Professional Documents
Culture Documents
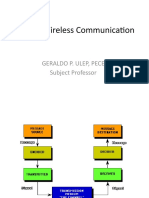
Standards For Wireless Comms
Standards For Wireless Comms
Uploaded by
Rajat KulshresthaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Standards For Wireless Comms
Standards For Wireless Comms
Uploaded by
Rajat KulshresthaCopyright:
Available Formats
2.
1
BITS, Pilani
Goa Campus
Standards of Wireless Communications
Standards of Wireless Communications
2.2
BITS, Pilani
Goa Campus
Standards of Wireless Communications
Standards Bodies
The European Conference of Postal and
Telecommunications Administrations - CEPT - was
established in 1959 by 19 countries, which expanded to
26 during its first ten years. Original members were
the monopoly-holding postal and telecommunications
administrations. CEPT's activities included co-operation on
commercial, operational, regulatory and technical
standardisation issues.
In 1988 CEPT decided to create ETSI, the European
Telecommunications Standards Institute, into which all its
telecommunication standardisation activities were
transferred.
2.3
BITS, Pilani
Goa Campus
Standards of Wireless Communications
Standards Bodies
European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI)
produces globally-applicable standards for Information and
Communications Technologies (ICT), including fixed, mobile,
radio, converged, broadcast and internet technologies.
Recognized by the European Union as a European Standards
Organization.
ETSI is a not-for-profit organization
WITH 766 member organizations
from 63 countries
across 5 continents world-wide.
2.4
BITS, Pilani
Goa Campus
Standards of Wireless Communications
Standards Bodies
International Telecommunication Union
United Nations agency for information and communication
technology issues
has coordinated the shared global use of the radio spectrum,
promoted international cooperation in assigning satellite orbits,
worked to improve telecommunication infrastructure in the
developing world & established the worldwide standards .
Handles issues from broadband Internet to latest-generation
wireless technologies, from aeronautical and maritime
navigation to radio astronomy and satellite-based meteorology,
from convergence in fixed-mobile phone, Internet access, data,
voice and TV broadcasting to next-generation networks.
ITU is based in Geneva, Switzerland, and its membership
includes 191 Member States and more than 700 Sector
Members and Associates.
2.5
BITS, Pilani
Goa Campus
Standards of Wireless Communications
Cordless telephony
Cordless Telephone 1 (CT-1)
Traditional 1st generation cordless phone used to get wireless access
to Public Switching Telephony Network (PSTN)
One BS & one mobile device
Limited mobility
Low speech quality
Residental usage
CT-2 introduced 1985 by CEPT
Allowed more mobility in with fixed BSs
Own phone could be used in dedicated areas
DECT (1992) Digital European Cordless Telephone until 1995 ->
Digital Enhanced Cordless Telecommunications, is an ETSI
standard for digital portable phones (cordless home telephones),
commonly used for domestic or corporate purposes.
DECT has been adopted by many countries all over the world.
Outside Europe, it is used in most of Asia, Australia and South
America. In the US accepted in 2005 with changed channelization
2.6
BITS, Pilani
Goa Campus
Standards of Wireless Communications
Cordless telephony
DECT services include
domestic cordless telephony, using a single base station to connect
one or more handsets to the public telecoms network
enterprise premises, using many base stations for coverage. Calls
continue as users move between different coverage cells, through
handover. Traffic both within and to the public telecom networks
public access, using large numbers of base stations to provide
building or urban area coverage as part of a public telecoms network
DECT standard allows the use of PABX - private automatic branch
exchange
To make connections among the internal telephones of a private
organization (usually business) and also connect them to PSTN.
Can handle exchange functionality for telephones, fax machines and
modems
primary advantage of PBXs is cost saving on internal phone calls
Currently also DECT/VoIP BSs available
2.7
BITS, Pilani
Goa Campus
Standards of Wireless Communications
GSM
GSM phase 1 (1991-1994)
Base of commercial GSM service
Only sub set of services was available
Phase 2 (1994-1995)
Full version of the standard
Signaling & protocols enhanced
Supplementary serives
Phase 2+ (1995->)
Speech quality -> GSM to accept different encoding algorithms
Group calls
GPRS
SMS service additions
2.8
BITS, Pilani
Goa Campus
Standards of Wireless Communications
Universal Personal Telecommunications
UPT is a special segment of the international telephone number
space for universal personal telephone numbers. This service
has been allocated country code +878. UPT numbers differ
significantly from Personal Numbers which are embedded as an
Area Code within the national Telephone numbering plan.
