware-Defined Networks: A Systems ApproachRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Aws Inspector UgDocument45 pagesAws Inspector UgdurgasainathNo ratings yet
- Curtain WallDocument32 pagesCurtain WallParas Gulia100% (7)
- Computer NetworkingDocument15 pagesComputer NetworkingkentNo ratings yet
- Computer Project 2nd SemDocument20 pagesComputer Project 2nd SemVeer RokhadeNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument20 pagesComputer NetworkyjnNo ratings yet
- What Is A Network?Document9 pagesWhat Is A Network?amrit singhaniaNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworksDocument17 pagesComputer Networksskartikeyyy222No ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Network Architecture Standard: Network Components and TerminologyDocument12 pagesLesson 1: Network Architecture Standard: Network Components and TerminologyHarvey James ChuaNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Basics of NetworkingDocument32 pagesCH 1 Basics of NetworkingRanganath KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Itfe ReportnetworkingDocument30 pagesItfe ReportnetworkingAizen DzNo ratings yet
- QUARTER 2 - ICT GRADE 9 Unit 2 NetworkingDocument6 pagesQUARTER 2 - ICT GRADE 9 Unit 2 Networkingbekanmusic05No ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument32 pagesComputer Networkcapt shivakumarNo ratings yet
- Basics of Networking & Designs of Simple Networks: ConfidentialDocument29 pagesBasics of Networking & Designs of Simple Networks: ConfidentialsharkapproachNo ratings yet
- Networking CSS 12Document11 pagesNetworking CSS 12Irene DausNo ratings yet
- Network Topology DevicesDocument33 pagesNetwork Topology DeviceshellomeranaamNo ratings yet
- Introduction To NetworkingDocument72 pagesIntroduction To NetworkingHimanshu GuptaNo ratings yet
- Activity 5 CNDocument15 pagesActivity 5 CNshifa dafedarNo ratings yet
- What Is A Computer Network - Lecture - 5aDocument6 pagesWhat Is A Computer Network - Lecture - 5atantos557No ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer NetworksDocument17 pagesIntroduction To Computer NetworkskhanpmansoorNo ratings yet
- Computer Network Notes Class 12Document14 pagesComputer Network Notes Class 12Mohit HoodaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of NetworkDocument52 pagesFundamentals of Networkumurita37No ratings yet
- IT Quiz ReviewerDocument34 pagesIT Quiz Reviewerjandy6734No ratings yet
- Computer NetworksDocument58 pagesComputer NetworksSavin ShettyNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument15 pagesComputer NetworktechtimeNo ratings yet
- NetworkingDocument24 pagesNetworkingAli AmarNo ratings yet
- Amarnath Sah Senior Technical Assistant NIELIT TezpurDocument17 pagesAmarnath Sah Senior Technical Assistant NIELIT TezpurAmarnath SahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. Introduction: Basic of NetworkingDocument28 pagesChapter 1. Introduction: Basic of NetworkingAmanNo ratings yet
- Computer Network Notes Class 12Document13 pagesComputer Network Notes Class 12om100% (4)
- Chapter 2 Lesson 1Document57 pagesChapter 2 Lesson 1casseyareolaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.2 Basic Computer NetworkDocument14 pagesChapter 2.2 Basic Computer NetworkCharity Rider TitomacoytvNo ratings yet
- W-10 Introduction To Network1Document28 pagesW-10 Introduction To Network1aminurrahman333No ratings yet
- © 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All Rights ReservedDocument26 pages© 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All Rights ReservedAlecsandro QueirozNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer NetworksDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Computer Networksankit_coolheadNo ratings yet
- Section 2 - COMPUTER NETWORKS AND WEB TECHNOLOGIESDocument73 pagesSection 2 - COMPUTER NETWORKS AND WEB TECHNOLOGIESgabriellestewart334No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Network TopologyDocument65 pagesChapter 8 - Network TopologyratZ_trgNo ratings yet
