Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Transformer (LVDT) Is The Most Broadly
Transformer (LVDT) Is The Most Broadly
Uploaded by
Arpita NayyarCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Power System Planning NotesDocument36 pagesPower System Planning NotesJanapareddy Veerendra Kumar67% (3)
- Wages For Electrical Chargeman Johor (Rev. 2023)Document4 pagesWages For Electrical Chargeman Johor (Rev. 2023)mohd aizat mohd sayuthiNo ratings yet
- Physics Porject Report Class 12th MathsDocument22 pagesPhysics Porject Report Class 12th MathsAaditya TomarNo ratings yet
- Linear Variable Differential Transformer (LVDT)Document9 pagesLinear Variable Differential Transformer (LVDT)Naveen kumarNo ratings yet
- LIST OF DPT PLN 2019 Rev1Document2 pagesLIST OF DPT PLN 2019 Rev1zulkifliharahap100% (1)
- Principle of LVDTDocument3 pagesPrinciple of LVDTShoaib MughalNo ratings yet
- Linear Variable Displacement Transducer (LVDT)Document3 pagesLinear Variable Displacement Transducer (LVDT)SE ElectricalNo ratings yet
- LVDTDocument12 pagesLVDTPratheep V.G. MTSNo ratings yet
- Linear Variable Differential TransformerDocument10 pagesLinear Variable Differential TransformerSoumik DasNo ratings yet
- Chapter1mechanicalmeasurement 160309072647Document19 pagesChapter1mechanicalmeasurement 160309072647bd9051No ratings yet
- LVDT: Basic Principle, Theory, Working, Explanation & Diagram - Linear Variable Differential TransformerDocument2 pagesLVDT: Basic Principle, Theory, Working, Explanation & Diagram - Linear Variable Differential TransformerAtul NagarkarNo ratings yet
- Linear Variable Differential Transformer (LVDT)Document5 pagesLinear Variable Differential Transformer (LVDT)nikitaNo ratings yet
- LVDTDocument8 pagesLVDTsadu1978100% (1)
- 2130903Document14 pages2130903mitaliNo ratings yet
- Study of Displacement Transducer AIM: TheoryDocument6 pagesStudy of Displacement Transducer AIM: Theoryneelam sanjeev kumarNo ratings yet
- LVDTDocument11 pagesLVDTDaystar YtNo ratings yet
- Displacement MeasurementDocument12 pagesDisplacement MeasurementmitaliNo ratings yet
- LVDTDocument15 pagesLVDTvishal joshiNo ratings yet
- Linear Variable Differential Transformer (LVDT) PDFDocument3 pagesLinear Variable Differential Transformer (LVDT) PDFSrirangam RajeshNo ratings yet
- LVDT PresentationDocument7 pagesLVDT PresentationAsif Sheikh100% (1)
- Linear Variable Differential Transformer (LVDT)Document13 pagesLinear Variable Differential Transformer (LVDT)Nikhil Waghalkar100% (1)
- Transducers 130331093736 Phpapp01Document21 pagesTransducers 130331093736 Phpapp01Ayush ThakurNo ratings yet
- Transducers & Sensors: Alsalama College of Sciences &technology Electrical Engineering DepartmentDocument14 pagesTransducers & Sensors: Alsalama College of Sciences &technology Electrical Engineering DepartmentAlamin IbrahimNo ratings yet
- ST Unit 4 NotesDocument25 pagesST Unit 4 Notesabc fun facts100% (1)
- I&M Lab EXP 6 Part 1Document4 pagesI&M Lab EXP 6 Part 1MathewNo ratings yet
- LVDTDocument20 pagesLVDTsindhu100% (1)
- Study of LVDTDocument10 pagesStudy of LVDTSubhash KNo ratings yet
- LVDTDocument30 pagesLVDTDEEPA KUNWARNo ratings yet
- Linear Variable Differential Transformer LVDTDocument5 pagesLinear Variable Differential Transformer LVDTPoonam YadavNo ratings yet
- ICS Day - 10 Lecture NotesDocument3 pagesICS Day - 10 Lecture NotesRavikiran MahendraNo ratings yet
- Linear Variable Differential Transformer LVDTDocument8 pagesLinear Variable Differential Transformer LVDTRakesh MahajanNo ratings yet
- LVDT: Linear Variable Differential Transformer: Presented By: Shantanu Inderesh Harsh Presentation Made By: ShantanuDocument10 pagesLVDT: Linear Variable Differential Transformer: Presented By: Shantanu Inderesh Harsh Presentation Made By: Shantanuindresh singhNo ratings yet
- What Is LVDTDocument8 pagesWhat Is LVDTKeerthana DNo ratings yet
- Inductive TransducerDocument8 pagesInductive TransducerAAKASHNo ratings yet
- LVDT: Liner Varying Differential Transducer: Presented By:-Anantha Sai 1005 2073 1082Document21 pagesLVDT: Liner Varying Differential Transducer: Presented By:-Anantha Sai 1005 2073 1082RuchitaNo ratings yet
- Star Academy of Technology & Management, Indore: Electronic Instrumentation (Ex-604) Lab ManualDocument3 pagesStar Academy of Technology & Management, Indore: Electronic Instrumentation (Ex-604) Lab ManualPraveen Kumar ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Eti Unit-2Document4 pagesEti Unit-2kalpanaNo ratings yet
- Siddharth PhyDocument12 pagesSiddharth Physiddharthdeuri476No ratings yet
- LVDT Working PrincipleDocument2 pagesLVDT Working Principlekulwinder030373No ratings yet
- Linear Variable Differential Transformer LVDTDocument7 pagesLinear Variable Differential Transformer LVDTRajeev ValunjkarNo ratings yet
- Linear Variable Differential Transformer Measurements: EET-027, Experiment # 9Document4 pagesLinear Variable Differential Transformer Measurements: EET-027, Experiment # 9nainesh goteNo ratings yet
- of LVDTDocument8 pagesof LVDTDebasisMohapatraNo ratings yet
- AnkurMondal 12030523017Document10 pagesAnkurMondal 12030523017ankurmondal039No ratings yet
- EE17401-M& I Inductive Transducer, Capacitive TransducerDocument31 pagesEE17401-M& I Inductive Transducer, Capacitive TransduceravsNo ratings yet
- TRANSFORMER (Levinesh)Document16 pagesTRANSFORMER (Levinesh)livinesh05rNo ratings yet
- Potentiometer and LVDTDocument4 pagesPotentiometer and LVDTAbhishek Kumar JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Linear Variable Differential TransformerDocument6 pagesLinear Variable Differential TransformerDaulat NathNo ratings yet
- ContentDocument12 pagesContentHarishNo ratings yet
- Module-1 TransformersDocument27 pagesModule-1 TransformersSuraj Gowda BHNo ratings yet
- Eee3352 L6&7&8Document54 pagesEee3352 L6&7&8Desmond CheweNo ratings yet
- TransformerDocument30 pagesTransformerASHISHNo ratings yet
- Construction & WorkingDocument22 pagesConstruction & WorkingShah Aizat Razali100% (1)
- Linear Variable Differential TransformerDocument19 pagesLinear Variable Differential TransformerPranesh100% (1)
- Directional-RelaysDocument11 pagesDirectional-RelaysYH TAnNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document39 pagesUnit 4swthsrisaiNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machine I-3140913Document44 pagesElectrical Machine I-3140913Patel KashyapNo ratings yet
- Capacitive Transducers-T06Document60 pagesCapacitive Transducers-T06Nikhil SinghNo ratings yet
- محاضرة آلات طيران المحاضرة التالتةDocument38 pagesمحاضرة آلات طيران المحاضرة التالتةomarjoker808No ratings yet
- TRANSFORMERSDocument24 pagesTRANSFORMERStmmbonelaNo ratings yet
- ELE290Document24 pagesELE290Muhammad Hamizan HakiemiNo ratings yet
- Linear Variable Differential TransformerDocument1 pageLinear Variable Differential TransformerAmit SinhaNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- LM NotesDocument86 pagesLM NotesArpita NayyarNo ratings yet
- Compile Time PolymorphismDocument14 pagesCompile Time PolymorphismArpita NayyarNo ratings yet
- Development Scada System For Monitoring and Controlling Various System ParametersDocument17 pagesDevelopment Scada System For Monitoring and Controlling Various System ParametersArpita NayyarNo ratings yet
- Assignment-I Msmes in India: Guided By: Submitted byDocument6 pagesAssignment-I Msmes in India: Guided By: Submitted byArpita Nayyar100% (1)
- Pe 2Document13 pagesPe 2Arpita NayyarNo ratings yet
- The Seven Types of Power Problems: White Paper 18Document21 pagesThe Seven Types of Power Problems: White Paper 18FELIXDEJNo ratings yet
- D Brochure TeleREC English 08Document12 pagesD Brochure TeleREC English 08wagnercrjrNo ratings yet
- DB en Quint4 Ps 1ac 110dc 4 109530 en 00Document48 pagesDB en Quint4 Ps 1ac 110dc 4 109530 en 00Asad NaeemNo ratings yet
- 12v Battery ChargersDocument45 pages12v Battery ChargersPhani Sharma100% (1)
- Magnetic BalanceDocument3 pagesMagnetic BalancegaladrialNo ratings yet
- BD FMP A1 TZ 015 F3015P Series Pro2.0 CEDocument15 pagesBD FMP A1 TZ 015 F3015P Series Pro2.0 CEVictor PATIÑONo ratings yet
- OE Spec DP01500D5S 12V FC TB 50Hz 2 14Document6 pagesOE Spec DP01500D5S 12V FC TB 50Hz 2 14خطاب الشاميNo ratings yet
- 20 MVA RusailDocument34 pages20 MVA RusailbxteoNo ratings yet
- Cat G3516A: Natural Gas Generator SetsDocument5 pagesCat G3516A: Natural Gas Generator SetsRecovery MailNo ratings yet
- Load Flow Analysis For Three Phase Unbalanced Distribution Feeders Using MatlabDocument5 pagesLoad Flow Analysis For Three Phase Unbalanced Distribution Feeders Using MatlabEdna LópezNo ratings yet
- Transformer Manufacturers Brochure - PadmavahiniDocument12 pagesTransformer Manufacturers Brochure - PadmavahiniPadmavahini Transformers Private Limited0% (1)
- Thermodynamic Cycles (Power Plant Engineering)Document6 pagesThermodynamic Cycles (Power Plant Engineering)Ravjit SinghNo ratings yet
- Elkay - Energy Management Product CatalogueDocument1 pageElkay - Energy Management Product CatalogueAnonymous XYAPaxjbYNo ratings yet
- Mov 150la20aDocument4 pagesMov 150la20aServicios TecnicosNo ratings yet
- Generator Inspection Checklist: Etwork Evelopment RoupDocument2 pagesGenerator Inspection Checklist: Etwork Evelopment RoupPhel Flores100% (1)
- Commercial and Utility: 2.1 Power Xpert Solar 250 KW InverterDocument78 pagesCommercial and Utility: 2.1 Power Xpert Solar 250 KW InverterMoshNo ratings yet
- Au Ind: FD2.1 FD2.2Document9 pagesAu Ind: FD2.1 FD2.2M SNo ratings yet
- Huawei Power Systems Acceptance Manual - Update - 20190621Document25 pagesHuawei Power Systems Acceptance Manual - Update - 20190621wawanNo ratings yet
- Product Data Sheet: Circuit Breaker Compact Nsx100H, 70 Ka at 415 Vac, TMD Trip Unit 100 A, 3 Poles 3DDocument3 pagesProduct Data Sheet: Circuit Breaker Compact Nsx100H, 70 Ka at 415 Vac, TMD Trip Unit 100 A, 3 Poles 3DJorge FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Gas-Insulated Switchgear For Substations: Common Characteristic Features of Switchgear InstallationDocument12 pagesGas-Insulated Switchgear For Substations: Common Characteristic Features of Switchgear Installationjoydeep_d3232No ratings yet
- Gujarat Energy Development AgencyDocument1 pageGujarat Energy Development AgencyJd ShaikhNo ratings yet
- L&T Relay BrochureDocument32 pagesL&T Relay BrochureSuranjana Das100% (1)
- ABB CircuitBreaker S260 S270 S280 S290 Spec D1103Document20 pagesABB CircuitBreaker S260 S270 S280 S290 Spec D1103Fernando Crespo MonsalveNo ratings yet
- Trasfo CurentDocument11 pagesTrasfo CurentAlonso CoradoNo ratings yet
- Scope and DelimitationDocument2 pagesScope and DelimitationGenieline Magalona83% (6)
- Telecommunication System Engineering Telephony Signal TransmissionDocument37 pagesTelecommunication System Engineering Telephony Signal TransmissionXafran KhanNo ratings yet
- Microgrid: Innovation, Challenges and ProspectsDocument8 pagesMicrogrid: Innovation, Challenges and ProspectsIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
Transformer (LVDT) Is The Most Broadly
Transformer (LVDT) Is The Most Broadly
Uploaded by
Arpita NayyarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Transformer (LVDT) Is The Most Broadly
Transformer (LVDT) Is The Most Broadly
Uploaded by
Arpita NayyarCopyright:
Available Formats
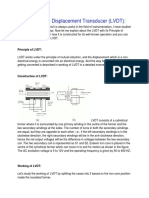
INTRODUCTION
LVDT
The Linear Variable Differential
Transformer (LVDT) is the most broadly
used variable-inductance transducer in
industry. It is an electro-mechanical
device designed to produce an AC voltage
output proportional to the relative
displacement of the transformer and the
armature.
PRINCIPLE
LVDT works under the principle of
mutual induction, and the displacement
which is a non-electrical energy is
converted into an electrical energy. And
the way how the energy is getting
converted is described in working of
LVDT in a detailed manner.
CONSTRUCTION
LVDT consists of a cylindrical former where
it is surrounded by one primary winding in
the centre of the former and the two
secondary windings at the sides. The
number of turns in both the secondary
windings are equal, but they are opposite to
each other, i.e., if the left secondary
windings is in the clockwise direction, the
right secondary windings will be in the anti-
clockwise direction, hence the net output
voltages will be the difference in voltages
between the two secondary coil. The two
secondary coil is represented as S1 and S2
Esteem iron core is placed in the centre of
the cylindrical former which can move in to
and fro motion as shown in the figure. The
AC excitation voltage is 5 to 12V and the
operating frequency is given by 50 to
400HZ.
WORKING OF LVDT
3 cases based on the iron core position
inside the insulated former.
Case 1:
On applying an external force which is the
displacement, if the core reminds in the null
position itself without providing any
movement then the voltage induced in both
the secondary windings are equal which
results in net output is equal to zero
i.e., Esec1-Esec2=0
Case 2:
When an external force is appilied and if the
steel iron core tends to move in the left hand
side direction then the emf voltage induced
in the secondary coil is greater when
compared to the emf induced in the
secondary coil 2. Therefore the net output
will be Esec1-Esec2
Case 3:
When an external force is applied and if the
steel iron core moves in the right hand side
direction then the emf induced in the
secondary coil 2 is greater when compared to
the emf voltage induced in the secondary coil 1.
therefore the net output voltage will be
Esec2-Esec1
ADVANTAGES OF LVDT
Infinite resolution is present in LVD
High output
LVDT gives High sensitivity
Very good linearity
Ruggedness
LVDT Provides Less friction
Low hysteresis
LVDT gives Low power consumption.
DISADVANTAGES OF LVDT
Very high displacement is required for
generating high voltages.
Shielding is required since it is sensitive to
magnetic field.
The performance of the transducer gets
affected by vibrations
Its is greatly affected by temperature
changes.
APPLICATION OF LVDT
LVDT is used to measure displacement
ranging from fraction millimeter to
centimeter.
Acting as a secondary transducer, LVDT can
be used as a device to measure force, weight
and pressure, etc..
THANK YOU!!!
You might also like
- Power System Planning NotesDocument36 pagesPower System Planning NotesJanapareddy Veerendra Kumar67% (3)
- Wages For Electrical Chargeman Johor (Rev. 2023)Document4 pagesWages For Electrical Chargeman Johor (Rev. 2023)mohd aizat mohd sayuthiNo ratings yet
- Physics Porject Report Class 12th MathsDocument22 pagesPhysics Porject Report Class 12th MathsAaditya TomarNo ratings yet
- Linear Variable Differential Transformer (LVDT)Document9 pagesLinear Variable Differential Transformer (LVDT)Naveen kumarNo ratings yet
- LIST OF DPT PLN 2019 Rev1Document2 pagesLIST OF DPT PLN 2019 Rev1zulkifliharahap100% (1)
- Principle of LVDTDocument3 pagesPrinciple of LVDTShoaib MughalNo ratings yet
- Linear Variable Displacement Transducer (LVDT)Document3 pagesLinear Variable Displacement Transducer (LVDT)SE ElectricalNo ratings yet
- LVDTDocument12 pagesLVDTPratheep V.G. MTSNo ratings yet
- Linear Variable Differential TransformerDocument10 pagesLinear Variable Differential TransformerSoumik DasNo ratings yet
- Chapter1mechanicalmeasurement 160309072647Document19 pagesChapter1mechanicalmeasurement 160309072647bd9051No ratings yet
- LVDT: Basic Principle, Theory, Working, Explanation & Diagram - Linear Variable Differential TransformerDocument2 pagesLVDT: Basic Principle, Theory, Working, Explanation & Diagram - Linear Variable Differential TransformerAtul NagarkarNo ratings yet
- Linear Variable Differential Transformer (LVDT)Document5 pagesLinear Variable Differential Transformer (LVDT)nikitaNo ratings yet
- LVDTDocument8 pagesLVDTsadu1978100% (1)
- 2130903Document14 pages2130903mitaliNo ratings yet
- Study of Displacement Transducer AIM: TheoryDocument6 pagesStudy of Displacement Transducer AIM: Theoryneelam sanjeev kumarNo ratings yet
- LVDTDocument11 pagesLVDTDaystar YtNo ratings yet
- Displacement MeasurementDocument12 pagesDisplacement MeasurementmitaliNo ratings yet
- LVDTDocument15 pagesLVDTvishal joshiNo ratings yet
- Linear Variable Differential Transformer (LVDT) PDFDocument3 pagesLinear Variable Differential Transformer (LVDT) PDFSrirangam RajeshNo ratings yet
- LVDT PresentationDocument7 pagesLVDT PresentationAsif Sheikh100% (1)
- Linear Variable Differential Transformer (LVDT)Document13 pagesLinear Variable Differential Transformer (LVDT)Nikhil Waghalkar100% (1)
- Transducers 130331093736 Phpapp01Document21 pagesTransducers 130331093736 Phpapp01Ayush ThakurNo ratings yet
- Transducers & Sensors: Alsalama College of Sciences &technology Electrical Engineering DepartmentDocument14 pagesTransducers & Sensors: Alsalama College of Sciences &technology Electrical Engineering DepartmentAlamin IbrahimNo ratings yet
- ST Unit 4 NotesDocument25 pagesST Unit 4 Notesabc fun facts100% (1)
- I&M Lab EXP 6 Part 1Document4 pagesI&M Lab EXP 6 Part 1MathewNo ratings yet
- LVDTDocument20 pagesLVDTsindhu100% (1)
- Study of LVDTDocument10 pagesStudy of LVDTSubhash KNo ratings yet
- LVDTDocument30 pagesLVDTDEEPA KUNWARNo ratings yet
- Linear Variable Differential Transformer LVDTDocument5 pagesLinear Variable Differential Transformer LVDTPoonam YadavNo ratings yet
- ICS Day - 10 Lecture NotesDocument3 pagesICS Day - 10 Lecture NotesRavikiran MahendraNo ratings yet
- Linear Variable Differential Transformer LVDTDocument8 pagesLinear Variable Differential Transformer LVDTRakesh MahajanNo ratings yet
- LVDT: Linear Variable Differential Transformer: Presented By: Shantanu Inderesh Harsh Presentation Made By: ShantanuDocument10 pagesLVDT: Linear Variable Differential Transformer: Presented By: Shantanu Inderesh Harsh Presentation Made By: Shantanuindresh singhNo ratings yet
- What Is LVDTDocument8 pagesWhat Is LVDTKeerthana DNo ratings yet
- Inductive TransducerDocument8 pagesInductive TransducerAAKASHNo ratings yet
- LVDT: Liner Varying Differential Transducer: Presented By:-Anantha Sai 1005 2073 1082Document21 pagesLVDT: Liner Varying Differential Transducer: Presented By:-Anantha Sai 1005 2073 1082RuchitaNo ratings yet
- Star Academy of Technology & Management, Indore: Electronic Instrumentation (Ex-604) Lab ManualDocument3 pagesStar Academy of Technology & Management, Indore: Electronic Instrumentation (Ex-604) Lab ManualPraveen Kumar ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Eti Unit-2Document4 pagesEti Unit-2kalpanaNo ratings yet
- Siddharth PhyDocument12 pagesSiddharth Physiddharthdeuri476No ratings yet
- LVDT Working PrincipleDocument2 pagesLVDT Working Principlekulwinder030373No ratings yet
- Linear Variable Differential Transformer LVDTDocument7 pagesLinear Variable Differential Transformer LVDTRajeev ValunjkarNo ratings yet
- Linear Variable Differential Transformer Measurements: EET-027, Experiment # 9Document4 pagesLinear Variable Differential Transformer Measurements: EET-027, Experiment # 9nainesh goteNo ratings yet
- of LVDTDocument8 pagesof LVDTDebasisMohapatraNo ratings yet
- AnkurMondal 12030523017Document10 pagesAnkurMondal 12030523017ankurmondal039No ratings yet
- EE17401-M& I Inductive Transducer, Capacitive TransducerDocument31 pagesEE17401-M& I Inductive Transducer, Capacitive TransduceravsNo ratings yet
- TRANSFORMER (Levinesh)Document16 pagesTRANSFORMER (Levinesh)livinesh05rNo ratings yet
- Potentiometer and LVDTDocument4 pagesPotentiometer and LVDTAbhishek Kumar JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Linear Variable Differential TransformerDocument6 pagesLinear Variable Differential TransformerDaulat NathNo ratings yet
- ContentDocument12 pagesContentHarishNo ratings yet
- Module-1 TransformersDocument27 pagesModule-1 TransformersSuraj Gowda BHNo ratings yet
- Eee3352 L6&7&8Document54 pagesEee3352 L6&7&8Desmond CheweNo ratings yet
- TransformerDocument30 pagesTransformerASHISHNo ratings yet
- Construction & WorkingDocument22 pagesConstruction & WorkingShah Aizat Razali100% (1)
- Linear Variable Differential TransformerDocument19 pagesLinear Variable Differential TransformerPranesh100% (1)
- Directional-RelaysDocument11 pagesDirectional-RelaysYH TAnNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document39 pagesUnit 4swthsrisaiNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machine I-3140913Document44 pagesElectrical Machine I-3140913Patel KashyapNo ratings yet
- Capacitive Transducers-T06Document60 pagesCapacitive Transducers-T06Nikhil SinghNo ratings yet
- محاضرة آلات طيران المحاضرة التالتةDocument38 pagesمحاضرة آلات طيران المحاضرة التالتةomarjoker808No ratings yet
- TRANSFORMERSDocument24 pagesTRANSFORMERStmmbonelaNo ratings yet
- ELE290Document24 pagesELE290Muhammad Hamizan HakiemiNo ratings yet
- Linear Variable Differential TransformerDocument1 pageLinear Variable Differential TransformerAmit SinhaNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- LM NotesDocument86 pagesLM NotesArpita NayyarNo ratings yet
- Compile Time PolymorphismDocument14 pagesCompile Time PolymorphismArpita NayyarNo ratings yet
- Development Scada System For Monitoring and Controlling Various System ParametersDocument17 pagesDevelopment Scada System For Monitoring and Controlling Various System ParametersArpita NayyarNo ratings yet
- Assignment-I Msmes in India: Guided By: Submitted byDocument6 pagesAssignment-I Msmes in India: Guided By: Submitted byArpita Nayyar100% (1)
- Pe 2Document13 pagesPe 2Arpita NayyarNo ratings yet
- The Seven Types of Power Problems: White Paper 18Document21 pagesThe Seven Types of Power Problems: White Paper 18FELIXDEJNo ratings yet
- D Brochure TeleREC English 08Document12 pagesD Brochure TeleREC English 08wagnercrjrNo ratings yet
- DB en Quint4 Ps 1ac 110dc 4 109530 en 00Document48 pagesDB en Quint4 Ps 1ac 110dc 4 109530 en 00Asad NaeemNo ratings yet
- 12v Battery ChargersDocument45 pages12v Battery ChargersPhani Sharma100% (1)
- Magnetic BalanceDocument3 pagesMagnetic BalancegaladrialNo ratings yet
- BD FMP A1 TZ 015 F3015P Series Pro2.0 CEDocument15 pagesBD FMP A1 TZ 015 F3015P Series Pro2.0 CEVictor PATIÑONo ratings yet
- OE Spec DP01500D5S 12V FC TB 50Hz 2 14Document6 pagesOE Spec DP01500D5S 12V FC TB 50Hz 2 14خطاب الشاميNo ratings yet
- 20 MVA RusailDocument34 pages20 MVA RusailbxteoNo ratings yet
- Cat G3516A: Natural Gas Generator SetsDocument5 pagesCat G3516A: Natural Gas Generator SetsRecovery MailNo ratings yet
- Load Flow Analysis For Three Phase Unbalanced Distribution Feeders Using MatlabDocument5 pagesLoad Flow Analysis For Three Phase Unbalanced Distribution Feeders Using MatlabEdna LópezNo ratings yet
- Transformer Manufacturers Brochure - PadmavahiniDocument12 pagesTransformer Manufacturers Brochure - PadmavahiniPadmavahini Transformers Private Limited0% (1)
- Thermodynamic Cycles (Power Plant Engineering)Document6 pagesThermodynamic Cycles (Power Plant Engineering)Ravjit SinghNo ratings yet
- Elkay - Energy Management Product CatalogueDocument1 pageElkay - Energy Management Product CatalogueAnonymous XYAPaxjbYNo ratings yet
- Mov 150la20aDocument4 pagesMov 150la20aServicios TecnicosNo ratings yet
- Generator Inspection Checklist: Etwork Evelopment RoupDocument2 pagesGenerator Inspection Checklist: Etwork Evelopment RoupPhel Flores100% (1)
- Commercial and Utility: 2.1 Power Xpert Solar 250 KW InverterDocument78 pagesCommercial and Utility: 2.1 Power Xpert Solar 250 KW InverterMoshNo ratings yet
- Au Ind: FD2.1 FD2.2Document9 pagesAu Ind: FD2.1 FD2.2M SNo ratings yet
- Huawei Power Systems Acceptance Manual - Update - 20190621Document25 pagesHuawei Power Systems Acceptance Manual - Update - 20190621wawanNo ratings yet
- Product Data Sheet: Circuit Breaker Compact Nsx100H, 70 Ka at 415 Vac, TMD Trip Unit 100 A, 3 Poles 3DDocument3 pagesProduct Data Sheet: Circuit Breaker Compact Nsx100H, 70 Ka at 415 Vac, TMD Trip Unit 100 A, 3 Poles 3DJorge FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Gas-Insulated Switchgear For Substations: Common Characteristic Features of Switchgear InstallationDocument12 pagesGas-Insulated Switchgear For Substations: Common Characteristic Features of Switchgear Installationjoydeep_d3232No ratings yet
- Gujarat Energy Development AgencyDocument1 pageGujarat Energy Development AgencyJd ShaikhNo ratings yet
- L&T Relay BrochureDocument32 pagesL&T Relay BrochureSuranjana Das100% (1)
- ABB CircuitBreaker S260 S270 S280 S290 Spec D1103Document20 pagesABB CircuitBreaker S260 S270 S280 S290 Spec D1103Fernando Crespo MonsalveNo ratings yet
- Trasfo CurentDocument11 pagesTrasfo CurentAlonso CoradoNo ratings yet
- Scope and DelimitationDocument2 pagesScope and DelimitationGenieline Magalona83% (6)
- Telecommunication System Engineering Telephony Signal TransmissionDocument37 pagesTelecommunication System Engineering Telephony Signal TransmissionXafran KhanNo ratings yet
- Microgrid: Innovation, Challenges and ProspectsDocument8 pagesMicrogrid: Innovation, Challenges and ProspectsIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet