Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Stick Diagrams
Stick Diagrams
Uploaded by
Anonymous BHcPexCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- 3D Granny Squares: 100 Crochet Patterns for Pop-Up Granny SquaresFrom Everand3D Granny Squares: 100 Crochet Patterns for Pop-Up Granny SquaresRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (12)
- Design A Compute Solution AZ - 305Document3 pagesDesign A Compute Solution AZ - 305Carlos Moríñigo Montisi (Mori)0% (1)
- Stick Diagrams and TutorialDocument38 pagesStick Diagrams and TutorialSangya Shrivastava0% (3)
- Stick DiagramDocument21 pagesStick DiagramVani Bindal AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Stick Diagrams 1Document19 pagesStick Diagrams 1ElakkiyaSelvarajNo ratings yet
- Stick Diagrams Layers LayoutsDocument36 pagesStick Diagrams Layers LayoutsRaghu RamNo ratings yet
- Unit - 3 Circuit Design ProcessDocument30 pagesUnit - 3 Circuit Design ProcessNagarjun RajputNo ratings yet
- Eec 401 Basic Vlsi Design: GitamDocument52 pagesEec 401 Basic Vlsi Design: Gitamcrush on creativityNo ratings yet
- 4-SNBhat - StickdiagraFile Setms - IUCEEEDocument38 pages4-SNBhat - StickdiagraFile Setms - IUCEEEranjithece1No ratings yet
- Layout Design: 18-322 Fall 2003Document40 pagesLayout Design: 18-322 Fall 2003Sai SadiqNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document61 pagesChapter 5Faiz MohdNo ratings yet
- Unit IiiDocument71 pagesUnit Iiicrush on creativityNo ratings yet
- Stick DiagramsDocument34 pagesStick DiagramsNagaraju NeelaNo ratings yet
- Stick DiagramDocument20 pagesStick DiagramPraveen AndrewNo ratings yet
- Stick DiagramDocument55 pagesStick Diagramsamiularefin2000No ratings yet
- CMOS Layout Design Rules - Girish GidayeDocument90 pagesCMOS Layout Design Rules - Girish GidayeGIRISH GIDAYENo ratings yet
- Stick DiagramDocument72 pagesStick DiagramBhanu Bond0% (1)
- Beaver InstructionsDocument29 pagesBeaver InstructionsMyles de BastionNo ratings yet
- PCIRF 3 1 LayoutDocument61 pagesPCIRF 3 1 LayoutMarius FerdyNo ratings yet
- 297 - 49023 - Co3 Stickdiagrams 28 7 15Document20 pages297 - 49023 - Co3 Stickdiagrams 28 7 15Krishna SaladiNo ratings yet
- CHP 2 - Mos Design and LayoutDocument104 pagesCHP 2 - Mos Design and Layoutkkece41No ratings yet
- Analog and Digital VLSI Design: Tutorial 2-LayoutsDocument13 pagesAnalog and Digital VLSI Design: Tutorial 2-LayoutsYash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Rebars (318-05)Document2 pagesRebars (318-05)Yan Naung KoNo ratings yet
- Stick DiagramsDocument30 pagesStick DiagramsGordon LaVelleNo ratings yet
- 1.5 Stick Diag + Layout Rules+ NWellCMOS-InverterFabricationDocument79 pages1.5 Stick Diag + Layout Rules+ NWellCMOS-InverterFabricationsreemurarik756No ratings yet
- Led Theo NhacDocument16 pagesLed Theo NhacNguyễn Thắng LợiNo ratings yet
- Analog Layout Design: Kanazawa University Microelectronics Research Lab. Akio KitagawaDocument48 pagesAnalog Layout Design: Kanazawa University Microelectronics Research Lab. Akio Kitagawaaminkhan83No ratings yet
- s.1 Stick DiagramsDocument44 pagess.1 Stick DiagramsUbaidNo ratings yet
- Lecture05 Ee474 Layout PDFDocument74 pagesLecture05 Ee474 Layout PDFKesani Venkat Narsimha ReddyNo ratings yet