ITU introduced this concept in 2001, referring to it as "global
number portability".
UPT phone number is intended to be an internationally
consistent number which an individual can acquire, which can
then be used to contact them via telephone or other services. A
UPT provider basically must have the ability to receive
connections from the international telephone network, and then
forward the called number to the individual's real number.
2.9
BITS, Pilani
Goa Campus
Standards of Wireless Communications
IMT-2000 A.K.A 3G
International Mobile Telecommunications-2000 (IMT-2000),
better known as 3G or 3rd Generation, is a family of standards
for mobile telecommunications defined by the ITU, which
includes GSM EDGE, UMTS, and CDMA2000 as well as DECT and
WiMAX[2007]. Services include wide-area wireless voice
telephone, video calls, and wireless data, all in a mobile
environment. Compared to 2G and 2.5G services, 3G allows
simultaneous use of speech and data services and higher data
rates.
There are evolutionary standards that are backwards-compatible
extensions to pre-existing 2G networks as well as revolutionary
standards that require all-new networks and frequency allocations.
The later group is the UMTS family, which consists of standards
developed for IMT-2000, as well as the independently-developed
standards DECT and WiMAX, which were included because they fit
the IMT-2000 definition.
2.10
BITS, Pilani
Goa Campus
Standards of Wireless Communications
UMTS
Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) is one of the third-generation (3G) mobile
telecommunications technologies, which is also being developed into a 4G technology. It is specified
by 3GPP and is part of the global ITU IMT-2000 standard. Being a complete network system, UMTS
covers the radio access network (UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network; UTRAN), the core network
(Mobile Application Part; MAP) as well as authentication of users via USIM cards (Subscriber Identity
Module).
UMTS requires new cell towers and new frequency allocations. However, it is closely related to
GSM/EDGE as it borrows and builds upon concepts from GSM. Further, most UMTS handsets also
support GSM, allowing seamless dual-mode operation. Therefore, UMTS is sometimes marketed as
3GSM, emphasizing the close relationship with GSM and differentiating it from competing
technologies.
Outside of Europe, the system is also known by other names such as FOMA (Freedom of Mobile
multimedia Access - 1st 3G service in Japan) or W-CDMA (air interface used in 3G mobile
telecommunications) In marketing, it is often just referred to as 3G.
In the case of GSM, there is an evolution path from 2G, to GPRS, also known as 2.5G. E-GPRS, or
EDGE, is a further evolution of GPRS and is based on more modern coding schemes. EDGE systems
are often referred as "2.75G Systems.
Since 2006, UMTS networks in many countries have been or are in the process of being upgraded
with High Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA), sometimes known as 3.5G. Currently, HSDPA
enables downlink transfer speeds of up to 21 Mbit/s. Work is also progressing on improving the uplink
transfer speed with the High-Speed Uplink Packet Access (HSUPA).
The first national consumer UMTS networks launched in 2002 with a heavy emphasis on telco-
provided mobile applications such as mobile TV and video calling. The high data speeds of UMTS are
now most often utilised for Internet access: experience has shown that user demand for video calls is
not high
2.11
BITS, Pilani
Goa Campus
Standards of Wireless Communications
IS-54, IS-136 -> D-AMPS
IS-54 and IS-136 are second-generation (2G) mobile phone
systems, known as Digital AMPS (D-AMPS) - > AMPS =
Advanced Mobile Phone System.
Used Americas, particularly in the United States and Canada. D-
AMPS is considered end-of-life, and existing networks have
been replaced by GSM/GPRS or CDMA2000 technologies.
IS-54/136 dual mode phone uses digital channels where
available and defaults to regular AMPS where they are not.
Backward compatible with analog cellular and indeed co-exists
on the same radio channels as AMPS. No analog customers
were left behind; they simply couldn't access IS-54's new
features. IS-54 also supported authentication preventing fraud
IS-136 added a number of features to the original IS-54
specification, including text messaging, circuit switched data
(CSD), and an improved compression protocol. SMS and CSD
were both implemented nearly identical fashion with GSM.
2.12
BITS, Pilani
Goa Campus
Standards of Wireless Communications
IS-95
IS-95 is the first CDMA-based digital cellular standard pioneered
by Qualcomm. The brand name for IS-95 is cdmaOne.
It is a 2G Standard that uses CDMA, a multiple access scheme
for digital radio, to send voice, data and signaling data between
mobile telephones and cell sites.
CDMA permits several radios to share the same frequencies.
Unlike TDMA "time division multiple access" of 2G GSM, all
radios can be active all the time, because network capacity does
not directly limit the number of active radios. Since larger
numbers of phones can be served by smaller numbers of cell-
sites, CDMA-based standards have a significant economic
advantage over TDMA-based standards, or the oldest cellular
standards that used frequency-division multiplexing.
In North America, the technology competed with Digital AMPS.
It is now being supplanted by CDMA2000
2.13
BITS, Pilani
Goa Campus
Standards of Wireless Communications
Personal Digital Cellular - PDC
Personal Digital Cellular (PDC) is a 2G mobile
telecommunications standard developed and used
exclusively in Japan
Like D-AMPS and GSM, PDC uses TDMA. The services
include voice, supplementary services (call waiting, voice
mail, three-way calling, call forwarding, and so on), data
service (up to 9.6 kbit/s CSD), and packet-switched
wireless data (up to 28.8 kbit/s PDC-P).
Compared to GSM, PDC's weak broadcast strength allows
small, portable phones with light batteries at the expense
of substandard voice quality and problems maintaining
the connection, particularly in enclosed spaces like
elevators.
2.14
BITS, Pilani
Goa Campus
Standards of Wireless Communications
Personal Handy-phone System - PHS
PHS is used mainly in Japan, China, Taiwan and some other Asian countries.
cordless telephone like DECT, with the capability to handover from one cell to another.
PHS cells are small, BS range typically measures in tens or at most hundreds of meters
as opposed to the multi-kilometer ranges of CDMA and GSM. This makes PHS suitable
for dense urban areas, but impractical for rural areas, and the small cell size also
makes it difficult to make calls from rapidly moving vehicles.
PHS support many value-added services such as high speed wireless data / Internet
connection (64 kbit/s and higher), e-mailing, text messaging and color image transfer.
PHS technology is also a popular option for providing a wireless local loop, where it is
used to bridge the "last mile" gap between the Plain old telephone service (POTS)
network and the subscriber's home. Actually, it was developed under the concept that
it makes up a wireless front-end of an ISDN network. So a base station of PHS has a
compatibility with, and is often connected directly to ISDN telephone exchange
equipment (A.K.A. a digital switch).
PHS phone has 3 modes:
Private mode -> Cordless phone at home or office
Public mode -> uses network operators wireless service outside office/home
Tranciever mode -> enables direct connection between terminals near by
You might also like
- Writing An APA Style Research Paper PDFFDocument5 pagesWriting An APA Style Research Paper PDFFAngela MenesesNo ratings yet
- Jonathan's Last Day: Reading Comprehension QuizDocument3 pagesJonathan's Last Day: Reading Comprehension QuizLoja Vtr43% (7)
- MonkDocument121 pagesMonkCindy Yusseny Ayala MenjivarNo ratings yet
- Love Stories of Shimla Hills - Chaudhry, MinakshiDocument251 pagesLove Stories of Shimla Hills - Chaudhry, MinakshiAnkit BhattNo ratings yet
- 4G Lte Vs WimaxDocument33 pages4G Lte Vs Wimaxjaja2901No ratings yet
- Essential 4G Guide: Learn 4G Wireless In One DayFrom EverandEssential 4G Guide: Learn 4G Wireless In One DayRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (12)
- Evolution of Mobile Radio CommunicationDocument4 pagesEvolution of Mobile Radio CommunicationmanjuNo ratings yet
- WCC VTU Module 2 Additional Data 1Document40 pagesWCC VTU Module 2 Additional Data 1Sushíl kanikeNo ratings yet
- WCC Mod - 2Document12 pagesWCC Mod - 2Robin MishraNo ratings yet
- Wireless Networks: There Are Four Main Types of Wireless NetworksDocument15 pagesWireless Networks: There Are Four Main Types of Wireless NetworksSyed ShahidNo ratings yet
- 2G and 3G: 2G (Or 2-G) Is Short For Second-Generation Wireless Telephone TechnologyDocument6 pages2G and 3G: 2G (Or 2-G) Is Short For Second-Generation Wireless Telephone TechnologyVijay Kumar ReddyNo ratings yet
- CCCCCCCCCCCCCC CC C: C C C CDocument10 pagesCCCCCCCCCCCCCC CC C: C C C CdadasariNo ratings yet
- Fig 1 Generation of Mobile GenerationDocument13 pagesFig 1 Generation of Mobile GenerationSindian AcerNo ratings yet
- International Mobile Telecommunications-2000 (IMT - 2000), Better Known As 3G or 3rd Generation, Is A Generation of Standards ForDocument2 pagesInternational Mobile Telecommunications-2000 (IMT - 2000), Better Known As 3G or 3rd Generation, Is A Generation of Standards Forswetha099No ratings yet
- Cellular TechnologiesDocument23 pagesCellular TechnologiesOlivin EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Huawei WCDMA System Overview CourseDocument245 pagesHuawei WCDMA System Overview Coursejkpllan3No ratings yet
- Mobile Technologies: - GSM - Cdma - Umts - GpsDocument21 pagesMobile Technologies: - GSM - Cdma - Umts - GpsGagan KhuranaNo ratings yet
- Past Applications of Multi-Carrier - COMDocument3 pagesPast Applications of Multi-Carrier - COMNipuna Nuwan NanayakkaraNo ratings yet
- (3G and Wcdma) : Project ReportDocument42 pages(3G and Wcdma) : Project ReportMukesh ManwaniNo ratings yet
- WC Unit 1Document30 pagesWC Unit 1ThanosNo ratings yet
- Mobile and Wireless Communication Complete Lecture Notes #2Document28 pagesMobile and Wireless Communication Complete Lecture Notes #2Student Lecture NotesNo ratings yet
- Third Generation" Redirects Here. For Third-Generation Immigrants, SeeDocument4 pagesThird Generation" Redirects Here. For Third-Generation Immigrants, Seeallen24No ratings yet
- Lec 4Document12 pagesLec 4xp4bwxnmbkNo ratings yet
- Report On 3G TechnologyDocument11 pagesReport On 3G TechnologySaransh DeswalNo ratings yet
- Special Topic Presentation: Subject: Wireless Communication Topic: Global System For Mobile CommunicationDocument18 pagesSpecial Topic Presentation: Subject: Wireless Communication Topic: Global System For Mobile Communicationtabish khatriNo ratings yet
- Third-Generation Mobile Phones: Digital Voice and DataDocument5 pagesThird-Generation Mobile Phones: Digital Voice and DataShanky KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document20 pagesUnit 1GANAPATHY SUNDARAM G 21CA018No ratings yet
- The Core To 4G Mobile Communications: Luis Eduardo Sánchez de LoeraDocument26 pagesThe Core To 4G Mobile Communications: Luis Eduardo Sánchez de LoeraEduardo S de LoeraNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Mobile PhonesDocument16 pagesEvolution of Mobile PhonesRaed Shahid100% (1)
- FeaturesDocument16 pagesFeaturesJyothirmaye SuneelNo ratings yet
- Lecture # 2Document27 pagesLecture # 2Shah Zeb YousafzaiNo ratings yet
- Report Name: GSM TECHNOLOGY: Premier University 1/A, O.R. Nizam Road, Panchlaish, Chittagong, BangladeshDocument29 pagesReport Name: GSM TECHNOLOGY: Premier University 1/A, O.R. Nizam Road, Panchlaish, Chittagong, BangladeshgiridharkumarabNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five: Public Land Mobile Network (PLMN)Document57 pagesChapter Five: Public Land Mobile Network (PLMN)eyasu abebeNo ratings yet
- Mod Overlay DesignDocument33 pagesMod Overlay DesignDevarajNo ratings yet
- CH 3Document49 pagesCH 3Prathamesh NaraleNo ratings yet
- Addis Ababa Science and Technology University: Wireless CommunicationsDocument12 pagesAddis Ababa Science and Technology University: Wireless CommunicationsKidus FelekeNo ratings yet
- Evolution of The Mobile MarketDocument26 pagesEvolution of The Mobile Markettariq qaisraniNo ratings yet
- Advanced Mobile Phone System or AMPS Is The Analog Mobile Phone System StandardDocument15 pagesAdvanced Mobile Phone System or AMPS Is The Analog Mobile Phone System StandardAsif AminNo ratings yet
- Wireless Technology: Submitted By:-Sumitted To: 1. Khemesh Kumar 1. KulshresthaDocument25 pagesWireless Technology: Submitted By:-Sumitted To: 1. Khemesh Kumar 1. KulshresthaRashmi PateriyaNo ratings yet
- Industrial Training Presentation On Telecommunication SystemDocument15 pagesIndustrial Training Presentation On Telecommunication SystemsajalNo ratings yet
- 3G-Technologies: AbstractDocument1 page3G-Technologies: AbstractRubia Ruby KNo ratings yet
- 4G Wireless Technology: Hertz in 1886-1888 Demonstrated The Transmission andDocument13 pages4G Wireless Technology: Hertz in 1886-1888 Demonstrated The Transmission andHarshita GopuNo ratings yet
- 17EC81 Module 1 NotesDocument48 pages17EC81 Module 1 NotesHarshitha LNo ratings yet
- Third PageDocument41 pagesThird Pageshilpy karnNo ratings yet
- Why People Choose 3G-Radio Access SystemDocument4 pagesWhy People Choose 3G-Radio Access SystemNur E'zzati RidzuanNo ratings yet
- 3G or 3rd Generation Mobile Telecommunications Is A Generation of Standards For Mobile Mobile Telecommunications-2000 (IMT-2000) Specifications by The International TelecommunicationDocument4 pages3G or 3rd Generation Mobile Telecommunications Is A Generation of Standards For Mobile Mobile Telecommunications-2000 (IMT-2000) Specifications by The International TelecommunicationSahil JoshiNo ratings yet
- mhdC8Vuv5Ntvq8MUqJCZI9Jo PDFDocument34 pagesmhdC8Vuv5Ntvq8MUqJCZI9Jo PDFAhmed58seribegawanNo ratings yet
- MCN-Unit-1 - Cellular Concepts - NotesDocument32 pagesMCN-Unit-1 - Cellular Concepts - Notesamey vermaNo ratings yet
- For Most Readers To Understand. Please: TechnicalDocument10 pagesFor Most Readers To Understand. Please: TechnicallouiefrNo ratings yet
- 3G, Short For Third Generation, Is The Third Generation of Wireless Mobile Telecommunications Technology. It Is The Upgrade For 2G andDocument7 pages3G, Short For Third Generation, Is The Third Generation of Wireless Mobile Telecommunications Technology. It Is The Upgrade For 2G andShah hussain KhanNo ratings yet
- EC803 Unit I Notes - 1708339717Document23 pagesEC803 Unit I Notes - 1708339717Mine InstrumentsNo ratings yet
- 3G, Short For Third Generation, Is The Third Generation of Wireless Mobile Telecommunications Technology. It Is The Upgrade For 2G andDocument7 pages3G, Short For Third Generation, Is The Third Generation of Wireless Mobile Telecommunications Technology. It Is The Upgrade For 2G andDaniel MarcuNo ratings yet
- GSM by Aman TenoDocument9 pagesGSM by Aman TenoAmanNo ratings yet
- Modern Wireless Communication Systems: 2.1 1G: First Generation NetworksDocument12 pagesModern Wireless Communication Systems: 2.1 1G: First Generation NetworksImran SikderNo ratings yet
- Definitions: Analog Cellular TechnologiesDocument10 pagesDefinitions: Analog Cellular TechnologiesdeardestinyNo ratings yet
- Information Technolgy: Submitted by Akhil Jose Parakkal Imbab 1020159Document8 pagesInformation Technolgy: Submitted by Akhil Jose Parakkal Imbab 1020159Saurabh KushwahaNo ratings yet
- MiscellaneousDocument8 pagesMiscellaneousGowtham VananNo ratings yet
- For Other Uses, SeeDocument11 pagesFor Other Uses, SeemangutoNo ratings yet
- 3 GDocument2 pages3 GRockyrocks RockyNo ratings yet
