Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Organs of The Immune System
Organs of The Immune System
Uploaded by
anjanakaveriOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Organs of The Immune System
Organs of The Immune System
Uploaded by
anjanakaveriCopyright:
Available Formats
By K.
Prameela,
Department of Biotechnology,
GIT, GITAM University
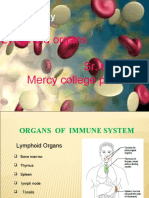
Organs Of Immune System
Primary Lymphoid Organs
Bone Marrow production and maturation of B- Cells
(In Birds Bursa fabricious B- Cell Maturation)
Thymus (T Cell Maturation Site)
Function: production and maturation of lymphocytes
Secondary Lymphoid Organs
Spleen,
lymph nodes,
MALT (mucosal associated lymphoid tissue)
GALT (gut associated lymphoid tissue)
CALT (Cutaneous Associated lymphoid tissue)
Funtion: Trap antigen, APC, Lymphocyte Proliferation
Classification of lymphoid organs
Bilobed Organ on Top of Heart
Reaches Max. Size During Puberty
70g infants, 3 g in adults
95-99% Of T Cells Die in Thymus
self reactivity or no reactivity to Ag
Consists of Cortex and Medulla
Rat Thymocytes Sensitive to Glucorticoids
Thymus
Thymus
Functions
1. Accessory cells: Cortical and medullary epethelial
cells, stromal cells, interdigitating cells and
macrophages.
- Differentiation of T cell precursors & their
migration to secondary lymphoid organs.
2. Thymus has an interactive role with endocrine
system.
3. Thymic epithelial cells produce hormones
thymosin, thymopoietin,
Bone marrow
Blood cells (yolk sac)
Liver
Spleen
Bone marrow
Plasma From Blood Seeps Into Tissue
Interstitial Fluid Either Goes Back or Becomes
Lymph
Lymph Enters Lymphatic Vessels
Thoracic Duct Is Largest Lymphatic Vessel
Empties Into Left Subclavian Vein
Lymphatic Vessel Depends On Muscle
Contractions For Movement
One Way Valves Ensure One Direction
Lymph Nodes Act As Filters For Antigens
Lymphatic System
Lymphatic System
Lymph Node
Lymph Node
Lymph Node
Lymph Node
Multiple Afferent Lymphatics
Cortex
B-cells, Follicular DCs, M, GCs, Primary Follicles
Paracortex
T
H
, M, DCs
Medulla
Plasma Cells
Post Capillary Venule
Allow Lymphocyte Migration From Circuilation Into Lymph
Node
One Efferent Lymphatic
Rich In Abs and Lymphocytes
Lymph Node
Largest accumulation of lymphoid tissue
Abundant phagocytic cellsdefense against
antigens in blood
Site of destruction of aged erythrocytes.
Production site of activated lymphocytes
which are delivered to the blood.
THUS, an important blood filter and
antibody-forming organ.
Spleen
Spleen
Mucous Membranes Surface Area = 400m
2
Mucous Membr. Most Common Pathogen Entry
Site (GIT, Respiratory tract, Urino genital tract
etc.)
