Professional Documents
Culture Documents
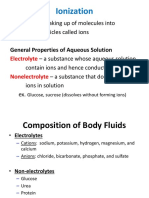
Acid Base (A)
Acid Base (A)
Uploaded by
Heather WrightCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Lab 5 Thermo FluidsDocument13 pagesLab 5 Thermo FluidsAimiWaniNo ratings yet
- Ch18Acid Base (A)Document45 pagesCh18Acid Base (A)Sam H. SalehNo ratings yet
- Ch18Acid Base (A)Document45 pagesCh18Acid Base (A)Michael Conan MaglaqueNo ratings yet
- Acid Base ReactionsDocument16 pagesAcid Base ReactionsInnocent AchayeNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Acid BaseDocument77 pagesTopic 5 Acid Basezila maskamNo ratings yet
- PH and pOHDocument16 pagesPH and pOHAngelo PunzalanNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base EquilibriaDocument121 pagesAcid-Base EquilibriaJaybe MovillaNo ratings yet
- Ionic EquilibriumDocument46 pagesIonic EquilibriumPadmalaya paloNo ratings yet
- Asam Dan Basa Serta Kesetimbangan Asam Dan BasaDocument74 pagesAsam Dan Basa Serta Kesetimbangan Asam Dan BasaDinda FirdasariNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument83 pagesAcids and BasesUtminju NimNo ratings yet
- Ionic Equilibrium: Acid-Base Equilibrium Salt Hydrolysis Buffer SystemDocument55 pagesIonic Equilibrium: Acid-Base Equilibrium Salt Hydrolysis Buffer SystemMuhammad Muaz MahmudNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument26 pagesAcids and BasesBharat SinghNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases - LESSON BIOCHEMDocument39 pagesAcids and Bases - LESSON BIOCHEMJohn CortezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Acids and BasesDocument40 pagesChapter 15 Acids and BasesCaryl Ann C. SernadillaNo ratings yet
- CHM271 - Chapter 3 - Ionic EquilibriumDocument49 pagesCHM271 - Chapter 3 - Ionic Equilibriumnur artikaNo ratings yet
- 13-Acids and BasesDocument44 pages13-Acids and BasesShamier Khent SamsonNo ratings yet
- CH 14. Acids and Bases: Chem 30ADocument52 pagesCH 14. Acids and Bases: Chem 30Avardhini pittlaNo ratings yet
- 4th Lecture 1Document62 pages4th Lecture 1bliss polleyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14 Acids and BasesDocument79 pagesLecture 14 Acids and BasesDuy Do MinhNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument81 pagesAcids and BasesShirmayne TangNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Equilibrium: See Aqueousions in Chemistry 1110 Online Notes For Review of Acid-Base Fundamentals!Document31 pagesAcid-Base Equilibrium: See Aqueousions in Chemistry 1110 Online Notes For Review of Acid-Base Fundamentals!Lissa HannahNo ratings yet
- CHM271 - Chapter 3 - Ionic EquilibriumDocument59 pagesCHM271 - Chapter 3 - Ionic Equilibriumnurulamalina173205No ratings yet
- Acid and BaseDocument24 pagesAcid and BaseEshan MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Ionic EquibliriumDocument63 pagesUnit 3 Ionic EquibliriumFiixaa B OlqabaaNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument47 pagesAcids and BasesIj BiagNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument48 pagesAcids and BaseschimNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases 1Document11 pagesAcids Bases 1Kelsey FarrugiaNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases To Buffers 2023Document86 pagesAcids and Bases To Buffers 2023Jetrille EspinozaNo ratings yet
