Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 viewsLab 5 - DNA Extraction From Strawberries and Liver Fall 2014
Lab 5 - DNA Extraction From Strawberries and Liver Fall 2014
Uploaded by
Amy HollingsworthThis document provides instructions and background information for a lab on extracting DNA from cells. The lab will have students extract and observe DNA from strawberry and chicken liver samples. They will learn that DNA is found in nearly every cell and takes the shape of a double helix, with nitrogenous bases forming the sides and sugars and phosphates making up the backbone. The document explains that DNA carries genetic information that is passed down from parents and makes each organism unique.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Biology Note For Grade 12 (Unit Three Molecular GeneticsDocument24 pagesBiology Note For Grade 12 (Unit Three Molecular GeneticsDaniel GtsadkanNo ratings yet
- International Standard: Iron Oxide Pigments - Specifications and Methods of TestDocument26 pagesInternational Standard: Iron Oxide Pigments - Specifications and Methods of TestHamid Damghani100% (1)
- The Sea Urchin Fertilization LabDocument5 pagesThe Sea Urchin Fertilization LabAmy HollingsworthNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 Enzymes and The Catalase LabDocument18 pagesLab 4 Enzymes and The Catalase LabAmy Hollingsworth100% (1)
- Lab 5 - DNA Extraction From CellsDocument15 pagesLab 5 - DNA Extraction From CellsAmy HollingsworthNo ratings yet
- Structure of Dna: Deoxyribonucleic Acid BY Kapish, Rithish, KrishwanthDocument7 pagesStructure of Dna: Deoxyribonucleic Acid BY Kapish, Rithish, KrishwanthRithish VikramNo ratings yet
- DNA en RNADocument48 pagesDNA en RNAdnielbrink27No ratings yet
- Dna Code of Life 2021 PresentationDocument41 pagesDna Code of Life 2021 Presentationsandilek124No ratings yet
- IB - MYP5 U6 How Docharacteristics Pass From One Generation To AnotherDocument77 pagesIB - MYP5 U6 How Docharacteristics Pass From One Generation To AnotherCoco LocoNo ratings yet
- What Is DNADocument22 pagesWhat Is DNASehar AslamNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure by NeerajDocument21 pagesDNA Structure by NeerajNeeraj BahugunaNo ratings yet
- III.C. DNA Its Role in Inheritance and Protein SynthesisDocument15 pagesIII.C. DNA Its Role in Inheritance and Protein SynthesisDarwin NoolNo ratings yet
- Week 1 DNADocument28 pagesWeek 1 DNAHonleth Jheney MamarilNo ratings yet
- Biology Year 10Document20 pagesBiology Year 10Your best fan HsNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication - PPT 1Document48 pagesDNA Replication - PPT 1Keira MendozaNo ratings yet
- Nicole Shane Abonal: Wag Kayo Mag Tanong PLS.:' ( (Document13 pagesNicole Shane Abonal: Wag Kayo Mag Tanong PLS.:' ( (Marcus LiamNo ratings yet
- Dna StructureDocument32 pagesDna StructureHONLETH ROMBLONNo ratings yet
- DNA StructureDocument22 pagesDNA StructureMehrul Singh RanavatNo ratings yet
- DnareplicationDocument15 pagesDnareplicationapi-248090384No ratings yet
- 3 DNA and RNADocument34 pages3 DNA and RNAjessicakylaalvarezNo ratings yet
- Module 9. Dna AnalysisDocument46 pagesModule 9. Dna AnalysisJunilie Pie LequitNo ratings yet
- Me Sci 10 q3 1301 PsDocument27 pagesMe Sci 10 q3 1301 PsCassy Leighz BagonocNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure and ReplicationDocument61 pagesDNA Structure and Replicationmanuela pardoNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 8 - The DNA - Structure, Function, and DiscoveryDocument18 pagesCHAPTER 8 - The DNA - Structure, Function, and Discoverybabylen bahalaNo ratings yet
- DNA JA NewDocument41 pagesDNA JA NewHamza TahaNo ratings yet
- Question: Why Don't We All Look Alike?: DNA - The Code For LifeDocument42 pagesQuestion: Why Don't We All Look Alike?: DNA - The Code For LifedoloresfilipinoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - 1A - Introduction To GeneticsDocument26 pagesLesson 1 - 1A - Introduction To Genetics宋臻若No ratings yet
- Lecture: Dna (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) : Kazhaleh MohammadiDocument17 pagesLecture: Dna (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) : Kazhaleh MohammadiAhmad PenjwenyNo ratings yet
- MBI MissionMBBS-L1Document73 pagesMBI MissionMBBS-L1Hitesh KhatriNo ratings yet
- Grp.2 DNA REPLICATION EMERALDDocument48 pagesGrp.2 DNA REPLICATION EMERALDLinda Ann BacunadorNo ratings yet
- Aristotle Dna Rna ReportDocument13 pagesAristotle Dna Rna ReportSarah Joy RiveraNo ratings yet
- DNA Paternity TestsDocument4 pagesDNA Paternity TestsIRFAN ZAIN ULABIDEENNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document10 pagesPresentation 1sharanvarmavegirajuNo ratings yet
- Dna-Structure ActivityDocument3 pagesDna-Structure Activityalindoganchristina85No ratings yet
- SCIE1106 Lec 6 DNA Structure 2023 MSTDocument27 pagesSCIE1106 Lec 6 DNA Structure 2023 MSTJamesNo ratings yet
- 7.16DNA WorksheetDocument8 pages7.16DNA WorksheetVanessa JuatcoNo ratings yet
- Strawberry DNA ExtractionDocument14 pagesStrawberry DNA ExtractionFakku SakkuNo ratings yet
- BIOC2600/MEDE2301 Lectures Overview: Dr. Alan Wong School of Biomedical SciencesDocument35 pagesBIOC2600/MEDE2301 Lectures Overview: Dr. Alan Wong School of Biomedical SciencesSeo Eun KimNo ratings yet
- Dna and RnaDocument21 pagesDna and RnaMaxxie LeonerioNo ratings yet
- How Your Genes Determine Who You AreDocument12 pagesHow Your Genes Determine Who You Areaerinimmmm3030No ratings yet
- L2 #: 75al 7" J: (4qepa Bnki (Kkcha $HKQ'Document5 pagesL2 #: 75al 7" J: (4qepa Bnki (Kkcha $HKQ'payal devdaNo ratings yet
- Mydna (Biochem 100) Day 1: InstructorDocument25 pagesMydna (Biochem 100) Day 1: InstructorJose R ZambranoNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Molecular Biology Chapter 10 PDFDocument115 pagesUnit 6 Molecular Biology Chapter 10 PDFc8kewaternotesNo ratings yet
- Dnachromosomes 1Document29 pagesDnachromosomes 1The PassionNo ratings yet
- Dna & RnaDocument70 pagesDna & RnaEvette dela PenaNo ratings yet
- Genetics and HeredityDocument50 pagesGenetics and HeredityZ AngeladaNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY INVESTIGATORY PROJECT Class 12Document21 pagesBIOLOGY INVESTIGATORY PROJECT Class 12SNIGDHA APPANABHOTLANo ratings yet
- 8.3 DNA Worksheet StudentDocument4 pages8.3 DNA Worksheet StudentVippo Montecillo0% (1)
- Ejercicio de ADN InglésDocument3 pagesEjercicio de ADN Inglésaxh3mst-28No ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument83 pagesMolecular Basis of InheritanceKeerthi Sagar100% (1)
- DNA StructureDocument38 pagesDNA Structuremuhdmoosa100% (3)
- DNA TestingDocument30 pagesDNA TestingJefferson OrgaNo ratings yet
- Genetics 1Document13 pagesGenetics 1Shivam PatelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Molecular Genetics - From DNA To ProteinDocument28 pagesChapter 7 - Molecular Genetics - From DNA To ProteinmaleskunNo ratings yet
- Your Genes Are Part of What Makes You The Person You AreDocument4 pagesYour Genes Are Part of What Makes You The Person You ArePrincess Lourdes CarinNo ratings yet
- DNA, Genes and ChromosomesDocument7 pagesDNA, Genes and ChromosomesblobfacewastakenNo ratings yet
- Bio ProjectDocument13 pagesBio ProjectSuyash AgrawalNo ratings yet
- DNA LJRNA AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS (AutoRecovered) (AutoRecovered)Document30 pagesDNA LJRNA AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS (AutoRecovered) (AutoRecovered)niris1hlovoNo ratings yet
- Chapter10 - Lecture - REPLI Transcription and Translation For Class 2022Document138 pagesChapter10 - Lecture - REPLI Transcription and Translation For Class 2022butvNo ratings yet
- DNA StructureDocument26 pagesDNA StructureSan SiddzNo ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument63 pagesGeneticsJRNo ratings yet
- IntrodnaDocument13 pagesIntrodnaapi-265734394No ratings yet
- Lab 3 - Diffusion and Osmosis Fall 2014Document19 pagesLab 3 - Diffusion and Osmosis Fall 2014Amy HollingsworthNo ratings yet
- Lab 12 - Biological Magnification Fall 2014Document16 pagesLab 12 - Biological Magnification Fall 2014Amy HollingsworthNo ratings yet
- Lab 7 - DNA Fingerprinting and Gel Electrophoresis Fall 2014Document25 pagesLab 7 - DNA Fingerprinting and Gel Electrophoresis Fall 2014Amy HollingsworthNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 - DNA Extraction From CellsDocument15 pagesLab 5 - DNA Extraction From CellsAmy HollingsworthNo ratings yet
- Lab 12 - Biological MagnificationDocument14 pagesLab 12 - Biological MagnificationAmy HollingsworthNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 - The Scientific Method and Termite Trails Fall 2014Document23 pagesLab 1 - The Scientific Method and Termite Trails Fall 2014Amy HollingsworthNo ratings yet
- Lab 9 - Antibiotic Resistance and The Susceptibility of Bacteria Lab Fall 2014Document17 pagesLab 9 - Antibiotic Resistance and The Susceptibility of Bacteria Lab Fall 2014Amy Hollingsworth100% (1)
- Lab 2 - Animal Behavior Bettas Fall 2014Document14 pagesLab 2 - Animal Behavior Bettas Fall 2014Amy Hollingsworth0% (1)
- Lab 7 - DNA Fingerprinting and Gel ElectrophoresisDocument22 pagesLab 7 - DNA Fingerprinting and Gel ElectrophoresisAmy Hollingsworth100% (1)
- Lab 8 - Natural SelectionDocument17 pagesLab 8 - Natural SelectionAmy Hollingsworth100% (1)
- HIMB Sea Urchin Fertilization LabDocument15 pagesHIMB Sea Urchin Fertilization LabAmy HollingsworthNo ratings yet
- Lab 11 - Carbon Footprint CalculationDocument13 pagesLab 11 - Carbon Footprint CalculationAmy HollingsworthNo ratings yet
- Lab 13 - Human Population Growth RateDocument15 pagesLab 13 - Human Population Growth RateAmy HollingsworthNo ratings yet
- Sea Urchin EmbryologyDocument6 pagesSea Urchin EmbryologyAmy HollingsworthNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 - The Scientific Method and TermiteDocument22 pagesLab 1 - The Scientific Method and TermiteAmy HollingsworthNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 - Diffusion and OsmosisDocument13 pagesLab 3 - Diffusion and OsmosisAmy HollingsworthNo ratings yet
- Peer Grading Rubric For Natural Science Biology Lab PresentationsDocument2 pagesPeer Grading Rubric For Natural Science Biology Lab PresentationsAmy HollingsworthNo ratings yet
- Lab 10 - Water Quality and The Observation of Aquatic Macroinvertebrate DiversityDocument21 pagesLab 10 - Water Quality and The Observation of Aquatic Macroinvertebrate DiversityAmy HollingsworthNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Guide - Material BehaviorDocument11 pagesCorrosion Guide - Material Behaviorkaruna346No ratings yet
- ChemicalEngineering - Chemical Engineering April 2023Document68 pagesChemicalEngineering - Chemical Engineering April 2023Lisa FosterNo ratings yet
- Detergent FormulationDocument4 pagesDetergent FormulationJehonadab Nwankwo67% (3)
- SMWW 3500-CaDocument2 pagesSMWW 3500-Calmb LaboratoriosNo ratings yet
- Graphenera Carbon NNDocument18 pagesGraphenera Carbon NNShri Narayan Agnihotri EPGDMAI Batch 1No ratings yet
- Concentrated Aqueous Emulsions (EW) : Innovation You Can Build On™Document6 pagesConcentrated Aqueous Emulsions (EW) : Innovation You Can Build On™zoilaNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Igcse ElectrolysisDocument86 pagesEdexcel Igcse ElectrolysisshoshoNo ratings yet
- Vydac Protein and Peptide HandbookDocument92 pagesVydac Protein and Peptide HandbookyonkaniNo ratings yet
- HCH111, Ionic Equilibrium, 2022Document164 pagesHCH111, Ionic Equilibrium, 2022Kelvin pfebveNo ratings yet
- J1300 Centrifugal Jig DS 2012-09-MTDocument2 pagesJ1300 Centrifugal Jig DS 2012-09-MTcarlos hurtadoNo ratings yet
- Plant Mineral NutritionDocument56 pagesPlant Mineral NutritionNam GonzalesNo ratings yet
- E18 RedoxDocument4 pagesE18 RedoxAnonymous 6kkvjfx3100% (1)
- Chemistryproject 170204054007Document18 pagesChemistryproject 170204054007Roy BoyNo ratings yet
- Titration Phosphoric AcidDocument1 pageTitration Phosphoric AcidKiany SirleyNo ratings yet
- Atom Percent Fission in Uranium and Plutonium Fuel (Neodymium-148 Method)Document9 pagesAtom Percent Fission in Uranium and Plutonium Fuel (Neodymium-148 Method)astewayb_964354182No ratings yet
- Con GuardDocument2 pagesCon Guardpravi3434No ratings yet
- Time: 1 Hrs Max. Marks: 87 Single Correct: OH OH OH OHDocument5 pagesTime: 1 Hrs Max. Marks: 87 Single Correct: OH OH OH OHlakshmi.vedanarayanan7785No ratings yet
- Zinc Gluconate TabletsDocument1 pageZinc Gluconate TabletsKasidit SornchaiNo ratings yet
- Anion Ide: Monoatomic: Change Ending ToDocument24 pagesAnion Ide: Monoatomic: Change Ending TodjkedslNo ratings yet
- Science 7 Quizzes and ExercisesDocument21 pagesScience 7 Quizzes and ExercisesBenes Salamanca Bolasco50% (2)
- Additive ComponentsDocument32 pagesAdditive ComponentsmaiatostiNo ratings yet
- The Traditional Herb Polygonum Hydropiper From ChiDocument16 pagesThe Traditional Herb Polygonum Hydropiper From ChiKhang Dương ThếNo ratings yet
- Astm E1209-2018Document8 pagesAstm E1209-2018Adrián CoudannesNo ratings yet
- Fertilizer TechnologyDocument6 pagesFertilizer TechnologySehjad khan BalochNo ratings yet
- Science PDFDocument4 pagesScience PDFAneez HassanNo ratings yet
- Polyaluminium Silicate Sulphate - A New Coagulant For Potable and Wastewater TreatmentDocument2 pagesPolyaluminium Silicate Sulphate - A New Coagulant For Potable and Wastewater TreatmentN'ZI KOUASSI JEAN JACQUESNo ratings yet
- Engineering PhysicsDocument128 pagesEngineering Physicsanamol gautam100% (9)
- SeminarDocument52 pagesSeminarSafalsha BabuNo ratings yet
Lab 5 - DNA Extraction From Strawberries and Liver Fall 2014
Lab 5 - DNA Extraction From Strawberries and Liver Fall 2014
Uploaded by
Amy Hollingsworth0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views16 pagesThis document provides instructions and background information for a lab on extracting DNA from cells. The lab will have students extract and observe DNA from strawberry and chicken liver samples. They will learn that DNA is found in nearly every cell and takes the shape of a double helix, with nitrogenous bases forming the sides and sugars and phosphates making up the backbone. The document explains that DNA carries genetic information that is passed down from parents and makes each organism unique.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides instructions and background information for a lab on extracting DNA from cells. The lab will have students extract and observe DNA from strawberry and chicken liver samples. They will learn that DNA is found in nearly every cell and takes the shape of a double helix, with nitrogenous bases forming the sides and sugars and phosphates making up the backbone. The document explains that DNA carries genetic information that is passed down from parents and makes each organism unique.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views16 pagesLab 5 - DNA Extraction From Strawberries and Liver Fall 2014
Lab 5 - DNA Extraction From Strawberries and Liver Fall 2014
Uploaded by
Amy HollingsworthThis document provides instructions and background information for a lab on extracting DNA from cells. The lab will have students extract and observe DNA from strawberry and chicken liver samples. They will learn that DNA is found in nearly every cell and takes the shape of a double helix, with nitrogenous bases forming the sides and sugars and phosphates making up the backbone. The document explains that DNA carries genetic information that is passed down from parents and makes each organism unique.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 16
Lab 5 - DNA Extraction
From Cells Lab
#NSB2014 1
After completing this activity,
students will be able to:
Observe the physical properties of DNA
Prepare a filtered extract of strawberry and
chicken liver DNA.
Demonstrate that DNA is a three dimensional
structure, and that it can be extracted from
nearly any cell.
Recognize DNA as the source of variation and
the common link between all living things
#NSB2014 2
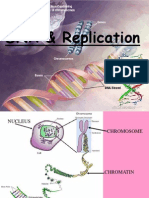
DNA stands for
deoxyribonucleic
acid
The shape of a DNA
molecule is a double
helix.
The scientists James
Watson and Francis
Crick are credited
with determining the
structure in 1953.
#NSB2014 3
Parts of a DNA molecule
Sugar and phosphate
these make up the backbone of the moleculethe
sides of the ladder
Nitrogenous bases (A, C, G, or T)
these are the steps of the ladder
The order (aka sequence) of nitrogenous bases
determines each of your genes
#NSB2014 4
The Shape of DNA: double
helix
#NSB2014 5
Deoxyribose
Sides of ladder
Nitrogenous bases
- Rungs of ladder
DNA Double Helix
Adenine (A)
Thymine (T)
Cytosine (C)
Guanine (G)
#NSB2014 6
A always goes with T
C always goes with G
#NSB2014 7
#NSB2014 8
CHROMOSOME
Human Karyotype - Diploid
#NSB2014 9
One set of
chromosomes
from your
mothers egg,
one set from
your fathers
sperm
Each organism has a different assemblage of DNA
sequences this variation is responsible for the
differences between all organisms
#NSB2014 10
DNA is in the nucleus of (almost) all
the cells in your body
#NSB2014 11
Red blood cells lack a
nucleus, thus lack DNA
Based on this figure, is there more
DNA in strawberries or liver?
#NSB2014 12
Why should I care about DNA?
Every living thing has DNA
The same four bases (in different
combinations) make up all living things
DNA can help us investigate our ancestors,
and understand how we may be genetically
predisposed in the future
Our unique DNA makes us who we are, like a
recipe for making an organism what it is.
#NSB2014 13
Lab Today
DNA molecules are long, slender molecules that carry the
heritable information of organisms on to future generations.
Because of its microscopic size, it is impossible to see a DNA
molecule with the naked eye. It would take about 300,000
DNA molecules side by side to make a bundle as thick as a
human hair.
When subjected to certain conditions, it is possible to collect
large amounts of DNA to make it visible.
#NSB2014 14
Why do we purify DNA?
The purification of chromosomal
DNA is frequently the first step in
molecular-cloning experiments.
DNA is insoluble in alcohol and so
it precipitates out of solution. This
helps remove small molecules,
such as salts, sugars, and amino
acids, from nucleic acid
precipitations because they remain
in the solution.
#NSB2014 15
Most animals are diploid (two copies of the
genome), but some plants can have more than
two copies
Strawberry plants are octoploid, that is, each
cell contains 8 sets of chromosomes.
The liver of animals may become polyploid
#NSB2014 16
You might also like
- Biology Note For Grade 12 (Unit Three Molecular GeneticsDocument24 pagesBiology Note For Grade 12 (Unit Three Molecular GeneticsDaniel GtsadkanNo ratings yet
- International Standard: Iron Oxide Pigments - Specifications and Methods of TestDocument26 pagesInternational Standard: Iron Oxide Pigments - Specifications and Methods of TestHamid Damghani100% (1)
- The Sea Urchin Fertilization LabDocument5 pagesThe Sea Urchin Fertilization LabAmy HollingsworthNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 Enzymes and The Catalase LabDocument18 pagesLab 4 Enzymes and The Catalase LabAmy Hollingsworth100% (1)
- Lab 5 - DNA Extraction From CellsDocument15 pagesLab 5 - DNA Extraction From CellsAmy HollingsworthNo ratings yet
- Structure of Dna: Deoxyribonucleic Acid BY Kapish, Rithish, KrishwanthDocument7 pagesStructure of Dna: Deoxyribonucleic Acid BY Kapish, Rithish, KrishwanthRithish VikramNo ratings yet
- DNA en RNADocument48 pagesDNA en RNAdnielbrink27No ratings yet
- Dna Code of Life 2021 PresentationDocument41 pagesDna Code of Life 2021 Presentationsandilek124No ratings yet
- IB - MYP5 U6 How Docharacteristics Pass From One Generation To AnotherDocument77 pagesIB - MYP5 U6 How Docharacteristics Pass From One Generation To AnotherCoco LocoNo ratings yet
- What Is DNADocument22 pagesWhat Is DNASehar AslamNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure by NeerajDocument21 pagesDNA Structure by NeerajNeeraj BahugunaNo ratings yet
- III.C. DNA Its Role in Inheritance and Protein SynthesisDocument15 pagesIII.C. DNA Its Role in Inheritance and Protein SynthesisDarwin NoolNo ratings yet
- Week 1 DNADocument28 pagesWeek 1 DNAHonleth Jheney MamarilNo ratings yet
- Biology Year 10Document20 pagesBiology Year 10Your best fan HsNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication - PPT 1Document48 pagesDNA Replication - PPT 1Keira MendozaNo ratings yet
- Nicole Shane Abonal: Wag Kayo Mag Tanong PLS.:' ( (Document13 pagesNicole Shane Abonal: Wag Kayo Mag Tanong PLS.:' ( (Marcus LiamNo ratings yet
- Dna StructureDocument32 pagesDna StructureHONLETH ROMBLONNo ratings yet
- DNA StructureDocument22 pagesDNA StructureMehrul Singh RanavatNo ratings yet
- DnareplicationDocument15 pagesDnareplicationapi-248090384No ratings yet
- 3 DNA and RNADocument34 pages3 DNA and RNAjessicakylaalvarezNo ratings yet
- Module 9. Dna AnalysisDocument46 pagesModule 9. Dna AnalysisJunilie Pie LequitNo ratings yet
- Me Sci 10 q3 1301 PsDocument27 pagesMe Sci 10 q3 1301 PsCassy Leighz BagonocNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure and ReplicationDocument61 pagesDNA Structure and Replicationmanuela pardoNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 8 - The DNA - Structure, Function, and DiscoveryDocument18 pagesCHAPTER 8 - The DNA - Structure, Function, and Discoverybabylen bahalaNo ratings yet
- DNA JA NewDocument41 pagesDNA JA NewHamza TahaNo ratings yet
- Question: Why Don't We All Look Alike?: DNA - The Code For LifeDocument42 pagesQuestion: Why Don't We All Look Alike?: DNA - The Code For LifedoloresfilipinoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - 1A - Introduction To GeneticsDocument26 pagesLesson 1 - 1A - Introduction To Genetics宋臻若No ratings yet
- Lecture: Dna (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) : Kazhaleh MohammadiDocument17 pagesLecture: Dna (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) : Kazhaleh MohammadiAhmad PenjwenyNo ratings yet
- MBI MissionMBBS-L1Document73 pagesMBI MissionMBBS-L1Hitesh KhatriNo ratings yet
- Grp.2 DNA REPLICATION EMERALDDocument48 pagesGrp.2 DNA REPLICATION EMERALDLinda Ann BacunadorNo ratings yet
- Aristotle Dna Rna ReportDocument13 pagesAristotle Dna Rna ReportSarah Joy RiveraNo ratings yet
- DNA Paternity TestsDocument4 pagesDNA Paternity TestsIRFAN ZAIN ULABIDEENNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document10 pagesPresentation 1sharanvarmavegirajuNo ratings yet
- Dna-Structure ActivityDocument3 pagesDna-Structure Activityalindoganchristina85No ratings yet
- SCIE1106 Lec 6 DNA Structure 2023 MSTDocument27 pagesSCIE1106 Lec 6 DNA Structure 2023 MSTJamesNo ratings yet
- 7.16DNA WorksheetDocument8 pages7.16DNA WorksheetVanessa JuatcoNo ratings yet
- Strawberry DNA ExtractionDocument14 pagesStrawberry DNA ExtractionFakku SakkuNo ratings yet
- BIOC2600/MEDE2301 Lectures Overview: Dr. Alan Wong School of Biomedical SciencesDocument35 pagesBIOC2600/MEDE2301 Lectures Overview: Dr. Alan Wong School of Biomedical SciencesSeo Eun KimNo ratings yet
- Dna and RnaDocument21 pagesDna and RnaMaxxie LeonerioNo ratings yet
- How Your Genes Determine Who You AreDocument12 pagesHow Your Genes Determine Who You Areaerinimmmm3030No ratings yet
- L2 #: 75al 7" J: (4qepa Bnki (Kkcha $HKQ'Document5 pagesL2 #: 75al 7" J: (4qepa Bnki (Kkcha $HKQ'payal devdaNo ratings yet
- Mydna (Biochem 100) Day 1: InstructorDocument25 pagesMydna (Biochem 100) Day 1: InstructorJose R ZambranoNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Molecular Biology Chapter 10 PDFDocument115 pagesUnit 6 Molecular Biology Chapter 10 PDFc8kewaternotesNo ratings yet
- Dnachromosomes 1Document29 pagesDnachromosomes 1The PassionNo ratings yet
- Dna & RnaDocument70 pagesDna & RnaEvette dela PenaNo ratings yet
- Genetics and HeredityDocument50 pagesGenetics and HeredityZ AngeladaNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY INVESTIGATORY PROJECT Class 12Document21 pagesBIOLOGY INVESTIGATORY PROJECT Class 12SNIGDHA APPANABHOTLANo ratings yet
- 8.3 DNA Worksheet StudentDocument4 pages8.3 DNA Worksheet StudentVippo Montecillo0% (1)
- Ejercicio de ADN InglésDocument3 pagesEjercicio de ADN Inglésaxh3mst-28No ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument83 pagesMolecular Basis of InheritanceKeerthi Sagar100% (1)
- DNA StructureDocument38 pagesDNA Structuremuhdmoosa100% (3)
- DNA TestingDocument30 pagesDNA TestingJefferson OrgaNo ratings yet
- Genetics 1Document13 pagesGenetics 1Shivam PatelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Molecular Genetics - From DNA To ProteinDocument28 pagesChapter 7 - Molecular Genetics - From DNA To ProteinmaleskunNo ratings yet
- Your Genes Are Part of What Makes You The Person You AreDocument4 pagesYour Genes Are Part of What Makes You The Person You ArePrincess Lourdes CarinNo ratings yet
- DNA, Genes and ChromosomesDocument7 pagesDNA, Genes and ChromosomesblobfacewastakenNo ratings yet
- Bio ProjectDocument13 pagesBio ProjectSuyash AgrawalNo ratings yet
- DNA LJRNA AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS (AutoRecovered) (AutoRecovered)Document30 pagesDNA LJRNA AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS (AutoRecovered) (AutoRecovered)niris1hlovoNo ratings yet
- Chapter10 - Lecture - REPLI Transcription and Translation For Class 2022Document138 pagesChapter10 - Lecture - REPLI Transcription and Translation For Class 2022butvNo ratings yet
- DNA StructureDocument26 pagesDNA StructureSan SiddzNo ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument63 pagesGeneticsJRNo ratings yet
- IntrodnaDocument13 pagesIntrodnaapi-265734394No ratings yet
- Lab 3 - Diffusion and Osmosis Fall 2014Document19 pagesLab 3 - Diffusion and Osmosis Fall 2014Amy HollingsworthNo ratings yet
- Lab 12 - Biological Magnification Fall 2014Document16 pagesLab 12 - Biological Magnification Fall 2014Amy HollingsworthNo ratings yet
- Lab 7 - DNA Fingerprinting and Gel Electrophoresis Fall 2014Document25 pagesLab 7 - DNA Fingerprinting and Gel Electrophoresis Fall 2014Amy HollingsworthNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 - DNA Extraction From CellsDocument15 pagesLab 5 - DNA Extraction From CellsAmy HollingsworthNo ratings yet
- Lab 12 - Biological MagnificationDocument14 pagesLab 12 - Biological MagnificationAmy HollingsworthNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 - The Scientific Method and Termite Trails Fall 2014Document23 pagesLab 1 - The Scientific Method and Termite Trails Fall 2014Amy HollingsworthNo ratings yet
- Lab 9 - Antibiotic Resistance and The Susceptibility of Bacteria Lab Fall 2014Document17 pagesLab 9 - Antibiotic Resistance and The Susceptibility of Bacteria Lab Fall 2014Amy Hollingsworth100% (1)
- Lab 2 - Animal Behavior Bettas Fall 2014Document14 pagesLab 2 - Animal Behavior Bettas Fall 2014Amy Hollingsworth0% (1)
- Lab 7 - DNA Fingerprinting and Gel ElectrophoresisDocument22 pagesLab 7 - DNA Fingerprinting and Gel ElectrophoresisAmy Hollingsworth100% (1)
- Lab 8 - Natural SelectionDocument17 pagesLab 8 - Natural SelectionAmy Hollingsworth100% (1)
- HIMB Sea Urchin Fertilization LabDocument15 pagesHIMB Sea Urchin Fertilization LabAmy HollingsworthNo ratings yet
- Lab 11 - Carbon Footprint CalculationDocument13 pagesLab 11 - Carbon Footprint CalculationAmy HollingsworthNo ratings yet
- Lab 13 - Human Population Growth RateDocument15 pagesLab 13 - Human Population Growth RateAmy HollingsworthNo ratings yet
- Sea Urchin EmbryologyDocument6 pagesSea Urchin EmbryologyAmy HollingsworthNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 - The Scientific Method and TermiteDocument22 pagesLab 1 - The Scientific Method and TermiteAmy HollingsworthNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 - Diffusion and OsmosisDocument13 pagesLab 3 - Diffusion and OsmosisAmy HollingsworthNo ratings yet
- Peer Grading Rubric For Natural Science Biology Lab PresentationsDocument2 pagesPeer Grading Rubric For Natural Science Biology Lab PresentationsAmy HollingsworthNo ratings yet
- Lab 10 - Water Quality and The Observation of Aquatic Macroinvertebrate DiversityDocument21 pagesLab 10 - Water Quality and The Observation of Aquatic Macroinvertebrate DiversityAmy HollingsworthNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Guide - Material BehaviorDocument11 pagesCorrosion Guide - Material Behaviorkaruna346No ratings yet
- ChemicalEngineering - Chemical Engineering April 2023Document68 pagesChemicalEngineering - Chemical Engineering April 2023Lisa FosterNo ratings yet
- Detergent FormulationDocument4 pagesDetergent FormulationJehonadab Nwankwo67% (3)
- SMWW 3500-CaDocument2 pagesSMWW 3500-Calmb LaboratoriosNo ratings yet
- Graphenera Carbon NNDocument18 pagesGraphenera Carbon NNShri Narayan Agnihotri EPGDMAI Batch 1No ratings yet
- Concentrated Aqueous Emulsions (EW) : Innovation You Can Build On™Document6 pagesConcentrated Aqueous Emulsions (EW) : Innovation You Can Build On™zoilaNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Igcse ElectrolysisDocument86 pagesEdexcel Igcse ElectrolysisshoshoNo ratings yet
- Vydac Protein and Peptide HandbookDocument92 pagesVydac Protein and Peptide HandbookyonkaniNo ratings yet
- HCH111, Ionic Equilibrium, 2022Document164 pagesHCH111, Ionic Equilibrium, 2022Kelvin pfebveNo ratings yet
- J1300 Centrifugal Jig DS 2012-09-MTDocument2 pagesJ1300 Centrifugal Jig DS 2012-09-MTcarlos hurtadoNo ratings yet
- Plant Mineral NutritionDocument56 pagesPlant Mineral NutritionNam GonzalesNo ratings yet
- E18 RedoxDocument4 pagesE18 RedoxAnonymous 6kkvjfx3100% (1)
- Chemistryproject 170204054007Document18 pagesChemistryproject 170204054007Roy BoyNo ratings yet
- Titration Phosphoric AcidDocument1 pageTitration Phosphoric AcidKiany SirleyNo ratings yet
- Atom Percent Fission in Uranium and Plutonium Fuel (Neodymium-148 Method)Document9 pagesAtom Percent Fission in Uranium and Plutonium Fuel (Neodymium-148 Method)astewayb_964354182No ratings yet
- Con GuardDocument2 pagesCon Guardpravi3434No ratings yet
- Time: 1 Hrs Max. Marks: 87 Single Correct: OH OH OH OHDocument5 pagesTime: 1 Hrs Max. Marks: 87 Single Correct: OH OH OH OHlakshmi.vedanarayanan7785No ratings yet
- Zinc Gluconate TabletsDocument1 pageZinc Gluconate TabletsKasidit SornchaiNo ratings yet
- Anion Ide: Monoatomic: Change Ending ToDocument24 pagesAnion Ide: Monoatomic: Change Ending TodjkedslNo ratings yet
- Science 7 Quizzes and ExercisesDocument21 pagesScience 7 Quizzes and ExercisesBenes Salamanca Bolasco50% (2)
- Additive ComponentsDocument32 pagesAdditive ComponentsmaiatostiNo ratings yet
- The Traditional Herb Polygonum Hydropiper From ChiDocument16 pagesThe Traditional Herb Polygonum Hydropiper From ChiKhang Dương ThếNo ratings yet
- Astm E1209-2018Document8 pagesAstm E1209-2018Adrián CoudannesNo ratings yet
- Fertilizer TechnologyDocument6 pagesFertilizer TechnologySehjad khan BalochNo ratings yet
- Science PDFDocument4 pagesScience PDFAneez HassanNo ratings yet
- Polyaluminium Silicate Sulphate - A New Coagulant For Potable and Wastewater TreatmentDocument2 pagesPolyaluminium Silicate Sulphate - A New Coagulant For Potable and Wastewater TreatmentN'ZI KOUASSI JEAN JACQUESNo ratings yet
- Engineering PhysicsDocument128 pagesEngineering Physicsanamol gautam100% (9)
- SeminarDocument52 pagesSeminarSafalsha BabuNo ratings yet