Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nuclear Battery
Nuclear Battery
Uploaded by
Udgam TiwariOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nuclear Battery
Nuclear Battery
Uploaded by
Udgam TiwariCopyright:
Available Formats
SEMINAR ON
+ NUCLEAR BATTERY -
Presented By
Shivam Pandey
Third year (EEE)
Guided By
Priyank Agrawal
Assistant
Professor
Raj Kumar Goel Engineering College,
Ghaziabad,UP
CONTENTS
Why Nuclear Battery ???
Historical Developments
Energy Production Mechanism
Advantages
Disadvantages
Applications
Conclusion
Q. Why Nuclear Battery
???
ANSWERS :
Need for compact reliable light weight and self-
contained power supplies.
Chemical batteries require frequent replacements
and are bulky.
Fuel and Solar cells are expensive and requires
sunlight respectively.
Can be used in in accessible and extreme
conditions.
Nuclear batteries have lifespan upto decades
and nearly 200 times more efficient.
Do not rely on nuclear reaction , so no
radioactive wastes.
Uses emissions from radioactive isotope to
generate electricity.
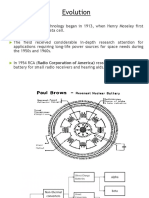
HISTORICAL DEVELOPMENTS
Nuclear battery technology began in 1913,when Henary
Mosley first demonstrated the beta celL.
The field received considerable in-depth research
attention for applications requiring long-life power
sources for space needs during the 1950s and 1960s.
ENERGY PRODUCTION MECHANISMS
Betavoltaics :
Uses energy from beta particles.
Provides extended battery life and power
density.
Absorbed radiation creates electron-hole pair.
Results in the generation of electric current.
Representation of basic beta voltaic
conversion
Electrode A (P-region) has a positive potential while
electrode B (N-region) is negative.
Before the radioactive source is introduced , no current flows as
the electrical forces are in equilibrium.
As a beta emitter is introduced , electrons are knocked out by its
energy.
Generates electron-hole pairs in the junction.
When beta particle imparts more than ionization potential the
electron rises to a higher level.
Potential difference drives electrons from electrode A through the
load where they give up the energy.
Beta Volatile Conversion
Direct Charging Generators:
This method makes use of kinetic energy as well as
the magnetic property of Alpha particles to generate
current.
It consists of a core composed of radioactive
elements.
Primary generator consists of a LC tank circuit.
LC circuit produces the oscillations required for
transformer operation.
Schematic Diagram of an LC resonant
circuit
1 Capacitor
2 Inductor
3 Core with radioactive elements
4 Transformer T primary winding
5 Resistance
6 _ Secondary winding
7 _ Load
WORKING
Oscillations induced in LCR circuit damp out due to loss of energy.
Here energy is imparted to the alpha particles during the decay of
elements in the core.
This energy is introduced to circuit when alpha particles are absorbed by
the inductor.
Oscillations sustain until amount of energy absorbed=amount of energy
dissipated in ohmic resistance.
This excess energy is delivered to the load connected across
transformer T secondary winding.
ADVANTAGES
Life span- minimum of 10 years.
Reliable electricity.
Amount of energy highest.
Lighter with high energy density.
Efficient
Reduces green house and associated effects.
Fuel used is the nuclear waste from nuclear fission.
DISADVANTAGES
High initial cost of production
Energy conversion methodologies are not much
advanced.
Regional and country-specific laws regarding
use and disposal of radioactive fuels.
To gain social acceptance.
APPLICATIONS
Space applications:
Unaffected by long period of darkness and radiation
Compact and lighter in weight.
Can avoid heating equipments required for storage batteries.
High power for long time independent of atmospheric
conditions.
NASA is trying to harness this technology in space applications.
Medical applications:
In Cardiac pacemakers
Batteries should have reliability and longevity to
avoid frequent replacements.
Mobile devices:
Nuclear powered laptop battery Xcell-N has 7000 - 8000 times more life.
No need for charging, battery replacing.
Automobiles:
No need for frequent recharging as in case of present electric
vehicles.
Military applications
Safe, longer life
Under-water sea probes and sea sensors:
In sensors working for long time.
At inaccessible and extreme conditions.
Use in coal mines and polar sensor applications too.
CONCLUSION
Small compact devices of future require small batteries.
Nuclear batteries increase functionality, reliability and
longevity.
Batteries of the near future.
With several features being added to this, nuclear cells are
going to be next best thing ever invented in the human history.
THANK YOU
You might also like
- Supercapacitors 101: A home Inventors HandbookFrom EverandSupercapacitors 101: A home Inventors HandbookRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Caravan and Motorhome Electrics: the complete guideFrom EverandCaravan and Motorhome Electrics: the complete guideRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Extended Cell Range (5G RAN6.1 - Draft A)Document30 pagesExtended Cell Range (5G RAN6.1 - Draft A)VVLNo ratings yet
- It Is Quite Another Electricity: Transmitting by One Wire and Without GroundingFrom EverandIt Is Quite Another Electricity: Transmitting by One Wire and Without GroundingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Nuclear Battery PP TDocument20 pagesNuclear Battery PP TPrabhat SharmaNo ratings yet
- 19Uk5A0410.. Technical SeminarDocument21 pages19Uk5A0410.. Technical SeminarSingasani SaiArunNo ratings yet
- Nuclearbattery1 120821135908 Phpapp01Document19 pagesNuclearbattery1 120821135908 Phpapp01PrabhaPowerNo ratings yet
- Nuclear BatteryDocument20 pagesNuclear BatterysuryaNo ratings yet
- On Nuclear MicrobatteriesDocument20 pagesOn Nuclear MicrobatteriesVikasmatrey50% (2)
- Seminar Presentation On Nuclear BatteriesDocument20 pagesSeminar Presentation On Nuclear BatteriesPratik PatilNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Micro GeneratorsDocument16 pagesNuclear Micro GeneratorsAnandhu cNo ratings yet
- Dheeraj Jain Ee-09Document15 pagesDheeraj Jain Ee-09markeloff27No ratings yet
- Nuclear (Autosaved)Document19 pagesNuclear (Autosaved)Abhishek S KakadeNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint Presentation - Nuclear BatteriesDocument26 pagesPowerpoint Presentation - Nuclear BatteriesMurali krishnanNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Nuclear BatteriesDocument22 pagesSeminar On Nuclear BatteriesPRABATH MADHAVANNo ratings yet
- Nuclear BatteryDocument22 pagesNuclear BatteryPrayag P NairNo ratings yet
- Super Capacitor 2018Document25 pagesSuper Capacitor 2018Atlarn MoreNo ratings yet
- Ultracapacitors (Supercapacitors)Document19 pagesUltracapacitors (Supercapacitors)praneethNo ratings yet
- Nuclear BatteryDocument26 pagesNuclear BatteryAnanta PatilNo ratings yet
- A Seminar Report On Nuclear PDFDocument28 pagesA Seminar Report On Nuclear PDFIsmail Rohit RebalNo ratings yet
- SeminarDocument23 pagesSeminarandrotipsNo ratings yet
- Aditya - Seminar 1Document10 pagesAditya - Seminar 1ASHUTOSH SAHOOLME011 (LME011)No ratings yet
- Nuclear Battery Seminar ReportDocument22 pagesNuclear Battery Seminar ReportPratik Patil100% (1)
- Nuclear BatteryDocument25 pagesNuclear Batteryprashanta padhiary100% (1)
- Super CapacitorDocument17 pagesSuper CapacitorShubham Pratap100% (1)
- Nuclear BatteryDocument22 pagesNuclear BatterySairajesh67% (3)
- Nuclear Battery: Subject:-SeminarDocument18 pagesNuclear Battery: Subject:-SeminarlipodNo ratings yet
- Nucl. BaDocument24 pagesNucl. BaDivyanshu nagarNo ratings yet
- A Presentation ON "Nuclear Battery": Mr. Rahul GuptaDocument27 pagesA Presentation ON "Nuclear Battery": Mr. Rahul Guptarvsharma02No ratings yet
- The Spark: Proffessional CircleDocument42 pagesThe Spark: Proffessional CircleChandan PrasadNo ratings yet
- Radioisotope Generator: Chain ReactionDocument25 pagesRadioisotope Generator: Chain ReactionDivyanshu nagarNo ratings yet
- U L A B T e yDocument26 pagesU L A B T e yDivyanshu nagarNo ratings yet
- WWW - Seminar: U L A B T E YDocument26 pagesWWW - Seminar: U L A B T E YpankajNo ratings yet
- Nuclear BatteryDocument22 pagesNuclear Batteryhasoleakash2177No ratings yet
- Ultracapacitor PPT 1Document24 pagesUltracapacitor PPT 1Blessy JoyNo ratings yet
- Ultracapacitor-Ppt 1Document21 pagesUltracapacitor-Ppt 1Shijin Varghese100% (1)
- Carbon Nanotube-Based Supercapacitors: Chunsheng Du and Ning PanDocument8 pagesCarbon Nanotube-Based Supercapacitors: Chunsheng Du and Ning PanTitus LeeNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Battery Seminar ReportDocument24 pagesNuclear Battery Seminar ReportHarsh Patel100% (2)
- Nirbhit Physics ProjectDocument15 pagesNirbhit Physics ProjectNirbhitNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Battery: Ajay Mahato, Ajay Kumar Pal, Dr. Bhagwan Shree Ram (Prof.), Mr. Basavareddy (Prof.)Document6 pagesNuclear Battery: Ajay Mahato, Ajay Kumar Pal, Dr. Bhagwan Shree Ram (Prof.), Mr. Basavareddy (Prof.)santhosh kumarNo ratings yet
- Super CapacitorDocument54 pagesSuper Capacitorharisri269No ratings yet
- Nuclear Battery: AbstractDocument2 pagesNuclear Battery: AbstractsuryaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear BatteryDocument20 pagesNuclear BatteryAkhil Menon100% (4)
- Nuclear BatteryDocument26 pagesNuclear Batteryjoby jacobNo ratings yet
- Next Generation Alternative Energy Storage Using Super Capacitors/ultra CapacitorsDocument25 pagesNext Generation Alternative Energy Storage Using Super Capacitors/ultra CapacitorsKonda Snigdha100% (1)
- A Photograph of The RTG That NASA's Apollo 14 Mission Carried To The Moon. The RTG Is The Gray Colored Device With Cooling FinsDocument17 pagesA Photograph of The RTG That NASA's Apollo 14 Mission Carried To The Moon. The RTG Is The Gray Colored Device With Cooling FinsDivyanshu nagarNo ratings yet
- 4.supercapacitors and Battery Power Management For Hybrid Vehicle Applications Using Multi Boost and Full Bridge ConvertersDocument48 pages4.supercapacitors and Battery Power Management For Hybrid Vehicle Applications Using Multi Boost and Full Bridge Convertersganjigoutham147No ratings yet
- ChaptersDocument17 pagesChaptersJairus OlimaNo ratings yet
- 22 Solar Cell Challenges and New DevelopmentsDocument22 pages22 Solar Cell Challenges and New DevelopmentsPatrice ETEMENo ratings yet
- Sumanth SeminorDocument25 pagesSumanth SeminorvamsiNo ratings yet
- Varun Kumar GDocument5 pagesVarun Kumar GVarun KumarNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Battery (NAG)Document30 pagesNuclear Battery (NAG)Ambady BalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- RAJU2Document23 pagesRAJU2morajNo ratings yet
- Ultracapacitors (Supercapacitors)Document21 pagesUltracapacitors (Supercapacitors)NamithaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear BatteryDocument20 pagesNuclear Batteryraghavprince80% (1)
- Graphene UltracapacitorsDocument6 pagesGraphene UltracapacitorsprathameshNo ratings yet
- Ee 147Document3 pagesEe 147Menchie LabadanNo ratings yet
- Nuclear BatteryDocument26 pagesNuclear BatterydivyamNo ratings yet
- INSTALL YOUR OWN Photovoltaic System: Hybrid, Stand Alone and Battery StorageFrom EverandINSTALL YOUR OWN Photovoltaic System: Hybrid, Stand Alone and Battery StorageNo ratings yet
- LRL Accelerators, The 184-Inch SynchrocyclotronFrom EverandLRL Accelerators, The 184-Inch SynchrocyclotronNo ratings yet
- Shift Schedule For Power Plant Date Shift E.Code Name Mobile No. Address 25-MarDocument2 pagesShift Schedule For Power Plant Date Shift E.Code Name Mobile No. Address 25-MarUdgam TiwariNo ratings yet
- Basic Phone: Beetel LandlineDocument50 pagesBasic Phone: Beetel LandlineUdgam TiwariNo ratings yet
- Vib 1Document2 pagesVib 1Udgam TiwariNo ratings yet
- Installation Operating & Maintenance Manual: Climatic 50 Roof-Top, Aircoolair & CompactairDocument75 pagesInstallation Operating & Maintenance Manual: Climatic 50 Roof-Top, Aircoolair & CompactairUdgam TiwariNo ratings yet
- N: Q, Z R .: Pecial HanksDocument13 pagesN: Q, Z R .: Pecial HanksUdgam Tiwari67% (3)
- Daily Power Consumption of 18th AprilDocument2 pagesDaily Power Consumption of 18th AprilUdgam TiwariNo ratings yet
- Shift Schedule-March-2020 - Power Plant & Substation Electrical MaintenanceDocument1 pageShift Schedule-March-2020 - Power Plant & Substation Electrical MaintenanceUdgam TiwariNo ratings yet
- (ROM) L-Kat UX Galaxy y Duos GT S6102 - Samsung Galaxy Y GT-S5360Document41 pages(ROM) L-Kat UX Galaxy y Duos GT S6102 - Samsung Galaxy Y GT-S5360Udgam Tiwari0% (1)
- Bank GK PDFDocument5 pagesBank GK PDFUdgam TiwariNo ratings yet
- (GUIDE) How To Port Different ROMS To Your de - Android Development and HackingDocument28 pages(GUIDE) How To Port Different ROMS To Your de - Android Development and HackingUdgam TiwariNo ratings yet
- SOFTRICKS - How To Run NFS Most Wanted Game in Full Screen Mode SolvedDocument22 pagesSOFTRICKS - How To Run NFS Most Wanted Game in Full Screen Mode SolvedUdgam Tiwari100% (1)
- Charu Raghav: Course Year Board/ University Division M.A (Psychology) 1 B.A 1stDocument1 pageCharu Raghav: Course Year Board/ University Division M.A (Psychology) 1 B.A 1stUdgam TiwariNo ratings yet
- B.tech. Format (2015 Passingout Batch)Document8 pagesB.tech. Format (2015 Passingout Batch)Udgam TiwariNo ratings yet
- Voltage Harmonics Mitigation Using DVR: Electrical & Electronics EngineeringDocument7 pagesVoltage Harmonics Mitigation Using DVR: Electrical & Electronics EngineeringUdgam TiwariNo ratings yet
- What Are The Combination Key To Hit Shots in Cricket 07Document3 pagesWhat Are The Combination Key To Hit Shots in Cricket 07Udgam TiwariNo ratings yet
- B-Tech 7th Sem CSE Major Project NoticeDocument2 pagesB-Tech 7th Sem CSE Major Project NoticeUdgam TiwariNo ratings yet
- A Synopsis On: 4G Wireless SystemDocument5 pagesA Synopsis On: 4G Wireless SystemUdgam TiwariNo ratings yet
- Voltage Regulation By: Grid Using PV PlantDocument19 pagesVoltage Regulation By: Grid Using PV PlantUdgam TiwariNo ratings yet
- Power Quality Problems: An Overview & Key IssuesDocument46 pagesPower Quality Problems: An Overview & Key IssuesUdgam TiwariNo ratings yet
- 4g Pa PRFDDGKJHK, HJHJHKLJLJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJDocument19 pages4g Pa PRFDDGKJHK, HJHJHKLJLJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJUdgam TiwariNo ratings yet
- Helix Traveling-Wave Tubes (TWT'S)Document9 pagesHelix Traveling-Wave Tubes (TWT'S)Mayur GambhirNo ratings yet
- DS Ltch00601daa0 R05Document4 pagesDS Ltch00601daa0 R05rajareddy235No ratings yet
- CyberPower UM SX650UDocument7 pagesCyberPower UM SX650UMuruganand RamalingamNo ratings yet
- 3260B User Manual Iss G PDFDocument225 pages3260B User Manual Iss G PDFkamtungNo ratings yet
- J910-YD16-P0ZEN-141012 - Rev.3 Cable Duct and Trench (AWC)Document29 pagesJ910-YD16-P0ZEN-141012 - Rev.3 Cable Duct and Trench (AWC)Devy MangimbaNo ratings yet
- Grounding System Theory and Practice R1Document33 pagesGrounding System Theory and Practice R1Muhammed Abdullah ÖZNo ratings yet
- 1E EJB Custom-Built Control Panels: Globally Certified-Individually CustomizedDocument8 pages1E EJB Custom-Built Control Panels: Globally Certified-Individually Customizedoctavinavarro8236No ratings yet
- German Airborne Radar DefDocument32 pagesGerman Airborne Radar Defadrcostache6515100% (1)
- Unacademy SyllabusDocument7 pagesUnacademy SyllabusAnkit PachouriNo ratings yet
- 2150907Document14 pages2150907Prashant ShahNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - DC SystemDocument50 pagesTutorial - DC SystemCarlos PuertoNo ratings yet
- Owner'S Manual: Full Channel AM/FM/SSB Mobile Built in Frequency Counter With Roger BeepDocument10 pagesOwner'S Manual: Full Channel AM/FM/SSB Mobile Built in Frequency Counter With Roger BeepnmvalleytechNo ratings yet
- 8th-Order, Lowpass, Switched-Capacitor Filters: MAX291/MAX292/ MAX295/MAX296Document10 pages8th-Order, Lowpass, Switched-Capacitor Filters: MAX291/MAX292/ MAX295/MAX296Faisal BashirNo ratings yet
- S08210Document610 pagesS08210jorgeeduardo1000100% (1)
- Ece3323antennas HWKDocument3 pagesEce3323antennas HWKMasoud Said Moh'dNo ratings yet
- Training VAMOS HUAWEIDocument51 pagesTraining VAMOS HUAWEIFouad Tehari100% (1)
- Manual de Uso RectificadorDocument33 pagesManual de Uso RectificadorLuis Luna CruzNo ratings yet
- Nema-C50 41Document45 pagesNema-C50 41navaratne dhammikaNo ratings yet
- 01 - Operating Manual Filter Plant - enDocument15 pages01 - Operating Manual Filter Plant - enGennius Flores100% (1)
- SMPS 200WDocument22 pagesSMPS 200WNAYEEMNo ratings yet
- High Speed Digital CMOS Input Buffer DesignDocument64 pagesHigh Speed Digital CMOS Input Buffer DesignbamagyiNo ratings yet
- P8100 Instruction Manual (PT8100) PDFDocument14 pagesP8100 Instruction Manual (PT8100) PDFmilenkoyanezNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Review of The Voltage Stability IndicesDocument12 pagesA Comprehensive Review of The Voltage Stability IndiceslauraNo ratings yet
- IRD811D User ManualDocument33 pagesIRD811D User ManualsubrataNo ratings yet
- 7ut86 - P1F143891 (9642)Document8 pages7ut86 - P1F143891 (9642)Humberto CeballosNo ratings yet
- EE3950 Class Notes Chapter 14Document23 pagesEE3950 Class Notes Chapter 14Jkun gamingNo ratings yet
- Masstrans - HTMS - 1 - Final - Mar 21Document32 pagesMasstrans - HTMS - 1 - Final - Mar 21Tejaswini ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Arris BGW210-700 ATTDocument32 pagesArris BGW210-700 ATTChad StrattonNo ratings yet
- Bipolar JN TransistorDocument23 pagesBipolar JN TransistorSheikh SaifNo ratings yet