Professional Documents
Culture Documents
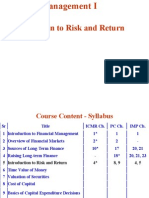
Analysis of Manufacturing and Processing Company
Analysis of Manufacturing and Processing Company
Uploaded by
शिशिर ढकालCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Case AssignmentDocument9 pagesCase Assignmentशिशिर ढकालNo ratings yet
- Full Download Solution Manual For Business Analytics 3rd Edition Jeffrey D Camm James J Cochran Michael J Fry Jeffrey W Ohlmann David R Anderson Dennis J Sweeney Thomas A Williams PDF Full ChapterDocument35 pagesFull Download Solution Manual For Business Analytics 3rd Edition Jeffrey D Camm James J Cochran Michael J Fry Jeffrey W Ohlmann David R Anderson Dennis J Sweeney Thomas A Williams PDF Full Chapterjocosevannerh98oj100% (25)
- World Lit Presentation Daydream of A Drunk WomanDocument4 pagesWorld Lit Presentation Daydream of A Drunk WomanAgnes Sugut100% (1)
- Mscfe CRT m2Document6 pagesMscfe CRT m2Manit Ahlawat100% (1)
- Case StarbucksDocument3 pagesCase StarbucksAlok CNo ratings yet
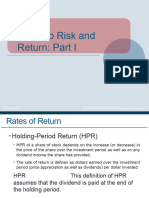
- Introduction To Risk and ReturnDocument59 pagesIntroduction To Risk and ReturnGaurav AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Bus3026w Obj5 MemoDocument4 pagesBus3026w Obj5 Memoapi-3708231No ratings yet
- Linear Regression Model Before EstimationDocument4 pagesLinear Regression Model Before EstimationAddisu TsegayeNo ratings yet
- Feruz BelarusDocument2 pagesFeruz BelarusabdulazizbakhshilloevNo ratings yet
- Risk and DiversificationDocument93 pagesRisk and DiversificationANIL_SHAR_MANo ratings yet
- Topic 10 (Ch. 24) Portfolio Performance EvaluationDocument82 pagesTopic 10 (Ch. 24) Portfolio Performance EvaluationasieNo ratings yet
- Risk & ResturnDocument6 pagesRisk & ResturnTashfa AbbasNo ratings yet
- Business-Statistics Set 2Document6 pagesBusiness-Statistics Set 2Rohit ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Business-Statistics Set 2Document6 pagesBusiness-Statistics Set 2Rohit ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- What Is Standard Deviation?Document4 pagesWhat Is Standard Deviation?MikaNo ratings yet
- Sta Chương15Document4 pagesSta Chương15Nguyễn Thu HươngNo ratings yet
- 4.0 Measures of Skewness - Dispersion - VariabilityDocument8 pages4.0 Measures of Skewness - Dispersion - VariabilityBridget MatutuNo ratings yet
- 2012 ECON 1203 S1 SolutionsDocument9 pages2012 ECON 1203 S1 SolutionsWayne ZhuNo ratings yet
- Business and Economic ForecastingDocument34 pagesBusiness and Economic ForecastingShekhar SinghNo ratings yet
- Portfolio Risk & Return Part 1Document59 pagesPortfolio Risk & Return Part 1Krishna MishraNo ratings yet
- Analytics Report: Fisher InvestmentsDocument4 pagesAnalytics Report: Fisher Investmentsapi-736250712No ratings yet
- Financial ManagementDocument6 pagesFinancial ManagementTashfa AbbasNo ratings yet
- CH 3Document42 pagesCH 3Aarya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Quantitative Methods & Statistics: Managerial ReportDocument5 pagesAdvanced Quantitative Methods & Statistics: Managerial ReportZ_RachidNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions - Quantitative - Reading 7Document13 pagesPractice Questions - Quantitative - Reading 7Khải HoànNo ratings yet
- Risk & ReturnDocument90 pagesRisk & ReturnRashi MehtaNo ratings yet
- Halima Shahid, Sp19-Baf-024 - UsaDocument13 pagesHalima Shahid, Sp19-Baf-024 - UsaMoeez KhanNo ratings yet
- RegressionDocument27 pagesRegressionLovedeep ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Fin Man Chapter 5Document48 pagesFin Man Chapter 5Yvette Pauline JovenNo ratings yet
- Risk ReturnDocument27 pagesRisk ReturnPrasaad TayadeNo ratings yet
- Fin 4600 Practice Mid Term Exam 1 Robert UptegraffDocument12 pagesFin 4600 Practice Mid Term Exam 1 Robert UptegraffNguyễn Thanh TùngNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Statistics PDFDocument51 pagesIntroduction To Statistics PDFEtoos EduNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Equity ValuationDocument28 pagesChapter 13 Equity ValuationSakthi PriyadharshiniNo ratings yet