Mucous Membrane is Protected by MALT
Tonsils 3 types (Lingual, palatine and
pharyngeal )
If tonsils infected it gets tonsillitis
Mucosal Associated Lymphoid
Tissue (MALT)
Tonsils
Appendix in small intestine protect from
food borne pathogens. If pathogens are
excess leads to appendicitis
Lamina Propia (below epithelium)
protect from food borne pathogens
M Cell Allows Ag Entry, Unique
Architecture
Gut Associated Lymphoid Tissue
(GALT)
M- Cells in Mucus membrane
Lamina Propria
Peyers patch
Cutaneous Associated Lymphoid Tissue
(CALT)
You might also like
- FSBGD Written Study Questions 2003Document201 pagesFSBGD Written Study Questions 2003velangniNo ratings yet
- Lesson2 Basic PK PDFDocument10 pagesLesson2 Basic PK PDFDeula DcruzNo ratings yet
- Presenation Fibrous Cavernous Tuberculois Teachers VersionDocument49 pagesPresenation Fibrous Cavernous Tuberculois Teachers VersionĆux 天主好 OkereNo ratings yet
- The Effect of A Cat's Purr On HealthDocument7 pagesThe Effect of A Cat's Purr On HealthBryan GraczykNo ratings yet
- Organs of The Immune SystemDocument23 pagesOrgans of The Immune SystembandarosNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document40 pagesLecture 2Emmanuel Thon MadingNo ratings yet
- Cells and Organs of The Immune SystemDocument39 pagesCells and Organs of The Immune Systembright nvachirawitNo ratings yet
- Cells and Organs of The Immune SystemDocument39 pagesCells and Organs of The Immune SystemDibash SarkarNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 ImmunologyDocument82 pagesUNIT 1 ImmunologySivarama KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Structure & Function - ImmunesysDocument35 pagesStructure & Function - Immunesyssazia gaurNo ratings yet
- 01a Demonstration of Lymphoid OrgansDocument37 pages01a Demonstration of Lymphoid Organsbatraarmaan8No ratings yet
- Sistem Limfatik Dan ImunitasDocument78 pagesSistem Limfatik Dan ImunitasMasna Arisah NasutionNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy Lymphatic System: Dr. Thontowi Djauhari NS, Mkes Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Muhammadiyah MalangDocument48 pagesHuman Anatomy Lymphatic System: Dr. Thontowi Djauhari NS, Mkes Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Muhammadiyah Malangd25No ratings yet
- It 4 - Sel Dan Jaringan Sistim ImunDocument90 pagesIt 4 - Sel Dan Jaringan Sistim Imunezra soNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System: By: Mohamad Aizuddin Bin Junaidi Class: Physical EducationDocument37 pagesLymphatic System: By: Mohamad Aizuddin Bin Junaidi Class: Physical EducationsepetjudinNo ratings yet
- Histology of Histology of Lymphoid Organs Lymphoid OrgansDocument34 pagesHistology of Histology of Lymphoid Organs Lymphoid OrgansrezkadehaNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic and Immune SystemsDocument94 pagesLymphatic and Immune Systemsistep100% (1)
- Sistem Limfatik Dan Imun: Siti Hamidatul Aliyah, S.PD, M.SC STIKES Harapan Ibu JambiDocument60 pagesSistem Limfatik Dan Imun: Siti Hamidatul Aliyah, S.PD, M.SC STIKES Harapan Ibu JambiPutriantiNo ratings yet
- Lymphoid Tissue: Dr. Archana Rani Associate Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP, LucknowDocument44 pagesLymphoid Tissue: Dr. Archana Rani Associate Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP, LucknowEunice Pallogan100% (1)
- Immunology: Lymphoid Organs Sr. Sarupya Mercy College PalakkadDocument28 pagesImmunology: Lymphoid Organs Sr. Sarupya Mercy College PalakkadTahir AzizNo ratings yet
- K - 3 Histology of Lymphoid OrganDocument34 pagesK - 3 Histology of Lymphoid OrganAbdusSomadNo ratings yet
- Organs of The Immune SystemDocument19 pagesOrgans of The Immune SystemprabuNo ratings yet
- ANP 1105 The Lymphatic SystemDocument23 pagesANP 1105 The Lymphatic SystemMathios TigerosNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Cells and Organs IIDocument30 pagesLecture 3 - Cells and Organs IIAhmed Examination100% (1)
- Basic ImmuneDocument38 pagesBasic ImmuneAseel BabikerNo ratings yet
- Lymphoid OrganDocument23 pagesLymphoid OrganSwetha RameshNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic-System SolidDocument23 pagesLymphatic-System Solidcontemporarysaad16No ratings yet
- Biology - Cells and Anatomy of The Immune SystemDocument9 pagesBiology - Cells and Anatomy of The Immune SystemFelix LupulescuNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System and ImmunityDocument44 pagesLymphatic System and ImmunitySony ArthurNo ratings yet
- Cells and Organs of Immune SystemDocument7 pagesCells and Organs of Immune Systemanumaria2024No ratings yet
- Review Histologi Sistem Imunologi Feb 2018 UHO - (1) .PPSXDocument47 pagesReview Histologi Sistem Imunologi Feb 2018 UHO - (1) .PPSXAmil MunduNo ratings yet
- Imm Lect 2Document22 pagesImm Lect 2samarsamar6000No ratings yet
- DR Salamah Alwahsh: Lymphoid SystemDocument35 pagesDR Salamah Alwahsh: Lymphoid SystemmmmmmmmmmmNo ratings yet
- Biology: Topic 7 (CHP 33) The Lymphatic and Immune SystemsDocument56 pagesBiology: Topic 7 (CHP 33) The Lymphatic and Immune SystemsIain Choong WKNo ratings yet
- Immunology Seminar by Hari HaranDocument26 pagesImmunology Seminar by Hari HaranToons rookieNo ratings yet
- Cells and Organs of The Immune SystemDocument34 pagesCells and Organs of The Immune SystemEmanuel MgheniNo ratings yet
- Immune System: Basic ImmunityDocument14 pagesImmune System: Basic ImmunityPLANARIANo ratings yet
- 4 Sistem Raspuns Imun 2011 PDFDocument63 pages4 Sistem Raspuns Imun 2011 PDFGigiEnergieNo ratings yet
- Immune System: Basic ImmunityDocument16 pagesImmune System: Basic ImmunityvicmomNo ratings yet
- Histology of The Lymphatic and Immune SystemDocument27 pagesHistology of The Lymphatic and Immune Systemirakozehugue14No ratings yet
- Cells and Organs of The Immune SystemDocument53 pagesCells and Organs of The Immune SystemZyma EmaNo ratings yet
- Lymphoid Organs in DetailDocument94 pagesLymphoid Organs in DetailKashishNo ratings yet
- IMMUNO LEC 2 Student PDFDocument76 pagesIMMUNO LEC 2 Student PDFApalisok GerardNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2023-24 BBIT305L TH VL2023240100183 2023-04-29 Reference-Material-IDocument21 pagesFALLSEM2023-24 BBIT305L TH VL2023240100183 2023-04-29 Reference-Material-IDrishti BisuiNo ratings yet
- Self Test 2Document5 pagesSelf Test 2202310446No ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument13 pagesLymphatic SystemBasant karn100% (6)
- Organs of The Immune SystemDocument117 pagesOrgans of The Immune SystemGanesh chowdaryNo ratings yet
- Cells Tissues and Organs of The Immune System ClassDocument57 pagesCells Tissues and Organs of The Immune System ClassKoushali Banerjee100% (2)
- Lymphatic CaseDocument6 pagesLymphatic CaseGlenn Arjay BataraoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document26 pagesChapter 4Rayonesh RayanaNo ratings yet
- 2 Organs of Immune SystemDocument25 pages2 Organs of Immune Systembright nvachirawitNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Intro and Overview of The Immune ResponseDocument67 pagesTopic 1 - Intro and Overview of The Immune ResponseAmber ChenNo ratings yet
- 01 Innate Immunity Student File1 2Document80 pages01 Innate Immunity Student File1 2Khadijah AsrarNo ratings yet
- The Immune SystemDocument150 pagesThe Immune SystemAshish ChangediyaNo ratings yet
- Leucocytes (White Blood Cells) : NeutrophilsDocument9 pagesLeucocytes (White Blood Cells) : NeutrophilsKhant Si ThuNo ratings yet
- Basic and Clinical Immunology PDFDocument86 pagesBasic and Clinical Immunology PDFAbbass El-Outa100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Cells and Organs of The Immune System PDFDocument61 pagesChapter 2 Cells and Organs of The Immune System PDFanaraudhatulNo ratings yet
- Unit II Cells & Organs of ImmuneDocument69 pagesUnit II Cells & Organs of ImmuneSAMUELNo ratings yet
- Lymphoid Tissue Common Notes Part 1Document31 pagesLymphoid Tissue Common Notes Part 1Mace DueñasNo ratings yet
- ImmunityDocument41 pagesImmunityBonzowoNo ratings yet
- Elements of The Immune SystemDocument53 pagesElements of The Immune SystemRochman MujayantoNo ratings yet
- Primary and Secondary Lymphoid Organs - Aditi SinghDocument50 pagesPrimary and Secondary Lymphoid Organs - Aditi SinghEunice PalloganNo ratings yet
- Immune System Docs 2019Document13 pagesImmune System Docs 2019David DavidNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to the Blood Cells, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Blood Cells, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisNo ratings yet
- Monoclonal Antibodies: K. Prameela Department of Biotechnology Gitam UniversityDocument20 pagesMonoclonal Antibodies: K. Prameela Department of Biotechnology Gitam Universityanjanakaveri100% (1)
- Using DNA Technology To Produce Transgenic AnimalsDocument16 pagesUsing DNA Technology To Produce Transgenic AnimalsanjanakaveriNo ratings yet
- Stem Cells: Introduction and Prospects in MedicineDocument25 pagesStem Cells: Introduction and Prospects in MedicineanjanakaveriNo ratings yet
- Pectinase GraphsDocument7 pagesPectinase GraphsanjanakaveriNo ratings yet
- Biomagnification 1Document9 pagesBiomagnification 1anjanakaveriNo ratings yet
- GLOBAL Warming PDocument3 pagesGLOBAL Warming PanjanakaveriNo ratings yet
- Annotated BibliographyDocument3 pagesAnnotated Bibliographyapi-354673353No ratings yet
- Full Report Malaria RDTsDocument110 pagesFull Report Malaria RDTsFionna PohanNo ratings yet
- Dry Socket ManagementDocument7 pagesDry Socket ManagementNuzhat Noor AyeshaNo ratings yet
- Principles of ATLSDocument23 pagesPrinciples of ATLSrutendonormamapurisaNo ratings yet
- Sri Lanka Agriculture Extension Association: National Symposium & Policy DialogueDocument22 pagesSri Lanka Agriculture Extension Association: National Symposium & Policy DialogueSunil GamageNo ratings yet
- An Examination of Adult Women S Sleep Quality and Sleep Routines in Relation To Pet Ownership and BedsharingDocument16 pagesAn Examination of Adult Women S Sleep Quality and Sleep Routines in Relation To Pet Ownership and BedsharingMcKenzie StaufferNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument8 pagesAnatomy and Physiologymhel03_chickmagnetNo ratings yet
- PalpationDocument44 pagesPalpationjenyNo ratings yet
- CellulitisDocument8 pagesCellulitisTricia Llorin100% (1)
- Periyar University: B.Sc. ZoologyDocument38 pagesPeriyar University: B.Sc. ZoologyMathematics KingNo ratings yet
- CMC Veterinary Technology Program Handbook PDFDocument38 pagesCMC Veterinary Technology Program Handbook PDFSandri Alexandra NegreanuNo ratings yet
- List of English Roots Suffixes and PrefixesDocument44 pagesList of English Roots Suffixes and PrefixesJithin VijayanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Skin Pekan 4 Kelompok 15 Blok Skin FixedDocument17 pagesTutorial Skin Pekan 4 Kelompok 15 Blok Skin Fixedkiki tuanaya1No ratings yet
- Animal Research Has Been Used For Several Centuries As Part of Efforts To Better Understand The World Around UsDocument2 pagesAnimal Research Has Been Used For Several Centuries As Part of Efforts To Better Understand The World Around UsAshwiniNo ratings yet
- How To Raise An Amazing ChildDocument197 pagesHow To Raise An Amazing ChildMersi Ta100% (8)
- The Devil in The Milk: A1 or A2? How Beta-Caseins Are Changing The Dairy IndustryDocument6 pagesThe Devil in The Milk: A1 or A2? How Beta-Caseins Are Changing The Dairy Industrynsk79inNo ratings yet
- BS MSC MS MPhil PHD Zoology PDFDocument103 pagesBS MSC MS MPhil PHD Zoology PDFGhulam HussainNo ratings yet
- BronchitisDocument13 pagesBronchitismuhammadsaliNo ratings yet
- 5.casts and MoldsDocument30 pages5.casts and MoldsKatrina PonceNo ratings yet
- Components of FoodDocument37 pagesComponents of Foodrathee1966No ratings yet
- 2020 Dental-CertificateDocument36 pages2020 Dental-Certificatebenz cadiongNo ratings yet
- Partogram Case StudiesDocument6 pagesPartogram Case StudiesnyangaraNo ratings yet
- Needle Stick Injury in JR DoctorsDocument5 pagesNeedle Stick Injury in JR DoctorsEstherThompsonNo ratings yet
- Gyne - Case 15 Benign Lesions of The Vulva & VaginaDocument2 pagesGyne - Case 15 Benign Lesions of The Vulva & Vaginacbac1990No ratings yet
- The Shadowrun Supplemental 019Document18 pagesThe Shadowrun Supplemental 019Данил КеллерNo ratings yet
- Unlike False LaborDocument29 pagesUnlike False LaborMEi .. ÜNo ratings yet