- Stick DiaDocument13 pagesStick DiaVarun KumarNo ratings yet
- GE8261 - EP MAnual 2023Document26 pagesGE8261 - EP MAnual 2023Santhosh KumarNo ratings yet
- CMOS Process Flow: Institute of Radio Physics & Electronics University of CalcuttaDocument28 pagesCMOS Process Flow: Institute of Radio Physics & Electronics University of CalcuttaSoumi RoyNo ratings yet
- Logic ProbeDocument3 pagesLogic ProbeVijay MirjeNo ratings yet
- 10 Stickdiagrams PDFDocument55 pages10 Stickdiagrams PDFrdanwaraNo ratings yet
- MAKE 18 Light BrickDocument10 pagesMAKE 18 Light BrickDumitrescu Leonard CezarNo ratings yet
- VLSI Module 3 PDFDocument34 pagesVLSI Module 3 PDFGovind M RoddannavarNo ratings yet
- A Practical Guide To High-Speed Printed Circuit Board LayoutDocument107 pagesA Practical Guide To High-Speed Printed Circuit Board LayoutsawtohNo ratings yet
- Layout For Analog Integrated Circuits: Analog IC Prof. Guoxing Wang 1Document40 pagesLayout For Analog Integrated Circuits: Analog IC Prof. Guoxing Wang 1Samvel YanNo ratings yet
- Cmos Design Rules Layout PDFDocument33 pagesCmos Design Rules Layout PDFkrishnaavNo ratings yet
- VLSIDocument140 pagesVLSINiranjan ReddyNo ratings yet
- Tu RCV 27MHz PCB Not AssembledDocument8 pagesTu RCV 27MHz PCB Not AssembledAndrei-Daniel BotezatuNo ratings yet
- How To Build Binaural MicrophonesDocument8 pagesHow To Build Binaural MicrophonesVictor Pastor RebolloNo ratings yet
- Concept Education Class 12 Sub Physics. Time 1.30 Min Max Mark 32Document2 pagesConcept Education Class 12 Sub Physics. Time 1.30 Min Max Mark 32TECHNICAL WE AND YOUNo ratings yet
- STick Diagrams - Design RulesDocument98 pagesSTick Diagrams - Design RulesRaja VidyaNo ratings yet
- Unit2 - 2 - MOS Layers & Stick Diagrams For NMOS - CMOS - BiCMOSDocument60 pagesUnit2 - 2 - MOS Layers & Stick Diagrams For NMOS - CMOS - BiCMOSneha yarrapothuNo ratings yet
- VLSI Stick Diagrams: Prof. Jagannadha Naidu KDocument23 pagesVLSI Stick Diagrams: Prof. Jagannadha Naidu KParth VijayNo ratings yet
- Circuit Characterization and Performance Estimation: Instructor Dr. İsmail Enis UnganDocument36 pagesCircuit Characterization and Performance Estimation: Instructor Dr. İsmail Enis UnganyousufnetNo ratings yet
- Practical Work 3Document15 pagesPractical Work 3Kalai ShanNo ratings yet
- StickDocument16 pagesStickBikram PaulNo ratings yet
- Can A Kit FM TransmitterDocument35 pagesCan A Kit FM TransmitterDhruv ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12 - Euler's Path and Stick DiagramDocument22 pagesLecture 12 - Euler's Path and Stick DiagramKarl Steven BaylonNo ratings yet
- 1diode PN SKDocument37 pages1diode PN SKKurma RaoNo ratings yet
- IMP MicrowindDocument12 pagesIMP Microwindrahul_rvm82No ratings yet
- Tu RCV 27MHz PCB AssembledDocument7 pagesTu RCV 27MHz PCB AssembledJay VoraNo ratings yet
- Canakit FMTransmitterDocument35 pagesCanakit FMTransmitterAkmal KhanNo ratings yet
- Can A Kit FM TransmitterDocument35 pagesCan A Kit FM TransmitterAnonymous dVKUjDNo ratings yet
- Automated Optical Inspection: Advancements in Computer Vision TechnologyFrom EverandAutomated Optical Inspection: Advancements in Computer Vision TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Jntu World: Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University HyderabadDocument13 pagesJntu World: Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University HyderabadAnonymous BHcPexNo ratings yet