- PH and BufferDocument68 pagesPH and BufferDileesha WeliwaththaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Ionic EquilibriumDocument55 pagesChapter 4 - Ionic EquilibriumNabilah SyazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Concept of Acid-Base NeutralisationDocument58 pagesChapter 3 - Concept of Acid-Base NeutralisationIkmal FikriNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument63 pagesAcids and Basesgarnettdalagan.bascNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Notes (Use For Chem 123)Document16 pagesAcid Base Notes (Use For Chem 123)Nate JamesNo ratings yet
- 7.0 Ionic Equilibria (Students)Document187 pages7.0 Ionic Equilibria (Students)Supia Nazma100% (1)
- 7.1 Acid and BasesDocument76 pages7.1 Acid and BasesMOHAMAD FIRDAUS BIN HARUN KM-PensyarahNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Practice Exercise by Lemuel QueenDocument26 pagesChemistry Practice Exercise by Lemuel QueenPOPPY OFFICIALNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument34 pagesAcids, Bases and SaltsAndrew John CellonaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2: Unit 3 Acids-Bases and SaltDocument96 pagesChemistry 2: Unit 3 Acids-Bases and SaltNoraziah ZulNo ratings yet
- Acids Base Equilibria NEHDocument123 pagesAcids Base Equilibria NEHLulwa KhaskiehNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Acids and BasesDocument39 pagesLecture 5 Acids and BasesAllen SiaNo ratings yet
- 7.0 Acid Base EquilibriaDocument20 pages7.0 Acid Base EquilibriaIVAN ANDRICH I�IGONo ratings yet
- IonisationDocument17 pagesIonisationDeepa DevanathanNo ratings yet
- Iodine ClockDocument42 pagesIodine ClockNino Jay FabrosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Acids BasesDocument42 pagesChapter 15 Acids BasesNapassorn WongduangpaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry: Dr. Rabih O. Al-Kaysi Ext: 47247 Email: Kaysir@ksau-Hs - Edu.saDocument43 pagesGeneral Chemistry: Dr. Rabih O. Al-Kaysi Ext: 47247 Email: Kaysir@ksau-Hs - Edu.saapi-19824406No ratings yet
- Chemistry I - Chapter 19 Chemistry I HD - Chapter 16 ICP - Chapter 23Document74 pagesChemistry I - Chapter 19 Chemistry I HD - Chapter 16 ICP - Chapter 23Johe GunsinNo ratings yet
- Acid Equilibrium and PH: Søren SørensenDocument16 pagesAcid Equilibrium and PH: Søren Sørensenmonster40lbsNo ratings yet
- Kimia Untuk Teknik Sipil: 3 Sks - Semester 1 (Wajib)Document51 pagesKimia Untuk Teknik Sipil: 3 Sks - Semester 1 (Wajib)Jimmy LauNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases NOTESDocument27 pagesAcids Bases NOTESsanele50% (2)
- Bronsted LowryDocument71 pagesBronsted LowryShaina NovicioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4.0 ACID-BASE EQUILIBRIUMDocument54 pagesChapter 4.0 ACID-BASE EQUILIBRIUMMuhd Mirza HizamiNo ratings yet
- Acid BasesDocument59 pagesAcid BasesNapassorn WongduangpaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 6 - Acids and BasesDocument14 pagesTutorial 6 - Acids and BasesdeanNo ratings yet
- 8 ACIDS Bases Buffers 09Document4 pages8 ACIDS Bases Buffers 09Sirine AjourNo ratings yet
- 15.1 Bronsted-Lowry Acids and BasesDocument6 pages15.1 Bronsted-Lowry Acids and BasesPatricia de LeonNo ratings yet
- Acid Base NotesDocument3 pagesAcid Base NoteszaneNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document45 pagesLecture 2NetflameNo ratings yet
