Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Theory and Models of Consumer Behavior
Theory and Models of Consumer Behavior
Uploaded by
NK ShresthaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Nursing Leadership and Management For Patient Safety and Quality Care PDFDocument409 pagesNursing Leadership and Management For Patient Safety and Quality Care PDFAnonymous FGqnrDuM94% (16)
- Alan Weiss - Big Book of Process Visuals PDFDocument101 pagesAlan Weiss - Big Book of Process Visuals PDFrubix123100% (1)
- Ch.1: Managing & The Manager's JobDocument97 pagesCh.1: Managing & The Manager's Jobcoldpassion80% (10)
- Public Administration and Public AffairsDocument535 pagesPublic Administration and Public AffairsJames C. Serrano100% (2)
- Topic: Howard Sheth ModelDocument12 pagesTopic: Howard Sheth ModelPhaniraj Lenkalapally100% (1)
- School Based ManagementDocument7 pagesSchool Based ManagementDhei Tomajin100% (2)
- A GIS-Assisted Optimal Urban Route Selection Based On Multi Criteria ApproachDocument13 pagesA GIS-Assisted Optimal Urban Route Selection Based On Multi Criteria ApproachReynaldo AldamarNo ratings yet
- Nicosia Model of Consumer BehaviourDocument10 pagesNicosia Model of Consumer BehaviourNaeem HaiderNo ratings yet
- Models of Consumer BehaviourDocument7 pagesModels of Consumer BehaviourHimanshu DarganNo ratings yet
- Nicosia Model of Consumer BehaviourDocument10 pagesNicosia Model of Consumer BehaviourBipul BiplavNo ratings yet
- Models of Consumer BehaviourDocument22 pagesModels of Consumer BehaviourZoheb Ali KNo ratings yet
- Consumer BehaviourOVKDocument22 pagesConsumer BehaviourOVKOmkar KaleNo ratings yet
- Nicosia and Howard Seth ModelDocument7 pagesNicosia and Howard Seth Modelshanti2699No ratings yet
- Reading 3 - CB ModelsDocument5 pagesReading 3 - CB Modelsmohitvarshney725No ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior ModelsDocument21 pagesConsumer Behavior ModelsPankaj AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour Unit - 2 PDFDocument22 pagesConsumer Behaviour Unit - 2 PDFPrashant TripathiNo ratings yet
- PIM COBB Unit 3MGSE01 Buying ModelsDocument10 pagesPIM COBB Unit 3MGSE01 Buying ModelspiyushsithaNo ratings yet
- Nicosia Model: Subfield 1 Firms Attribute Subfield 2 Consumers Attributes (Especially PredispositionDocument6 pagesNicosia Model: Subfield 1 Firms Attribute Subfield 2 Consumers Attributes (Especially Predispositionanon_80127205No ratings yet
- ModelDocument22 pagesModelArchana DeepakNo ratings yet
- ModelDocument22 pagesModelArchana DeepakNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior Models and Consumer Behavior in TourismDocument41 pagesConsumer Behavior Models and Consumer Behavior in TourismShwetaBajiraoNo ratings yet
- Consumer BehaviourDocument5 pagesConsumer BehaviourvikkiNo ratings yet
- Chapter - Iii Consumer Behaviour ModelsDocument11 pagesChapter - Iii Consumer Behaviour ModelsRAGHU M SNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour Models: Mayank Sharma Assistant Professor - Marketing, IMS GhaziabadDocument11 pagesConsumer Behaviour Models: Mayank Sharma Assistant Professor - Marketing, IMS GhaziabadManish AroraNo ratings yet
- MODEL OF CONSUMER by MadhuDocument6 pagesMODEL OF CONSUMER by MadhuRadhika RocksNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Models of CB - Unit of Analysis-Individual-Psychological ManDocument10 pagesCognitive Models of CB - Unit of Analysis-Individual-Psychological ManVishnu ShankerNo ratings yet
- Buyer BehaviourDocument5 pagesBuyer BehaviourjimNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour Unit3Document10 pagesConsumer Behaviour Unit3Sumit YadavNo ratings yet
