Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mechanisms NewSJMechanism
Mechanisms NewSJMechanism
Uploaded by
Pets Perez0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
41 views54 pagesThis document discusses mechanisms and their analysis and design. It provides examples of common mechanisms including four-bar linkages, slider-crank mechanisms, gears, and cams. It also categorizes mechanisms based on their function, such as function generation, motion generation, and path generation mechanisms. Primary joints and higher order joints are also discussed.
Original Description:
sfdgh
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses mechanisms and their analysis and design. It provides examples of common mechanisms including four-bar linkages, slider-crank mechanisms, gears, and cams. It also categorizes mechanisms based on their function, such as function generation, motion generation, and path generation mechanisms. Primary joints and higher order joints are also discussed.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
41 views54 pagesMechanisms NewSJMechanism
Mechanisms NewSJMechanism
Uploaded by
Pets PerezThis document discusses mechanisms and their analysis and design. It provides examples of common mechanisms including four-bar linkages, slider-crank mechanisms, gears, and cams. It also categorizes mechanisms based on their function, such as function generation, motion generation, and path generation mechanisms. Primary joints and higher order joints are also discussed.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 54
Mechanism Synthesis and Analysis
Synthesis design a mechanism to perform a
desired function
Analysis given a mechanism, perform kinematics
and kinetics analysis
Graphical techniques
Analytical methods
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
2
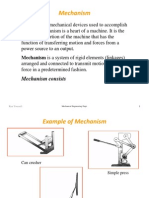
Mechanism
Machines are mechanical devices used to accomplish
work. A mechanism is a heart of a machine. It is the
mechanical portion of the machine that has the
function of transferring motion and forces from a
power source to an output.
Mechanism is a system of rigid elements (linkages)
arranged and connected to transmit motion and/or
force in a predetermined fashion.
Mechanism consists of linkages and joints.
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
3
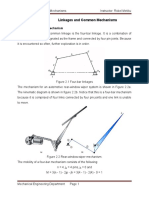
Four-Bar Linkage
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
4
The Slider-Crank Mechanism
Input link,
crank
Coupler link,
connecting rod
Output link,
piston (slider)
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
5
Example of Mechanism
Can crusher
Simple press
Rear-window wiper
1
3
2
4
5
3
4
2
1
6
4
3
2
1
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
6
Example of Mechanisms
Moves packages from an assembly
bench to a conveyor
Six bar
5
3
4
2
1
6
Lift platform
Six bar
5
3
4
2
1
6
Microwave carrier to assist
people on wheelchair
Six bar
5
3
4
2
1
6
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
7
Example of Mechanisms
Lift platform
Front loader
Device to close the
top flap of boxes
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
8
Example of Mechanisms
Stair climbing mechanism
A box that
turns itself off
Airplane landing
gear mechanism
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
9
Example of Mechanisms
Conceptual design for an
exercise machine
Rowing type exercise machine
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
10
Example of Mechanisms
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
11
Example of Mechanisms
Six-bar linkage prosthetic
knee mechanism
Extension position
Flexed position
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
12
Four-Bar Linkage Categories
Case I shortest link + longest link < summation of the other two links
a) Shortest link is the driver with
either one of the adjacent links
as the ground link (fixed). The
result is two different types of
crank-rocker mechanisms, input
link rotates 360 (crank) and
output link oscillates (rocker)
fixed
fixed
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
13
Four-Bar Linkage Categories
Case I shortest link + longest link < summation of the other two links
b) Shortest link is fixed. The
result is a double-crank
mechanism. Both, input and
output links rotate 360.
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
14
Four-Bar Linkage Categories
c) The longest link is fixed and
either one of the intermediate
links is the driver. The result is a
double-rocker mechanism.
Both, input and output links
oscillate.
Grashof condition one link rotates 360
Case I shortest link + longest link < summation of the other two links
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
15
Four-Bar Linkage Categories
Case I I shortest link + longest link > summation of the other two links
There are four possible
mechanisms depending on
which link is fixed. All
mechanisms are double-rockers.
Case I I I shortest link + longest link = summation of the other two links
Same mechanisms as in case I
with the addition of a
branching point (all links
become collinear).
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
16
4-Bar mechanisms
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
17
4-Bar mechanisms
S + l > p + q
4 double rocker
mechanisms
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
18
The Slider-Crank Mechanism
Input link,
crank
Coupler link,
connecting rod
Output link,
piston (slider)
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
19
Slider-Crank Mechanism
Offset slider-crank mechanism
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
20
Slider-Crank Mechanism
In-line slider crank mechanism
The mechanism has a
stroke B
1
B
2
equal twice
the crank length r
2
.
Locations B
1
and B
2
are
called the extreme
positions (limiting) of
the slider
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
21
The Slider-Crank Mechanism
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
22
Slider-Crank Mechanism - I nversion
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
23
Categories of Mechanisms
Function generation mechanisms
Output is a specified function of input
Motion generation mechanisms
Path generation mechanisms
The orientation of the object is important,
rigid body guidance
A point on a link moves on a specified path
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
24
Mechanism Categories
Function Generation Mechanisms
A function generator is a linkage in which the relative motion
between links connected to the ground is of interest.
A four-bar hand actuated wheelchair
brake mechanism
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
25
Mechanism Categories
Function Generation Mechanisms
A four-bar drive linkage for a lawn sprinkler
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
26
Mechanism Categories
Function Generation Mechanisms
A four-bar function generation mechanism to
operate an artificial hand used for gripping.
A four-bar function generation
mechanism to lower an attic stairway.
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
27
Mechanism Categories
Motion Generation Mechanisms
In motion generation, the entire motion of the coupler link
is of interest (rigid body guidance).
New Rollerblade brake system
Fixed pivot points
2
4
3
Moving joints
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
28
Mechanism Categories
Motion Generation Mechanisms
Four-bar automobile hood linkage design
Mechanism Categories
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
29
Lift platform
Six bar
5
3
4
2
1
6
Microwave carrier to assist
people on wheelchair
Six bar
5
3
4
2
1
6
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
30
Mechanism Categories
Path Generation Mechanisms
In path generation, we are concerned only with the path of a
tracer point and not with the motion (rotation) of the
coupler link.
Crane straight line motion
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
31
Mechanism Categories
Path Generation Mechanisms
with timing
A four-bar path generation mechanism as
part of an arm-actuated propulsion system
for a wheelchair
A four-bar path generation mechanism to guide a
thread in an automatic sewing machine
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
32
Primary J oints
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
33
Higher Order J oints
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
34
Motion Generation Mechanisms
Rotating a monitor into a storage position
Moving a storage bin from an
accessible position to a stored position
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
35
Motion Generation Mechanisms
Lifting a boat out of water
Moving a trash pan from the floor up over
a trash bin and into a dump position
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
36
Straight line Mechanisms
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
37
Straight line
Mechanisms
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
38
Straight Line Mechanism
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
39
Straight Line Mechanism - Application
Straight line mechanism
with dwell
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
40
Scotch Yoke Mechanism
Example car window
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
41
Geneva Mechanism
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
42
Linear Geneva Mechanism
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
43
Ratchet Mechanism
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
44
Straight Beam Walking Mechanism
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
45
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
46
Roller and Flat Follower Cams
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
47
Cylindrical Cam Mechanism
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
48
Gears Rack and Pinion
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
49
Gears
Worm Gear Sets Bevel gears Planetary Gear set
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
50
V-8 Engine
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
51
Type of Motion and Mechanisms
Translation to Translation
Most power sources that are readily available today are either of the pure
rotational motion type, such as electric motor or hand crank, or of the
pure translational type, such as pneumatic or hydraulic cylinder, or linear
actuators.
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
52
Type of Motion and Mechanisms
Rotational to Rotational
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
53
Type of Motion and Mechanisms
Rotation to Translation
Ken Youssefi Mechanical Engineering Dept.
54
References
Mechanism Design, Analysis and Synthesis by
Erdman and sander, fourth edition, Prentice-Hall,
Machines and Mechanisms by Uicker, Pennock
and Shigley, third edition, Oxford
Machines and Mechanisms by Myszka, Prentice-
Hall
You might also like
- Elbow MechanismDocument61 pagesElbow MechanismSourav Kotgund100% (2)
- MechanismsDocument55 pagesMechanismsAmy Leigh WilliamsNo ratings yet
- MechanismsDocument50 pagesMechanismsmithunNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms 1Document23 pagesMechanisms 1Nishanth ShannmugamNo ratings yet
- MechanismsDocument9 pagesMechanismsMeet Mac PatelNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms PDFDocument56 pagesMechanisms PDFamk2009No ratings yet
- Mechanism: Mechanism Is An Assembly of Rigid ElementsDocument23 pagesMechanism: Mechanism Is An Assembly of Rigid ElementsTiffany LewisNo ratings yet
- Experiment:-01: "To Investigate The Functionality of Different Mechanisms"Document23 pagesExperiment:-01: "To Investigate The Functionality of Different Mechanisms"UsamaIjazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 MechanismDocument82 pagesChapter 1 MechanismMohsan AbbasNo ratings yet
- Instructor:: Kinematics & Dynamics of Machines MECE 3270UDocument45 pagesInstructor:: Kinematics & Dynamics of Machines MECE 3270UMadison BratinaNo ratings yet
- JyotChoksi PortfolioDocument46 pagesJyotChoksi PortfolioJyot ChoksiNo ratings yet
- JyotChoksi PortfolioDocument46 pagesJyotChoksi PortfolioJyot ChoksiNo ratings yet
- Final TOM Lab Manual New PDFDocument10 pagesFinal TOM Lab Manual New PDFdab111No ratings yet
- Geneva MechanismDocument25 pagesGeneva MechanismYoussef SamehNo ratings yet
- Mom Final ReportDocument23 pagesMom Final ReportAsim ShehzadNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Geneva ConveyorDocument22 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Geneva ConveyorBhumit HambireNo ratings yet
- Mini Conveyor Using Geneva MechanismDocument3 pagesMini Conveyor Using Geneva MechanismLokeshvarma RNo ratings yet
- "Mini Conveyor Using Geneva Mechanism": Synopsis of The Proposed Research Work ONDocument5 pages"Mini Conveyor Using Geneva Mechanism": Synopsis of The Proposed Research Work ONNithin JainNo ratings yet
- Lake Travis High School Principles of Engineering 3A Compound Mechanisms LabDocument4 pagesLake Travis High School Principles of Engineering 3A Compound Mechanisms Labapi-336931682No ratings yet
- Rad Sa TomomDocument4 pagesRad Sa Tomomdusanmih86No ratings yet
- CCMMS2014 Ivanov AutomaticboxDocument15 pagesCCMMS2014 Ivanov AutomaticboxRenoNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - MechanismsDocument41 pagesModule 1 - MechanismsB03Kavya MNo ratings yet
- Kom ReportDocument18 pagesKom ReportNamanNo ratings yet
- Gearless Transmission FinalDocument21 pagesGearless Transmission Finalutkarsh67% (3)
- 2020me518 MomDocument43 pages2020me518 MomMuhammad HammadNo ratings yet
- Study of Coupled Wheel of Locomotive: Sau. Shantidevi Chavhan Pol. Bhoras, Tal. Chalisgaon Dist. Jalgaon (424101)Document6 pagesStudy of Coupled Wheel of Locomotive: Sau. Shantidevi Chavhan Pol. Bhoras, Tal. Chalisgaon Dist. Jalgaon (424101)Rakesh MahajanNo ratings yet
- Syllabus (New2013 Pattern) - TOM-IDocument14 pagesSyllabus (New2013 Pattern) - TOM-IAkshayNo ratings yet
- 13e.project Report SampleDocument34 pages13e.project Report SampleArunkuma81No ratings yet
- JSS3 Scheme of WorkDocument5 pagesJSS3 Scheme of WorkAbdullateef Adedoyin0% (1)
- Final Term Paper of DomDocument12 pagesFinal Term Paper of DomAvinash RajputNo ratings yet
- Roboclimber: MCL211 Design of Machines Final SubmissionDocument33 pagesRoboclimber: MCL211 Design of Machines Final SubmissionNavneet GoyalNo ratings yet
- Automation & Robotics (RME078) : Lecture Notes OnDocument10 pagesAutomation & Robotics (RME078) : Lecture Notes Onمقدس ألم Μυφυαδδας ΑιαΜNo ratings yet
- Kom Project ReportDocument19 pagesKom Project ReportNamanNo ratings yet
- Kindexing MechanismsDocument7 pagesKindexing MechanismsSMBEAUTYNo ratings yet
- Design & Fabrication of Eight Legged Walking MachineDocument9 pagesDesign & Fabrication of Eight Legged Walking Machinecharan prabhaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1. Introduction To KOM PDFDocument40 pagesUNIT 1. Introduction To KOM PDFAravind MuddebihalNo ratings yet
- KMDocument120 pagesKMsady1967No ratings yet
- KOM ProjectDocument15 pagesKOM ProjectArvene Binmer JesaryNo ratings yet
- Automatic Transmission SystemDocument23 pagesAutomatic Transmission SystemAJAY08No ratings yet
- Kinematic of Machines Part ADocument13 pagesKinematic of Machines Part Adraj1875977No ratings yet
- Preared By: Dr. J. N. KERAITA: Emg 2404: Mechanics of Machines IiiDocument9 pagesPreared By: Dr. J. N. KERAITA: Emg 2404: Mechanics of Machines IiiMuthoka VincentNo ratings yet
- Crank and Slotted Lever Quick Return (Rev2)Document9 pagesCrank and Slotted Lever Quick Return (Rev2)Vipin YadavNo ratings yet
- Theory of Machines-Lecture 1Document31 pagesTheory of Machines-Lecture 1Mohammed Al-OdatNo ratings yet
- Module 4 1Document27 pagesModule 4 1Sawai PareshNo ratings yet
- Synthesis and Analysis of The Five-Link Rear Suspension System Used in AutomobilesDocument18 pagesSynthesis and Analysis of The Five-Link Rear Suspension System Used in AutomobilesManish RajNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms Final ReportDocument44 pagesMechanisms Final ReportOmar SaleemNo ratings yet
- STEM Education - PulleysDocument10 pagesSTEM Education - PulleysRokenbok100% (1)
- Project 1.1.6 Compound Machine DesignDocument10 pagesProject 1.1.6 Compound Machine Designapi-271240497No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 HandoutDocument12 pagesChapter 2 HandoutRobel Metiku100% (1)
- Omnidirectional Drive Systems: Ian MackenzieDocument35 pagesOmnidirectional Drive Systems: Ian MackenzieAtif MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Planar Linkage Synthesis: A modern CAD based approachFrom EverandPlanar Linkage Synthesis: A modern CAD based approachNo ratings yet
- Transfer Matrix Method for Multibody Systems: Theory and ApplicationsFrom EverandTransfer Matrix Method for Multibody Systems: Theory and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Flexible Multibody Dynamics: Efficient Formulations and ApplicationsFrom EverandFlexible Multibody Dynamics: Efficient Formulations and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Multiple Models Approach in Automation: Takagi-Sugeno Fuzzy SystemsFrom EverandMultiple Models Approach in Automation: Takagi-Sugeno Fuzzy SystemsNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of Large-Range Compliant Micropositioning SystemsFrom EverandDesign and Implementation of Large-Range Compliant Micropositioning SystemsNo ratings yet
- Construction and Manufacture of AutomobilesFrom EverandConstruction and Manufacture of AutomobilesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Produced by An Autodesk Educational ProductDocument1 pageProduced by An Autodesk Educational ProductPets PerezNo ratings yet
- Peer Cheers To Fifteen Years Peer Cheers To Fifteen YearsDocument1 pagePeer Cheers To Fifteen Years Peer Cheers To Fifteen YearsPets PerezNo ratings yet
- We Wanna See Jesus Lifted HighDocument2 pagesWe Wanna See Jesus Lifted HighPets PerezNo ratings yet
- Claim LetterDocument1 pageClaim LetterPets PerezNo ratings yet
- 95.5pb2sn2.5ag Solder AlloyDocument128 pages95.5pb2sn2.5ag Solder AlloyIrfan Irshad100% (1)
- Theory of Natural Philosophy BoscovichDocument495 pagesTheory of Natural Philosophy BoscovichJimmy Pappas100% (4)
- Surveying EquipmentDocument25 pagesSurveying EquipmentAbhishek SharmaNo ratings yet
- The Origin of The Lagrangian: by Matt GuthrieDocument4 pagesThe Origin of The Lagrangian: by Matt GuthrieNathanNo ratings yet
- Danfoss White Paper RA-DVDocument8 pagesDanfoss White Paper RA-DV윤병택No ratings yet
- Aircraft SextantsDocument1 pageAircraft SextantstatmattdNo ratings yet
- Phy13L E402Document5 pagesPhy13L E402Arn LagdaNo ratings yet
- Computer Aided Analysis of The Structural Behaviour of Sloped Open Lattice Towers 1Document24 pagesComputer Aided Analysis of The Structural Behaviour of Sloped Open Lattice Towers 1Oladunni AfolabiNo ratings yet
- Transfer Function State Space Representation RLC Circuit Example 1Document4 pagesTransfer Function State Space Representation RLC Circuit Example 1Caio CabralNo ratings yet
- Grade 8: Lesson 1 in GeometryDocument4 pagesGrade 8: Lesson 1 in GeometryYnaNo ratings yet
- Hussain Kassim Ahmad (Thesis) .pdf اطروحه dfig PDFDocument157 pagesHussain Kassim Ahmad (Thesis) .pdf اطروحه dfig PDFAmmar Al-KindyNo ratings yet
- Bermuda and Dragon TriangleDocument2 pagesBermuda and Dragon TriangleSyed Mohsin Ali NaqviNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic 10Document5 pagesUltrasonic 10Mahade Hasan Dipu100% (1)
- Practical 7: Determination of Ash Date of Experiment: 15 June 2020 Laboratory Group: TuesdayDocument10 pagesPractical 7: Determination of Ash Date of Experiment: 15 June 2020 Laboratory Group: TuesdayNadhirah Hamzah100% (1)
- Start GD&TDocument81 pagesStart GD&TVijay Pawar100% (1)
- UG 45 CalculationDocument7 pagesUG 45 CalculationnirgaNo ratings yet
- Excel Solutions To The Chemical Engineering Problem SetDocument59 pagesExcel Solutions To The Chemical Engineering Problem SetSakura NuguishiNo ratings yet
- CH 06Document6 pagesCH 06Enjie Elrassi100% (1)
- Determination of The Melting Enthalpy of A Pure SubstanceDocument5 pagesDetermination of The Melting Enthalpy of A Pure SubstanceLuis GuevaraNo ratings yet
- A Turkish Description of The Tower of The WindsDocument3 pagesA Turkish Description of The Tower of The WindschriswarNo ratings yet
- Direct Current Hybrid BreakersDocument195 pagesDirect Current Hybrid BreakersquangspktNo ratings yet
- 371 ARMOX 370T Class1 UK Data SheetDocument2 pages371 ARMOX 370T Class1 UK Data SheetemregnesNo ratings yet
- Chart Projections PDFDocument2 pagesChart Projections PDFSanjay WaghmodeNo ratings yet
- HWBDocument3 pagesHWB洪語祥No ratings yet
- FEM For FramesDocument12 pagesFEM For Framesrohit100% (1)
- Fea Thermal Analysis of Piston Using AnsysDocument4 pagesFea Thermal Analysis of Piston Using AnsysSardar Umair AshrafNo ratings yet
- UK Designers Handbook SteelgridHR Rev2 - 2Document55 pagesUK Designers Handbook SteelgridHR Rev2 - 2Kenneth Knox100% (1)
- College Physics: Phys 111 Dr. Tribble Summary Material On FluidsDocument6 pagesCollege Physics: Phys 111 Dr. Tribble Summary Material On FluidsEL Jann MalbuyoNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Specific Appendix I - SOP TemplateDocument13 pagesLaboratory Specific Appendix I - SOP TemplateBalachandar KumarNo ratings yet
- Error of ClosureDocument5 pagesError of Closurepraisejah moyoNo ratings yet