- Uploaded by Chandan MishraDocument15 pagesUploaded by Chandan MishraKarthik KeyanNo ratings yet
- Networking G 11Document26 pagesNetworking G 11Jiel Añonuevo QuilantangNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks: Presented byDocument34 pagesComputer Networks: Presented byJadedGoth100% (2)
- Chapter-8: Types of NetworksDocument16 pagesChapter-8: Types of NetworksElias YeshanawNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Overview of Internet and Network 1Document7 pagesUnit 1 Overview of Internet and Network 1Dudzayi KasiyoNo ratings yet
- Lecture1 1Document17 pagesLecture1 1هلال العمديNo ratings yet
- 9d M1 - Network Tools Types To Device of NetworkDocument15 pages9d M1 - Network Tools Types To Device of NetworkMarc AeruNo ratings yet
- NetworksDocument5 pagesNetworksErichelle EspineliNo ratings yet
- Basic Computer Network PDFDocument35 pagesBasic Computer Network PDFTep TepNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks: Computer Network Connects Two or More Autonomous ComputersDocument14 pagesComputer Networks: Computer Network Connects Two or More Autonomous ComputersRiajiminNo ratings yet
- 1 Introduction To Computer NetworkingDocument50 pages1 Introduction To Computer NetworkingSaurabh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document23 pagesLecture 1tsigeredaNo ratings yet
- 3 Introduction To ComputersDocument32 pages3 Introduction To ComputersTHE VIDEO LABNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 PDFDocument43 pagesChapter 1 PDFKavya ParasharNo ratings yet
- Computer 8T1 Tutorial 2021 2022Document21 pagesComputer 8T1 Tutorial 2021 2022FaheemNo ratings yet
- Computer Networking 2Document9 pagesComputer Networking 2Muhammad Najib NordinNo ratings yet
- Computer Network: A Computer Network Is A Group of InterconnectedDocument19 pagesComputer Network: A Computer Network Is A Group of InterconnectedKiran DherwaniNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document5 pagesLesson 2chloealexisvergeireNo ratings yet
- W-10 Introduction To InternetDocument44 pagesW-10 Introduction To InternetUmair AhmadNo ratings yet
- CPT 1Document184 pagesCPT 1Alan VikramNo ratings yet
- 1 Introduction To Computer NetworkingDocument53 pages1 Introduction To Computer Networkingabel emmanuel100% (1)
- Computer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1From EverandComputer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Reliance Increasing Income Insurance Plan Sum Assured To Premium For Babu Bava PDFDocument3 pagesReliance Increasing Income Insurance Plan Sum Assured To Premium For Babu Bava PDFPavan KumarNo ratings yet
- Hirens Boot DVDDocument3 pagesHirens Boot DVDPavan KumarNo ratings yet
- Plans in Reliance LifeDocument5 pagesPlans in Reliance LifePavan KumarNo ratings yet
- South India Fake-Company List-Year of 2010Document22 pagesSouth India Fake-Company List-Year of 2010Prithivirajan CuddaloreNo ratings yet
- 331 Network DesignDocument132 pages331 Network DesignXozanNo ratings yet
- Approach Sight Singing Fifth EditionDocument3 pagesApproach Sight Singing Fifth Editionfbshow0% (2)
- Stop and Wait Protocol Using NS2Document7 pagesStop and Wait Protocol Using NS2miraclesureshNo ratings yet
- NSE Company Profile - Update Sept 2018 PDFDocument22 pagesNSE Company Profile - Update Sept 2018 PDFAnusapati SingosariNo ratings yet
- Chain Link Fencing: Galvanised Green Pve Coated/Galvanised CoreDocument3 pagesChain Link Fencing: Galvanised Green Pve Coated/Galvanised CorevanmurthyNo ratings yet
- Grating and Expanded Metal CatalogDocument68 pagesGrating and Expanded Metal CatalogsivaNo ratings yet
- WildFly Cookbook - Sample ChapterDocument35 pagesWildFly Cookbook - Sample ChapterPackt Publishing100% (1)