- Contorl Systems: Frequency Response AnalysisDocument2 pagesContorl Systems: Frequency Response AnalysisAnonymous BHcPexNo ratings yet
- 07a4ec11 Analogcommunications12Document5 pages07a4ec11 Analogcommunications12Anonymous BHcPexNo ratings yet
- Ac Unit 5 Question BankDocument1 pageAc Unit 5 Question BankAnonymous BHcPexNo ratings yet
- Vlsi Design Quiz PaperDocument8 pagesVlsi Design Quiz PaperAnonymous BHcPexNo ratings yet
- R07 Set No. 2Document8 pagesR07 Set No. 2Anonymous BHcPexNo ratings yet
- MidTerm CSNB534 Exam Sep10Document2 pagesMidTerm CSNB534 Exam Sep10hzulcefliNo ratings yet
- DatasheetDocument2 pagesDatasheetStuxnetNo ratings yet
- Debug 1214Document3 pagesDebug 1214'Stagionaire' Signore Leone 'Primavera'No ratings yet
- Microsoft Azure Pre AssessmentDocument4 pagesMicrosoft Azure Pre AssessmentAmit SharmaNo ratings yet
- WSOS01-DOC-102 Protocol Configuration ManualDocument38 pagesWSOS01-DOC-102 Protocol Configuration ManualCata CatalinNo ratings yet
- EC8501 - DIGITAL COMMUNICATION (Syllabus) 2017-Regulation Anna UniversityDocument4 pagesEC8501 - DIGITAL COMMUNICATION (Syllabus) 2017-Regulation Anna UniversitymenakadevieceNo ratings yet
- Principles of Electric Circuits, Conventional Flow, 9 EdDocument26 pagesPrinciples of Electric Circuits, Conventional Flow, 9 EdKit Meng LimNo ratings yet
- JVL MotoWare32 Programming Software For JVL ControllersDocument2 pagesJVL MotoWare32 Programming Software For JVL ControllersElectromateNo ratings yet
- R911338962 - 04 - IndraDrive Control SectionsDocument158 pagesR911338962 - 04 - IndraDrive Control SectionsEwerton BalarezNo ratings yet
- Product Briefing ATN950 Ver1Document19 pagesProduct Briefing ATN950 Ver1Musoft AmasoftNo ratings yet
- C# PROGRAMDocument58 pagesC# PROGRAMVijay Nayak100% (1)
- TIB BW 5.13.0 Installation PDFDocument26 pagesTIB BW 5.13.0 Installation PDFharanadhcNo ratings yet
- C# BK SQLDocument2 pagesC# BK SQLHieuDevNo ratings yet
- Experiment:1: Write A Shell Script To Generate A Multiplication TableDocument48 pagesExperiment:1: Write A Shell Script To Generate A Multiplication Tablegdayanand4uNo ratings yet
- Test For DGM & Civil EngineeringDocument8 pagesTest For DGM & Civil EngineeringMuhammad IqbalNo ratings yet
- Hydra 1.0 Pro - How To Improve My BoostDocument32 pagesHydra 1.0 Pro - How To Improve My BoostConection lostNo ratings yet
- Ideapad 100 15IBY 15IBD Platform Specifications PDFDocument2 pagesIdeapad 100 15IBY 15IBD Platform Specifications PDFmanocaoNo ratings yet
- Sensors and Sensing Lab 1: Arduino Motor Control and ROSDocument7 pagesSensors and Sensing Lab 1: Arduino Motor Control and ROSFebri Rizky PratamaNo ratings yet
- Distributed Systems-A Brief IntroductionDocument30 pagesDistributed Systems-A Brief IntroductionkhoadplaNo ratings yet
- CP R80.20.20 1500 1600 1800 Appliance Series AdminGuide Centrally ManagedDocument179 pagesCP R80.20.20 1500 1600 1800 Appliance Series AdminGuide Centrally ManagedruancarlossNo ratings yet
- Brocade Password Recovery For All FOSDocument12 pagesBrocade Password Recovery For All FOSephemeronNo ratings yet