- Analysis Sums - 3Document10 pagesAnalysis Sums - 3Jessy NairNo ratings yet
- Data Acqusition Final ReportDocument17 pagesData Acqusition Final ReportRevathy PNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Research Results: Variables Proxy Mean Median Stdev. Min Max ObsDocument10 pagesChapter 4: Research Results: Variables Proxy Mean Median Stdev. Min Max ObsFestusNo ratings yet
- Evans Analytics2e PPT 04Document47 pagesEvans Analytics2e PPT 04txuanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Equity ValuationDocument33 pagesChapter 13 Equity Valuationsharktale2828No ratings yet
- CH 8Document25 pagesCH 8Mike M. MalimNo ratings yet
- SPSS 4Document10 pagesSPSS 4Lehar GabaNo ratings yet
- Standard ScoresDocument46 pagesStandard ScoresRochelle D. Tuddao-Lim100% (1)
- Investment Company Paige Begody Regression Discussion 13 MARCH 2023Document3 pagesInvestment Company Paige Begody Regression Discussion 13 MARCH 2023api-700591109No ratings yet
- Financial Statement Ratios and AnalysisDocument19 pagesFinancial Statement Ratios and Analysismnadeem_248131No ratings yet
- Multiple Regression in SPSS: X X X y X X y X X yDocument13 pagesMultiple Regression in SPSS: X X X y X X y X X yRohit SikriNo ratings yet
- Simple$MultipleLinearRegression RobinTeotiaDocument15 pagesSimple$MultipleLinearRegression RobinTeotiahani.sharma324No ratings yet
- SPSS 4 - RemovedDocument9 pagesSPSS 4 - RemovedLehar GabaNo ratings yet
- Nu - Edu.kz Econometrics-I Assignment 3 Answer KeyDocument7 pagesNu - Edu.kz Econometrics-I Assignment 3 Answer KeyAidanaNo ratings yet
- CH 3 - Risk and ReturnDocument26 pagesCH 3 - Risk and ReturnALEMU TADESSENo ratings yet
- 14 Chapter 5Document43 pages14 Chapter 5Neetu KumariNo ratings yet
- Valuation of Risk and Return in Mutual FundDocument23 pagesValuation of Risk and Return in Mutual FundDarshit ThakkarNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Economic Concepts: ©2008 Thomson South-WesternDocument27 pagesFundamental Economic Concepts: ©2008 Thomson South-WesternMangalah Gauari MahaletchnanNo ratings yet
- Insititute of Business and Technology (Biztek)Document59 pagesInsititute of Business and Technology (Biztek)Asad MazharNo ratings yet
- Why Study Dispersion?: Spread of The DataDocument31 pagesWhy Study Dispersion?: Spread of The DataAshekin MahadiNo ratings yet
- BF Notes Risk and Return Single AssetDocument5 pagesBF Notes Risk and Return Single AssetMac SilaNo ratings yet
- Overview of PortfolioDocument22 pagesOverview of PortfolioLindsay DavisNo ratings yet
- 277 Discussion Assingment RegressionDocument5 pages277 Discussion Assingment Regressionapi-661554832No ratings yet
- Measure of Variability ReportDocument18 pagesMeasure of Variability ReportYudna YuNo ratings yet
- 4-Accuracy in Forecasting PDFDocument43 pages4-Accuracy in Forecasting PDFAmber KiranNo ratings yet
- Risk & Return An Overview of Capital Market TheoryDocument20 pagesRisk & Return An Overview of Capital Market TheoryVaishnav KumarNo ratings yet
- IUBFINMAN5555Document25 pagesIUBFINMAN5555Sajan Razzak AkonNo ratings yet
- MISDocument2 pagesMISशिशिर ढकालNo ratings yet
- Instructions - FDP On SEMDocument1 pageInstructions - FDP On SEMशिशिर ढकालNo ratings yet
- MisDocument1 pageMisशिशिर ढकालNo ratings yet
- Basics of Management AccountingDocument2 pagesBasics of Management Accountingशिशिर ढकालNo ratings yet
- Development of Water Park at BiratnagarDocument1 pageDevelopment of Water Park at Biratnagarशिशिर ढकालNo ratings yet
- 2 Statement of Problem For CAMEL AnalysisDocument1 page2 Statement of Problem For CAMEL Analysisशिशिर ढकालNo ratings yet
- Family HealthDocument148 pagesFamily Healthशिशिर ढकालNo ratings yet
- Host EL Boy Host EL Girl: KMC School Students' Out Pass KMC School Students' Out PassDocument1 pageHost EL Boy Host EL Girl: KMC School Students' Out Pass KMC School Students' Out Passशिशिर ढकालNo ratings yet