- Video NotesDocument45 pagesVideo Notesjim tannerNo ratings yet
- Chem I - Unit 15 - Acids and BasesDocument19 pagesChem I - Unit 15 - Acids and BasesVarun WadhwaNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Equilibria 1Document67 pagesAcid Base Equilibria 1Yvette Malubay AlpuertoNo ratings yet
- Solution Conc Raoults ClligativeDocument66 pagesSolution Conc Raoults ClligativeHeather WrightNo ratings yet
- Percent Yield and Limiting Reactants - 2Document24 pagesPercent Yield and Limiting Reactants - 2Heather WrightNo ratings yet
- Chapter10 NotesDocument33 pagesChapter10 NotesHeather WrightNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 The Behavior of GasesDocument59 pagesChapter 14 The Behavior of GasesHeather Wright100% (2)
- Lead Acid BatteryDocument23 pagesLead Acid BatteryBrahmpal BhardwajNo ratings yet
- RectiDocument7 pagesRectiaskj78100% (1)
- Ventilation Cost CalculationsDocument15 pagesVentilation Cost CalculationsestebanmarinkovicNo ratings yet
- 3D CamDocument16 pages3D CamShin EscaresesNo ratings yet
- Unit 1. Common StructuresDocument21 pagesUnit 1. Common Structuresmaimai003bnNo ratings yet
- Decision Trees - 2022Document49 pagesDecision Trees - 2022Soubhav ChamanNo ratings yet
- The Gmo Emperor Has No Clothes PDFDocument251 pagesThe Gmo Emperor Has No Clothes PDFkouadio yao Armand100% (1)
- SECOND Periodic Test in AP 4 With TOS SY 2022 2023Document6 pagesSECOND Periodic Test in AP 4 With TOS SY 2022 2023MICHAEL VERINANo ratings yet
- Lien 2020Document11 pagesLien 2020Puraghan cahya herawanNo ratings yet
- Act1102 - Cfas - Course SyllabusDocument19 pagesAct1102 - Cfas - Course SyllabusFrancein CequenaNo ratings yet
- Chafi2009Document7 pagesChafi2009radhakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Process Meter K3Nx: Cat. No. N090-E1-1BDocument120 pagesProcess Meter K3Nx: Cat. No. N090-E1-1Bej ejazNo ratings yet
- Leed NDDocument2 pagesLeed NDElnaz YousefzadehNo ratings yet
- The Genesis Project PDFDocument19 pagesThe Genesis Project PDFvikas kansalNo ratings yet
- Z370 AORUS Gaming 3: User's ManualDocument48 pagesZ370 AORUS Gaming 3: User's ManualAtrocitus RedNo ratings yet
- CAAP Telephone Public Directory PDFDocument4 pagesCAAP Telephone Public Directory PDFMaria Angelica Rodriguez AlonsoNo ratings yet
- Eng WEEK 3 v2Document44 pagesEng WEEK 3 v2Chel CalejaNo ratings yet
- ICoT 5200 - 5300 - 5400 Ordering GuideDocument1 pageICoT 5200 - 5300 - 5400 Ordering GuidePeter RhoadsNo ratings yet
- Time Response AnalysisDocument43 pagesTime Response AnalysisAkmal IsnaeniNo ratings yet
- Tax Invoice: Billing Address Installation Address Invoice DetailsDocument1 pageTax Invoice: Billing Address Installation Address Invoice DetailsRohithNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 NotesDocument17 pagesUnit-3 Notesj79494793No ratings yet
- The Importance of Reading To Expand KnowledgeDocument8 pagesThe Importance of Reading To Expand KnowledgeAnindhita NabilahNo ratings yet
- Physics Project of Class 11 IscDocument1 pagePhysics Project of Class 11 Iscpratima patelNo ratings yet
- TLE6 Module5 Propagating Tress and Fruit-Bearing TreesDocument29 pagesTLE6 Module5 Propagating Tress and Fruit-Bearing TreesLorranne Maice D. Morano100% (1)
- Cttplus HandbookDocument36 pagesCttplus HandbookgcarreongNo ratings yet