- Day 04Document5 pagesDay 04Aymen AdlineNo ratings yet
- Report On Internet Banking Using Django By:-Naman ChaturvediDocument42 pagesReport On Internet Banking Using Django By:-Naman ChaturvediNaman Chaturvedi100% (2)
- Computer Computer A AW Wareness Areness: Chapter - 1 Chapter - 1Document13 pagesComputer Computer A AW Wareness Areness: Chapter - 1 Chapter - 1uppaliNo ratings yet
- Guía de Procesadores RyzenDocument44 pagesGuía de Procesadores Ryzenyuri100% (1)
- 3PAR 銷售技巧 8200 Training - DawningDocument30 pages3PAR 銷售技巧 8200 Training - DawningreibolinhNo ratings yet
- Oracle DBA Workshop IIDocument4 pagesOracle DBA Workshop IIpgupta101No ratings yet
- HC-A Training Manual en V1.1 Filled inDocument60 pagesHC-A Training Manual en V1.1 Filled inptamásNo ratings yet
- C, C++ and JAVA: The Magic of Computer Programming LanguageDocument3 pagesC, C++ and JAVA: The Magic of Computer Programming LanguageInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
Stick Diagrams
Stick Diagrams
Uploaded by
Anonymous BHcPexOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Stick Diagrams
Stick Diagrams
Uploaded by
Anonymous BHcPexCopyright:
Available Formats
1
Ravikiran
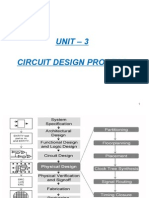
STI CK DI AGRAMS
VLSI DESIGN FLOW
D.Ravikiran babu
Assoc.Professor
Dept of ECE.,
JITS, Karimnagar.
drkbabu1@gmail.com
2
D.R.K.Babu
VLSI DESIGN FLOW
3
D.R.K.Babu
4
D.R.K.Babu
5
D.R.K.Babu
Stick Diagrams
6
Stick Diagrams
D.R.K.Babu
Stick Diagrams
Objectives:
To know what is meant by stick diagram.
To understand the capabilities and limitations of stick
diagram.
To learn how to draw stick diagrams for a given MOS
circuit.
Outcome:
At the end of this module the students will be able
draw the stick diagram for simple MOS circuits.
7
Stick Diagrams
D.R.K.Babu
Stick Diagrams
8
N+ N+
Stick Diagrams
D.R.K.Babu
Stick Diagrams
9
Gnd
V
DD
x
x
X
X
X
X
V
DD
x
x
Gnd
Stick
Diagram
Stick Diagrams
D.R.K.Babu
Stick Diagrams
10
Gnd
V
DD
x
x
X
X
X
X
V
DD
x
x
Gnd
Stick Diagrams
D.R.K.Babu
Stick Diagrams
VLSI design aims to translate circuit concepts
onto silicon.
stick diagrams are a means of capturing
topography and layer information using simple
diagrams.
Stick diagrams convey layer information
through colour codes (or monochrome
encoding).
Acts as an interface between symbolic circuit
and the actual layout.
11
Stick Diagrams
D.R.K.Babu
12
Stick Diagrams
Does show all components/vias.
It shows relative placement of components.
Goes one step closer to the layout
Helps plan the layout and routing
A stick diagram is a cartoon of a layout.
Stick Diagrams
D.R.K.Babu
13
Stick Diagrams
Does not show
Exact placement of components
Transistor sizes
Wire lengths, wire widths, tub boundaries.
Any other low level details such as parasitics..
Stick Diagrams
D.R.K.Babu
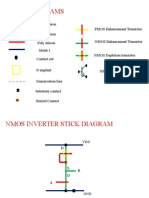
Stick encoding(n-mos & p-mos)
N-diffusion
14
P-diffusion
Metal 1
Contact Cut
Implant
Polysilicon
14
N-diffusion
P-diffusion
Metal 1
Contact Cut
Implant
::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::
:::::
Poly Silicon
Buried contact
Color Coding Monochrome Coding
15
Stick diagram:
green,, yellow n-diffusion, p-difffusion
Red Polysilicon
Blue Metal
Yellow Implant
Black Contact areas
16
Contact cuts
17
Electrical connections
Rule 1.