- 1st Lecture Notes - Wire & Wireless CommunicationDocument22 pages1st Lecture Notes - Wire & Wireless CommunicationJordan-James OlivoNo ratings yet
- GSM Basics Tutorial and OverviewDocument81 pagesGSM Basics Tutorial and OverviewMwai Janna100% (1)
- Evolution of Mobile CommunicationDocument6 pagesEvolution of Mobile CommunicationIroshan Priyantha100% (2)
- 1G, 2G and 3G Spectrum: 1G (Or 1-G) Refers To The First-Generation ofDocument6 pages1G, 2G and 3G Spectrum: 1G (Or 1-G) Refers To The First-Generation ofEkta RaiNo ratings yet
- Product Strategy of Maruti SuzukiDocument42 pagesProduct Strategy of Maruti SuzukiIndira ThayilNo ratings yet
- Role of Open Surgical Drainage or Aspiration in Management of Amoebic Liver AbscessDocument9 pagesRole of Open Surgical Drainage or Aspiration in Management of Amoebic Liver AbscessIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- 5mm LED Datasheet PDFDocument1 page5mm LED Datasheet PDFAlex ZXNo ratings yet
- J.C. Wilder - Last Night in VegasDocument9 pagesJ.C. Wilder - Last Night in Vegassidharth trikhaNo ratings yet
- Full Download Test Bank For Workshop Statistics Discovery With Data 4th Edition Allan J Rossman Beth L Chance PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Test Bank For Workshop Statistics Discovery With Data 4th Edition Allan J Rossman Beth L Chance PDF Full Chapterpithsomeknockingsawv100% (24)
- ABB Control TP180DA DatasheetDocument3 pagesABB Control TP180DA Datasheetntdien923100% (1)
- CAR-T TherapyDocument14 pagesCAR-T TherapyrameshaachariarNo ratings yet
- SPM30 PDF Eng PDFDocument0 pagesSPM30 PDF Eng PDFValdemar Miguel SilvaNo ratings yet
- GSX R600k7e3 PDFDocument104 pagesGSX R600k7e3 PDFAdolfoNo ratings yet
- NOTH Menu Aug 22Document10 pagesNOTH Menu Aug 22Devin SwanepoelNo ratings yet
- Ministry Planning Made EasyDocument48 pagesMinistry Planning Made Easym28181920No ratings yet
- FCG - List of Top 100 Stockholders Q1 (Common Shares) Ending 31 March 2024Document5 pagesFCG - List of Top 100 Stockholders Q1 (Common Shares) Ending 31 March 2024Amino BenitoNo ratings yet
- Project Eagle QualitativeDocument188 pagesProject Eagle QualitativeCheriel Anne EsnardoNo ratings yet
- Fussion3000 MackieDocument8 pagesFussion3000 MackieMarco BruceNo ratings yet
- Cost Effective Housing PDFDocument16 pagesCost Effective Housing PDFSaurav ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four: The Cost of Capital 4.1. The Concept of Cost of CapitalDocument9 pagesChapter Four: The Cost of Capital 4.1. The Concept of Cost of Capitalmelat felekeNo ratings yet
- New Hptu Syllabus CSEDocument138 pagesNew Hptu Syllabus CSEerankursharma1985No ratings yet
- Example 3 Relating Downhole Rate With The Rate at Standard ConditionsDocument8 pagesExample 3 Relating Downhole Rate With The Rate at Standard ConditionsMaisam AbbasNo ratings yet
- SMART VTS Wireless Solutions: Features SVTS-500 SVTS-600 SVTS-700 SVTS-900 SVTS-1200Document6 pagesSMART VTS Wireless Solutions: Features SVTS-500 SVTS-600 SVTS-700 SVTS-900 SVTS-1200Sri KanthNo ratings yet
- What Is Underground Mining?Document2 pagesWhat Is Underground Mining?Taha YousafNo ratings yet
- Production Planning - 095252Document13 pagesProduction Planning - 095252Jocidelle LubricoNo ratings yet
- For Which Value Of, Will The Lines Represented by The Following Pair of Linear Equations Be ParallelDocument54 pagesFor Which Value Of, Will The Lines Represented by The Following Pair of Linear Equations Be ParallelAmit SinghNo ratings yet
- Motion For Joinder Moe UDDocument7 pagesMotion For Joinder Moe UDalanesqNo ratings yet
- 6th Grade Worksheet BundleDocument65 pages6th Grade Worksheet BundleLisa Ward0% (1)
- Word Formation - Practice 0Document4 pagesWord Formation - Practice 0Kim Ngân PhanNo ratings yet
- 04 Prescription InterpretationDocument32 pages04 Prescription InterpretationBalsam Zahi Al-HasanNo ratings yet