- Ecological Impact of Rubber Plantations: Tripura PerspectiveDocument8 pagesEcological Impact of Rubber Plantations: Tripura Perspectivekunwar satyabeer chauhanNo ratings yet
- Placement Prep PDFDocument30 pagesPlacement Prep PDFAshwin BalajiNo ratings yet
- (Guy - Exton) - Brexit and Game Theory A Single-Case AnalysisDocument9 pages(Guy - Exton) - Brexit and Game Theory A Single-Case AnalysisAmairani IbáñezNo ratings yet
- PVC-O PipesDocument40 pagesPVC-O PipesMichaelNo ratings yet
Acid Base (A)
Acid Base (A)
Uploaded by
Heather WrightOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Acid Base (A)
Acid Base (A)
Uploaded by
Heather WrightCopyright:
Available Formats
Acid-Base Equilibrium
Chapter 18
Acids and Bases
Arrhenius
acids: generate H
+
in water
bases: generate OH
-
in water
Brnsted-Lowry
acids: H
+
donors
bases: H
+
acceptors
HCl + H
2
O Cl
+ H
3
O
+
acid base
Conjugate acid-base pairs
Conjugate base:
remains after H
+
is lost
acid: HCl conj. base: Cl
-
Conjugate acid:
remains after H
+
is gained
base: NH
3
conj. acid: NH
4
+
Base Acid + Acid Base +
Conjugate Pair
Conjugate Pair
Strong and Weak Acids
Strong: 100% dissociation
good H
+
donor
equilibrium lies far to right (HNO
3
)
generates weak base (NO
3
-
)
Weak: <100% dissociation
not-as-good H
+
donor
equilibrium lies far to left (CH
3
COOH)
generates strong base (CH
3
COO
-
)
Very strong
Strong
Weak
Very weak
Relative Acid
Strength
Relative Conj.
Base Strength
Very weak
Weak
Strong
Very strong
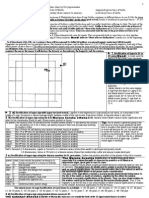
Acid Dissociation Constant
O H A O H HA
3
-
2
[HA]
] ][A [H
[HA]
] ][A O [H
K
- -
3
a
K
a
I
n
c
r
e
a
s
e
s
Strength
vs. K
a
C at
o
25 10 1 ] ][OH O [H K
14 -
3 w
Acid Base Conj. Acid Conj. Base
Water is amphoteric
[H
3
O
+
] and [OH
-
]
[H
3
O
+
] 1x10
0
to 1x10
-14
in water
[OH
-
] 1x10
-14
to 1x10
0
in water
] O [H
K
] [OH
3
w
-
14 -
3 w
10 1 ] ][OH O [H K
] [OH
K
] O [H
-
w
3
Finding [H
3
O
+
] and [OH
-
]
pH Scale
] log[H - ] O log[H - pH
3
14 -
3 w
10 1 ] ][OH O [H K
pH 0 to 14 in water
] log[OH - ] log[OH - pOH
pOH 14 to 0 in water
pK
w
= pH + pOH = 14
H
+
H
+
H
+
OH
-
OH
-
OH
-
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
Acidic Neutral Basic
pH and pOH
As [H
3
O
+
] rises, [OH
-
] falls
As pH falls, pOH rises
Indicators
Strength of Bases
Strong:
100% dissociation
OH
-
supplied to solution
NaOH
(s)
Na
+
(aq)
+ OH
-
(aq)
Weak:
<100% dissociation
OH
-
by reaction with water
CH
3
NH
2(aq)
+ H
2
O
(l)
CH
3
NH
2(aq)
+ OH
-
(aq)
Base Dissociation Constant
OH BH O H B
2
-
] [B
] [BH][OH
K
-
-
b
K
w
, K
a
and K
b
14 -
3 w
10 1 ] ][OH O [H K
14
b a w
10 1 K K K
K
K
K
b
w
a
K
K
K
a
w
b
Lewis Acids and Bases
Lewis Acid: electron pair acceptor
Lewis Base: electron pair donor
A l
3 +
+ 6
H
O
H
A l O
H
H
6
3 +
Acid Base
Buffers
Buffer solution: a mixture of conjugate acid and base
that resists pH changes.
A buffer contains a weak acid and a salt of the same
acid.
A buffer contains a weak base and a salt of the same
base.
pH of buffers
For a weak acid, HA, we have
HA = H
+
+ A
[H
+
] [A
]
K
a
=
[HA]
[A
]
log K
a
= log [H
+
] log
[HA]
[A
] [A
]
pK
a
= pH log pH = pK
a
+ log
[HA] [HA]
[salt]
[acid
pH = pKa + log salt / acid
pH = pKb + log salt / base
The Common Ion Effect
CommonIon Effect: the change in the
equilibrium that results from the addition of
an ion that is involved in the equilibrium.
You might also like
- Lab 5 Thermo FluidsDocument13 pagesLab 5 Thermo FluidsAimiWaniNo ratings yet
- Ch18Acid Base (A)Document45 pagesCh18Acid Base (A)Sam H. SalehNo ratings yet
- Ch18Acid Base (A)Document45 pagesCh18Acid Base (A)Michael Conan MaglaqueNo ratings yet
- Acid Base ReactionsDocument16 pagesAcid Base ReactionsInnocent AchayeNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Acid BaseDocument77 pagesTopic 5 Acid Basezila maskamNo ratings yet
- PH and pOHDocument16 pagesPH and pOHAngelo PunzalanNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base EquilibriaDocument121 pagesAcid-Base EquilibriaJaybe MovillaNo ratings yet
- Ionic EquilibriumDocument46 pagesIonic EquilibriumPadmalaya paloNo ratings yet
- Asam Dan Basa Serta Kesetimbangan Asam Dan BasaDocument74 pagesAsam Dan Basa Serta Kesetimbangan Asam Dan BasaDinda FirdasariNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument83 pagesAcids and BasesUtminju NimNo ratings yet
- Ionic Equilibrium: Acid-Base Equilibrium Salt Hydrolysis Buffer SystemDocument55 pagesIonic Equilibrium: Acid-Base Equilibrium Salt Hydrolysis Buffer SystemMuhammad Muaz MahmudNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument26 pagesAcids and BasesBharat SinghNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases - LESSON BIOCHEMDocument39 pagesAcids and Bases - LESSON BIOCHEMJohn CortezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Acids and BasesDocument40 pagesChapter 15 Acids and BasesCaryl Ann C. SernadillaNo ratings yet
- CHM271 - Chapter 3 - Ionic EquilibriumDocument49 pagesCHM271 - Chapter 3 - Ionic Equilibriumnur artikaNo ratings yet
- 13-Acids and BasesDocument44 pages13-Acids and BasesShamier Khent SamsonNo ratings yet
- CH 14. Acids and Bases: Chem 30ADocument52 pagesCH 14. Acids and Bases: Chem 30Avardhini pittlaNo ratings yet
- 4th Lecture 1Document62 pages4th Lecture 1bliss polleyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14 Acids and BasesDocument79 pagesLecture 14 Acids and BasesDuy Do MinhNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument81 pagesAcids and BasesShirmayne TangNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Equilibrium: See Aqueousions in Chemistry 1110 Online Notes For Review of Acid-Base Fundamentals!Document31 pagesAcid-Base Equilibrium: See Aqueousions in Chemistry 1110 Online Notes For Review of Acid-Base Fundamentals!Lissa HannahNo ratings yet
- CHM271 - Chapter 3 - Ionic EquilibriumDocument59 pagesCHM271 - Chapter 3 - Ionic Equilibriumnurulamalina173205No ratings yet
- Acid and BaseDocument24 pagesAcid and BaseEshan MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Ionic EquibliriumDocument63 pagesUnit 3 Ionic EquibliriumFiixaa B OlqabaaNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument47 pagesAcids and BasesIj BiagNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument48 pagesAcids and BaseschimNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases 1Document11 pagesAcids Bases 1Kelsey FarrugiaNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases To Buffers 2023Document86 pagesAcids and Bases To Buffers 2023Jetrille EspinozaNo ratings yet
- PH and BufferDocument68 pagesPH and BufferDileesha WeliwaththaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Ionic EquilibriumDocument55 pagesChapter 4 - Ionic EquilibriumNabilah SyazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Concept of Acid-Base NeutralisationDocument58 pagesChapter 3 - Concept of Acid-Base NeutralisationIkmal FikriNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument63 pagesAcids and Basesgarnettdalagan.bascNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Notes (Use For Chem 123)Document16 pagesAcid Base Notes (Use For Chem 123)Nate JamesNo ratings yet
- 7.0 Ionic Equilibria (Students)Document187 pages7.0 Ionic Equilibria (Students)Supia Nazma100% (1)
- 7.1 Acid and BasesDocument76 pages7.1 Acid and BasesMOHAMAD FIRDAUS BIN HARUN KM-PensyarahNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Practice Exercise by Lemuel QueenDocument26 pagesChemistry Practice Exercise by Lemuel QueenPOPPY OFFICIALNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument34 pagesAcids, Bases and SaltsAndrew John CellonaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2: Unit 3 Acids-Bases and SaltDocument96 pagesChemistry 2: Unit 3 Acids-Bases and SaltNoraziah ZulNo ratings yet
- Acids Base Equilibria NEHDocument123 pagesAcids Base Equilibria NEHLulwa KhaskiehNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Acids and BasesDocument39 pagesLecture 5 Acids and BasesAllen SiaNo ratings yet
- 7.0 Acid Base EquilibriaDocument20 pages7.0 Acid Base EquilibriaIVAN ANDRICH I�IGONo ratings yet
- IonisationDocument17 pagesIonisationDeepa DevanathanNo ratings yet
- Iodine ClockDocument42 pagesIodine ClockNino Jay FabrosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Acids BasesDocument42 pagesChapter 15 Acids BasesNapassorn WongduangpaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry: Dr. Rabih O. Al-Kaysi Ext: 47247 Email: Kaysir@ksau-Hs - Edu.saDocument43 pagesGeneral Chemistry: Dr. Rabih O. Al-Kaysi Ext: 47247 Email: Kaysir@ksau-Hs - Edu.saapi-19824406No ratings yet
- Chemistry I - Chapter 19 Chemistry I HD - Chapter 16 ICP - Chapter 23Document74 pagesChemistry I - Chapter 19 Chemistry I HD - Chapter 16 ICP - Chapter 23Johe GunsinNo ratings yet
- Acid Equilibrium and PH: Søren SørensenDocument16 pagesAcid Equilibrium and PH: Søren Sørensenmonster40lbsNo ratings yet
- Kimia Untuk Teknik Sipil: 3 Sks - Semester 1 (Wajib)Document51 pagesKimia Untuk Teknik Sipil: 3 Sks - Semester 1 (Wajib)Jimmy LauNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases NOTESDocument27 pagesAcids Bases NOTESsanele50% (2)
- Bronsted LowryDocument71 pagesBronsted LowryShaina NovicioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4.0 ACID-BASE EQUILIBRIUMDocument54 pagesChapter 4.0 ACID-BASE EQUILIBRIUMMuhd Mirza HizamiNo ratings yet
- Acid BasesDocument59 pagesAcid BasesNapassorn WongduangpaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 6 - Acids and BasesDocument14 pagesTutorial 6 - Acids and BasesdeanNo ratings yet
- 8 ACIDS Bases Buffers 09Document4 pages8 ACIDS Bases Buffers 09Sirine AjourNo ratings yet
- 15.1 Bronsted-Lowry Acids and BasesDocument6 pages15.1 Bronsted-Lowry Acids and BasesPatricia de LeonNo ratings yet
- Acid Base NotesDocument3 pagesAcid Base NoteszaneNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document45 pagesLecture 2NetflameNo ratings yet
- Video NotesDocument45 pagesVideo Notesjim tannerNo ratings yet
- Chem I - Unit 15 - Acids and BasesDocument19 pagesChem I - Unit 15 - Acids and BasesVarun WadhwaNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Equilibria 1Document67 pagesAcid Base Equilibria 1Yvette Malubay AlpuertoNo ratings yet