- By: Vikram.G.B Lecturer, P.G. Dept. of Commerce Vivekananda Degree CollegeDocument28 pagesBy: Vikram.G.B Lecturer, P.G. Dept. of Commerce Vivekananda Degree CollegeShaamAhmedNo ratings yet
- Consumer Decision Models - (Nicosia, Howard-Sheth, and Ekb) : Module - 2Document52 pagesConsumer Decision Models - (Nicosia, Howard-Sheth, and Ekb) : Module - 2prathibakb0% (1)
- Ps Module 4 Understanding Buyers Week 7-8Document35 pagesPs Module 4 Understanding Buyers Week 7-8Marian Rivera DiazNo ratings yet
- Marketing Research:: ApplicationsDocument35 pagesMarketing Research:: ApplicationsEmad Bin SaifNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavour Ch-3Document5 pagesConsumer Behavour Ch-3Ilma GirmaNo ratings yet
- Models of Consumer Behavior: - Engel, Blackwell and Miniard (EBM) - Howard Sheth Model of Buying BehaviourDocument20 pagesModels of Consumer Behavior: - Engel, Blackwell and Miniard (EBM) - Howard Sheth Model of Buying BehaviourroshniNo ratings yet
- Howard Sheth ModelDocument12 pagesHoward Sheth ModelibmahapatraNo ratings yet
- Buyerbehaviourmodels1 150926125257 Lva1 App6892Document29 pagesBuyerbehaviourmodels1 150926125257 Lva1 App6892KrishnakaparNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Models of Consumer BehaviourDocument24 pagesChapter 5 Models of Consumer BehaviourMohammad mahfuz alam abidNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour: Individual Decision-MakingDocument36 pagesConsumer Behaviour: Individual Decision-MakingYanira BorobiaNo ratings yet
- Role of Research in Understanding Consumer BehaviourDocument50 pagesRole of Research in Understanding Consumer Behaviouraqib_khan55No ratings yet
- Unit 2: Models of Consumer BehaviourDocument50 pagesUnit 2: Models of Consumer BehaviourMr. Padmanabha BNo ratings yet
- CB ModelsDocument9 pagesCB ModelssharadguptaaNo ratings yet
- CB - ModelDocument3 pagesCB - ModelSandhya AsagoduNo ratings yet
- Marketing Research ApplicationDocument35 pagesMarketing Research ApplicationSaurabh TeamworkNo ratings yet
- Howard and Sheth Model of Consumer BehaviourDocument2 pagesHoward and Sheth Model of Consumer BehaviourGauri sharmaNo ratings yet
- Models of Consumer Behaviour: UNIT-2Document11 pagesModels of Consumer Behaviour: UNIT-2Karthick PNo ratings yet
- Howard Sheth ModelDocument5 pagesHoward Sheth Modelrahul viju100% (1)
- Consumer Behaviour and InsightDocument13 pagesConsumer Behaviour and InsightRadha JoshiNo ratings yet
- Howard ShethDocument5 pagesHoward Shethjmpnv007No ratings yet
- Topic: Howard Sheth ModelDocument12 pagesTopic: Howard Sheth ModelPhaniraj Lenkalapally87% (15)
- E-Note 14811 Content Document 20240103110324AMDocument34 pagesE-Note 14811 Content Document 20240103110324AMytmandar29No ratings yet
- MKT301E Chap4Document18 pagesMKT301E Chap4k60.2112140083No ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour Models IIDocument11 pagesConsumer Behaviour Models IINation LameNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour MM-4Document19 pagesConsumer Behaviour MM-4anujbeniwalNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Consumer Behaviour Part IDocument21 pagesDynamics of Consumer Behaviour Part IMahima YadavNo ratings yet
- Roxas, Dan - POM - Assignment3Document6 pagesRoxas, Dan - POM - Assignment3DAN CARLO ROXASNo ratings yet
- Modelsofconsumerbehaviour 131015040649 Phpapp02Document33 pagesModelsofconsumerbehaviour 131015040649 Phpapp02rajeevrawal86No ratings yet
- Unit 4 CBDocument13 pagesUnit 4 CBAnilBahugunaNo ratings yet
- CB ModelsDocument21 pagesCB ModelsRagini MandyalNo ratings yet
- 02 Consumer+Behaviour+ModelsDocument29 pages02 Consumer+Behaviour+Modelsanupam18100% (1)
- Industrial Buying ProcessDocument29 pagesIndustrial Buying ProcessDeepa ShettyNo ratings yet
- Models of Consumer BehaviourDocument28 pagesModels of Consumer BehaviourGirija mirje100% (1)
- Consumer Decision Making Process & Characteristics of Industrial Markets Characteristics of Industrial MarketsDocument26 pagesConsumer Decision Making Process & Characteristics of Industrial Markets Characteristics of Industrial MarketssagarNo ratings yet
- Various Models of Consumer BehaviourDocument48 pagesVarious Models of Consumer BehaviourPrathamesh Pawar100% (1)
- A Study On Customer Attitudes Towards Pet Care and Pet IndustryDocument12 pagesA Study On Customer Attitudes Towards Pet Care and Pet Industryjuan felipe giraldoNo ratings yet
- Education Management Information SystemDocument6 pagesEducation Management Information SystemAfnan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Practical ResearchDocument37 pagesPractical ResearchVinz Canoza100% (1)
- Goal ProgrammingDocument9 pagesGoal ProgrammingCheslyn EspadaNo ratings yet
- Research MethdologyDocument133 pagesResearch MethdologySachin HolkarNo ratings yet
- Planning Programming 1Document19 pagesPlanning Programming 1Athel BellidoNo ratings yet
- Orange Book Management of RiskDocument48 pagesOrange Book Management of RiskNelson LimaNo ratings yet
- Institute of Business Administration ECO501-Managerial Economics Fall 2020Document4 pagesInstitute of Business Administration ECO501-Managerial Economics Fall 2020SaadAminNo ratings yet
- A Strategic Environmental Assessment: Benefits ofDocument5 pagesA Strategic Environmental Assessment: Benefits ofMOHD SUKRI BIN MOHD YUSOFF MoeNo ratings yet
- The Dangers of GroupthinkDocument2 pagesThe Dangers of GroupthinkRandy Howe0% (1)
- Holistic Youth Development: A Short Guide ToDocument28 pagesHolistic Youth Development: A Short Guide Toshamsukarim2009No ratings yet
- Management Information System: The Business School, University of JammuDocument10 pagesManagement Information System: The Business School, University of Jammuanon_945457258No ratings yet
- Stufflebeam, Daniel. Meta-EvaluationDocument121 pagesStufflebeam, Daniel. Meta-Evaluationbetica_00100% (1)
- IPD For Public and Private Owners - 0Document45 pagesIPD For Public and Private Owners - 0Mohammed NizamNo ratings yet
- mc-2 cmptd30-12-2019 3-1 SEC-B PDFDocument37 pagesmc-2 cmptd30-12-2019 3-1 SEC-B PDFvijay100% (1)
- Ethics - PPT (Bus1301)Document51 pagesEthics - PPT (Bus1301)shefali1988100% (2)
- Chapter 2. Patient Assessment and ConsultationDocument21 pagesChapter 2. Patient Assessment and ConsultationMonica CiorneiNo ratings yet
- M Business 5th Edition Ferrell Test Bank 1Document51 pagesM Business 5th Edition Ferrell Test Bank 1carrie100% (51)
- 1 3 7-RevisionDocument38 pages1 3 7-RevisionPrashantNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Homework Chapter 8Document4 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Homework Chapter 8Elsa Tan XQNo ratings yet
- Oliva 27s Ten AxiomsDocument20 pagesOliva 27s Ten Axiomsapi-458180003No ratings yet
- Influences of Adolescents On Family PurchasingDocument9 pagesInfluences of Adolescents On Family PurchasingWassie GetahunNo ratings yet
- Public PolicyDocument92 pagesPublic PolicyCalendar PMS100% (7)
- Fundamentals of Management Unit II PlanningDocument11 pagesFundamentals of Management Unit II PlanningAvesh QureshiNo ratings yet
Theory and Models of Consumer Behavior
Theory and Models of Consumer Behavior
Uploaded by
NK ShresthaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Theory and Models of Consumer Behavior
Theory and Models of Consumer Behavior
Uploaded by
NK ShresthaCopyright:
Available Formats
Theory and Models of Consumer
Behavior
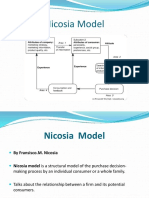
Nicosia Model
proposed by Nicosia (1976)
focuses on the relationship between the firm and
its potential consumers.
Field One:- concentrates on the firm's attempts to
communicate with the consumer, and the
consumers' predisposition to act in a certain way
Field Two:- involves the consumer in a search
evaluation process, which is influenced by
attitudes.
Field Three:- actual purchase process
Field Four:- post-purchase feedback process
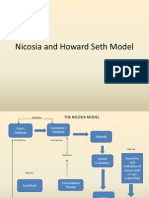
Nicosia Model of Consumer Decision
Making Process
Field 1
Attitude
Field 2: Search
And evaluation
Of mean/end(s)
Experience relation(s)
(Preaction field)
Motivation
Field 4:
Feedback
Field 3: Act of
Purchase
Purchasing
Behavior
Message
Exposure
Subfield 1
Firms
Attribute
Subfield 2
Consumers
Attributes
(Especially
Predisposition
Search
and evaluation
Decision
(Action)
Consumption
Nicosia Model of Consumer
Decision Making Process
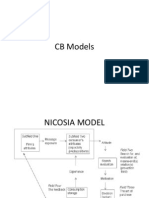
Nicosia Model:- Field 1
Field 1:- The consumer attitude based on the
firms messages.
The first field is divided into two subfields.
first subfield deals with the firms marketing
environment and communication efforts that affect
consumer attitudes, the competitive environment,
and characteristics of target market.
Subfield two specifies the consumer characteristics
e.g., experience, personality, and how he perceives
the promotional idea toward the product in this stage
the consumer forms his attitude toward the firms
product based on his interpretation of the message.
Nicosia Model:- Field 2
Field 2: search and evaluation
consumer will start to search for other firms
brand and evaluate the firms brand in
comparison with alternate brands
the firm motivates the consumer to purchase its
brands.
Nicosia Model:- Field 3
Field 3: The act of the purchase
The result of motivation will arise by convincing
the consumer to purchase the firm products from
a specific retailer.
Nicosia Model:- Field 4
Field 4: Feed back
model analyses the feedback of both the firm
and the consumer after purchasing the product
firm will benefit from its sales data as a feedback,
and the consumer will use his experience with the
product affects the individuals attitude and
predispositions concerning future messages from
the firm.
Nicosia Model:- Limitation
offers no detail explanation of the internal
factors, which may affect the personality of
the consumer, and how the consumer
develops his attitude toward the product
the consumer may find the firms message very
interesting, but virtually he cannot buy the firms
brand because it contains something prohibited
according to his beliefs
Howard-Sheth Model
This model suggests three levels of decision
making:
The first level describes the extensive problem
solving
The second level is limited problem solving
The third level is a habitual response behavior
Howard-Sheth Model
First level describes the extensive problem
solving
At this level the consumer does not have any
basic information or knowledge about the brand
and he does not have any preferences for any
product.
In this situation, the consumer will seek
information about all the different brands in the
market before purchasing.
Howard-Sheth Model
second level is limited problem solving.
This situation exists for consumers who have
little knowledge about the market, or partial
knowledge about what they want to purchase.
In order to arrive at a brand preference some
comparative brand information is sought.
Howard-Sheth Model
third level is a habitual response behavior.
In this level the consumer knows very well about
the different brands and he can differentiate
between the different characteristics of each
product, and he already decides to purchase a
particular product.
Howard-Sheth Model
According to the Howard-Sheth model there
are four major sets of variables; namely:
Inputs
Perceptual and Learning Constructs
Outputs
Exogenous(External) variables
Howard-Sheth Model
Howard-Sheth Model-Inputs
These input variables consist of three distinct types of
stimuli (information sources) in the consumers
environment.
The marketer in the form of product or brand information
furnishes physical brand characteristics (significative
stimuli)
Quality, Price, Distinctive, Service, Availability
and verbal or visual product characteristics (symbolic
stimuli).
Quality, Price, Distinctive, Service, Availability
The third type is provided by the consumers social
environment (family, reference group, and social class).
All three types of stimuli provide inputs concerning the
product class or specific brands to the specific
consumer.
Howard-Sheth Model- Perceptual and
Learning Constructs
central part of the model deals with the
psychological variables involved when the
consumer is contemplating a decision
Some of the variables are perceptual in nature, and
are concerned with how the consumer receives
and understands the information from the input
stimuli and other parts
Perceptual bias occurs if the consumer distorts the
information received so that it fits his or her
established needs or experience.
consumers goals, information about brands,
criteria for evaluation alternatives, preferences and
buying intentions are all included
Howard-Sheth Model-Outputs
The outputs are the results of the perceptual
and learning variables and how the
consumers will response to these variables
(attention, brand comprehension, attitudes,
and intention).
Howard-Sheth Model-
Exogenous(External) variables
Exogenous variables are not directly part of
the decision-making process.
However, some relevant exogenous variables
include the importance of the purchase,
consumer personality traits, religion, and
time pressure
Howard-Sheth Model
The decision-making process, which Howard-Sheth
Model tries to explain, takes place at three Inputs
stages: Significance, Symbolic and Social stimuli.
In both significative and symbolic stimuli, the model
emphasizes on material aspects such as price and
quality.
These stimuli are not applicable in every society.
While in social stimuli the model does not mention the
basis of decision-making in this stimulus, such as what
influence the family decision? This may differ from
one society to another.
Howard-Sheth Model
Finally, no direct relation was drawn on the
role of religion in influencing the consumers
decision-making processes.
Religion was considered as external factor
with no real influence on consumer, which
give the model obvious weakness in
anticipation the consumer decision.
Engel-Kollat-Blackwell Model
Engel-Kollat-Blackwell Model
This model was created to describe the increasing, fast-
growing body of knowledge concerning consumer
behavior.
This model, like in other models, has gone through
many revisions to improve its descriptive ability of the
basic relationships between components and sub-
components, this model consists also of four stages;
First stage: decision-process stages
Second stage: Information input
Third stage: information processing
Fourth stage: variables influencing the decision process
Engel-Kollat-Blackwell Model
First stage: decision-process stages
The central focus of the model is on five basic
decision-process stages: Problem recognition,
search for alternatives, alternate evaluation (during
which beliefs may lead to the formation of
attitudes, which in turn may result in a purchase
intention) purchase, and outcomes.
But it is not necessary for every consumer to go
through all these stages; it depends on whether it is
an extended or a routine problem-solving behavior.
Engel-Kollat-Blackwell Model
Second stage: Information input
At this stage the consumer gets information from
marketing and non-marketing sources, which also
influence the problem recognition stage of the
decision-making process.
If the consumer still does not arrive to a specific
decision, the search for external information will be
activated in order to arrive to a choice or in some
cases if the consumer experience dissonance because
the selected alternative is less satisfactory than
expected.
Engel-Kollat-Blackwell Model
Third stage: information processing
This stage consists of the consumers exposure,
attention, perception, acceptance, and retention
of incoming information.
The consumer must first be exposed to the
message, allocate space for this information,
interpret the stimuli, and retain the message by
transferring the input to long-term memory.
Engel-Kollat-Blackwell Model
Fourth stage: variables influencing the decision
process
This stage consists of individual and environmental
influences that affect all five stages of the decision
process.
Individual characteristics include motives, values,
lifestyle, and personality; the social influences are
culture, reference groups, and family.
Situational influences, such as a consumers financial
condition, also influence the decision process.
Engel-Kollat-Blackwell Model
This model incorporates many items, which
influence consumer decision-making such as
values, lifestyle, personality and culture.
The model did not show what factors shape these
items, and why different types of personality can
produce different decision-making? How will we
apply these values to cope with different
personalities?
Religion can explain some behavioral characteristics
of the consumer, and this will lead to better
understanding of the model and will give more
comprehensive view on decision-making.
You might also like
- Nursing Leadership and Management For Patient Safety and Quality Care PDFDocument409 pagesNursing Leadership and Management For Patient Safety and Quality Care PDFAnonymous FGqnrDuM94% (16)
- Alan Weiss - Big Book of Process Visuals PDFDocument101 pagesAlan Weiss - Big Book of Process Visuals PDFrubix123100% (1)
- Ch.1: Managing & The Manager's JobDocument97 pagesCh.1: Managing & The Manager's Jobcoldpassion80% (10)
- Public Administration and Public AffairsDocument535 pagesPublic Administration and Public AffairsJames C. Serrano100% (2)
- Topic: Howard Sheth ModelDocument12 pagesTopic: Howard Sheth ModelPhaniraj Lenkalapally100% (1)
- School Based ManagementDocument7 pagesSchool Based ManagementDhei Tomajin100% (2)
- A GIS-Assisted Optimal Urban Route Selection Based On Multi Criteria ApproachDocument13 pagesA GIS-Assisted Optimal Urban Route Selection Based On Multi Criteria ApproachReynaldo AldamarNo ratings yet
- Nicosia Model of Consumer BehaviourDocument10 pagesNicosia Model of Consumer BehaviourNaeem HaiderNo ratings yet
- Models of Consumer BehaviourDocument7 pagesModels of Consumer BehaviourHimanshu DarganNo ratings yet
- Nicosia Model of Consumer BehaviourDocument10 pagesNicosia Model of Consumer BehaviourBipul BiplavNo ratings yet
- Models of Consumer BehaviourDocument22 pagesModels of Consumer BehaviourZoheb Ali KNo ratings yet
- Consumer BehaviourOVKDocument22 pagesConsumer BehaviourOVKOmkar KaleNo ratings yet
- Nicosia and Howard Seth ModelDocument7 pagesNicosia and Howard Seth Modelshanti2699No ratings yet
- Reading 3 - CB ModelsDocument5 pagesReading 3 - CB Modelsmohitvarshney725No ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior ModelsDocument21 pagesConsumer Behavior ModelsPankaj AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour Unit - 2 PDFDocument22 pagesConsumer Behaviour Unit - 2 PDFPrashant TripathiNo ratings yet
- PIM COBB Unit 3MGSE01 Buying ModelsDocument10 pagesPIM COBB Unit 3MGSE01 Buying ModelspiyushsithaNo ratings yet
- Nicosia Model: Subfield 1 Firms Attribute Subfield 2 Consumers Attributes (Especially PredispositionDocument6 pagesNicosia Model: Subfield 1 Firms Attribute Subfield 2 Consumers Attributes (Especially Predispositionanon_80127205No ratings yet
- ModelDocument22 pagesModelArchana DeepakNo ratings yet
- ModelDocument22 pagesModelArchana DeepakNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior Models and Consumer Behavior in TourismDocument41 pagesConsumer Behavior Models and Consumer Behavior in TourismShwetaBajiraoNo ratings yet
- Consumer BehaviourDocument5 pagesConsumer BehaviourvikkiNo ratings yet
- Chapter - Iii Consumer Behaviour ModelsDocument11 pagesChapter - Iii Consumer Behaviour ModelsRAGHU M SNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour Models: Mayank Sharma Assistant Professor - Marketing, IMS GhaziabadDocument11 pagesConsumer Behaviour Models: Mayank Sharma Assistant Professor - Marketing, IMS GhaziabadManish AroraNo ratings yet
- MODEL OF CONSUMER by MadhuDocument6 pagesMODEL OF CONSUMER by MadhuRadhika RocksNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Models of CB - Unit of Analysis-Individual-Psychological ManDocument10 pagesCognitive Models of CB - Unit of Analysis-Individual-Psychological ManVishnu ShankerNo ratings yet