When two or more sticks of the same type
cross or touch each other that represents
electrical contact.
Contact cuts
18
Contact cut
Buried contact
Rule 2.
When two or more sticks of different type cross or
touch each other there is no electrical contact.
(If electrical contact is needed we have to show the connection
explicitly).
Contd.
19
Butting Contact
Via
20
N-diffusion
Ploy silicon
Nmos enhancement transistor:
Rule 3.
When a poly crosses diffusion it represents a transistor.
Note: If a contact is shown then it is not a transistor.
21
N-diffusion
Ploy silicon
Implant
Nmos depletion transistor:
22
pmos enhancement transistor:
23
p-diffusion
Ploy silicon
pmos DEPLETION MODE transistor:
24
P-diffusion
Ploy silicon
Implant
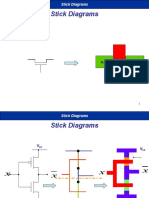
Stick diagram for nmos inverter:
25
vin
gnd
Step1:
Draw metal(blue) V
DD
and GND rails in parallel
with enough separation
26
V
DD
GND
vin
Step2:
27
Forming transistors
gnd
V
DD
GND
Step2-1:
28
vin
gnd
Vin
V
DD
GND
Step3:
29
vin
gnd
Vout
Vin
V
DD
GND
Step4:
30
vin
gnd
V
DD
GND
Vout
Vin
31
32
Vdd
Vss
N mos NAND GATE
A
Ploy(G)
Ploy(G)
s
s
D
D
B
Ploy(G)
Vout(A nand B)
Vout(A nor B)
N mos NOR GATE
33
33
Vdd
Vss
A
Ploy(G)
Ploy(G)
s s
D D
B
CMOS ENCODING
34
35
Cmos inverter:
36
Demarcation line
VDD
GND
37
input
output
Vdd contact
Vss contact
38
39
Demarcation
Line
Vdd contact
Vss contact
Vdd
Vss
Vout(A nand B)
A
Ploy(G)
Ploy(G)
Ploy(G)
Ploy(G)
B
s s
s
s
D
D
D
D
Cmos NAND GATE
40
Vdd contact
Vss contact
Vdd
Vss
Demarcation
Line
Vout(A nor B)
A
Ploy(G)
Ploy(G)
Ploy(G)
Ploy(G)
s
s
s s
D
D
D
D
B
Cmos Nor GATE
Vss contact
Vdd
Vss
Demarcation
Line
Vout
Vdd contact
BiCmos inverter
42
Vss contact
Vdd
Vss
Vout
Vdd contact
BiCmos inverter
You might also like
- 3D Granny Squares: 100 Crochet Patterns for Pop-Up Granny SquaresFrom Everand3D Granny Squares: 100 Crochet Patterns for Pop-Up Granny SquaresRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (12)
- Design A Compute Solution AZ - 305Document3 pagesDesign A Compute Solution AZ - 305Carlos Moríñigo Montisi (Mori)0% (1)
- Stick Diagrams and TutorialDocument38 pagesStick Diagrams and TutorialSangya Shrivastava0% (3)
- Stick DiagramDocument21 pagesStick DiagramVani Bindal AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Stick Diagrams 1Document19 pagesStick Diagrams 1ElakkiyaSelvarajNo ratings yet
- Stick Diagrams Layers LayoutsDocument36 pagesStick Diagrams Layers LayoutsRaghu RamNo ratings yet
- Unit - 3 Circuit Design ProcessDocument30 pagesUnit - 3 Circuit Design ProcessNagarjun RajputNo ratings yet
- Eec 401 Basic Vlsi Design: GitamDocument52 pagesEec 401 Basic Vlsi Design: Gitamcrush on creativityNo ratings yet
- 4-SNBhat - StickdiagraFile Setms - IUCEEEDocument38 pages4-SNBhat - StickdiagraFile Setms - IUCEEEranjithece1No ratings yet
- Layout Design: 18-322 Fall 2003Document40 pagesLayout Design: 18-322 Fall 2003Sai SadiqNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document61 pagesChapter 5Faiz MohdNo ratings yet
- Unit IiiDocument71 pagesUnit Iiicrush on creativityNo ratings yet