- Solution Conc Raoults ClligativeDocument66 pagesSolution Conc Raoults ClligativeHeather WrightNo ratings yet
- Percent Yield and Limiting Reactants - 2Document24 pagesPercent Yield and Limiting Reactants - 2Heather WrightNo ratings yet
- Chapter10 NotesDocument33 pagesChapter10 NotesHeather WrightNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 The Behavior of GasesDocument59 pagesChapter 14 The Behavior of GasesHeather Wright100% (2)
- Lead Acid BatteryDocument23 pagesLead Acid BatteryBrahmpal BhardwajNo ratings yet
- RectiDocument7 pagesRectiaskj78100% (1)
- Ventilation Cost CalculationsDocument15 pagesVentilation Cost CalculationsestebanmarinkovicNo ratings yet
- 3D CamDocument16 pages3D CamShin EscaresesNo ratings yet
- Unit 1. Common StructuresDocument21 pagesUnit 1. Common Structuresmaimai003bnNo ratings yet
- Decision Trees - 2022Document49 pagesDecision Trees - 2022Soubhav ChamanNo ratings yet
- The Gmo Emperor Has No Clothes PDFDocument251 pagesThe Gmo Emperor Has No Clothes PDFkouadio yao Armand100% (1)
- SECOND Periodic Test in AP 4 With TOS SY 2022 2023Document6 pagesSECOND Periodic Test in AP 4 With TOS SY 2022 2023MICHAEL VERINANo ratings yet
- Lien 2020Document11 pagesLien 2020Puraghan cahya herawanNo ratings yet
- Act1102 - Cfas - Course SyllabusDocument19 pagesAct1102 - Cfas - Course SyllabusFrancein CequenaNo ratings yet
- Chafi2009Document7 pagesChafi2009radhakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Process Meter K3Nx: Cat. No. N090-E1-1BDocument120 pagesProcess Meter K3Nx: Cat. No. N090-E1-1Bej ejazNo ratings yet
- Leed NDDocument2 pagesLeed NDElnaz YousefzadehNo ratings yet
- The Genesis Project PDFDocument19 pagesThe Genesis Project PDFvikas kansalNo ratings yet
- Z370 AORUS Gaming 3: User's ManualDocument48 pagesZ370 AORUS Gaming 3: User's ManualAtrocitus RedNo ratings yet
- CAAP Telephone Public Directory PDFDocument4 pagesCAAP Telephone Public Directory PDFMaria Angelica Rodriguez AlonsoNo ratings yet
- Eng WEEK 3 v2Document44 pagesEng WEEK 3 v2Chel CalejaNo ratings yet
- ICoT 5200 - 5300 - 5400 Ordering GuideDocument1 pageICoT 5200 - 5300 - 5400 Ordering GuidePeter RhoadsNo ratings yet
- Time Response AnalysisDocument43 pagesTime Response AnalysisAkmal IsnaeniNo ratings yet
- Tax Invoice: Billing Address Installation Address Invoice DetailsDocument1 pageTax Invoice: Billing Address Installation Address Invoice DetailsRohithNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 NotesDocument17 pagesUnit-3 Notesj79494793No ratings yet
- The Importance of Reading To Expand KnowledgeDocument8 pagesThe Importance of Reading To Expand KnowledgeAnindhita NabilahNo ratings yet
- Physics Project of Class 11 IscDocument1 pagePhysics Project of Class 11 Iscpratima patelNo ratings yet
- TLE6 Module5 Propagating Tress and Fruit-Bearing TreesDocument29 pagesTLE6 Module5 Propagating Tress and Fruit-Bearing TreesLorranne Maice D. Morano100% (1)
- Cttplus HandbookDocument36 pagesCttplus HandbookgcarreongNo ratings yet
- Ecological Impact of Rubber Plantations: Tripura PerspectiveDocument8 pagesEcological Impact of Rubber Plantations: Tripura Perspectivekunwar satyabeer chauhanNo ratings yet
- Placement Prep PDFDocument30 pagesPlacement Prep PDFAshwin BalajiNo ratings yet
- (Guy - Exton) - Brexit and Game Theory A Single-Case AnalysisDocument9 pages(Guy - Exton) - Brexit and Game Theory A Single-Case AnalysisAmairani IbáñezNo ratings yet
- PVC-O PipesDocument40 pagesPVC-O PipesMichaelNo ratings yet