- List of Commercial Banks in NepalDocument1 pageList of Commercial Banks in Nepalशिशिर ढकालNo ratings yet
- Objective of The StudyDocument1 pageObjective of The Studyशिशिर ढकालNo ratings yet
- Marketing Budget Plan PersonnelDocument2 pagesMarketing Budget Plan Personnelशिशिर ढकालNo ratings yet
- Sample Businesss PlanDocument17 pagesSample Businesss Planशिशिर ढकालNo ratings yet
- Prabhu BankDocument2 pagesPrabhu Bankशिशिर ढकालNo ratings yet
- Beta Management Company AnalysisDocument1 pageBeta Management Company Analysisशिशिर ढकाल0% (1)
- Bowzo CaseDocument3 pagesBowzo Caseशिशिर ढकालNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire On Preference On Smart PhoneDocument4 pagesQuestionnaire On Preference On Smart Phoneशिशिर ढकालNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire DesignDocument24 pagesQuestionnaire Designशिशिर ढकालNo ratings yet
- Causes of Unemployment in NepalDocument3 pagesCauses of Unemployment in Nepalशिशिर ढकाल100% (1)
- What Gregory of Nyssa Owes To Plato's Ideas and Practices of The Self? Convergences and Divergences Between Plato's Alcibiades and Gregory of Nyssa's Treatise On Virginity.Document13 pagesWhat Gregory of Nyssa Owes To Plato's Ideas and Practices of The Self? Convergences and Divergences Between Plato's Alcibiades and Gregory of Nyssa's Treatise On Virginity.Guilherme Rodrigues FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Ejemplo ArtículoDocument11 pagesEjemplo ArtículoAmaia AitanaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemistry - Print - Quizizz2Document10 pagesIntroduction To Chemistry - Print - Quizizz2andieNo ratings yet
- Yob 2014Document564 pagesYob 2014chuNo ratings yet
- Ucla PGP Pro BrochureDocument28 pagesUcla PGP Pro BrochureTarapada MishraNo ratings yet
- Niranjana Ramesh - PHD ThesisDocument311 pagesNiranjana Ramesh - PHD Thesissurya RNo ratings yet
- Et Cetera DiscordiaDocument126 pagesEt Cetera DiscordiakesherNo ratings yet
- Arthanaya Capital - WriteupDocument1 pageArthanaya Capital - WriteupAryan GargNo ratings yet
- Gnuradio ProjectosDocument4 pagesGnuradio ProjectosartovolastiNo ratings yet
- ADE 420 Spring 2015 Assignment #1 GuidelinesDocument2 pagesADE 420 Spring 2015 Assignment #1 Guidelinesapi-20975547No ratings yet
- Cost of CapitalDocument4 pagesCost of Capitalshan50% (2)
- Oman Tech Company EmailDocument48 pagesOman Tech Company Emailcontact.joana01No ratings yet
- Summary Standard CostingDocument2 pagesSummary Standard CostingMaria Callista LovinaNo ratings yet
- Othello Research ExampleDocument6 pagesOthello Research ExampleValerie SmithNo ratings yet
- Financial Results For The Year 2019 20Document35 pagesFinancial Results For The Year 2019 20Akshaya SwaminathanNo ratings yet
- Aluminium Doors Windows and VentilatorsDocument21 pagesAluminium Doors Windows and VentilatorsPoorna ChinnapaNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Rewards and Punishments On The Academic Performance of Students of The College of Teacher EducationDocument9 pagesThe Effects of Rewards and Punishments On The Academic Performance of Students of The College of Teacher EducationMarjorie AlbanoNo ratings yet
- MTH401 23FEB2011FINALPAPERBYShiningStarDocument9 pagesMTH401 23FEB2011FINALPAPERBYShiningStarMuhammad AtharNo ratings yet
- Juvenile Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument30 pagesJuvenile Rheumatoid ArthritisAnonymous dFSZ2k2IUNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes: Manila Cavite Laguna Cebu Cagayan de Oro DavaoDocument5 pagesLecture Notes: Manila Cavite Laguna Cebu Cagayan de Oro DavaoDenny June CraususNo ratings yet
- How Does Marijuana Affect The BrainDocument3 pagesHow Does Marijuana Affect The BrainWanNurAtikahNo ratings yet
- Running Head: Customer Relationship Management Report 1Document11 pagesRunning Head: Customer Relationship Management Report 1fenil voraNo ratings yet