- Stick DiagramsDocument34 pagesStick DiagramsNagaraju NeelaNo ratings yet
- Stick DiagramDocument20 pagesStick DiagramPraveen AndrewNo ratings yet
- Stick DiagramDocument55 pagesStick Diagramsamiularefin2000No ratings yet
- CMOS Layout Design Rules - Girish GidayeDocument90 pagesCMOS Layout Design Rules - Girish GidayeGIRISH GIDAYENo ratings yet
- Stick DiagramDocument72 pagesStick DiagramBhanu Bond0% (1)
- Beaver InstructionsDocument29 pagesBeaver InstructionsMyles de BastionNo ratings yet
- PCIRF 3 1 LayoutDocument61 pagesPCIRF 3 1 LayoutMarius FerdyNo ratings yet
- 297 - 49023 - Co3 Stickdiagrams 28 7 15Document20 pages297 - 49023 - Co3 Stickdiagrams 28 7 15Krishna SaladiNo ratings yet
- CHP 2 - Mos Design and LayoutDocument104 pagesCHP 2 - Mos Design and Layoutkkece41No ratings yet
- Analog and Digital VLSI Design: Tutorial 2-LayoutsDocument13 pagesAnalog and Digital VLSI Design: Tutorial 2-LayoutsYash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Rebars (318-05)Document2 pagesRebars (318-05)Yan Naung KoNo ratings yet
- Stick DiagramsDocument30 pagesStick DiagramsGordon LaVelleNo ratings yet
- 1.5 Stick Diag + Layout Rules+ NWellCMOS-InverterFabricationDocument79 pages1.5 Stick Diag + Layout Rules+ NWellCMOS-InverterFabricationsreemurarik756No ratings yet
- Led Theo NhacDocument16 pagesLed Theo NhacNguyễn Thắng LợiNo ratings yet
- Analog Layout Design: Kanazawa University Microelectronics Research Lab. Akio KitagawaDocument48 pagesAnalog Layout Design: Kanazawa University Microelectronics Research Lab. Akio Kitagawaaminkhan83No ratings yet
- s.1 Stick DiagramsDocument44 pagess.1 Stick DiagramsUbaidNo ratings yet
- Lecture05 Ee474 Layout PDFDocument74 pagesLecture05 Ee474 Layout PDFKesani Venkat Narsimha ReddyNo ratings yet
- Stick DiaDocument13 pagesStick DiaVarun KumarNo ratings yet
- GE8261 - EP MAnual 2023Document26 pagesGE8261 - EP MAnual 2023Santhosh KumarNo ratings yet
- CMOS Process Flow: Institute of Radio Physics & Electronics University of CalcuttaDocument28 pagesCMOS Process Flow: Institute of Radio Physics & Electronics University of CalcuttaSoumi RoyNo ratings yet
- Logic ProbeDocument3 pagesLogic ProbeVijay MirjeNo ratings yet
- 10 Stickdiagrams PDFDocument55 pages10 Stickdiagrams PDFrdanwaraNo ratings yet
- MAKE 18 Light BrickDocument10 pagesMAKE 18 Light BrickDumitrescu Leonard CezarNo ratings yet
- VLSI Module 3 PDFDocument34 pagesVLSI Module 3 PDFGovind M RoddannavarNo ratings yet
- A Practical Guide To High-Speed Printed Circuit Board LayoutDocument107 pagesA Practical Guide To High-Speed Printed Circuit Board LayoutsawtohNo ratings yet
- Layout For Analog Integrated Circuits: Analog IC Prof. Guoxing Wang 1Document40 pagesLayout For Analog Integrated Circuits: Analog IC Prof. Guoxing Wang 1Samvel YanNo ratings yet
- Cmos Design Rules Layout PDFDocument33 pagesCmos Design Rules Layout PDFkrishnaavNo ratings yet
- VLSIDocument140 pagesVLSINiranjan ReddyNo ratings yet
- Tu RCV 27MHz PCB Not AssembledDocument8 pagesTu RCV 27MHz PCB Not AssembledAndrei-Daniel BotezatuNo ratings yet