- Lecture 7Document40 pagesLecture 7Ekala Xuhalx100% (2)
- CseDocument31 pagesCsepradeep_dgsNo ratings yet
- VXL Instruments Limited, House of Excellence', No 17 Electronics City, Hosur Road, Bangalore 560 100, IndiaDocument2 pagesVXL Instruments Limited, House of Excellence', No 17 Electronics City, Hosur Road, Bangalore 560 100, Indiamana1345No ratings yet
- SAP Personas OverviewDocument31 pagesSAP Personas OverviewsekhardattaNo ratings yet
- Autocad 2dDocument123 pagesAutocad 2dglazetmNo ratings yet
- Bathroom Collection April 2015 Aw1lr Low ResDocument58 pagesBathroom Collection April 2015 Aw1lr Low ReschamindaNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Windows Group Policy GuideDocument758 pagesMicrosoft Windows Group Policy GuideSilentMaleonKasel100% (2)
- Local Media1789920838894189764Document1 pageLocal Media1789920838894189764Jelo VecencioNo ratings yet
- Raspberry PiDocument12 pagesRaspberry PiYuvaraj YuvarajNo ratings yet
- RMD Super Slim Soldiers BrochureDocument16 pagesRMD Super Slim Soldiers BrochureWai Wai LeeNo ratings yet
- Cypetherm SuiteDocument72 pagesCypetherm SuitevickersNo ratings yet
- History of The InternetDocument13 pagesHistory of The InternetFlorencio CoquillaNo ratings yet
- Art December 2013 I IDocument26 pagesArt December 2013 I IArtdataNo ratings yet
- Aggregates FMDocument5 pagesAggregates FMabualamalNo ratings yet
- Austria: Valley, Salzburg and The Sound of Music Lake DistrictDocument5 pagesAustria: Valley, Salzburg and The Sound of Music Lake DistrictPaul SchnellNo ratings yet
- Stinger CR Datasheet FINALDocument2 pagesStinger CR Datasheet FINALDavid IbañezNo ratings yet
- Cisco Content Security Virtual Appliance Install GuideDocument12 pagesCisco Content Security Virtual Appliance Install GuidePablo De la Quintana100% (1)
- Types of ConcreteDocument38 pagesTypes of Concretesameer khanNo ratings yet
- Construction ManagementDocument55 pagesConstruction Managementkmmansaf100% (1)
- Cloud IT NetworkDocument3 pagesCloud IT NetworkClaudian PaduraruNo ratings yet
Networking: What Is A Network ?
Networking: What Is A Network ?
Uploaded by
Pavan KumarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Networking: What Is A Network ?
Networking: What Is A Network ?
Uploaded by
Pavan KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
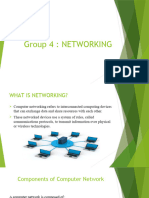
NETWORKING
What is a Network ?
Uses of Networking
TYPES OF NETWORKS
LAN: Local Area Network
MAN: Metropolitan Area Network
WAN: Wide Area Network
Local Area Network (LAN)
The Local Area
Network can be a
group of computers
and other devices in a
limited geographical
area (say the size of an
office building)
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
MAN is a network for
a cluster of buildings,
or two or more
buildings within a
short distance of each
other in a city
Wide Area Network (WAN)
A Wide Area Network
(WAN) can be a group
of computers and other
devices in a larger
geographical area
(say cities, states and
even countries)
Network Models
Sneaker net
Peer-to-Peer
Client/Server
Sneaker Net
The transfer
information, by
physically carrying
removable media from
one computer to
another.
Peer-to-Peer Networks
The peer-to-peer model
is one in which resources
are shared by computers
which are considered
approximately equals
in the network
administration hierarchy.
Client/Server Model
In this Model, a single
computer called a
'server' is given the
duty to provide a
particular service to
one or more 'client'
computers.
SCOPE OF NETWORK
Internet
An internet (or internetwork) is a network of networks, which
are connected together to facilitate sharing resources and
information among users.
Intranet
An intranet is a network that is specific to a single organization.
LAN.
Extranet
An extranet is a network that allows a business to connect with
suppliers, vendors, customers, stockholders or others related to
its business.
NETWORK TOPOLOGIES
Mesh Network
Linear Bus Network
Star Network
Ring Network
Tree Network
Linear Bus Network
The Bus network
uses a single cable
that all devices to
interconnect.
Star Network
A Star topology is
designed with each
node (file server,
workstations, and
peripherals) connected
directly to a central
network Switch/Hub.
Ring Network
Instead of a central
hub as found in the
Star Network, a MAU
(Media Access Unit) is
the center point in
Ring Network.
Inside the MAU is a
logical ring.
FULL Mesh Network
In a Mesh network,
every device has a
physical connection
directly to every other
device
PARTIAL MESH TOPOLOGY
Tree Network
A Tree Topology
combines
characteristics of
linear bus and star
topologies
NETWORKING HARDWARE
Network Interface Cards (NIC)
Switches/Hubs
Repeaters
Routers
Network Interface Cards
The Network
Interface Card (NIC)
provides the physical
connection between the
network and the
computer workstation
Hubs & Switches
Hub is a device that
provides a central
connection point for
cables from
workstations, servers,
and peripherals.
Repeaters
A repeater is a device
that boosts a
network's signal as it
passes through.
Routers
A router translates
information from one
network to another
Wireless Access Point
A Wireless Access
Point (WAP or AP) is a
device that allows
wireless communication
devices to connect to a
wireless network using
Wi-Fi, Bluetooth or
related standards.
You might also like
- Introduction To Computer NetworkDocument37 pagesIntroduction To Computer NetworkUtpal KantNo ratings yet
- Software-Defined Networks: A Systems ApproachFrom EverandSoftware-Defined Networks: A Systems ApproachRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Aws Inspector UgDocument45 pagesAws Inspector UgdurgasainathNo ratings yet
- Curtain WallDocument32 pagesCurtain WallParas Gulia100% (7)
- Computer NetworkingDocument15 pagesComputer NetworkingkentNo ratings yet
- Computer Project 2nd SemDocument20 pagesComputer Project 2nd SemVeer RokhadeNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument20 pagesComputer NetworkyjnNo ratings yet
- What Is A Network?Document9 pagesWhat Is A Network?amrit singhaniaNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworksDocument17 pagesComputer Networksskartikeyyy222No ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Network Architecture Standard: Network Components and TerminologyDocument12 pagesLesson 1: Network Architecture Standard: Network Components and TerminologyHarvey James ChuaNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Basics of NetworkingDocument32 pagesCH 1 Basics of NetworkingRanganath KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Itfe ReportnetworkingDocument30 pagesItfe ReportnetworkingAizen DzNo ratings yet
- QUARTER 2 - ICT GRADE 9 Unit 2 NetworkingDocument6 pagesQUARTER 2 - ICT GRADE 9 Unit 2 Networkingbekanmusic05No ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument32 pagesComputer Networkcapt shivakumarNo ratings yet
- Basics of Networking & Designs of Simple Networks: ConfidentialDocument29 pagesBasics of Networking & Designs of Simple Networks: ConfidentialsharkapproachNo ratings yet
- Networking CSS 12Document11 pagesNetworking CSS 12Irene DausNo ratings yet
- Network Topology DevicesDocument33 pagesNetwork Topology DeviceshellomeranaamNo ratings yet
- Introduction To NetworkingDocument72 pagesIntroduction To NetworkingHimanshu GuptaNo ratings yet
- Activity 5 CNDocument15 pagesActivity 5 CNshifa dafedarNo ratings yet
- What Is A Computer Network - Lecture - 5aDocument6 pagesWhat Is A Computer Network - Lecture - 5atantos557No ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer NetworksDocument17 pagesIntroduction To Computer NetworkskhanpmansoorNo ratings yet
- Computer Network Notes Class 12Document14 pagesComputer Network Notes Class 12Mohit HoodaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of NetworkDocument52 pagesFundamentals of Networkumurita37No ratings yet
- IT Quiz ReviewerDocument34 pagesIT Quiz Reviewerjandy6734No ratings yet
- Computer NetworksDocument58 pagesComputer NetworksSavin ShettyNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument15 pagesComputer NetworktechtimeNo ratings yet
- NetworkingDocument24 pagesNetworkingAli AmarNo ratings yet
- Amarnath Sah Senior Technical Assistant NIELIT TezpurDocument17 pagesAmarnath Sah Senior Technical Assistant NIELIT TezpurAmarnath SahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. Introduction: Basic of NetworkingDocument28 pagesChapter 1. Introduction: Basic of NetworkingAmanNo ratings yet
- Computer Network Notes Class 12Document13 pagesComputer Network Notes Class 12om100% (4)
- Chapter 2 Lesson 1Document57 pagesChapter 2 Lesson 1casseyareolaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.2 Basic Computer NetworkDocument14 pagesChapter 2.2 Basic Computer NetworkCharity Rider TitomacoytvNo ratings yet
- W-10 Introduction To Network1Document28 pagesW-10 Introduction To Network1aminurrahman333No ratings yet
- © 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All Rights ReservedDocument26 pages© 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All Rights ReservedAlecsandro QueirozNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer NetworksDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Computer Networksankit_coolheadNo ratings yet
- Section 2 - COMPUTER NETWORKS AND WEB TECHNOLOGIESDocument73 pagesSection 2 - COMPUTER NETWORKS AND WEB TECHNOLOGIESgabriellestewart334No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Network TopologyDocument65 pagesChapter 8 - Network TopologyratZ_trgNo ratings yet
- Uploaded by Chandan MishraDocument15 pagesUploaded by Chandan MishraKarthik KeyanNo ratings yet
- Networking G 11Document26 pagesNetworking G 11Jiel Añonuevo QuilantangNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks: Presented byDocument34 pagesComputer Networks: Presented byJadedGoth100% (2)
- Chapter-8: Types of NetworksDocument16 pagesChapter-8: Types of NetworksElias YeshanawNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Overview of Internet and Network 1Document7 pagesUnit 1 Overview of Internet and Network 1Dudzayi KasiyoNo ratings yet
- Lecture1 1Document17 pagesLecture1 1هلال العمديNo ratings yet
- 9d M1 - Network Tools Types To Device of NetworkDocument15 pages9d M1 - Network Tools Types To Device of NetworkMarc AeruNo ratings yet
- NetworksDocument5 pagesNetworksErichelle EspineliNo ratings yet
- Basic Computer Network PDFDocument35 pagesBasic Computer Network PDFTep TepNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks: Computer Network Connects Two or More Autonomous ComputersDocument14 pagesComputer Networks: Computer Network Connects Two or More Autonomous ComputersRiajiminNo ratings yet
- 1 Introduction To Computer NetworkingDocument50 pages1 Introduction To Computer NetworkingSaurabh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document23 pagesLecture 1tsigeredaNo ratings yet
- 3 Introduction To ComputersDocument32 pages3 Introduction To ComputersTHE VIDEO LABNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 PDFDocument43 pagesChapter 1 PDFKavya ParasharNo ratings yet
- Computer 8T1 Tutorial 2021 2022Document21 pagesComputer 8T1 Tutorial 2021 2022FaheemNo ratings yet
- Computer Networking 2Document9 pagesComputer Networking 2Muhammad Najib NordinNo ratings yet
- Computer Network: A Computer Network Is A Group of InterconnectedDocument19 pagesComputer Network: A Computer Network Is A Group of InterconnectedKiran DherwaniNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document5 pagesLesson 2chloealexisvergeireNo ratings yet
- W-10 Introduction To InternetDocument44 pagesW-10 Introduction To InternetUmair AhmadNo ratings yet
- CPT 1Document184 pagesCPT 1Alan VikramNo ratings yet
- 1 Introduction To Computer NetworkingDocument53 pages1 Introduction To Computer Networkingabel emmanuel100% (1)
- Computer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1From EverandComputer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Reliance Increasing Income Insurance Plan Sum Assured To Premium For Babu Bava PDFDocument3 pagesReliance Increasing Income Insurance Plan Sum Assured To Premium For Babu Bava PDFPavan KumarNo ratings yet
- Hirens Boot DVDDocument3 pagesHirens Boot DVDPavan KumarNo ratings yet
- Plans in Reliance LifeDocument5 pagesPlans in Reliance LifePavan KumarNo ratings yet
- South India Fake-Company List-Year of 2010Document22 pagesSouth India Fake-Company List-Year of 2010Prithivirajan CuddaloreNo ratings yet
- 331 Network DesignDocument132 pages331 Network DesignXozanNo ratings yet
- Approach Sight Singing Fifth EditionDocument3 pagesApproach Sight Singing Fifth Editionfbshow0% (2)
- Stop and Wait Protocol Using NS2Document7 pagesStop and Wait Protocol Using NS2miraclesureshNo ratings yet
- NSE Company Profile - Update Sept 2018 PDFDocument22 pagesNSE Company Profile - Update Sept 2018 PDFAnusapati SingosariNo ratings yet
- Chain Link Fencing: Galvanised Green Pve Coated/Galvanised CoreDocument3 pagesChain Link Fencing: Galvanised Green Pve Coated/Galvanised CorevanmurthyNo ratings yet
- Grating and Expanded Metal CatalogDocument68 pagesGrating and Expanded Metal CatalogsivaNo ratings yet
- WildFly Cookbook - Sample ChapterDocument35 pagesWildFly Cookbook - Sample ChapterPackt Publishing100% (1)
- Lecture 7Document40 pagesLecture 7Ekala Xuhalx100% (2)
- CseDocument31 pagesCsepradeep_dgsNo ratings yet
- VXL Instruments Limited, House of Excellence', No 17 Electronics City, Hosur Road, Bangalore 560 100, IndiaDocument2 pagesVXL Instruments Limited, House of Excellence', No 17 Electronics City, Hosur Road, Bangalore 560 100, Indiamana1345No ratings yet
- SAP Personas OverviewDocument31 pagesSAP Personas OverviewsekhardattaNo ratings yet
- Autocad 2dDocument123 pagesAutocad 2dglazetmNo ratings yet
- Bathroom Collection April 2015 Aw1lr Low ResDocument58 pagesBathroom Collection April 2015 Aw1lr Low ReschamindaNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Windows Group Policy GuideDocument758 pagesMicrosoft Windows Group Policy GuideSilentMaleonKasel100% (2)
- Local Media1789920838894189764Document1 pageLocal Media1789920838894189764Jelo VecencioNo ratings yet
- Raspberry PiDocument12 pagesRaspberry PiYuvaraj YuvarajNo ratings yet
- RMD Super Slim Soldiers BrochureDocument16 pagesRMD Super Slim Soldiers BrochureWai Wai LeeNo ratings yet
- Cypetherm SuiteDocument72 pagesCypetherm SuitevickersNo ratings yet
- History of The InternetDocument13 pagesHistory of The InternetFlorencio CoquillaNo ratings yet
- Art December 2013 I IDocument26 pagesArt December 2013 I IArtdataNo ratings yet
- Aggregates FMDocument5 pagesAggregates FMabualamalNo ratings yet
- Austria: Valley, Salzburg and The Sound of Music Lake DistrictDocument5 pagesAustria: Valley, Salzburg and The Sound of Music Lake DistrictPaul SchnellNo ratings yet
- Stinger CR Datasheet FINALDocument2 pagesStinger CR Datasheet FINALDavid IbañezNo ratings yet
- Cisco Content Security Virtual Appliance Install GuideDocument12 pagesCisco Content Security Virtual Appliance Install GuidePablo De la Quintana100% (1)
- Types of ConcreteDocument38 pagesTypes of Concretesameer khanNo ratings yet
- Construction ManagementDocument55 pagesConstruction Managementkmmansaf100% (1)
- Cloud IT NetworkDocument3 pagesCloud IT NetworkClaudian PaduraruNo ratings yet