- Bank BuildingDocument47 pagesBank BuildingVijay GanapathyNo ratings yet
- Leadership and Management ProjectDocument12 pagesLeadership and Management Projectshian ramdialNo ratings yet
- (PC) Porras v. Woodward - Document No. 3Document2 pages(PC) Porras v. Woodward - Document No. 3Justia.comNo ratings yet
- Homophobic Transphobic Bullying Pe Focus1Document2 pagesHomophobic Transphobic Bullying Pe Focus1api-440470277No ratings yet
- Isha Joseph - Internship Logbook 2020-2021Document12 pagesIsha Joseph - Internship Logbook 2020-2021avinal malikNo ratings yet
- CH 2 - WSDocument3 pagesCH 2 - WSNANNo ratings yet
Analysis of Manufacturing and Processing Company
Analysis of Manufacturing and Processing Company
Uploaded by
शिशिर ढकालOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Analysis of Manufacturing and Processing Company
Analysis of Manufacturing and Processing Company
Uploaded by
शिशिर ढकालCopyright:
Available Formats
Presentation on Statistical
Analysis of
Manufacturing and Processing
Company
By Group :- B Date :- 15
th
July 2013
INTRODUCTION
Introduction to manufacturing company
Objectives of the study
Variables under study
Net worth per share
Net profit
Paid up capital
Hypothesis
Null hypothesis: There is no significant impact of Net
Profit and Paid up capital on Net worth per Share.
Alternative hypothesis: There is significant impact of
Net profit and Paid up capital on Net worth per Share.
Level of significance: 5%
Methodology
secondary information and data
DESCRIPTIVE ANALYSIS
Descriptive statistics is the discipline of quantitatively
describing the main features of a collection of data or
the quantitative description itself.
Some measures that are commonly used to describe a
data set are measures of central tendency and
measures of variability or dispersion.
Mean
Median
Mode
Standard deviation
Box-plot summary
A box plot provide a graphical representation of the
data based on five number summary.
Box-Plot
MIN=-50.42
MAX=444.04
Q1= -9.145 Q2= -0.62 Q3=19.0825
It indicates that it is right skewed. It is because the distance between
the median and the highest value is greater than distance between
the lowest value and the median value. Right tail is longer than the
left tail.
Coefficient of variation (C.V)
The coefficient of variation measures the scatter in the data relative to the
mean. It is the measure of consistency of the data. The coefficient of
variation denotes the variation or riskiness.
Skewness
Skewness is the measure of asymmetry of the probability distribution of a
real-valued random variable. It can be positive or negative, or even
undefined. Skewness is an important consideration when examining
investment returns
Kurtosis
Kurtosis measures whether the data is sharp or flat relative to a normal
distribution. It focuses on how returns are ranged around the mean.
Descriptive statistics
Net worth per share Net profit Paid up capital
Mean -24.72 39.53 148.08
Standard Error 145.43 37.80 42.53
Median 83.10 -0.62 106.54
Mode N/A N/A N/A
Standard Deviation 503.79 130.95 147.34
Sample Variance 253800.19 17147.55 21710.41
Kurtosis 4.91 10.37 -0.43
Skewness -1.66 3.15 0.89
Range 2117.39 494.46 421.62
Minimum -1370.27 -50.42 12.93
Maximum 747.12 444.04 434.55
Sum -296.69 474.37 1777.01
Count 12.00 12.00 12.00
Interpretation
Net worth per share
The mean is -24.72
The median is 83.90
The standard deviation is 503.79,
The skewness is -1.66, which shows that the data is left skewed.
The minimum is worth per share is -1370.27
The maximum worth per share is 747.12.
Since frequency is not available, mode cannot be calculated.
The kurtosis is 4.91, which shows leptokurtic distribution.
Net profit
The mean is 39.53
The median is 0.62
The standard deviation is 130.95
Since frequency is not available, mode cannot be
calculated.
the minimum profit is -50.42 and maximum profit is 444.04
The skewness is 3.15, which shows that the data is right
skewed.
The kurtosis is 10.37, which shows leptokurtic distribution.
Paid up capital
The mean is 148.08
The median is 106.54
The mode cannot be calculated here because of
unavailability of frequency.
The standard deviation is 147.34
The skewness is 0.89 which shows that the data is right
skewed.
The kurtosis is -0.43, which shows plautikurtic distribution
The minimum value is 12.93 and the maximum value is
434.55
CORRELATION AND
REGRESSION ANALYSIS
Correlation
correlation matrix
Net worth per share Net profit Paid up capital
Net worth per share 1
Net Profit 0.54 1
Paid up capital 0.04 -0.21 1
Calculation of Variance Inflation Factor (VIF):
Between paid up capital and net profit
VIF = 1/ 1-r
2
= 1/ (1- (-0.21)
2
)
= 1.05
Since VIF between net profit and paid up capital is less
than 10 the multi-co-linearity does not exist. Therefore
we now compute the regression equation.
Regression
Regression is a way of describing how one variable, the outcome, is
numerically related to predictor variables.
Y = +
1
x
1
+
2
x
2
+...+
n
x
n
Regression table
Coefficients Standard Error t Stat P-value
Net worth per share -192.20 205.90 -0.93 0.37
Net profit 2.21 1.08 2.04 0.07
Paid up capital 0.54 0.96 0.56 0.59
The estimated regression equation :
Y= +
1
X
1
+
2
X
2
Y= -192.20 + (2.21*X
1
) + (0.54*X
2)
(-0.93) (2.04)
*
(0.56)
Note: * signify the significance level at 1%.
= -192.20. It indicates that when net profit and paid up capital are
zero, the net worth per share is -192.20 which indicates there is
negative net worth per share or decreasing net worth per share.
1=2.21 indicates that if net profit is increased by 1 more unit then
the net worth per share increases by 2.21 unit keeping paid up
capital at its constant level.
2=0.54 indicates that if paid up capital is increased by 1 more unit
then the net worth per share increases by 0.54 unit keeping net profit
constant at its same level.
Regression Statistics
Multiple R 0.56
R Square 0.32
Adjusted R Square 0.17
Standard Error 460.32
Observations 12
ANOVA
Df SS MS F Significance F
Regression 2 884743.40 442371.70 2.09 0.18
Residual 9 1907058.67 211895.41
Total 11 2791802.08
Interpretation
R= 0.56 means the multiple correlation between the net worth
per share and net profit and paid up capital is 56%.
R
2
= 0.32 means 32% of variation in net worth per share is
explained by linear relationship of net profit and paid up
capital, while 68% of variation remains unexplained.
F= 2.09 using the 0.05 level of significance from the table the
critical value of F distribution is more than the F statistical
value, we accept the null hypothesis and conclude that the net
worth per share is significantly related to the net profit and
paid up capital.
CONCLUSION
P value of x variable 2 i.e.: Paid up capital is greater than the significance
level so there is no significant relation between Paid up capital and Net
worth per share.
P value of x variable 1 i.e.: Net Profit is greater than the level of
significance so there is no significant relation between Net Profit and Net
worth per share.
Since R2=32% these two factors are responsible to describe 32% of change
in return other remaining (68%) remains unexplained.
Now from the ANOVA table, we have F=2.09 which is smaller than the
F(table)=4.26 hence Null hypothesis is accepted.
Since there is no significant linear relationship between dependent variable
(Return) and independent variables (Net Profit and Paid Up Capital) Null
hypothesis is accepted.
Any Queries
THANK YOU!!!!!
You might also like
- Case AssignmentDocument9 pagesCase Assignmentशिशिर ढकालNo ratings yet
- Full Download Solution Manual For Business Analytics 3rd Edition Jeffrey D Camm James J Cochran Michael J Fry Jeffrey W Ohlmann David R Anderson Dennis J Sweeney Thomas A Williams PDF Full ChapterDocument35 pagesFull Download Solution Manual For Business Analytics 3rd Edition Jeffrey D Camm James J Cochran Michael J Fry Jeffrey W Ohlmann David R Anderson Dennis J Sweeney Thomas A Williams PDF Full Chapterjocosevannerh98oj100% (25)
- World Lit Presentation Daydream of A Drunk WomanDocument4 pagesWorld Lit Presentation Daydream of A Drunk WomanAgnes Sugut100% (1)
- Mscfe CRT m2Document6 pagesMscfe CRT m2Manit Ahlawat100% (1)
- Case StarbucksDocument3 pagesCase StarbucksAlok CNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Risk and ReturnDocument59 pagesIntroduction To Risk and ReturnGaurav AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Bus3026w Obj5 MemoDocument4 pagesBus3026w Obj5 Memoapi-3708231No ratings yet
- Linear Regression Model Before EstimationDocument4 pagesLinear Regression Model Before EstimationAddisu TsegayeNo ratings yet
- Feruz BelarusDocument2 pagesFeruz BelarusabdulazizbakhshilloevNo ratings yet
- Risk and DiversificationDocument93 pagesRisk and DiversificationANIL_SHAR_MANo ratings yet
- Topic 10 (Ch. 24) Portfolio Performance EvaluationDocument82 pagesTopic 10 (Ch. 24) Portfolio Performance EvaluationasieNo ratings yet
- Risk & ResturnDocument6 pagesRisk & ResturnTashfa AbbasNo ratings yet
- Business-Statistics Set 2Document6 pagesBusiness-Statistics Set 2Rohit ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Business-Statistics Set 2Document6 pagesBusiness-Statistics Set 2Rohit ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- What Is Standard Deviation?Document4 pagesWhat Is Standard Deviation?MikaNo ratings yet
- Sta Chương15Document4 pagesSta Chương15Nguyễn Thu HươngNo ratings yet
- 4.0 Measures of Skewness - Dispersion - VariabilityDocument8 pages4.0 Measures of Skewness - Dispersion - VariabilityBridget MatutuNo ratings yet
- 2012 ECON 1203 S1 SolutionsDocument9 pages2012 ECON 1203 S1 SolutionsWayne ZhuNo ratings yet
- Business and Economic ForecastingDocument34 pagesBusiness and Economic ForecastingShekhar SinghNo ratings yet
- Portfolio Risk & Return Part 1Document59 pagesPortfolio Risk & Return Part 1Krishna MishraNo ratings yet
- Analytics Report: Fisher InvestmentsDocument4 pagesAnalytics Report: Fisher Investmentsapi-736250712No ratings yet
- Financial ManagementDocument6 pagesFinancial ManagementTashfa AbbasNo ratings yet
- CH 3Document42 pagesCH 3Aarya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Quantitative Methods & Statistics: Managerial ReportDocument5 pagesAdvanced Quantitative Methods & Statistics: Managerial ReportZ_RachidNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions - Quantitative - Reading 7Document13 pagesPractice Questions - Quantitative - Reading 7Khải HoànNo ratings yet
- Risk & ReturnDocument90 pagesRisk & ReturnRashi MehtaNo ratings yet
- Halima Shahid, Sp19-Baf-024 - UsaDocument13 pagesHalima Shahid, Sp19-Baf-024 - UsaMoeez KhanNo ratings yet
- RegressionDocument27 pagesRegressionLovedeep ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Fin Man Chapter 5Document48 pagesFin Man Chapter 5Yvette Pauline JovenNo ratings yet
- Risk ReturnDocument27 pagesRisk ReturnPrasaad TayadeNo ratings yet
- Fin 4600 Practice Mid Term Exam 1 Robert UptegraffDocument12 pagesFin 4600 Practice Mid Term Exam 1 Robert UptegraffNguyễn Thanh TùngNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Statistics PDFDocument51 pagesIntroduction To Statistics PDFEtoos EduNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Equity ValuationDocument28 pagesChapter 13 Equity ValuationSakthi PriyadharshiniNo ratings yet
- Analysis Sums - 3Document10 pagesAnalysis Sums - 3Jessy NairNo ratings yet
- Data Acqusition Final ReportDocument17 pagesData Acqusition Final ReportRevathy PNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Research Results: Variables Proxy Mean Median Stdev. Min Max ObsDocument10 pagesChapter 4: Research Results: Variables Proxy Mean Median Stdev. Min Max ObsFestusNo ratings yet
- Evans Analytics2e PPT 04Document47 pagesEvans Analytics2e PPT 04txuanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Equity ValuationDocument33 pagesChapter 13 Equity Valuationsharktale2828No ratings yet
- CH 8Document25 pagesCH 8Mike M. MalimNo ratings yet
- SPSS 4Document10 pagesSPSS 4Lehar GabaNo ratings yet
- Standard ScoresDocument46 pagesStandard ScoresRochelle D. Tuddao-Lim100% (1)
- Investment Company Paige Begody Regression Discussion 13 MARCH 2023Document3 pagesInvestment Company Paige Begody Regression Discussion 13 MARCH 2023api-700591109No ratings yet
- Financial Statement Ratios and AnalysisDocument19 pagesFinancial Statement Ratios and Analysismnadeem_248131No ratings yet
- Multiple Regression in SPSS: X X X y X X y X X yDocument13 pagesMultiple Regression in SPSS: X X X y X X y X X yRohit SikriNo ratings yet
- Simple$MultipleLinearRegression RobinTeotiaDocument15 pagesSimple$MultipleLinearRegression RobinTeotiahani.sharma324No ratings yet
- SPSS 4 - RemovedDocument9 pagesSPSS 4 - RemovedLehar GabaNo ratings yet
- Nu - Edu.kz Econometrics-I Assignment 3 Answer KeyDocument7 pagesNu - Edu.kz Econometrics-I Assignment 3 Answer KeyAidanaNo ratings yet
- CH 3 - Risk and ReturnDocument26 pagesCH 3 - Risk and ReturnALEMU TADESSENo ratings yet
- 14 Chapter 5Document43 pages14 Chapter 5Neetu KumariNo ratings yet
- Valuation of Risk and Return in Mutual FundDocument23 pagesValuation of Risk and Return in Mutual FundDarshit ThakkarNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Economic Concepts: ©2008 Thomson South-WesternDocument27 pagesFundamental Economic Concepts: ©2008 Thomson South-WesternMangalah Gauari MahaletchnanNo ratings yet
- Insititute of Business and Technology (Biztek)Document59 pagesInsititute of Business and Technology (Biztek)Asad MazharNo ratings yet
- Why Study Dispersion?: Spread of The DataDocument31 pagesWhy Study Dispersion?: Spread of The DataAshekin MahadiNo ratings yet
- BF Notes Risk and Return Single AssetDocument5 pagesBF Notes Risk and Return Single AssetMac SilaNo ratings yet
- Overview of PortfolioDocument22 pagesOverview of PortfolioLindsay DavisNo ratings yet
- 277 Discussion Assingment RegressionDocument5 pages277 Discussion Assingment Regressionapi-661554832No ratings yet
- Measure of Variability ReportDocument18 pagesMeasure of Variability ReportYudna YuNo ratings yet
- 4-Accuracy in Forecasting PDFDocument43 pages4-Accuracy in Forecasting PDFAmber KiranNo ratings yet
- Risk & Return An Overview of Capital Market TheoryDocument20 pagesRisk & Return An Overview of Capital Market TheoryVaishnav KumarNo ratings yet
- IUBFINMAN5555Document25 pagesIUBFINMAN5555Sajan Razzak AkonNo ratings yet
- MISDocument2 pagesMISशिशिर ढकालNo ratings yet
- Instructions - FDP On SEMDocument1 pageInstructions - FDP On SEMशिशिर ढकालNo ratings yet
- MisDocument1 pageMisशिशिर ढकालNo ratings yet
- Basics of Management AccountingDocument2 pagesBasics of Management Accountingशिशिर ढकालNo ratings yet
- Development of Water Park at BiratnagarDocument1 pageDevelopment of Water Park at Biratnagarशिशिर ढकालNo ratings yet
- 2 Statement of Problem For CAMEL AnalysisDocument1 page2 Statement of Problem For CAMEL Analysisशिशिर ढकालNo ratings yet
- Family HealthDocument148 pagesFamily Healthशिशिर ढकालNo ratings yet
- Host EL Boy Host EL Girl: KMC School Students' Out Pass KMC School Students' Out PassDocument1 pageHost EL Boy Host EL Girl: KMC School Students' Out Pass KMC School Students' Out Passशिशिर ढकालNo ratings yet
- List of Commercial Banks in NepalDocument1 pageList of Commercial Banks in Nepalशिशिर ढकालNo ratings yet
- Objective of The StudyDocument1 pageObjective of The Studyशिशिर ढकालNo ratings yet
- Marketing Budget Plan PersonnelDocument2 pagesMarketing Budget Plan Personnelशिशिर ढकालNo ratings yet
- Sample Businesss PlanDocument17 pagesSample Businesss Planशिशिर ढकालNo ratings yet
- Prabhu BankDocument2 pagesPrabhu Bankशिशिर ढकालNo ratings yet
- Beta Management Company AnalysisDocument1 pageBeta Management Company Analysisशिशिर ढकाल0% (1)
- Bowzo CaseDocument3 pagesBowzo Caseशिशिर ढकालNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire On Preference On Smart PhoneDocument4 pagesQuestionnaire On Preference On Smart Phoneशिशिर ढकालNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire DesignDocument24 pagesQuestionnaire Designशिशिर ढकालNo ratings yet
- Causes of Unemployment in NepalDocument3 pagesCauses of Unemployment in Nepalशिशिर ढकाल100% (1)
- What Gregory of Nyssa Owes To Plato's Ideas and Practices of The Self? Convergences and Divergences Between Plato's Alcibiades and Gregory of Nyssa's Treatise On Virginity.Document13 pagesWhat Gregory of Nyssa Owes To Plato's Ideas and Practices of The Self? Convergences and Divergences Between Plato's Alcibiades and Gregory of Nyssa's Treatise On Virginity.Guilherme Rodrigues FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Ejemplo ArtículoDocument11 pagesEjemplo ArtículoAmaia AitanaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemistry - Print - Quizizz2Document10 pagesIntroduction To Chemistry - Print - Quizizz2andieNo ratings yet
- Yob 2014Document564 pagesYob 2014chuNo ratings yet
- Ucla PGP Pro BrochureDocument28 pagesUcla PGP Pro BrochureTarapada MishraNo ratings yet
- Niranjana Ramesh - PHD ThesisDocument311 pagesNiranjana Ramesh - PHD Thesissurya RNo ratings yet
- Et Cetera DiscordiaDocument126 pagesEt Cetera DiscordiakesherNo ratings yet
- Arthanaya Capital - WriteupDocument1 pageArthanaya Capital - WriteupAryan GargNo ratings yet
- Gnuradio ProjectosDocument4 pagesGnuradio ProjectosartovolastiNo ratings yet
- ADE 420 Spring 2015 Assignment #1 GuidelinesDocument2 pagesADE 420 Spring 2015 Assignment #1 Guidelinesapi-20975547No ratings yet
- Cost of CapitalDocument4 pagesCost of Capitalshan50% (2)
- Oman Tech Company EmailDocument48 pagesOman Tech Company Emailcontact.joana01No ratings yet
- Summary Standard CostingDocument2 pagesSummary Standard CostingMaria Callista LovinaNo ratings yet
- Othello Research ExampleDocument6 pagesOthello Research ExampleValerie SmithNo ratings yet
- Financial Results For The Year 2019 20Document35 pagesFinancial Results For The Year 2019 20Akshaya SwaminathanNo ratings yet
- Aluminium Doors Windows and VentilatorsDocument21 pagesAluminium Doors Windows and VentilatorsPoorna ChinnapaNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Rewards and Punishments On The Academic Performance of Students of The College of Teacher EducationDocument9 pagesThe Effects of Rewards and Punishments On The Academic Performance of Students of The College of Teacher EducationMarjorie AlbanoNo ratings yet
- MTH401 23FEB2011FINALPAPERBYShiningStarDocument9 pagesMTH401 23FEB2011FINALPAPERBYShiningStarMuhammad AtharNo ratings yet
- Juvenile Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument30 pagesJuvenile Rheumatoid ArthritisAnonymous dFSZ2k2IUNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes: Manila Cavite Laguna Cebu Cagayan de Oro DavaoDocument5 pagesLecture Notes: Manila Cavite Laguna Cebu Cagayan de Oro DavaoDenny June CraususNo ratings yet
- How Does Marijuana Affect The BrainDocument3 pagesHow Does Marijuana Affect The BrainWanNurAtikahNo ratings yet
- Running Head: Customer Relationship Management Report 1Document11 pagesRunning Head: Customer Relationship Management Report 1fenil voraNo ratings yet
- Bank BuildingDocument47 pagesBank BuildingVijay GanapathyNo ratings yet
- Leadership and Management ProjectDocument12 pagesLeadership and Management Projectshian ramdialNo ratings yet
- (PC) Porras v. Woodward - Document No. 3Document2 pages(PC) Porras v. Woodward - Document No. 3Justia.comNo ratings yet
- Homophobic Transphobic Bullying Pe Focus1Document2 pagesHomophobic Transphobic Bullying Pe Focus1api-440470277No ratings yet
- Isha Joseph - Internship Logbook 2020-2021Document12 pagesIsha Joseph - Internship Logbook 2020-2021avinal malikNo ratings yet
- CH 2 - WSDocument3 pagesCH 2 - WSNANNo ratings yet