- How To Build Binaural MicrophonesDocument8 pagesHow To Build Binaural MicrophonesVictor Pastor RebolloNo ratings yet
- Concept Education Class 12 Sub Physics. Time 1.30 Min Max Mark 32Document2 pagesConcept Education Class 12 Sub Physics. Time 1.30 Min Max Mark 32TECHNICAL WE AND YOUNo ratings yet
- STick Diagrams - Design RulesDocument98 pagesSTick Diagrams - Design RulesRaja VidyaNo ratings yet
- Unit2 - 2 - MOS Layers & Stick Diagrams For NMOS - CMOS - BiCMOSDocument60 pagesUnit2 - 2 - MOS Layers & Stick Diagrams For NMOS - CMOS - BiCMOSneha yarrapothuNo ratings yet
- VLSI Stick Diagrams: Prof. Jagannadha Naidu KDocument23 pagesVLSI Stick Diagrams: Prof. Jagannadha Naidu KParth VijayNo ratings yet
- Circuit Characterization and Performance Estimation: Instructor Dr. İsmail Enis UnganDocument36 pagesCircuit Characterization and Performance Estimation: Instructor Dr. İsmail Enis UnganyousufnetNo ratings yet
- Practical Work 3Document15 pagesPractical Work 3Kalai ShanNo ratings yet
- StickDocument16 pagesStickBikram PaulNo ratings yet
- Can A Kit FM TransmitterDocument35 pagesCan A Kit FM TransmitterDhruv ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12 - Euler's Path and Stick DiagramDocument22 pagesLecture 12 - Euler's Path and Stick DiagramKarl Steven BaylonNo ratings yet
- 1diode PN SKDocument37 pages1diode PN SKKurma RaoNo ratings yet
- IMP MicrowindDocument12 pagesIMP Microwindrahul_rvm82No ratings yet
- Tu RCV 27MHz PCB AssembledDocument7 pagesTu RCV 27MHz PCB AssembledJay VoraNo ratings yet
- Canakit FMTransmitterDocument35 pagesCanakit FMTransmitterAkmal KhanNo ratings yet
- Can A Kit FM TransmitterDocument35 pagesCan A Kit FM TransmitterAnonymous dVKUjDNo ratings yet
- Automated Optical Inspection: Advancements in Computer Vision TechnologyFrom EverandAutomated Optical Inspection: Advancements in Computer Vision TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Jntu World: Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University HyderabadDocument13 pagesJntu World: Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University HyderabadAnonymous BHcPexNo ratings yet
- Contorl Systems: Frequency Response AnalysisDocument2 pagesContorl Systems: Frequency Response AnalysisAnonymous BHcPexNo ratings yet
- 07a4ec11 Analogcommunications12Document5 pages07a4ec11 Analogcommunications12Anonymous BHcPexNo ratings yet
- Ac Unit 5 Question BankDocument1 pageAc Unit 5 Question BankAnonymous BHcPexNo ratings yet
- Vlsi Design Quiz PaperDocument8 pagesVlsi Design Quiz PaperAnonymous BHcPexNo ratings yet
- R07 Set No. 2Document8 pagesR07 Set No. 2Anonymous BHcPexNo ratings yet
- MidTerm CSNB534 Exam Sep10Document2 pagesMidTerm CSNB534 Exam Sep10hzulcefliNo ratings yet
- DatasheetDocument2 pagesDatasheetStuxnetNo ratings yet
- Debug 1214Document3 pagesDebug 1214'Stagionaire' Signore Leone 'Primavera'No ratings yet
- Microsoft Azure Pre AssessmentDocument4 pagesMicrosoft Azure Pre AssessmentAmit SharmaNo ratings yet
- WSOS01-DOC-102 Protocol Configuration ManualDocument38 pagesWSOS01-DOC-102 Protocol Configuration ManualCata CatalinNo ratings yet
