Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Distribution Channles and Logistics Management
Distribution Channles and Logistics Management
Uploaded by
Hon Nana Osei SomuahOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Distribution Channles and Logistics Management
Distribution Channles and Logistics Management
Uploaded by
Hon Nana Osei SomuahCopyright:
Available Formats
12-1
Chapter 12
Distribution Channels
and
Logistics Management
PRINCIPLES OF MARKETING
12-2
Distribution Channels
A set of interdependent organizations
(intermediaries) involved in the process
of making a product or service available
for use or consumption.
Channel decisions
affect other marketing decisions
involve long-term commitments
12-3
Role of Intermediaries
Greater efficiency in making goods
available to target markets.
Intermediaries provide
Contacts
Experience
Specialization
Scale of operation
Match supply and demand.
12-4
Channel Functions
Information
Promotion
Contact
Matching
Negotiation
Physical Distribution
Financing
Risk taking
12-5
Channel Levels
Manufacturer
Wholesaler
Retailer
Consumer
12-6
Channel Behavior and Conflict
The channel will be most effective when:
each member is assigned tasks it can do best.
all members cooperate to attain overall channel goals
and satisfy the target market.
Focus on individual goals leads to conflict
Horizontal Conflict occurs among firms at the same level
of the channel.
Vertical Conflict occurs between different levels of the
same channel.
12-7
Vertical Marketing Systems
Corporate
common ownership at different channel levels
Contractual
contractual agreement among channel members
Administered
leadership assumed by dominant members
12-8
Innovations in Marketing Systems
Horizontal Marketing
System
Hybrid Marketing
System
Two or more
companies at one
channel level join
together to increase
coverage
Example:Banks in
Grocery Stores
A single firm sets up
two or more
marketing channels
to increase coverage
Example:Retailers,
Catalogs, and Sales
Force
12-9
Channel Design Decisions
Analyzing Consumer Service Needs
Setting Channel Objectives & Constraints
Exclusive
Distribution
Selective
Distribution
Intensive
Distribution
Identifying Major Alternatives
Evaluating the Major Alternatives
12-10
Channel Management Decisions
Selecting
Motivating
Evaluating
F
E
E
D
B
A
C
K
12-11
Logistics
Involves entire supply chain
Increasing importance of logistics
effective logistics is becoming a key to winning and
keeping customers.
logistics is a major cost element for most
companies.
the explosion in product variety has created a need
for improved logistics management.
information technology has created opportunities
for major gains in distribution efficiency.
12-12
Goals of Logistics system
Provide a Targeted Level of Customer Service at
the Least Cost.
Maximize Profits, Not Sales.
Higher Distribution Costs/
Higher Customer Service
Levels
Lower Distribution Costs/
Lower Customer Service
Levels
12-13
Logistics Functions
Order Processing
Warehousing
Inventory Management
Transportation
Design system to minimize costs of attaining
objectives
12-14
Transportation Modes
Rail
Nations largest carrier, cost-effective
for shipping bulk products, piggyback
Truck
Flexible in routing & time schedules, efficient
for short-hauls of high value goods
Water
Low cost for shipping bulky, low-value
goods, slowest form
Pipeline
Ship petroleum, natural gas, and chemicals
from sources to markets
Air
High cost, ideal when speed is needed or to
ship high-value, low-bulk items
12-15
Integrated Logistics Management
Concept Recognizes that Providing Better Customer
Service and Trimming Distribution Costs Requires
Teamwork, Both Inside the Company and Among All
the Marketing Channel Organizations.
Cross-Functional Teamwork inside
the Company
Building Channel Partnerships
Third-Party Logistics
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5822)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
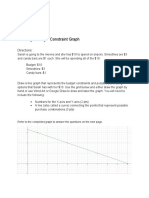
- Economics: Creating A Budget Constraint GraphDocument2 pagesEconomics: Creating A Budget Constraint GraphOsiris HernandezNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Intermediate Microeconomics 8th Edition Varian Solution Manual (PDFDrive)Document8 pagesIntermediate Microeconomics 8th Edition Varian Solution Manual (PDFDrive)Sneha0% (1)
- HDPE Project ReportDocument4 pagesHDPE Project ReportMahaveer P Upadhye100% (1)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Solution Manual For Microeconomics 4th Edition by BesankoDocument21 pagesSolution Manual For Microeconomics 4th Edition by Besankoa28978213333% (3)
- Professional Salesmanship Midterm ExamDocument12 pagesProfessional Salesmanship Midterm ExamChoe Yoek SoekNo ratings yet
- CH 4Document31 pagesCH 4Jaylan A ElwailyNo ratings yet
- Module 1 AdvertisingDocument17 pagesModule 1 AdvertisingRavindra SharmaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4-The Market Forces of Supply and Demand: True/FalseDocument121 pagesCHAPTER 4-The Market Forces of Supply and Demand: True/FalseTriệu Nghi Lê PhùngNo ratings yet
- Types of Business According To ActivitiesDocument11 pagesTypes of Business According To ActivitiesCamille Joy Alba0% (1)
- Lecture 1: Welcome To Managerial Economics: Abdul Quadir XlriDocument31 pagesLecture 1: Welcome To Managerial Economics: Abdul Quadir XlriAbhishek ShuklaNo ratings yet
- B.Sc. Economics Honours - Detailed SyllabusDocument49 pagesB.Sc. Economics Honours - Detailed SyllabusNeelarka RoyNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Economics Self Assessment Exam Style Question's Answers - Section 2Document9 pagesIGCSE Economics Self Assessment Exam Style Question's Answers - Section 2DesreNo ratings yet
- Frank7e Chapter01 Micro Accessible FinalDocument34 pagesFrank7e Chapter01 Micro Accessible FinalismaylalmasudNo ratings yet
- Toys R Us Digital Marketing AssignmentDocument28 pagesToys R Us Digital Marketing AssignmentDavid Shadrach ChandraNo ratings yet
- Foreign Exchange MarketsDocument9 pagesForeign Exchange MarketsAnil ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Business Studies Paper 1 June 2004 PDFDocument4 pagesBusiness Studies Paper 1 June 2004 PDFPanashe MusengiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Micro EconomicsDocument32 pagesIntroduction To Micro EconomicsGauravs100% (1)
- SCM MCQSDocument8 pagesSCM MCQSRao Nawaz Naji100% (3)
- Tutorial Mkt243 Chapter 5: Define Product and Differentiate Types of Consumer ProductDocument2 pagesTutorial Mkt243 Chapter 5: Define Product and Differentiate Types of Consumer Productmuhammad nurNo ratings yet
- CH 003 HWKDocument11 pagesCH 003 HWKdwm1855100% (1)
- 5th Semester AssignmentsDocument17 pages5th Semester Assignments181 Mudasar PatoliNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 8 Monetary Theory BBs 2nd YearDocument22 pagesCHAPTER 8 Monetary Theory BBs 2nd YearSTAR Digital Arts100% (1)
- Engineering Economics and ManagementDocument63 pagesEngineering Economics and Managementsrinivas gangishettiNo ratings yet
- HyperpptDocument22 pagesHyperpptnanthigaNo ratings yet
- New Electronic Trading Systems in The Foreign Exchange MarketsDocument37 pagesNew Electronic Trading Systems in The Foreign Exchange MarketsDev GogoiNo ratings yet
- Diskusi 6.docx Ekonomi ManajerialDocument5 pagesDiskusi 6.docx Ekonomi ManajerialBoby RahmanNo ratings yet
- Financial MarketDocument8 pagesFinancial Marketindusekar83No ratings yet
- Material Downloaded From - 1 / 4Document4 pagesMaterial Downloaded From - 1 / 4Gamer ChannelNo ratings yet
- Chamberlin, E. H. (1961) - The Origin and Early Development of Monopolistic Competition TheoryDocument30 pagesChamberlin, E. H. (1961) - The Origin and Early Development of Monopolistic Competition Theorycarlos rodriguesNo ratings yet
- Retail CRMDocument14 pagesRetail CRMIpsita AcharyaNo ratings yet