- Buyer BehaviourDocument5 pagesBuyer BehaviourjimNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour Unit3Document10 pagesConsumer Behaviour Unit3Sumit YadavNo ratings yet
- By: Vikram.G.B Lecturer, P.G. Dept. of Commerce Vivekananda Degree CollegeDocument28 pagesBy: Vikram.G.B Lecturer, P.G. Dept. of Commerce Vivekananda Degree CollegeShaamAhmedNo ratings yet
- Consumer Decision Models - (Nicosia, Howard-Sheth, and Ekb) : Module - 2Document52 pagesConsumer Decision Models - (Nicosia, Howard-Sheth, and Ekb) : Module - 2prathibakb0% (1)
- Ps Module 4 Understanding Buyers Week 7-8Document35 pagesPs Module 4 Understanding Buyers Week 7-8Marian Rivera DiazNo ratings yet
- Marketing Research:: ApplicationsDocument35 pagesMarketing Research:: ApplicationsEmad Bin SaifNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavour Ch-3Document5 pagesConsumer Behavour Ch-3Ilma GirmaNo ratings yet
- Models of Consumer Behavior: - Engel, Blackwell and Miniard (EBM) - Howard Sheth Model of Buying BehaviourDocument20 pagesModels of Consumer Behavior: - Engel, Blackwell and Miniard (EBM) - Howard Sheth Model of Buying BehaviourroshniNo ratings yet
- Howard Sheth ModelDocument12 pagesHoward Sheth ModelibmahapatraNo ratings yet
- Buyerbehaviourmodels1 150926125257 Lva1 App6892Document29 pagesBuyerbehaviourmodels1 150926125257 Lva1 App6892KrishnakaparNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Models of Consumer BehaviourDocument24 pagesChapter 5 Models of Consumer BehaviourMohammad mahfuz alam abidNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour: Individual Decision-MakingDocument36 pagesConsumer Behaviour: Individual Decision-MakingYanira BorobiaNo ratings yet
- Role of Research in Understanding Consumer BehaviourDocument50 pagesRole of Research in Understanding Consumer Behaviouraqib_khan55No ratings yet
- Unit 2: Models of Consumer BehaviourDocument50 pagesUnit 2: Models of Consumer BehaviourMr. Padmanabha BNo ratings yet
- CB ModelsDocument9 pagesCB ModelssharadguptaaNo ratings yet
- CB - ModelDocument3 pagesCB - ModelSandhya AsagoduNo ratings yet
- Marketing Research ApplicationDocument35 pagesMarketing Research ApplicationSaurabh TeamworkNo ratings yet
- Howard and Sheth Model of Consumer BehaviourDocument2 pagesHoward and Sheth Model of Consumer BehaviourGauri sharmaNo ratings yet
- Models of Consumer Behaviour: UNIT-2Document11 pagesModels of Consumer Behaviour: UNIT-2Karthick PNo ratings yet
- Howard Sheth ModelDocument5 pagesHoward Sheth Modelrahul viju100% (1)
- Consumer Behaviour and InsightDocument13 pagesConsumer Behaviour and InsightRadha JoshiNo ratings yet
- Howard ShethDocument5 pagesHoward Shethjmpnv007No ratings yet
- Topic: Howard Sheth ModelDocument12 pagesTopic: Howard Sheth ModelPhaniraj Lenkalapally87% (15)
- E-Note 14811 Content Document 20240103110324AMDocument34 pagesE-Note 14811 Content Document 20240103110324AMytmandar29No ratings yet
- MKT301E Chap4Document18 pagesMKT301E Chap4k60.2112140083No ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour Models IIDocument11 pagesConsumer Behaviour Models IINation LameNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour MM-4Document19 pagesConsumer Behaviour MM-4anujbeniwalNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Consumer Behaviour Part IDocument21 pagesDynamics of Consumer Behaviour Part IMahima YadavNo ratings yet
- Roxas, Dan - POM - Assignment3Document6 pagesRoxas, Dan - POM - Assignment3DAN CARLO ROXASNo ratings yet
- Modelsofconsumerbehaviour 131015040649 Phpapp02Document33 pagesModelsofconsumerbehaviour 131015040649 Phpapp02rajeevrawal86No ratings yet
- Unit 4 CBDocument13 pagesUnit 4 CBAnilBahugunaNo ratings yet
- CB ModelsDocument21 pagesCB ModelsRagini MandyalNo ratings yet
- 02 Consumer+Behaviour+ModelsDocument29 pages02 Consumer+Behaviour+Modelsanupam18100% (1)
- Industrial Buying ProcessDocument29 pagesIndustrial Buying ProcessDeepa ShettyNo ratings yet
- Models of Consumer BehaviourDocument28 pagesModels of Consumer BehaviourGirija mirje100% (1)
- Consumer Decision Making Process & Characteristics of Industrial Markets Characteristics of Industrial MarketsDocument26 pagesConsumer Decision Making Process & Characteristics of Industrial Markets Characteristics of Industrial MarketssagarNo ratings yet
- Various Models of Consumer BehaviourDocument48 pagesVarious Models of Consumer BehaviourPrathamesh Pawar100% (1)
- A Study On Customer Attitudes Towards Pet Care and Pet IndustryDocument12 pagesA Study On Customer Attitudes Towards Pet Care and Pet Industryjuan felipe giraldoNo ratings yet
- Education Management Information SystemDocument6 pagesEducation Management Information SystemAfnan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Practical ResearchDocument37 pagesPractical ResearchVinz Canoza100% (1)
- Goal ProgrammingDocument9 pagesGoal ProgrammingCheslyn EspadaNo ratings yet
- Research MethdologyDocument133 pagesResearch MethdologySachin HolkarNo ratings yet
- Planning Programming 1Document19 pagesPlanning Programming 1Athel BellidoNo ratings yet
- Orange Book Management of RiskDocument48 pagesOrange Book Management of RiskNelson LimaNo ratings yet
- Institute of Business Administration ECO501-Managerial Economics Fall 2020Document4 pagesInstitute of Business Administration ECO501-Managerial Economics Fall 2020SaadAminNo ratings yet
- A Strategic Environmental Assessment: Benefits ofDocument5 pagesA Strategic Environmental Assessment: Benefits ofMOHD SUKRI BIN MOHD YUSOFF MoeNo ratings yet
- The Dangers of GroupthinkDocument2 pagesThe Dangers of GroupthinkRandy Howe0% (1)
- Holistic Youth Development: A Short Guide ToDocument28 pagesHolistic Youth Development: A Short Guide Toshamsukarim2009No ratings yet
- Management Information System: The Business School, University of JammuDocument10 pagesManagement Information System: The Business School, University of Jammuanon_945457258No ratings yet
- Stufflebeam, Daniel. Meta-EvaluationDocument121 pagesStufflebeam, Daniel. Meta-Evaluationbetica_00100% (1)
- IPD For Public and Private Owners - 0Document45 pagesIPD For Public and Private Owners - 0Mohammed NizamNo ratings yet
- mc-2 cmptd30-12-2019 3-1 SEC-B PDFDocument37 pagesmc-2 cmptd30-12-2019 3-1 SEC-B PDFvijay100% (1)
- Ethics - PPT (Bus1301)Document51 pagesEthics - PPT (Bus1301)shefali1988100% (2)
- Chapter 2. Patient Assessment and ConsultationDocument21 pagesChapter 2. Patient Assessment and ConsultationMonica CiorneiNo ratings yet
- M Business 5th Edition Ferrell Test Bank 1Document51 pagesM Business 5th Edition Ferrell Test Bank 1carrie100% (51)
- 1 3 7-RevisionDocument38 pages1 3 7-RevisionPrashantNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Homework Chapter 8Document4 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Homework Chapter 8Elsa Tan XQNo ratings yet
- Oliva 27s Ten AxiomsDocument20 pagesOliva 27s Ten Axiomsapi-458180003No ratings yet
- Influences of Adolescents On Family PurchasingDocument9 pagesInfluences of Adolescents On Family PurchasingWassie GetahunNo ratings yet
- Public PolicyDocument92 pagesPublic PolicyCalendar PMS100% (7)
- Fundamentals of Management Unit II PlanningDocument11 pagesFundamentals of Management Unit II PlanningAvesh QureshiNo ratings yet