- EC8501 - DIGITAL COMMUNICATION (Syllabus) 2017-Regulation Anna UniversityDocument4 pagesEC8501 - DIGITAL COMMUNICATION (Syllabus) 2017-Regulation Anna UniversitymenakadevieceNo ratings yet
- Principles of Electric Circuits, Conventional Flow, 9 EdDocument26 pagesPrinciples of Electric Circuits, Conventional Flow, 9 EdKit Meng LimNo ratings yet
- JVL MotoWare32 Programming Software For JVL ControllersDocument2 pagesJVL MotoWare32 Programming Software For JVL ControllersElectromateNo ratings yet
- R911338962 - 04 - IndraDrive Control SectionsDocument158 pagesR911338962 - 04 - IndraDrive Control SectionsEwerton BalarezNo ratings yet
- Product Briefing ATN950 Ver1Document19 pagesProduct Briefing ATN950 Ver1Musoft AmasoftNo ratings yet
- C# PROGRAMDocument58 pagesC# PROGRAMVijay Nayak100% (1)
- TIB BW 5.13.0 Installation PDFDocument26 pagesTIB BW 5.13.0 Installation PDFharanadhcNo ratings yet
- C# BK SQLDocument2 pagesC# BK SQLHieuDevNo ratings yet
- Experiment:1: Write A Shell Script To Generate A Multiplication TableDocument48 pagesExperiment:1: Write A Shell Script To Generate A Multiplication Tablegdayanand4uNo ratings yet
- Test For DGM & Civil EngineeringDocument8 pagesTest For DGM & Civil EngineeringMuhammad IqbalNo ratings yet
- Hydra 1.0 Pro - How To Improve My BoostDocument32 pagesHydra 1.0 Pro - How To Improve My BoostConection lostNo ratings yet
- Ideapad 100 15IBY 15IBD Platform Specifications PDFDocument2 pagesIdeapad 100 15IBY 15IBD Platform Specifications PDFmanocaoNo ratings yet
- Sensors and Sensing Lab 1: Arduino Motor Control and ROSDocument7 pagesSensors and Sensing Lab 1: Arduino Motor Control and ROSFebri Rizky PratamaNo ratings yet
- Distributed Systems-A Brief IntroductionDocument30 pagesDistributed Systems-A Brief IntroductionkhoadplaNo ratings yet
- CP R80.20.20 1500 1600 1800 Appliance Series AdminGuide Centrally ManagedDocument179 pagesCP R80.20.20 1500 1600 1800 Appliance Series AdminGuide Centrally ManagedruancarlossNo ratings yet
- Brocade Password Recovery For All FOSDocument12 pagesBrocade Password Recovery For All FOSephemeronNo ratings yet
- Day 04Document5 pagesDay 04Aymen AdlineNo ratings yet
- Report On Internet Banking Using Django By:-Naman ChaturvediDocument42 pagesReport On Internet Banking Using Django By:-Naman ChaturvediNaman Chaturvedi100% (2)
- Computer Computer A AW Wareness Areness: Chapter - 1 Chapter - 1Document13 pagesComputer Computer A AW Wareness Areness: Chapter - 1 Chapter - 1uppaliNo ratings yet
- Guía de Procesadores RyzenDocument44 pagesGuía de Procesadores Ryzenyuri100% (1)
- 3PAR 銷售技巧 8200 Training - DawningDocument30 pages3PAR 銷售技巧 8200 Training - DawningreibolinhNo ratings yet
- Oracle DBA Workshop IIDocument4 pagesOracle DBA Workshop IIpgupta101No ratings yet
- HC-A Training Manual en V1.1 Filled inDocument60 pagesHC-A Training Manual en V1.1 Filled inptamásNo ratings yet
- C, C++ and JAVA: The Magic of Computer Programming LanguageDocument3 pagesC, C++ and JAVA: The Magic of Computer Programming LanguageInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet